云原生学习K8s的扩展技能(CRD)
Posted 跳楼梯企鹅
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了云原生学习K8s的扩展技能(CRD)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
博主昵称:跳楼梯企鹅
博主主页面链接:博主主页传送门博主专栏页面连接:专栏传送门--网路安全技术
创作初心:本博客的初心为与技术朋友们相互交流,每个人的技术都存在短板,博主也是一样,虚心求教,希望各位技术友给予指导。
博主座右铭:发现光,追随光,成为光,散发光;
博主研究方向:渗透测试、机器学习 ;
博主寄语:感谢各位技术友的支持,您的支持就是我前进的动力 ;
目录
一、CRD 扩展 Kubernetes 集群
1.什么是 CRD
CRD 本身是一种 Kubernetes 内置的资源类型,是 CustomResourceDefinition 的缩写,可以通过
kubectlget命令查看集群内定义的 CRD 资源。

$kubectl get crd
NAME CREATED AT
apps.app.my.cn 2022-09-25T07:02:47Z
microservices.app.my.cn 2022-09-25T07:02:47Z2.CRD 能做什么
(1)微服务管理总览
App负责管理整个应用的生命周期,MicroService负责管理微服务的生命周期。① 部署方面:App可以直接管理多个MicroService,同时MicroService利用控制器模式,可以为每个版本创建一个Deployment, 实现多个版本同时部署。
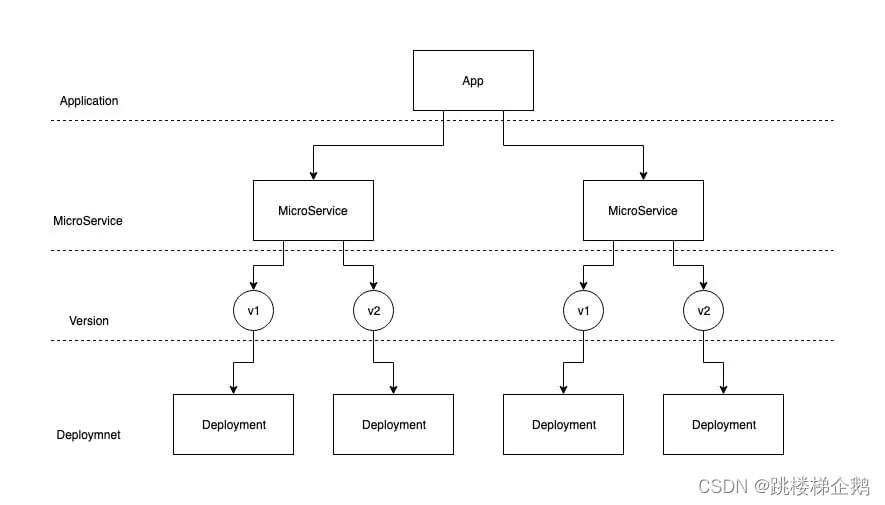
MicroService为自己创建 1 个的LoadBalance,也为每个版本创建了Service。如下图所示,MicroService下的每个版本(对应每个Deployment)都有Service,而本身也有LoadBalance,即总共拥有n+1个Service
(2)创建 Yaml 配置
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
controller-tools.k8s.io: "1.0"
# 名称必须与下面的spec字段匹配,格式为: <plural>.<group>
name: apps.app.o0w0o.cn
spec:
# 用于REST API的组名称: /apis/<group>/<version>
group: app.o0w0o.cn
names:
# kind字段使用驼峰命名规则. 资源清单使用如此
kind: App
# URL中使用的复数名称: /apis/<group>/<version>/<plural>
plural: apps
# 指定crd资源作用范围在命名空间或集群
scope: Namespaced
# 自定义资源的子资源的描述
subresources:
# 启用状态子资源
status:
# 验证机制
validation:
# openAPIV3Schema is the schema for validating custom objects.
openAPIV3Schema:
properties:
...
(3)自定义 Controller 逻辑
func (r *ReconcileApp) Reconcile(request reconcile.Request) (reconcile.Result, error)
...
// 状态 App 同步
if err := r.syncAppStatus(instance); err != nil
log.Info("Sync App error", err)
return reconcile.Result, err
// 协调资源 MicroService
if err := r.reconcileMicroService(request, instance); err != nil
log.Info("Creating MicroService error", err)
return reconcile.Result, err
...
func (r *ReconcileMicroService) Reconcile(request reconcile.Request) (reconcile.Result, error)
...
// 同步 MicroService 状态
if err := r.syncMicroServiceStatus(instance); err != nil
log.Info("Sync MicroServiceStatus error", err)
return reconcile.Result, err
// 协调实例
if err := r.reconcileInstance(instance); err != nil
log.Info("Reconcile Instance Versions error", err)
return reconcile.Result, err
// 协调负载均衡器
if err := r.reconcileLoadBalance(instance); err != nil
log.Info("Reconcile LoadBalance error", err)
return reconcile.Result, err
...
二、CRD 字段校验
1.校验方式
kubernetes 目前提供了两种方式来对 CR 的校验
语法校验(
OpenAPI v3 schema)语义校验(
validatingadmissionwebhook)
2.举例
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
# name must match the spec fields below, and be in the form: <plural>.<group>
name: kubernetesclusters.ecs.yun.com
spec:
# group name to use for REST API: /apis/<group>/<version>
group: ecs.yun.com
# list of versions supported by this CustomResourceDefinition
versions:
- name: v1
# Each version can be enabled/disabled by Served flag.
served: true
# One and only one version must be marked as the storage version.
storage: true
# either Namespaced or Cluster
scope: Namespaced
names:
# plural name to be used in the URL: /apis/<group>/<version>/<plural>
plural: kubernetesclusters
# singular name to be used as an alias on the CLI and for display
singular: kubernetescluster
# kind is normally the CamelCased singular type. Your resource manifests use this.
kind: KubernetesCluster
# listKind
listKind: KubernetesClusterList
# shortNames allow shorter string to match your resource on the CLI
shortNames:
- ecs
#CRD 对象
apiVersion: ecs.yun.com/v1
kind: KubernetesCluster
metadata:
name: test-cluster
spec:
clusterType: kubernetes
serviceCIDR: ''
masterList:
- ip: 192.168.1.10
nodeList:
- ip: 192.168.1.11
privateSSHKey: ''
scaleUp: 0
scaleDown: 03.API的常用方式
- 使用CRD(CustomResourceDefinitions)自定义资源类型
- 开发自定义的APIServer并聚合至主API Server
- 及定制扩展API Server源码。这其中,CRD最为易用但限制颇多,自定义API Server更富于弹性但代码工作量偏大,而仅在必须添加新的核心类型才能确保专用的Kberneves集群功能正常,才应该定制系统源码
- 其中CRD与CRT一般由开发或服务供应商提供
- CRD只是定义一个类型Kind,但实际把kind运行起来CR需要有Controller来对资源进行控制,所有只有定义CRD定义没有并没有实际意义,当然也可以通过定义现在kind来运行,比如deployment 通过定义 RC来运行
(1)配置
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1 #API群组和版本
kind: CustomResourceDefinition #资源类别
metadata:
-name <string> #资源名称
spec:
conversion <object> #定义不同版本间的格式转换方式
strategy <string># 不同版本间的自定义资源转换策略,有None和webhook两种取值
webhook <0bject>#如何调用用于进行格式转换的webhook
group <string>#资源所属的API群组
names <object># 自定义资源的类型,即该CRD创建资源规范时使用的kind
categories <[]string>#资源所属的类别编目,例如"kubectl get all"中的all
kind <string> #kind名称,必选字段
listKind <string> #资源列表名称,默认为"`kind`List"
plural <string> #复数,用于API路径`/apis/<group>/<version>/. . ./<plural>"
shortNames <[string>#该资源的kind的缩写格式
singular <string>#资源kind的单数形式,必须使用全小写字母,默认为小写的kind名称
preserveUnknownFields <boolean> #预留的非知名字段,kind等都是知名的预留字段
scope <string> #作用域,可用值为Cluster和Namespaced
versions <[]object>#版本号定义
additionalPrinterColumns <[]0bject> #需要返回的额外信息
name <string> #形如vM[alphaN|betaN]格式的版本名称,例如v1或vlalpha2等
schema <object> #该资源的数据格式(schema)定义,必选字段
openAPIV3Schema <object> #用于校验字段的schema对象,格式请参考相关手册
served <boolean> #是否允许通过RESTful API调度该版本,必选字段
storage <boolean> #将自定义资源存储于etcd中时是不是使用该版本
subresources <0bject>#子资源定义
scale <0bject># 启用scale子资源,通过autoscaling/v1.Scale发送负荷
status <map[string]># 启用status子资源,为资源生成/status端点(2)查看文件
calico的yaml文件
[root@k8s-master plugin]# vim calico.yaml
...
---
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ippools.crd.projectcalico.org
spec:
......
...
[root@k8s-master plugin]# kubectl get CustomResourceDefinition
NAME CREATED AT
bgpconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
bgppeers.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
blockaffinities.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
clusterinformations.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
felixconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
globalnetworkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
globalnetworksets.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
hostendpoints.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
ipamblocks.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
ipamconfigs.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
ipamhandles.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
ippools.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
kubecontrollersconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
networkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z
networksets.crd.projectcalico.org 2022-08-25T14:33:24Z(3)自定义CRD模型
[root@k8s-master crd]# cat user-cr-demo.yaml
apiVersion: auth.ilinux.io/v1alpha1
kind: User
metadata:
name: admin
namespace: default
spec:
userID: 1
email: test@test.com
groups:
- superusers
- adminstrators
password: ikubernetes.io
[root@k8s-master crd]# kubectl apply -f user-cr-demo.yaml
user.auth.ilinux.io/admin created
[root@k8s-master crd]# kubectl get User
NAME AGE
admin 14s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl describe User admin
Name: admin
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
API Version: auth.ilinux.io/v1alpha1
Kind: User
Metadata:
Creation Timestamp: 2022-09-25T14:51:53Z
Generation: 1
Managed Fields:
API Version: auth.ilinux.io/v1alpha1
Fields Type: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:metadata:
f:annotations:
.:
f:kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration:
f:spec:
.:
f:email:
f:groups:
f:password:
f:userID:
Manager: kubectl-client-side-apply
Operation: Update
Time: 2022-09-25T14:51:53Z
Resource Version: 2583010
Self Link: /apis/auth.ilinux.io/v1alpha1/namespaces/default/users/admin
UID: 5af89454-e067-4f30-83b7-cc2ad82e3526
Spec:
Email: test@test.com
Groups:
superusers
adminstrators
Password: ikubernetes.io
User ID: 1
Events: <none>
解锁云原生 AI 技能 - 开发你的机器学习工作流
按照上篇文章《解锁云原生 AI 技能 | 在 Kubernetes 上构建机器学习系统》搭建了一套 Kubeflow Pipelines 之后,我们一起小试牛刀,用一个真实的案例,学习如何开发一套基于 Kubeflow Pipelines 的机器学习工作流。
准备工作
机器学习工作流是一个任务驱动的流程,同时也是数据驱动的流程,这里涉及到数据的导入和准备、模型训练 Checkpoint 的导出评估、到最终模型的导出。这就需要分布式存储作为传输的媒介,此处使用 NAS 作为分布式存储。
- 创建分布式存储,这里以 NAS 为例。此处
NFS_SERVER_IP需要替换成真实 NAS 服务器地址
- 创建阿里云 NAS 服务,可以参考文档
- 需要在 NFS Server 中创建
/data
# mkdir -p /nfs # mount -t nfs -o vers=4.0 NFS_SERVER_IP:/ /nfs # mkdir -p /data # cd / # umount /nfs
- 创建对应的 Persistent Volume
# cat nfs-pv.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: user-susan labels: user-susan: pipelines spec: persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain capacity: storage: 10Gi accessModes: - ReadWriteMany nfs: server: NFS_SERVER_IP path: "/data" # kubectl create -f nfs-pv.yaml 创建 Persistent Volume Claim # cat nfs-pvc.yaml apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: user-susan annotations: description: "this is the mnist demo" owner: Tom spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany resources: requests: storage: 5Gi selector: matchLabels: user-susan: pipelines # kubectl create -f nfs-pvc.yaml
开发 Pipeline
由于 Kubeflow Pipelines 提供的例子都是依赖于 Google 的存储服务,这导致国内的用户无法真正体验 Pipelines 的能力。为此,阿里云容器服务团队提供了基于 NAS 存储训练 MNIST 模型的例子,方便您在阿里云上使用和学习 Kubeflow Pipelines。具体步骤分 3 步:
- (1) 下载数据
- (2) 利用 TensorFlow 进行模型训练
- (3) 模型导出
在这 3 个步骤中,后一个步骤都依赖于前一个步骤而完成。
Kubeflow Pipelines 中可以用 Python 代码描述这样一个流程, 完整代码可以查看 standalone_pipeline.py。
我们在例子中使用了基于开源项目 Arena 的 arena_op ,这是对于 Kubeflow 默认的 container_op 封装,它能够实现对于分布式训练 MPI 和 PS 模式的无缝衔接,另外也支持使用 GPU 和 RDMA 等异构设备和分布式存储的简单接入,同时方便从 git 源同步代码,是一个比较实用的工具 API。
@dsl.pipeline( name=‘pipeline to run jobs‘, description=‘shows how to run pipeline jobs.‘ ) def sample_pipeline(learning_rate=‘0.01‘, dropout=‘0.9‘, model_version=‘1‘, commit=‘f097575656f927d86d99dd64931042e1a9003cb2‘): """A pipeline for end to end machine learning workflow.""" data=["user-susan:/training"] gpus=1 # 1. prepare data prepare_data = arena.standalone_job_op( name="prepare-data", image="byrnedo/alpine-curl", data=data, command="mkdir -p /training/dataset/mnist && \ cd /training/dataset/mnist && curl -O https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code/raw/master/data/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz && \ curl -O https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code/raw/master/data/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz && \ curl -O https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code/raw/master/data/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz && \ curl -O https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code/raw/master/data/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz") # 2. downalod source code and train the models train = arena.standalone_job_op( name="train", image="tensorflow/tensorflow:1.11.0-gpu-py3", sync_source="https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code.git", env=["GIT_SYNC_REV=%s" % (commit)], gpus=gpus, data=data, command=‘‘‘ echo %s;python code/tensorflow-sample-code/tfjob/docker/mnist/main.py --max_steps 500 --data_dir /training/dataset/mnist --log_dir /training/output/mnist --learning_rate %s --dropout %s‘‘‘ % (prepare_data.output, learning_rate, dropout), metrics=["Train-accuracy:PERCENTAGE"]) # 3. export the model export_model = arena.standalone_job_op( name="export-model", image="tensorflow/tensorflow:1.11.0-py3", sync_source="https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code.git", env=["GIT_SYNC_REV=%s" % (commit)], data=data, command="echo %s;python code/tensorflow-sample-code/tfjob/docker/mnist/export_model.py --model_version=%s --checkpoint_path=/training/output/mnist /training/output/models" % (train.output, model_version))
Kubeflow Pipelines 会将上面的代码转化成一个有向无环图 (DAG), 其中的每一个节点就是 Component (组件),而 Component (组件)之间的连线代表它们之间的依赖关系。从 Pipelines UI 可以看到 DAG 图:

首先具体理解一下数据准备的部分,这里我们提供了 arena.standalone_job_op 的 Python API, 需要指定该步骤的名称: name; 需要使用的容器镜像: image; 要使用的数据以及其对应到容器内部的挂载目录: data。
这里的 data 是一个数组格式, 如 data=["user-susan:/training"],表示可以挂载到多个数据。 其中 user-susan 是之前创建的 Persistent Volume Claim, 而 /training 为容器内部的挂载目录。
prepare_data = arena.standalone_job_op( name="prepare-data", image="byrnedo/alpine-curl", data=data, command="mkdir -p /training/dataset/mnist && \ cd /training/dataset/mnist && curl -O https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code/raw/master/data/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz && \ curl -O https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code/raw/master/data/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz && \ curl -O https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code/raw/master/data/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz && \ curl -O https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code/raw/master/data/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz")
而上述步骤实际上是从指定地址利用 curl 下载数据到分布式存储对应的目录 /training/dataset/mnist,请注意这里的 /training 为分布式存储的根目录,类似大家熟悉的根 mount 点;而 /training/dataset/mnist 是子目录。其实后面的步骤可以通过使用同样的根 mount 点,读到数据,进行运算。
第二步是利用下载到分布式存储的数据,并通过 git 指定固定 commit id 下载代码,并进行模型训练。
train = arena.standalone_job_op( name="train", image="tensorflow/tensorflow:1.11.0-gpu-py3", sync_source="https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code.git", env=["GIT_SYNC_REV=%s" % (commit)], gpus=gpus, data=data, command=‘‘‘ echo %s;python code/tensorflow-sample-code/tfjob/docker/mnist/main.py --max_steps 500 --data_dir /training/dataset/mnist --log_dir /training/output/mnist --learning_rate %s --dropout %s‘‘‘ % (prepare_data.output, learning_rate, dropout), metrics=["Train-accuracy:PERCENTAGE"])
可以看到这个步骤比数据准备要相对复杂一点,除了和第一步骤中的 name, image, data 和 command 一样需要指定之外,在模型训练步骤中,还需要指定:
- 获取代码的方式: 从可重现实验的角度来看,对于运行试验代码的追本溯源,是非常重要的一环。可以在 API 调用时指定
sync_source的 git 代码源,同时通过设定env中GIT_SYNC_REV指定训练代码的 commit id; - gpu: 默认为 0,就是不使用 GPU;如果为大于 0 的整数值,就代表该步骤需要这个数量的 GPU 数;
- metrics: 同样是从可重现和可比较的实验目的出发,用户可以将需要的一系列指标导出,并且通过 Pipelines UI 进行直观的显示和比较。具体使用方法分为两步:1. 在调用 API 时以数组的形式指定要收集指标的 metrics name 和指标的展示格式 PERCENTAGE 或者是 RAW,比如
metrics=["Train-accuracy:PERCENTAGE"]。 2. 由于 Pipelines 默认会从 stdout 日志中收集指标,你需要在真正运行的模型代码中输出 metrics name=value 或者 metrics name:value, 可以参考具体样例代码。

值得注意的是:
在本步骤中指定了和
prepare_data相同的data参数 ["user-susan:/training"],就可以在训练代码中读到对应的数据,比如--data_dir /training/dataset/mnist。另外由于该步骤依赖于
prepare_data,可以在方法中通过指定prepare_data.output表示两个步骤的依赖关系。
最后 export_model 是基于 train 训练产生的 checkpoint,生成训练模型:
export_model = arena.standalone_job_op( name="export-model", image="tensorflow/tensorflow:1.11.0-py3", sync_source="https://code.aliyun.com/xiaozhou/tensorflow-sample-code.git", env=["GIT_SYNC_REV=%s" % (commit)], data=data, command="echo %s;python code/tensorflow-sample-code/tfjob/docker/mnist/export_model.py --model_version=%s --checkpoint_path=/training/output/mnist /training/output/models" % (train.output, model_version))
export_model 和第二步 train 类似,甚至要更为简单,它只是从 git 同步模型导出代码并且利用共享目录 /training/output/mnist 中的 checkpoint 执行模型导出。
整个工作流程看起来还是很直观的, 下面就可以定义一个 Python 方法将整个流程贯穿在一起:
@dsl.pipeline( name=‘pipeline to run jobs‘, description=‘shows how to run pipeline jobs.‘ ) def sample_pipeline(learning_rate=‘0.01‘, dropout=‘0.9‘, model_version=‘1‘, commit=‘f097575656f927d86d99dd64931042e1a9003cb2‘):
@dsl.pipeline 是表示工作流的装饰器,这个装饰器中需要定义两个属性,分别是
name和description。入口方法
sample_pipeline中定义了 4 个参数:learning_rate,dropout,model_version和commit, 分别可以在上面的train和export_model阶段使用。这里的参数的值实际上是 dsl.PipelineParam 类型,定义成 dsl.PipelineParam 的目的在于可以通过 Kubeflow Pipelines 的原生 UI 将其转换成输入表单,表单的关键字是参数名称,而默认值为参数的值。值得注意的是,这里的 dsl.PipelineParam 对应值实际上只能是字符串和数字型;而数组和 map,以及自定义类型都是无法通过转型进行变换的。
实际上,这些参数都可以在用户提交工作流时进行覆盖,以下就是提交工作流对应的 UI:

提交 Pipeline
您可以在自己的 Kubernetes 内将前面开发工作流的 Python DSL 提交到 Kubeflow Pipelines 服务中, 实际提交代码很简单:
KFP_SERVICE="ml-pipeline.kubeflow.svc.cluster.local:8888" import kfp.compiler as compiler compiler.Compiler().compile(sample_pipeline, __file__ + ‘.tar.gz‘) client = kfp.Client(host=KFP_SERVICE) try: experiment_id = client.get_experiment(experiment_name=EXPERIMENT_NAME).id except: experiment_id = client.create_experiment(EXPERIMENT_NAME).id run = client.run_pipeline(experiment_id, RUN_ID, __file__ + ‘.tar.gz‘, params=‘learning_rate‘:learning_rate, ‘dropout‘:dropout, ‘model_version‘:model_version, ‘commit‘:commit)
利用
compiler.compile将 Python 代码编译成执行引擎 (Argo) 识别的 DAG 配置文件;通过 Kubeflow Pipeline 的客户端创建或者找到已有的实验,并且提交之前编译出的 DAG 配置文件。
在集群内准备一个 python3 的环境,并且安装 Kubeflow Pipelines SDK:
# kubectl create job pipeline-client --namespace kubeflow --image python:3 -- sleep infinity # kubectl exec -it -n kubeflow $(kubectl get po -l job-name=pipeline-client -n kubeflow | grep -v NAME| awk ‘print $1‘) bash
登录到 Python3 的环境后,执行如下命令,连续提交两个不同参数的任务:
# pip3 install http://kubeflow.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/kfp/0.1.14/kfp.tar.gz --upgrade # pip3 install http://kubeflow.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/kfp-arena/kfp-arena-0.4.tar.gz --upgrade # curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cheyang/pipelines/update_standalone_sample/samples/arena-samples/standalonejob/standalone_pipeline.py # python3 standalone_pipeline.py --learning_rate 0.0001 --dropout 0.8 --model_version 2 # python3 standalone_pipeline.py --learning_rate 0.0005 --dropout 0.8 --model_version 3
查看运行结果
登录到 Kubeflow Pipelines 的 UI: https://pipeline地址/pipeline/#/experiments, 比如:
https://11.124.285.171/pipeline/#/experiments
点击 Compare runs 按钮,可以比较两个实验的输入、花费的时间和精度等一系列指标。让实验可追溯是让实验可重现的第一步,而利用 Kubeflow Pipelines 本身的实验管理能力则是开启实验可重现的第一步。

总结
实现一个可以运行的 Kubeflow Pipeline 需要的步骤是:
- 构建 Pipeline (流水线)中需要的最小执行单元 Component (组件),如果是利用原生定义的
dsl.container_ops, 需要构建两部分代码:
- 构建运行时代码:通常是为每个步骤构建容器镜像,作为 Pipelines 和真正执行业务逻辑代码之间的适配器。它所做的事情为获取 Pipelines 上下文的输入参数,调用业务逻辑代码,并且将需要传递到下个步骤的输出按照 Pipelines 的规则放到容器内的指定位置,由底层工作流组件负责传递。 这样产生的结果是运行时代码与业务逻辑代码会耦合在一起。可以参考 Kubeflow Pipelines 的例子;
- 构建客户端代码:这个步骤通常是长成下面的样子, 熟悉 Kubernetes 的朋友会发现这个步骤实际上就是在编写 Pod Spec:
container_op = dsl.ContainerOp( name=name, image=‘<train-image>‘, arguments=[ ‘--input_dir‘, input_dir, ‘--output_dir‘, output_dir, ‘--model_name‘, model_name, ‘--model_version‘, model_version, ‘--epochs‘, epochs ], file_outputs=‘output‘: ‘/output.txt‘ ) container_op.add_volume(k8s_client.V1Volume( host_path=k8s_client.V1HostPathVolumeSource( path=persistent_volume_path), name=persistent_volume_name)) container_op.add_volume_mount(k8s_client.V1VolumeMount( mount_path=persistent_volume_path, name=persistent_volume_name))
利用原生定义的 dsl.container_ops 的好处在于灵活,由于开放了和 Pipelines 的交互接口,用户可以在 container_ops 这个层面做许多事情。但是它的问题在于:
- 复用度低。每个 Component 都需要构建镜像和开发运行时代码;
- 复杂度高。使用者需要了解 Kubernetes 的概念,比如 resource limit, PVC, node selector 等一系列概念;
- 支持分布式训练困难。由于
container_op为单容器操作,如果需要支持分布式训练就需要在 container_ops 中提交和管理类似 TFJob 的任务。这里会带来复杂度和安全性的双重挑战,复杂度比较好理解,安全性是说提交 TFJob 这类任务的权限会需要开放额外的权限给 Pipeline 的开发者。
另一种方式是使用 arena_op 这种可以重用的 Component API,它使用通用运行时代码,可以免去重复构建运行时代码的工作;同时利用通用一套的 arena_op API 简化用户的使用;也支持 Parameter Server 和 MPI 等场景。建议您使用这种方式编译 Pipelines。
- 将构建好的 Component (组件)拼接成 Pipeline (流水线);
- 将 Pipeline (流水线)编译成 Argo 的执行引擎 (Argo) 识别的 DAG 配置文件, 并提交 DAG 配置文件到 Kubeflow Pipelines, 利用 Kubeflow Pipelines 自身的 UI 查看流程结果。
以上是关于云原生学习K8s的扩展技能(CRD)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章