postgresqL 的Btree 与gin索引
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了postgresqL 的Btree 与gin索引相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 一.gin索引需要安装第三方插件yum install postgresql96-contrib -- 安装插件
find / -name extension --可以看到btree_gin.control存在
create extension btree_gin; -- 添加索引
二.测试数据基本属性介绍
总共使用3个表,表结构和数据量完全一致。
表数据量:10522369
表字段:id ,basic_acc_no,id_card,name,sex,telephone,json_t
1)索引的配置情况:
basic_account_info_al -- btree
basic_account_info_al2 --gin
basic_account_info_al3 -- btree multi
basic_account_info_al 单列索引 id,basic_acc_no,name,json_t
basic_account_info_al2 gin索引 (id,basic_acc_no,id_card,name),(json_t)
basic_account_info_al3 复合索引 (id,basic_acc_no),(name,id)(json_t,id)
basic_account_info_al 表达式索引 (json_t->>id)
basic_account_info_al2表达式索引 ((json_t->>'id'))
三.测试结果
1.唯一值属性:索引字段都是唯一 id,basic_acc_no
查询语句
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al2 where id = 29699221 ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al where id = 29699221 ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al3 where id = 29699221 ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al2 where basic_acc_no = 'XFK2990134' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al where basic_acc_no = 'XFK2990134' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al3 where basic_acc_no = 'XFK2990134' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al2 where basic_acc_no = 'XFK9780134' and id = 29699221;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al where basic_acc_no = 'XFK9780134' and id = 29699221;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al3 where basic_acc_no = 'XFK9780134' and id = 29699221;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al2 where id = 29699221 and basic_acc_no = 'XFK9780134' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al where id = 29699221 and basic_acc_no = 'XFK9780134' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al3 where id = 29699221 and basic_acc_no = 'XFK9780134' ;
2.重复值属性: name是有重复值的。
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al where name ='张燕洪';
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al3 where name ='张燕洪';
explain analyse select *from basic_account_info_al2 where name ='张燕洪';
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al2 where id = 24426014 and name = '周杨' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al where id = 24426014 and name = '周杨' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al3 where id = 24426014 and name = '周杨' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al2 where name = '周杨' and id = 24426014 ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al where name = '周杨' and id = 24426014 ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al3 where name = '周杨' and id = 24426014 ;
3.jsonb属性
create index inx_gin_json on basic_account_info_al2 using gin (json_t);
create index inx_btree_json on basic_account_info_al (json_t);
create index inx_btree_2_js on basic_account_info_al3 (json_t,id );
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al where json_t ='"id": 21782879, "sex": 0, "name": "刘乐典"';
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al2 where json_t ='"id": 21782879, "sex": 0, "name": "刘乐典"';
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al3 where json_t ='"id": 21782879, "sex": 0, "name": "刘乐典"';
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al WHERE json_t @> '"id": 21782879';
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al2 WHERE json_t @> '"id": 21782879';
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al3 WHERE json_t @> '"id": 21782879';
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al where (json_t->>id)= '24426014' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al2 where (json_t->>id)= '24426014' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al3 where (json_t->>id)='24426014' ;
4.jsonb表达式索引
查询条件 表名 查询时使用的索引名称 查询时间(5次平均)/ms
(json_t->>id)= '24426014' basic_account_info_al inx_json_id 0.040
basic_account_info_al3 inx_json_id_2 0.039
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al where (json_t->>id)= '24426014' ;
explain analyse select * from basic_account_info_al2 where (json_t->>id)= '24426014' ;
四.获相同的结果使用Jsonb与btree对比
jsonb支持两种特有的GIN索引jsonb_ops和jsonb_path_ops。 jsonb_ops调用gin_extract_jsonb函数生成key,每个键和值都作为一个单独的索引项。而jsonb_path_ops使用函数gin_extract_jsonb_path抽取:只为每个值创建一个索引项。“foo”:“bar”,”baz”, jsonb_ops生成3个索引项,jsonb_path_ops由foo,bar,baz组合一个hash值作为一个索引项。jsonb_path_ops索引要比jsonb_ops的小很多,性能上也会有所提升。
create index inx_gin_patn_json ON public.basic_account_info_al4 USING gin (json_t jsonb_path_ops); -- jsonb_path_ops
create index inx_gin_json on basic_account_info_al2 using gin (json_t); --jsonb_ops
1.精确查询
2.范围查询
下表显示了gin索引对于jsonb数据类型可使用的操作符。
名称 索引数据类型 可索引操作符
jsonb_ops jsonb ? ?& ?| @>
json_path_ops jsonb @>
注:? ?& ?| 索引key是否包含在jsonb中
对于范围(json_t->>'id')< 20000079,这样的条件 gin索引不起作用, 这里采用表达式索引方式,查询条件的两边数据类型相同才可以做索引查询,否则全表扫描。
CREATE INDEX inx_json_id_2 ON public.basic_account_info_al2 USING btree (((json_t->>'id')::int));
总结: 当仅有一个条件查询时,gin索引与btree索引的性能差异不大,但有多个条件查询时,gin,btree单
列索引没有btree复合索引的性能高。jsonb是以二进制格式存储且不保证键的顺序。可以使用表达式索引指定到jsonb的具体键值,但是如果不能提前知道查询数据中的哪个键,确定定义GIN索引和使用@>(或者其他有利于索引的操作符)查询。
五.jsonb添加数据属性
例如:
"id":20000241,"name":"陈敏","sex":1 -> "age":"18","id":20000241,"name":"陈敏","sex":1
一旦创建了索引,就不需要进一步的干预:当表被修改时,系统将更新索引,当执行计划认为使用索引比顺序的表扫描更有效的时候,它会使用索引。
UPDATE basic_account_info_al4 SET json_t = json_t || '"age":"18"'::jsonb; -- 更新语句
gin索引名称 索引方式 修改前大小 修改后大小 带索引更新时间
inx_gin_patn_json jsonb_path_ops 574M 615M 643561.004 ms
inx_gin_json jsonb_ops 665M 695M 时间过长超过1h
jsonb_ops方式建立的索引大量更新时,执行时间太长。当插入更新时gin索引比较慢,如果要向一张大表中插入大量数据时,最好先把gin索引删除,插入数据后再重建索引。
当json_t为"id":20000241,"name":"陈敏","sex":1 数据量为10522369 创建gin索引时间
130372.955 ms
当json_t为"age":"18","id":20000241,"name":"陈敏","sex":1 数据量为10522369 创建gin索引时间
148971.011 ms
Postgresql GIN索引
GIN概念介绍:
GIN是Generalized Inverted Index的缩写。就是所谓的倒排索引。它处理的数据类型的值不是原子的,而是由元素构成。我们称之为复合类型。如(‘hank’, ‘15:3 21:4’)中,表示hank在15:3和21:4这两个位置出现过,下面会从具体的例子更加清晰的认识GIN索引。
全文搜索
GIN的主要应用领域是加速全文搜索,所以,这里我们使用全文搜索的例子介绍一下GIN索引。
如下,建一张表,doc_tsv是文本搜索类型,可以自动排序并消除重复的元素:
postgres=# create table ts(doc text, doc_tsv tsvector); postgres=# insert into ts(doc) values (\'Can a sheet slitter slit sheets?\'), (\'How many sheets could a sheet slitter slit?\'), (\'I slit a sheet, a sheet I slit.\'), (\'Upon a slitted sheet I sit.\'), (\'Whoever slit the sheets is a good sheet slitter.\'), (\'I am a sheet slitter.\'), (\'I slit sheets.\'), (\'I am the sleekest sheet slitter that ever slit sheets.\'), (\'She slits the sheet she sits on.\'); postgres=# update ts set doc_tsv = to_tsvector(doc); postgres=# create index on ts using gin(doc_tsv);
postgresql tsvector 文档链接:http://www.postgres.cn/docs/9.6/datatype-textsearch.html
该GIN索引结构如下,黑色方块是TID编号,白色为单词,注意这里是单向链表,不同于B-tree的双向链表:
posgresql tid ,ctid 参考链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_34372728/article/details/90591262
https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/181315.html
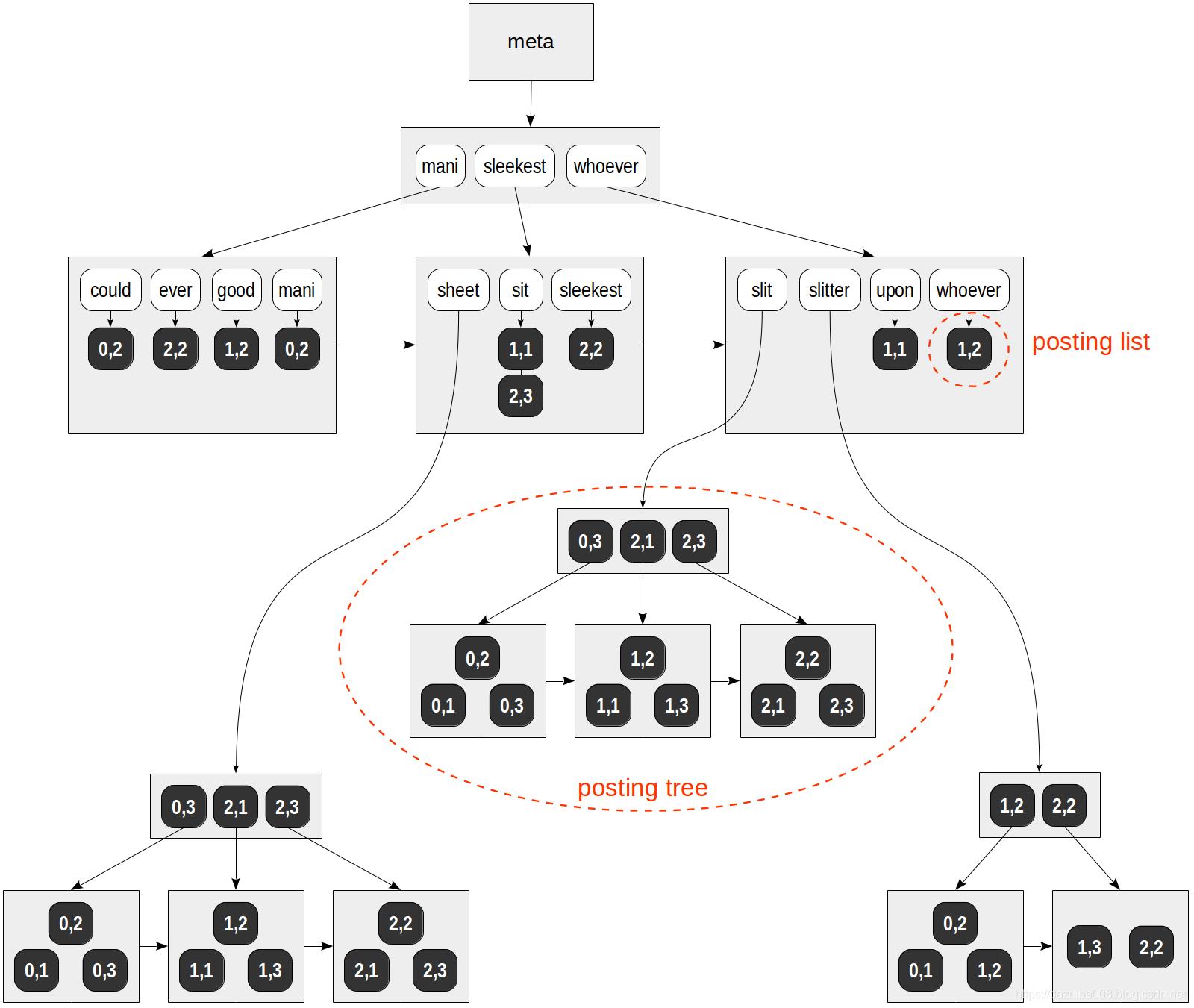
GIN索引在物理存储上包含如下内容:
1. Entry:GIN索引中的一个元素,可以认为是一个词位,也可以理解为一个key 2. Entry tree:在Entry上构建的B树 3. posting list:一个Entry出现的物理位置(heap ctid, 堆表行号)的链表 4. posting tree:在一个Entry出现的物理位置链表(heap ctid, 堆表行号)上构建的B树,所以posting tree的KEY是ctid,而entry tree的KEY是被索引的列的值 5. pending list:索引元组的临时存储链表,用于fastupdate模式的插入操作
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/flying-tiger/p/6704931.html
hank=# select ctid,doc, doc_tsv from ts; ctid | doc | doc_tsv --------+--------------------------------------------------------+--------------------------------------------------------- (0,1) | Can a sheet slitter slit sheets? | \'sheet\':3,6 \'slit\':5 \'slitter\':4 (0,2) | How many sheets could a sheet slitter slit? | \'could\':4 \'mani\':2 \'sheet\':3,6 \'slit\':8 \'slitter\':7 (0,3) | I slit a sheet, a sheet I slit. | \'sheet\':4,6 \'slit\':2,8 (1,1) | Upon a slitted sheet I sit. | \'sheet\':4 \'sit\':6 \'slit\':3 \'upon\':1 (1,2) | Whoever slit the sheets is a good sheet slitter. | \'good\':7 \'sheet\':4,8 \'slit\':2 \'slitter\':9 \'whoever\':1 (1,3) | I am a sheet slitter. | \'sheet\':4 \'slitter\':5 (2,1) | I slit sheets. | \'sheet\':3 \'slit\':2 (2,2) | I am the sleekest sheet slitter that ever slit sheets. | \'ever\':8 \'sheet\':5,10 \'sleekest\':4 \'slit\':9 \'slitter\':6 (2,3) | She slits the sheet she sits on. | \'sheet\':4 \'sit\':6 \'slit\':2 (9 rows)
由上可见,sheet,slit,slitter出现在多行之中,所有会有多个TID,这样就会生成一个TID列表,并为之生成一棵单独的B-tree。
以下语句可以找出多少行出现过该单词。
hank=# select (unnest(doc_tsv)).lexeme, count(*) from ts group by 1 order by 2 desc; lexeme | count ----------+------- sheet | 9 slit | 8 slitter | 5 sit | 2 upon | 1 mani | 1 whoever | 1 sleekest | 1 good | 1 could | 1 ever | 1 (11 rows)
所以执行以下语句,可以走用到GIN索引:
--这里由于数据量较小,所以禁用全表扫描 hank=# set enable_seqscan TO off; SET hank=# explain(costs off) select doc from ts where doc_tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'many & slitter\'); QUERY PLAN --------------------------------------------------------------------- Bitmap Heap Scan on ts Recheck Cond: (doc_tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'many & slitter\'::text)) -> Bitmap Index Scan on ts_doc_tsv_idx Index Cond: (doc_tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'many & slitter\'::text)) (4 rows) hank=# select amop.amopopr::regoperator, amop.amopstrategy from pg_opclass opc, pg_opfamily opf, pg_am am, pg_amop amop where opc.opcname = \'tsvector_ops\' and opf.oid = opc.opcfamily and am.oid = opf.opfmethod and amop.amopfamily = opc.opcfamily and am.amname = \'gin\' and amop.amoplefttype = opc.opcintype; amopopr | amopstrategy -----------------------+-------------- @@(tsvector,tsquery) | 1 matching search query @@@(tsvector,tsquery) | 2 synonym for @@ (for backward compatibility) (2 rows)
下图分别找mani和slitter
mani — (0,2).
slitter — (0,1), (0,2), (1,2), (1,3), (2,2).
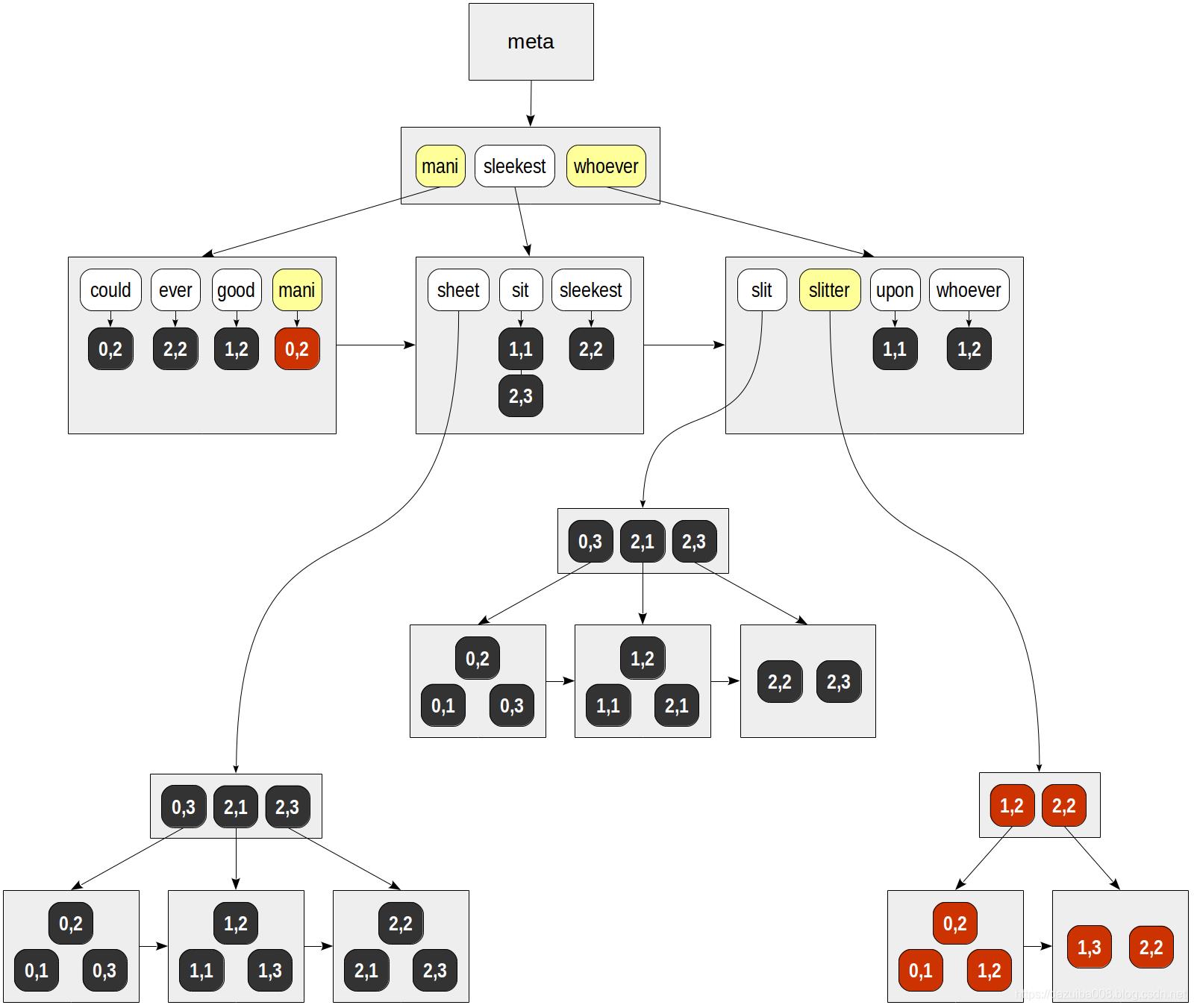
最后,看一下找到的相关行,并且条件是and,所以只能返回(0,2)。
| | | consistency | | | function TID | mani | slitter | slit & slitter -------+------+---------+---------------- (0,1) | f | T | f (0,2) | T | T | T (1,2) | f | T | f (1,3) | f | T | f (2,2) | f | T | f postgres=# select doc from ts where doc_tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'many & slitter\'); doc --------------------------------------------- How many sheets could a sheet slitter slit? (1 row)
文本搜索运算符参考文档: http://www.postgres.cn/docs/9.6/functions-textsearch.html
更新缓慢
GIN索引中的数据插入或更新非常慢。因为每行通常包含许多要索引的单词元素。因此,当添加或更新一行时,我们必须大量更新索引树。
另一方面,如果同时更新多个行,它们的某些单词元素可能是相同的,所以总的代价小于一行一行单独更新文档时的代价。
GIN索引具有 fastupdate 存储参数,我们可以在创建索引时指定它,并在以后更新:
postgres=# create index on ts using gin(doc_tsv) with (fastupdate = true);
fastupdate 参考链接: https://www.cnblogs.com/flying-tiger/p/6704931.html
启用此参数后,更新将累积在单独的无序列表中。当此列表足够大时或vacuum期间,所有累积的更新将立即对索引操作。这个“足够大”的列表由“ gin_pending_list_limit”配置参数或创建索引时同名的存储参数确定。
部分匹配搜索
查询包含slit打头的doc
hank=# select doc from ts where doc_tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'slit:*\'); doc -------------------------------------------------------- Can a sheet slitter slit sheets? How many sheets could a sheet slitter slit? I slit a sheet, a sheet I slit. Upon a slitted sheet I sit. Whoever slit the sheets is a good sheet slitter. I am a sheet slitter. I slit sheets. I am the sleekest sheet slitter that ever slit sheets. She slits the sheet she sits on. (9 rows)
同样可以使用索引加速:
postgres=# explain (costs off) select doc from ts where doc_tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'slit:*\'); QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------------------------- Bitmap Heap Scan on ts Recheck Cond: (doc_tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'slit:*\'::text)) -> Bitmap Index Scan on ts_doc_tsv_idx Index Cond: (doc_tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'slit:*\'::text)) (4 rows)
频翻和不频繁
制造一些数据,下载地址: http://oc.postgrespro.ru/index.php/s/fRxTZ0sVfPZzbmd/download
fts=# alter table mail_messages add column tsv tsvector; fts=# update mail_messages set tsv = to_tsvector(body_plain); fts=# create index on mail_messages using gin(tsv); --这里不使用unnest统计单词出现在行的次数,因为数据量比较大,我们使用ts_stat函数来进行计算 fts=# select word, ndoc from ts_stat(\'select tsv from mail_messages\') order by ndoc desc limit 3; word | ndoc -------+-------- re | 322141 wrote | 231174 use | 176917 (3 rows)
例如我们查询邮件信息里很少出现的单词,如“tattoo”:
fts=# select word, ndoc from ts_stat(\'select tsv from mail_messages\') where word = \'tattoo\'; word | ndoc --------+------ tattoo | 2 (1 row)
两个单词同一行出现的次数,wrote和tattoo同时出现的行只有一行
fts=# select count(*) from mail_messages where tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'wrote & tattoo\'); count ------- 1 (1 row)
我们来看看是如何执行的,如上所述,如果我们要获得两个词的TID列表,则搜索效率显然很低下:因为将必须遍历20多万个值,而只取一个值。但是通过统计信息,该算法可以了解到“wrote”经常出现,而“ tattoo”则很少出现。因此,将执行不经常使用的词的搜索,然后从检索到的两行中检查是否存在“wrote”。这样就可以快速得出查询结果:
fts=# \\timing on fts=# select count(*) from mail_messages where tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'wrote & tattoo\'); count ------- 1 (1 row) Time: 0,959 ms
查询wrote将话费更长的时间
fts=# select count(*) from mail_messages where tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'wrote\'); count -------- 231174 (1 row) Time: 2875,543 ms (00:02,876)
这种优化当然不只是两个单词元素搜索有效,其他更复杂的搜索也有效。
限制查询结果
GIN的一个特点是,结果总是以位图的形式返回:该方法不能按TID返回所需数据的TID。因此,本文中的所有查询计划都使用位图扫描。
因此,使用LIMIT子句限制索引扫描结果的效率不是很高。注意操作的预计成本(“limit”节点的“cost”字段):
fts=# explain (costs off) select * from mail_messages where tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'wrote\') limit 1; QUERY PLAN ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Limit (cost=1283.61..1285.13 rows=1) -> Bitmap Heap Scan on mail_messages (cost=1283.61..209975.49 rows=137207) Recheck Cond: (tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'wrote\'::text)) -> Bitmap Index Scan on mail_messages_tsv_idx (cost=0.00..1249.30 rows=137207) Index Cond: (tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'wrote\'::text)) (5 rows)
估计成本为1285.13,比构建整个位图1249.30的成本(“Bitmap Index Scan”节点的“cost”字段)稍大。
因此,索引具有限制结果数量的功能。该阈值gin_fuzzy_search_limit配置参数中指定,并且默认情况下等于零(没有限制)。但是我们可以设置阈值:
fts=# set gin_fuzzy_search_limit = 1000; fts=# select count(*) from mail_messages where tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'wrote\'); count ------- 5746 (1 row) fts=# set gin_fuzzy_search_limit = 10000; fts=# select count(*) from mail_messages where tsv @@ to_tsquery(\'wrote\'); count ------- 14726 (1 row)
我们可以看到,查询返回的行数对于不同的参数值是不同的(如果使用索引访问)。限制并不严格:可以返回多于指定行的行,这证明参数名称的“模糊”部分是合理的。
GIN索引比较小,不会占用太多空间。首先,如果在多行中出现相同的单词,则它仅在索引中存储一次。其次,TID以有序的方式存储在索引中,这使我们能够使用一种简单的压缩方式:列表中的下一个TID实际上与上一个TID是不同的;这个数字通常很小,与完整的六字节TID相比,所需的位数要小得多。
为了了解其大小,我们从消息文本构建B树:
- GIN建立在不同的数据类型(“ tsvector”而不是“ text”)上,该数据类型较小
- 同时,B树的消息大小必须缩短到大约2 KB。
fts=# create index mail_messages_btree on mail_messages(substring(body_plain for 2048));
创建一个gist索引:
fts=# create index mail_messages_gist on mail_messages using gist(tsv);
分别看一下gin,gist,btree的大小:
fts=# select pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size(\'mail_messages_tsv_idx\')) as gin, pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size(\'mail_messages_gist\')) as gist, pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size(\'mail_messages_btree\')) as btree; gin | gist | btree --------+--------+-------- 179 MB | 125 MB | 546 MB (1 row)
由于GIN索引更节省空间,我们从Oracle迁移到postgresql过程中可以使用GIN索引来代替位图索引。通常,位图索引用于唯一值很少的字段,这对于GIN也是非常有效的。而且,PostgreSQL可以基于任何索引(包括GIN)动态构建位图。
使用GiST还是GIN
一般来说,GIN在准确性和搜索速度上均胜过GiST。如果数据更新不频繁并且需要快速搜索,则可以选择GIN。
另一方面,如果对数据进行密集更新,则更新GIN的开销成本可能太大。在这种情况下,我们将不得不比较这两种索引,并选择其相关特征更适合的索引。
数组
使用GIN的另一个示例是数组的索引。在这种情况下,数组元素进入索引,这可以加快对数组的许多操作:
postgres=# select amop.amopopr::regoperator, amop.amopstrategy from pg_opclass opc, pg_opfamily opf, pg_am am, pg_amop amop where opc.opcname = \'array_ops\' and opf.oid = opc.opcfamily and am.oid = opf.opfmethod and amop.amopfamily = opc.opcfamily and am.amname = \'gin\' and amop.amoplefttype = opc.opcintype; amopopr | amopstrategy -----------------------+-------------- &&(anyarray,anyarray) | 1 intersection @>(anyarray,anyarray) | 2 contains array <@(anyarray,anyarray) | 3 contained in array =(anyarray,anyarray) | 4 equality (4 rows)
数组运算符符文档链接: http://postgres.cn/docs/9.6/functions-array.html
还是以以前航班数据库为例:(我也不知道原博主的航班数据库在哪里。。。)
demo=# select departure_airport_name, arrival_airport_name, days_of_week from routes where flight_no = \'PG0049\'; departure_airport_name | arrival_airport_name | days_of_week ------------------------+----------------------+-------------- Vnukovo | Gelendzhik | {2,4,7} (1 row)
新建一张表并创建索引:
demo=# create table routes_t as select * from routes; demo=# create index on routes_t using gin(days_of_week);
现在,我们可以使用该索引来获取在星期二,星期四和星期日出发的所有航班:
demo=# explain (costs off) select * from routes_t where days_of_week = ARRAY[2,4,7]; QUERY PLAN ----------------------------------------------------------- Bitmap Heap Scan on routes_t Recheck Cond: (days_of_week = \'{2,4,7}\'::integer[]) -> Bitmap Index Scan on routes_t_days_of_week_idx Index Cond: (days_of_week = \'{2,4,7}\'::integer[]) (4 rows)
可以看到出现六趟航班:
demo=# select flight_no, departure_airport_name, arrival_airport_name, days_of_week from routes_t where days_of_week = ARRAY[2,4,7]; flight_no | departure_airport_name | arrival_airport_name | days_of_week -----------+------------------------+----------------------+-------------- PG0005 | Domodedovo | Pskov | {2,4,7} PG0049 | Vnukovo | Gelendzhik | {2,4,7} PG0113 | Naryan-Mar | Domodedovo | {2,4,7} PG0249 | Domodedovo | Gelendzhik | {2,4,7