Hadoop学习之路(十九)MapReduce框架排序
Posted 扎心了,老铁
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Hadoop学习之路(十九)MapReduce框架排序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
流量统计项目案例
样本示例
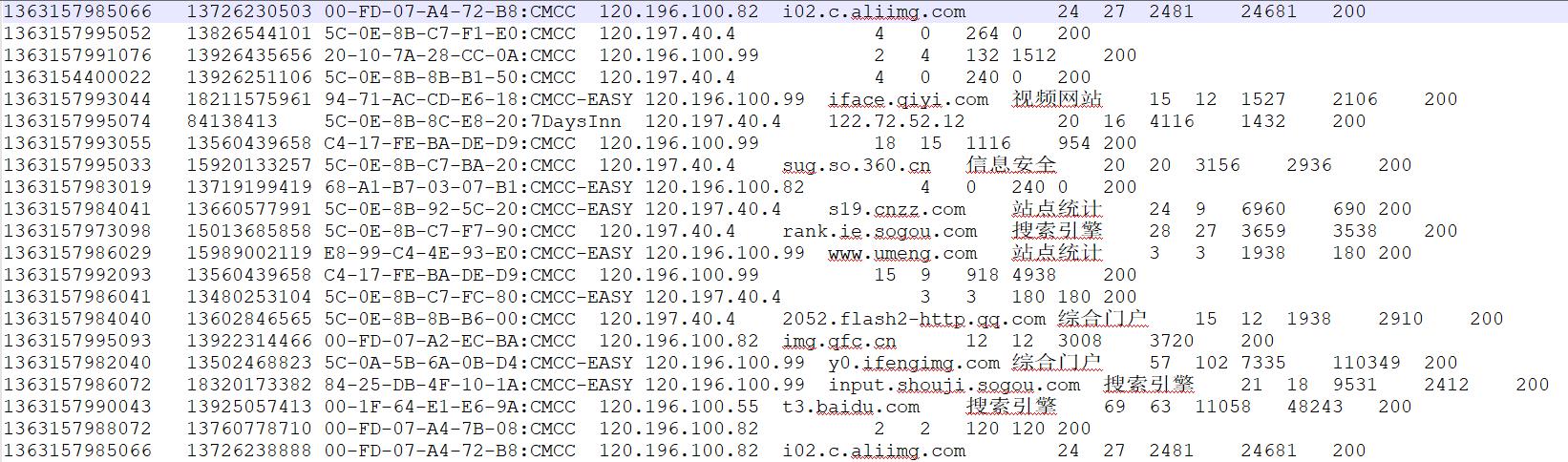
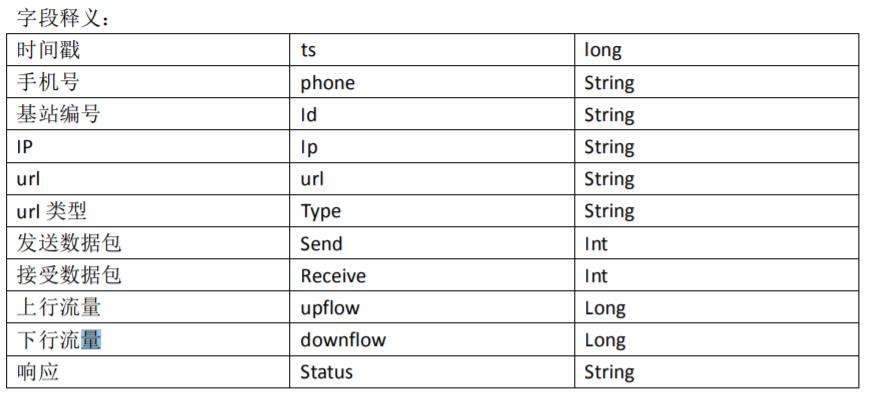
需求
1、 统计每一个用户(手机号)所耗费的总上行流量、总下行流量,总流量
2、 得出上题结果的基础之上再加一个需求:将统计结果按照总流量倒序排序
3、 将流量汇总统计结果按照手机归属地不同省份输出到不同文件中
第一题
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; /** * 第一题:统计每一个用户(手机号)所耗费的总上行流量、总下行流量,总流量 */ public class FlowSumMR { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "FlowSumMR"); job.setJarByClass(FlowSumMR.class); job.setMapperClass(FlowSumMRMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(FlowSumMRReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("E:/bigdata/flow/input/")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("E:/bigdata/flow/output_sum")); boolean isDone = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(isDone ? 0 : 1); } public static class FlowSumMRMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{ /** * value = 1363157993044 18211575961 94-71-AC-CD-E6-18:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.99 * iface.qiyi.com 视频网站 15 12 1527 2106 200 */ @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] split = value.toString().split("\\t"); String outkey = split[1]; String outValue = split[8] + "\\t" + split[9]; context.write(new Text(outkey), new Text(outValue)); } } public static class FlowSumMRReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{ @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int upFlow = 0; int downFlow = 0; int sumFlow = 0; for(Text t : values){ String[] split = t.toString().split("\\t"); int upTempFlow = Integer.parseInt(split[0]); int downTempFlow = Integer.parseInt(split[1]); upFlow+=upTempFlow; downFlow += downTempFlow; } sumFlow = upFlow + downFlow; context.write(key, new Text(upFlow + "\\t" + downFlow + "\\t" + sumFlow)); } } }
第二题
import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import comg.ghgj.mr.pojo.FlowBean; /** * 需求: 第二个题目,就是对第一个题目的结果数据,进行按照总流量倒叙排序 * * */ public class FlowSortMR { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "FlowSumMR"); job.setJarByClass(FlowSortMR.class); job.setMapperClass(FlowSortMRMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(FlowSortMRReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("E:/bigdata/flow/output_sum")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("E:/bigdata/flow/output_sort_777")); boolean isDone = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(isDone ? 0 : 1); } public static class FlowSortMRMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, FlowBean, NullWritable>{ /** * value = 13602846565 26860680 40332600 67193280 */ @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] split = value.toString().split("\\t"); FlowBean fb = new FlowBean(split[0], Long.parseLong(split[1]), Long.parseLong(split[2])); context.write(fb, NullWritable.get()); } } public static class FlowSortMRReducer extends Reducer<FlowBean, NullWritable, FlowBean, NullWritable>{ @Override protected void reduce(FlowBean key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { for(NullWritable nvl : values){ context.write(key, nvl); } } } }
FlowBean.java

1 import java.io.DataInput; 2 import java.io.DataOutput; 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 6 7 /** 8 * 第一,定义好属性 9 * 第二,定义好属性的getter 和 setter方法 10 * 第三,定义好构造方法(有参,无参) 11 * 第四:定义好toString(); 12 * 13 * 14 * 详细解释: 15 * 16 * 如果一个自定义对象要作为key 必须要实现 WritableComparable 接口, 而不能实现 Writable, Comparable 17 * 18 * 如果一个自定义对象要作为value,那么只需要实现Writable接口即可 19 */ 20 public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable<FlowBean>{ 21 //public class FlowBean implements Comparable<FlowBean>{ 22 23 private String phone; 24 private long upFlow; 25 private long downFlow; 26 private long sumFlow; 27 public String getPhone() { 28 return phone; 29 } 30 public void setPhone(String phone) { 31 this.phone = phone; 32 } 33 public long getUpFlow() { 34 return upFlow; 35 } 36 public void setUpFlow(long upFlow) { 37 this.upFlow = upFlow; 38 } 39 public long getDownFlow() { 40 return downFlow; 41 } 42 public void setDownFlow(long downFlow) { 43 this.downFlow = downFlow; 44 } 45 public long getSumFlow() { 46 return sumFlow; 47 } 48 public void setSumFlow(long sumFlow) { 49 this.sumFlow = sumFlow; 50 } 51 public FlowBean(String phone, long upFlow, long downFlow, long sumFlow) { 52 super(); 53 this.phone = phone; 54 this.upFlow = upFlow; 55 this.downFlow = downFlow; 56 this.sumFlow = sumFlow; 57 } 58 public FlowBean(String phone, long upFlow, long downFlow) { 59 super(); 60 this.phone = phone; 61 this.upFlow = upFlow; 62 this.downFlow = downFlow; 63 this.sumFlow = upFlow + downFlow; 64 } 65 public FlowBean() { 66 super(); 67 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 68 } 69 @Override 70 public String toString() { 71 return phone + "\\t" + upFlow + "\\t" + downFlow + "\\t" + sumFlow; 72 } 73 74 75 76 77 /** 78 * 把当前这个对象 --- 谁掉用这个write方法,谁就是当前对象 79 * 80 * FlowBean bean = new FlowBean(); 81 * 82 * bean.write(out) 把bean这个对象的四个属性序列化出去 83 * 84 * this = bean 85 */ 86 @Override 87 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 88 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 89 90 out.writeUTF(phone); 91 out.writeLong(upFlow); 92 out.writeLong(downFlow); 93 out.writeLong(sumFlow); 94 95 } 96 97 98 // 序列化方法中的写出的字段顺序, 一定一定一定要和 反序列化中的 接收顺序一致。 类型也一定要一致 99 100 101 /** 102 * bean.readField(); 103 * 104 * upFlow = 105 */ 106 @Override 107 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 108 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 109 110 phone = in.readUTF(); 111 upFlow = in.readLong(); 112 downFlow = in.readLong(); 113 sumFlow = in.readLong(); 114 115 } 116 117 118 119 /** 120 * Hadoop的序列化机制为什么不用 java自带的实现 Serializable这种方式? 121 * 122 * 本身Hadoop就是用来解决大数据问题的。 123 * 124 * 那么实现Serializable接口这种方式,在进行序列化的时候。除了会序列化属性值之外,还会携带很多跟当前这个对象的类相关的各种信息 125 * 126 * Hadoop采取了一种全新的序列化机制;只需要序列化 每个对象的属性值即可。 127 */ 128 129 130 131 /*@Override 132 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 133 value = in.readLong(); 134 } 135 136 @Override 137 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 138 out.writeLong(value); 139 }*/ 140 141 142 /** 143 * 用来指定排序规则 144 */ 145 @Override 146 public int compareTo(FlowBean fb) { 147 148 long diff = this.getSumFlow() - fb.getSumFlow(); 149 150 if(diff == 0){ 151 return 0; 152 }else{ 153 return diff > 0 ? -1 : 1; 154 } 155 156 } 157 }
第三题
package comg.ghgj.mr.flow; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition.ProvincePartitioner; public class FlowPartitionerMR { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "FlowSumMR"); job.setJarByClass(FlowPartitionerMR.class); job.setMapperClass(FlowPartitionerMRMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(FlowPartitionerMRReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); /** * 非常重要的两句代码 */ job.setPartitionerClass(ProvincePartitioner.class); job.setNumReduceTasks(10); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("E:\\\\bigdata\\\\flow\\\\input")); Path outputPath = new Path("E:\\\\bigdata\\\\flow\\\\output_ptn2"); if(fs.exists(outputPath)){ fs.delete(outputPath, true); } FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath); boolean isDone = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(isDone ? 0 : 1); } public static class FlowPartitionerMRMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{ /** * value = 13502468823 101663100 1529437140 1631100240 */ @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] split = value.toString().split("\\t"); String outkey = split[1]; String outValue = split[8] + "\\t" + split[9]; context.write(new Text(outkey), new Text(outValue)); } } public static class FlowPartitionerMRReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{ @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int upFlow = 0; int downFlow = 0; int sumFlow = 0; for(Text t : values){ String[] split = t.toString().split("\\t"); int upTempFlow = Integer.parseInt(split[0]); int downTempFlow = Integer.parseInt(split[1]); upFlow+=upTempFlow; downFlow += downTempFlow; } sumFlow = upFlow + downFlow; context.write(key, new Text(upFlow + "\\t" + downFlow + "\\t" + sumFlow)); } } }
以上是关于Hadoop学习之路(十九)MapReduce框架排序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
