Android 11 SystemUI(状态/导航栏)-状态栏下拉时图标的隐藏与通知面板的半透黑色背景
Posted ansondroider
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android 11 SystemUI(状态/导航栏)-状态栏下拉时图标的隐藏与通知面板的半透黑色背景相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
概述
本文续自:Android 11 的状态栏的隐藏
PS
本文虽然同属于SystemUI, 但目前并 没有 打算整理成专橍或撰写一个系列的想法.
仅仅为了记录一些过程, 留下那些容易被遗忘的点滴.
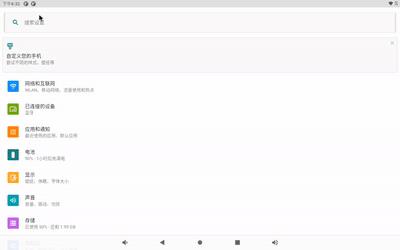
开始下拉时状态栏图标被隐藏
状态橍的图标在用户开始触摸(ACTION_DOWN)后, 会开始展开, 显示扩展面板, 同时, 隐藏状态橍上的通知和状态图标. 在手机上表现有可能不同, 在android 13上, 在点击没有作用, 只有下拉一定的距离,才会开始隐藏.
device-2022-12-21-190046

隐藏从触摸下按开始, 参照下图:

忽略过程代码, 直接上最后一部分:
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI//src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/phone/CollapsedStatusBarFragment.java
@Override
public void disable(int displayId, int state1, int state2, boolean animate)
if (displayId != getContext().getDisplayId())
return;
state1 = adjustDisableFlags(state1);
final int old1 = mDisabled1;
final int diff1 = state1 ^ old1;
mDisabled1 = state1;
if ((diff1 & DISABLE_SYSTEM_INFO) != 0)
if ((state1 & DISABLE_SYSTEM_INFO) != 0)
hideSystemIconArea(animate);
hideOperatorName(animate);
else
showSystemIconArea(animate);
showOperatorName(animate);
if ((diff1 & DISABLE_NOTIFICATION_ICONS) != 0)
if ((state1 & DISABLE_NOTIFICATION_ICONS) != 0)
hideNotificationIconArea(animate);
else
showNotificationIconArea(animate);
// The clock may have already been hidden, but we might want to shift its
// visibility to GONE from INVISIBLE or vice versa
if ((diff1 & DISABLE_CLOCK) != 0 || mClockView.getVisibility() != clockHiddenMode())
if ((state1 & DISABLE_CLOCK) != 0)
hideClock(animate);
else
showClock(animate);
protected int adjustDisableFlags(int state)
boolean headsUpVisible = mStatusBarComponent.headsUpShouldBeVisible();
if (headsUpVisible)
state |= DISABLE_CLOCK;
if (!mKeyguardStateController.isLaunchTransitionFadingAway()
&& !mKeyguardStateController.isKeyguardFadingAway()
&& shouldHideNotificationIcons()
&& !(mStatusBarStateController.getState() == StatusBarState.KEYGUARD
&& headsUpVisible))
state |= DISABLE_NOTIFICATION_ICONS;
state |= DISABLE_SYSTEM_INFO;
state |= DISABLE_CLOCK;
if (mNetworkController != null && EncryptionHelper.IS_DATA_ENCRYPTED)
if (mNetworkController.hasEmergencyCryptKeeperText())
state |= DISABLE_NOTIFICATION_ICONS;
if (!mNetworkController.isRadioOn())
state |= DISABLE_SYSTEM_INFO;
// The shelf will be hidden when dozing with a custom clock, we must show notification
// icons in this occasion.
if (mStatusBarStateController.isDozing()
&& mStatusBarComponent.getPanelController().hasCustomClock())
state |= DISABLE_CLOCK | DISABLE_SYSTEM_INFO;
return state;
关于CollapsedStatusBarFragment
在读到CollapsedStatusBarFragment相关代码的时候, 一时没办法把Fragment与SystemUI串联起来, 这源于传统Fragment的使用习惯: 在Activity中, 获取一个FragmentManager, 创建各种Fragment, 调用replace, show, hide…
难道SystemUI也吃这一套? 状态栏和导航栏不一直是通过WindowManager.addView()直接往里面丢的么!
CollapsedStatusBarFragment 本身没什么特别的, 它只是一个android.app.Fragment, 没有特殊的地方, 特殊的是FragmentController, 它与传统的Fragment使用方法完全不同, 参考 frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/fragments/FragmentHostManager.java
编写一段测试代码, 以便更直观了解它的用法:
public class TestActivity extends Activity
void testFragmentController(Context ctx, Handler h, int winAnim)
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.M)
FragmentController fragCtrl = FragmentController.createController(new FragmentHostCallback<Object>(ctx, h, 0)
@Override
public Object onGetHost()
return null;
@Override
public <T extends View> T onFindViewById(int id)
return findViewById(id);
);
//java.lang.IllegalStateException: Activity has been destroyed
// at android.app.FragmentManagerImpl.enqueueAction(FragmentManager.java:1913)
fragCtrl.attachHost(null);
fragCtrl.dispatchCreate();
fragCtrl.dispatchStart();
fragCtrl.dispatchResume();
//java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: No view found for id 0x7f08007c (com.android.factorytest:id/flRoot) for fragment SimpleFragment2b5da47 #0 id=0x7f08007c
fragCtrl.getFragmentManager()
.beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.flRoot, new SimpleFragment())
.commit();
public static class SimpleFragment extends Fragment
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState)
TextView tv = new TextView(getActivity());
tv.setLayoutParams(new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(UiTools.MATCH_PARENT, UiTools.MATCH_PARENT));
tv.setText("FragmentController");
tv.setTextSize(36);
return tv;
重点关注代码中的createController和FragmentHostCallback, 当创建完成后, 便可以通过 FragmentController的getFragmentManager获取FragmentManager, 接下来就是熟悉的操作, 不多描述.
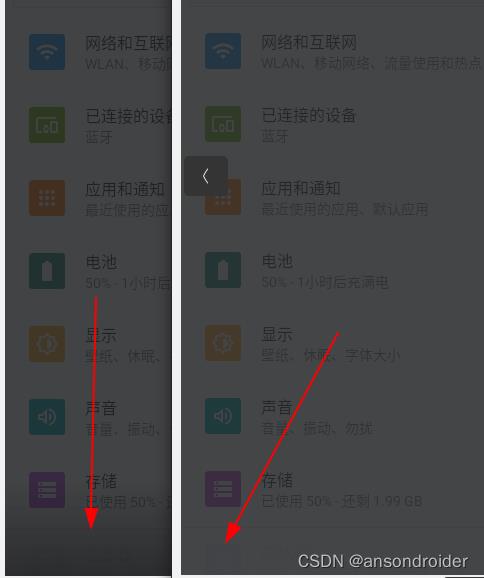
下拉通知黑色背景
在下拉通知面板的过程中, 存在两部分的半透明背景, 第一部分(上)比较明显, 第二部分比较隐藏晦.
效果如下图:

这是一个自定义的View, 从layout文件中可以找到它: ScrimView
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/res/layout/super_notification_shade.xml
<com.android.systemui.statusbar.phone.NotificationShadeWindowView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:sysui="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true">
<!-- 省略代码 -->
<com.android.systemui.statusbar.ScrimView
android:id="@+id/scrim_behind"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:importantForAccessibility="no"
sysui:ignoreRightInset="true"
/>
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/ScrimView.java
diff --git a/frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/ScrimView.java b/frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/ScrimView.java
index 7f30009cda..907d58c267 100644
--- a/frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/ScrimView.java
+++ b/frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/ScrimView.java
@@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ public class ScrimView extends View
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
- if (mDrawable.getAlpha() > 0)
+ if (false && mDrawable.getAlpha() > 0) //强制不进行绘制, 就不会出现半透明背景
mDrawable.draw(canvas);
第二部分只有在下拉到底部时才会出现(不仔细分辨很难看出来):
同样, 来自另一个自定义控件:AlphaOptimizedView
frameworks\\base\\packages\\SystemUI\\res\\layout\\status_bar_expanded.xml
<com.android.systemui.statusbar.AlphaOptimizedView
android:id="@+id/qs_navbar_scrim"
android:layout_height="66dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:visibility="invisible"
android:background="@drawable/qs_navbar_scrim" />
扩展
Dagger, 绕得脑壳疼, 记录下out下的路径
out/soong/.intermediates/frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/SystemUI-core/android_common/kapt/gen/sources/com/android/systemui/dagger/DaggerSystemUIRootComponent.java
public final class DaggerSystemUIRootComponent implements SystemUIRootComponent
private Provider<SystemUIRootComponent> systemUIRootComponentProvider;
this.systemUIRootComponentProvider = InstanceFactory.create((SystemUIRootComponent) this);
private Provider<FragmentService> fragmentServiceProvider;
this.fragmentServiceProvider =
DoubleCheck.provider(
FragmentService_Factory.create(
systemUIRootComponentProvider, provideConfigurationControllerProvider));
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/SystemUIAppComponentFactory.java
@NonNull
@Override
public Application instantiateApplicationCompat(
@NonNull ClassLoader cl, @NonNull String className)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException
Application app = super.instantiateApplicationCompat(cl, className);
if (app instanceof ContextInitializer)
((ContextInitializer) app).setContextAvailableCallback(
context ->
SystemUIFactory.createFromConfig(context);
SystemUIFactory.getInstance().getRootComponent().inject(
SystemUIAppComponentFactory.this);
);
return app;
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/SystemUIFactory.java
private void init(Context context)
mRootComponent = buildSystemUIRootComponent(context);
// Every other part of our codebase currently relies on Dependency, so we
// really need to ensure the Dependency gets initialized early on.
Dependency dependency = new Dependency();
mRootComponent.createDependency().createSystemUI(dependency);
dependency.start();
public static void createFromConfig(Context context)
if (mFactory != null)
return;
final String clsName = context.getString(R.string.config_systemUIFactoryComponent);
if (clsName == null || clsName.length() == 0)
throw new RuntimeException("No SystemUIFactory component configured");
try
Class<?> cls = null;
cls = context.getClassLoader().loadClass(clsName);
mFactory = (SystemUIFactory) cls.newInstance();
mFactory.init(context);
catch (Throwable t)
Log.w(TAG, "Error creating SystemUIFactory component: " + clsName, t);
throw new RuntimeException(t);
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/Dependency.java
@Inject Lazy<FragmentService> mFragmentService;
protected void start()
mProviders.put(FragmentService.class, mFragmentService::get);
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/phone/StatusBar.java
FragmentHostManager.get(mPhoneStatusBarWindow)
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/fragments/FragmentHostManager.java
public static FragmentHostManager get(View view)
try
return Dependency.get(FragmentService.class).getFragmentHostManager(view);
catch (ClassCastException e)
// TODO: Some auto handling here?
throw e;
frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/fragments/FragmentService.java
public FragmentHostManager getFragmentHostManager(View view)
View root = view.getRootView();
FragmentHostState state = mHosts.get(root);
if (state == null)
state = new FragmentHostState(root);
mHosts.put(root, state);
return state.getFragmentHostManager();
参考
SystemUI源码分析之PhoneStatusBar初始化布局简单分析
Android SystemUI 状态栏网络图标显示分析(Android 11)
SystemUI之状态图标控制
Android 8.0 SystemUI(三):一说顶部 StatusBar
Android 8.0 SystemUI(四):二说顶部 StatusBar
Dagger 基础知识
在 Android 应用中使用 Dagger
android SystemUI 流程分析
android4 SystemUI 流程分析
什么是SystemUI?
对于Phone来说SystemUI指的是:StatusBar(状态栏)、NavigationBar(导航栏)。而对于Tablet或者是TV来说SystemUI指的是:
CombinedBar(包括了StatusBar和NavigationBar)。
启动后Phone界面上的信号,蓝牙标志,Wifi标志等等这些状态显示标志都会在StatusBar上显示。当我们的设备开机后,首先
需要给用户呈现的就是各种界面同时也包括了我们的SystemUI,因此对于整个Android系统来说,SystemUI都有举足轻重的作用。
现在就从代码开始一步步的分析
1、启动流程
代码路径:fameworks/base/packages/SystemUI
建立工程导入到eclipse中代码具体图示:
先从 AndroidManifest.xml 看看有哪些东东,以前说过Android中有四大组件,这里就有如下的三大部分:
系统服务 Service :
SystemUIService
TakeScreenshotService
LoadAverageService
广播接收器 BroadcastReceive:
BootReceiver
Activity 应用:
USB的挺多哟...
UsbStorageActivity
UsbConfirmActivity
UsbPermissionActivity
UsbStorageActivity
UsbAccessoryUriActivity
NetworkOverLimitActivity
<!-- started from ... somewhere -->
Nyandroid
具体定义请看 AndroidManifest.xml 文件,上面只是简单的列一下
先看第一个Activity -- Nyandroid 这里做了什么呢?
就是网上传说中的 好多安卓机器人飞过去。。。。其中代码很简单,简单说一下动画效果的代码:
- <span style="font-size:14px">public class FlyingCat extends ImageView {
- public FlyingCat(Context context, AttributeSet as) {
- super(context, as);
- setImageResource(R.drawable.nyandroid_anim); // @@@
- if (DEBUG) setBackgroundColor(0x80FF0000);
- }
- ...
- }</span>
定义在 frameworks\base\packages\SystemUI\res\drawable\nyandroid_anim.xml
- <span style="font-size:14px"><animation-list
- xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:oneshot="false">
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid00" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid01" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid02" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid03" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid04" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid05" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid06" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid07" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid08" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid09" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid10" android:duration="80" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/nyandroid11" android:duration="80" />
- </animation-list></span>
相关图片在: frameworks\base\packages\SystemUI\res\drawable-nodpi 如图示:
然后再看最重要的服务:SystemUIService
一般来说,Service启动一般由开机广播或者StartService/BindService这几种方式来启动。既然这个Service是一个系统
服务,应该是由系统这边启动,那么看下 SystemServer.java ,果然发现如下启动代码:
- <span style="font-size:14px">startSystemUi(contextF);
- static final void startSystemUi(Context context) {
- Intent intent = new Intent();
- intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.android.systemui",
- "com.android.systemui.SystemUIService"));
- Slog.d(TAG, "Starting service: " + intent);
- context.startService(intent);
- }</span>
对于Android启动流程请看如下系统文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/andyhuabing/article/details/7346203 android启动--深入理解init进程
http://blog.csdn.net/andyhuabing/article/details/7349986 android启动--深入理解zygote
http://blog.csdn.net/andyhuabing/article/details/7351691 android启动--深入理解zygote (II)
http://blog.csdn.net/andyhuabing/article/details/7353910 android启动--深入理解启动HOME
那么就继续跟踪 SystemUIService 中代码:
- <span style="font-size:14px">/**
- * The class names of the stuff to start.
- */
- final Object[] SERVICES = new Object[] {
- 0, // system bar or status bar, filled in below.
- com.android.systemui.power.PowerUI.class,
- };
- @Override
- public void onCreate() {
- // Pick status bar or system bar.
- IWindowManager wm = IWindowManager.Stub.asInterface(
- ServiceManager.getService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE));
- try {
- SERVICES[0] = wm.canStatusBarHide()
- ? R.string.config_statusBarComponent
- : R.string.config_systemBarComponent;
- } catch (RemoteException e) {
- Slog.w(TAG, "Failing checking whether status bar can hide", e);
- }
- final int N = SERVICES.length;
- mServices = new SystemUI[N];
- for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
- Class cl = chooseClass(SERVICES[i]);
- Slog.d(TAG, "loading: " + cl);
- try {
- mServices[i] = (SystemUI)cl.newInstance();
- } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
- throw new RuntimeException(ex);
- } catch (InstantiationException ex) {
- throw new RuntimeException(ex);
- }
- mServices[i].mContext = this;
- Slog.d(TAG, "running: " + mServices[i]);
- mServices[i].start();
- }
- }</span>
在这代码中:
- <span style="font-size:14px">SERVICES[0] = wm.canStatusBarHide()
- ? R.string.config_statusBarComponent
- : R.string.config_systemBarComponent;
- </span>
通过AIDL获取WindowManager对象并调用 wm.canStatusBarHide() 这个代码在哪里呢?
查看: frameworks/base/policy/src/com/android/internal/policy/impl/PhoneWindowManager.java
- <span style="font-size:14px"> public boolean canStatusBarHide() {
- return mStatusBarCanHide;
- }
- public void setInitialDisplaySize(int width, int height) {
- ...
- // Determine whether the status bar can hide based on the size
- // of the screen. We assume sizes > 600dp are tablets where we
- // will use the system bar.
- int shortSizeDp = shortSize
- * DisplayMetrics.DENSITY_DEFAULT
- / DisplayMetrics.DENSITY_DEVICE;
- mStatusBarCanHide = shortSizeDp < 600;
- }</span>
从以上代码来看,shortSizeDp小于600dp时,则系统会认为该设备是Phone反之则认为是Tablet。
根据mStatusBarCanHide的值,设定StatusBar或者SystemBar(CombinedBar)的高度,以及是否显示NavigationBar。
2、StatusBar(状态栏)及NavigationBar(导航栏)
如果是 StatusBar 则 SERVICES[0] 存放 com.android.systemui.statusbar.phone.PhoneStatusBar 否则存放
com.android.systemui.statusbar.tablet.TabletStatusBar
SERVICES[1] 存放 com.android.systemui.power.PowerUI.class
从我的机器上打印来看,
E/SystemServer( 1299): Starting service: Intent { cmp=com.android.systemui/.SystemUIService }
D/SystemUIService( 1382): running: [email protected]
D/SystemUIService( 1382): running: [email protected]
I/PowerUI ( 1382): start
然后调用 mServices[i].start();那么就分析 TabletStatusBar 中的start方法吧
- <span style="font-size:14px"> @Override
- public void start() {
- super.start(); // will add the main bar view
- }</span>
调用到 frameworks/base/packages/SystemUI/src/com/android/systemui/statusbar/StatusBar.Java
- <span style="font-size:14px">public void start() {
- // First set up our views and stuff.
- View sb = makeStatusBarView();
- // Connect in to the status bar manager service
- StatusBarIconList iconList = new StatusBarIconList();
- ArrayList<IBinder> notificationKeys = new ArrayList<IBinder>();
- ArrayList<StatusBarNotification> notifications = new ArrayList<StatusBarNotification>();
- mCommandQueue = new CommandQueue(this, iconList);
- mBarService = IStatusBarService.Stub.asInterface(
- ServiceManager.getService(Context.STATUS_BAR_SERVICE));
- int[] switches = new int[7];
- ArrayList<IBinder> binders = new ArrayList<IBinder>();
- try {
- mBarService.registerStatusBar(mCommandQueue, iconList, notificationKeys, notifications,
- switches, binders);
- } catch (RemoteException ex) {
- // If the system process isn‘t there we‘re doomed anyway.
- }
- disable(switches[0]);
- setSystemUiVisibility(switches[1]);
- topAppWindowChanged(switches[2] != 0);
- // StatusBarManagerService has a back up of IME token and it‘s restored here.
- setImeWindowStatus(binders.get(0), switches[3], switches[4]);
- setHardKeyboardStatus(switches[5] != 0, switches[6] != 0);
- // Set up the initial icon state
- int N = iconList.size();
- int viewIndex = 0;
- for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
- StatusBarIcon icon = iconList.getIcon(i);
- if (icon != null) {
- addIcon(iconList.getSlot(i), i, viewIndex, icon);
- viewIndex++;
- }
- }
- // Set up the initial notification state
- N = notificationKeys.size();
- if (N == notifications.size()) {
- for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
- addNotification(notificationKeys.get(i), notifications.get(i));
- }
- } else {
- Log.wtf(TAG, "Notification list length mismatch: keys=" + N
- + " notifications=" + notifications.size());
- }
- // Put up the view
- final int height = getStatusBarHeight();
- final WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = new WindowManager.LayoutParams(
- ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,
- height,
- WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_STATUS_BAR,
- WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE
- | WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_TOUCHABLE_WHEN_WAKING
- | WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH,
- PixelFormat.OPAQUE);
- // the status bar should be in an overlay if possible
- final Display defaultDisplay
- = ((WindowManager)mContext.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE))
- .getDefaultDisplay();
- if (ActivityManager.isHighEndGfx(defaultDisplay)) {
- lp.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED;
- }
- lp.gravity = getStatusBarGravity();
- lp.setTitle("StatusBar");
- lp.packageName = mContext.getPackageName();
- lp.windowAnimations = R.style.Animation_StatusBar;
- WindowManagerImpl.getDefault().addView(sb, lp);
- if (SPEW) {
- Slog.d(TAG, "Added status bar view: gravity=0x" + Integer.toHexString(lp.gravity)
- + " icons=" + iconList.size()
- + " disabled=0x" + Integer.toHexString(switches[0])
- + " lights=" + switches[1]
- + " menu=" + switches[2]
- + " imeButton=" + switches[3]
- );
- }
- mDoNotDisturb = new DoNotDisturb(mContext);
- }</span>
在这里,完成了SystemUI的整个初始化以及设置过程,并最终呈现到界面上。
启动过程中完成如下操作:
1、获取icon list,addIcon(iconList.getSlot(i), i, viewIndex, icon);
2、获取notification,addNotification(notificationKeys.get(i), notifications.get(i));
3、显示StatusBar,WindowManagerImpl.getDefault().addView(sb, lp);
显示NavigationBar,WindowManagerImpl.getDefault().addView(
mNavigationBarView, getNavigationBarLayoutParams());
时序图如下:
3、最近任务缩略图显示
长按home键,列出最近启动过的任务缩略图,重要的两个类
// Recent apps
private RecentsPanelView mRecentsPanel;
private RecentTasksLoader mRecentTasksLoader;
SystemUI 获取按键事件,获取缩略图并将其显示出来,最后响应view上按键响应相应事件:
对于我们来说,关注点主要有如下几个:
1、缩略图如何获取
- <span style="font-size:14px">RecentsPanelView.java 中
- refreshRecentTasksList(recentTaskDescriptions);
- -->
- mRecentTaskDescriptions = mRecentTasksLoader.getRecentTasks();
- -->
- RecentTasksLoader.java 中
- // return a snapshot of the current list of recent apps
- ArrayList<TaskDescription> getRecentTasks() {
- cancelLoadingThumbnails();
- ArrayList<TaskDescription> tasks = new ArrayList<TaskDescription>();
- final PackageManager pm = mContext.getPackageManager();
- final ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager)
- mContext.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
- final List<ActivityManager.RecentTaskInfo> recentTasks =
- am.getRecentTasks(MAX_TASKS, ActivityManager.RECENT_IGNORE_UNAVAILABLE);
- ActivityInfo homeInfo = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_MAIN).addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME)
- .resolveActivityInfo(pm, 0);
- HashSet<Integer> recentTasksToKeepInCache = new HashSet<Integer>();
- int numTasks = recentTasks.size();
- // skip the first task - assume it‘s either the home screen or the current activity.
- final int first = 1;
- recentTasksToKeepInCache.add(recentTasks.get(0).persistentId);
- for (int i = first, index = 0; i < numTasks && (index < MAX_TASKS); ++i) {
- final ActivityManager.RecentTaskInfo recentInfo = recentTasks.get(i);
- TaskDescription item = createTaskDescription(recentInfo.id,
- recentInfo.persistentId, recentInfo.baseIntent,
- recentInfo.origActivity, recentInfo.description, homeInfo);
- if (item != null) {
- tasks.add(item);
- ++index;
- }
- }
- // when we‘re not using the TaskDescription cache, we load the thumbnails in the
- // background
- loadThumbnailsInBackground(new ArrayList<TaskDescription>(tasks));
- return tasks;
- }
- </span>
这里利用 ActivityManager 中的方法:getRecentTasks 获取当前任务的列表,然后再利用 getTaskThumbnails 获取
按键View 就是几个按键相应的View
- <span style="font-size:14px"> public View getRecentsButton() {
- return mCurrentView.findViewById(R.id.recent_apps);
- }
- public View getMenuButton() {
- return mCurrentView.findViewById(R.id.menu);
- }
- public View getBackButton() {
- return mCurrentView.findViewById(R.id.back);
- }
- public View getHomeButton() {
- return mCurrentView.findViewById(R.id.home);
- }</span>
相应的应用缩略图,调用序列图如下:
2、显示缩略图
public void show(boolean show, boolean animate,
ArrayList<TaskDescription> recentTaskDescriptions) {
if (show) {
// Need to update list of recent apps before we set visibility so this view‘s
// content description is updated before it gets focus for TalkBack mode
refreshRecentTasksList(recentTaskDescriptions);
// if there are no apps, either bring up a "No recent apps" message, or just
// quit early
boolean noApps = (mRecentTaskDescriptions.size() == 0);
if (mRecentsNoApps != null) { // doesn‘t exist on large devices
mRecentsNoApps.setVisibility(noApps ? View.VISIBLE : View.INVISIBLE);
} else {
if (noApps) {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Nothing to show");
return;
}
}
}else {
mRecentTasksLoader.cancelLoadingThumbnails();
mRecentTasksDirty = true;
}
...
}
如果 mRecentsNoApps 为空则表示没有任务,显示 "No recent apps" 否则显示应用列表
否则则显示任务的缩略图。时序图如下:
3、点击某个缩略图执行
这里分为点击某个缩略图执行程序及长按缩略图执行程序
这里直接继承了 View.OnItemClickListener 所以可以直接执行子项按键事件
- public class RecentsPanelView extends RelativeLayout implements OnItemClickListener, RecentsCallback,
- StatusBarPanel, Animator.AnimatorListener, View.OnTouchListener
处理点击事件方法:
- public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
- handleOnClick(view);
- }
- public void handleOnClick(View view) {
- TaskDescription ad = ((ViewHolder) view.getTag()).taskDescription;
- final Context context = view.getContext();
- final ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager)
- context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
- if (ad.taskId >= 0) {
- // This is an active task; it should just go to the foreground.
- am.moveTaskToFront(ad.taskId, ActivityManager.MOVE_TASK_WITH_HOME);
- } else {
- Intent intent = ad.intent;
- intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_LAUNCHED_FROM_HISTORY
- | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_TASK_ON_HOME
- | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
- if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "Starting activity " + intent);
- context.startActivity(intent);
- }
- hide(true);
- }
注意代码:context.startActivity(intent); 这里就是执行对应的 Activity
处理长按键点击事件方法:
- public void handleLongPress(
- final View selectedView, final View anchorView, final View thumbnailView) {
- thumbnailView.setSelected(true);
- PopupMenu popup = new PopupMenu(mContext, anchorView == null ? selectedView : anchorView);
- popup.getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.recent_popup_menu, popup.getMenu());
- popup.setOnMenuItemClickListener(new PopupMenu.OnMenuItemClickListener() {
- public boolean onMenuItemClick(MenuItem item) {
- if (item.getItemId() == R.id.recent_remove_item) {
- mRecentsContainer.removeViewInLayout(selectedView);
- } else if (item.getItemId() == R.id.recent_inspect_item) {
- ViewHolder viewHolder = (ViewHolder) selectedView.getTag();
- if (viewHolder != null) {
- final TaskDescription ad = viewHolder.taskDescription;
- startApplicationDetailsActivity(ad.packageName);
- mBar.animateCollapse();
- } else {
- throw new IllegalStateException("Oops, no tag on view " + selectedView);
- }
- } else {
- return false;
- }
- return true;
- }
- });
- popup.setOnDismissListener(new PopupMenu.OnDismissListener() {
- public void onDismiss(PopupMenu menu) {
- thumbnailView.setSelected(false);
- }
- });
- popup.show();
- }
这里弹出一个PopupMenu,分别是 A:"Remove from list" 及 B:"App Info"
其中A项表示将此任务移除出列表,执行 mRecentsContainer.removeViewInLayout(selectedView);
另外B是启动另外一个Acitivty列出应用信息:
- private void startApplicationDetailsActivity(String packageName) {
- Intent intent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_APPLICATION_DETAILS_SETTINGS,
- Uri.fromParts("package", packageName, null));
- intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
- getContext().startActivity(intent);
- }
总结:
这里详细的对SystemUI 的两个最重要的 StatusBar NavigationBar(SystemUIService) 及缩略图代码流程分析。
因此各家厂商根据自家的需求,需要定制SystemUI或者美化SystemUI,不同的平台也会有不同的修改,但大体框架是没有变的,
无非是在原有基础上的修修改改或者增加一些自己的类等等。
以上是关于Android 11 SystemUI(状态/导航栏)-状态栏下拉时图标的隐藏与通知面板的半透黑色背景的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章



