索引属性
唯一索引
索引的惟一属性会导致MongoDB拒绝索引字段的重复值。除了唯一的约束之外,独特的索引与其他MongoDB索引在功能上是可互换的。
部分索引
部分索引只在满足指定筛选器表达式的集合中索引文档。通过对集合中的文档子集进行索引,部分索引具有较低的存储需求,并降低了索引创建和维护的性能成本。部分索引提供了稀疏索引功能的超集,优于稀疏索引。
稀疏索引
索引的稀疏属性确保索引只包含有索引字段的文档的条目。索引跳过没有索引字段的文档。您可以将稀疏索引选项与惟一索引选项组合起来,以拒绝对字段具有重复值的文档,而忽略没有索引键的文档
TTL索引
TTL索引是MongoDB可以用来在一定时间后自动从集合中删除文档的特殊索引。这对于某些类型的信息非常理想,比如机器生成的事件数据、日志和会话信息,这些信息只需要在数据库中保存有限的时间。
索引的种类和使用
很多时候,数据库性能变差,查询变慢,都与索引有密切的关系.如何建立适当的索引对于查询优化至关重要.
- 数据量很大时,查询使用索引可大幅度提高效率
- 如果 数据量非常大,创建索引需要消耗一定的时间,这时需要在使用数据库之前就将索引创建完毕,否则会对数据库性能造成较大影响
相关操作
| 命令 | 操作 |
|---|---|
db.collection.createIndex() |
在集合上构建索引。 |
db.collection.dropIndex() |
移除集合上的指定索引 |
db.collection.dropIndexes() |
删除集合上的所有索引。 |
db.collection.getIndexes() |
返回描述集合中现有索引的文档数组。 |
其他参考这里
ensureIndex参数
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| background | Boolean | 建索引过程会阻塞其它数据库操作,background可指定以后台方式创建索引,即增加 "background" 可选参数。 "background" 默认值为false。 |
| unique | Boolean | 建立的索引是否唯一。指定为true创建唯一索引。默认值为false. |
| name | string | 索引的名称。如果未指定,MongoDB的通过连接索引的字段名和排序顺序生成一个索引名称。 |
| dropDups | Boolean | 在建立唯一索引时是否删除重复记录,指定 true 创建唯一索引。默认值为 false. |
| sparse | Boolean | 对文档中不存在的字段数据不启用索引;这个参数需要特别注意,如果设置为true的话,在索引字段中不会查询出不包含对应字段的文档.。默认值为 false. |
| expireAfterSeconds | integer | 指定一个以秒为单位的数值,完成 TTL设定,设定集合的生存时间。 |
| v | index version | 索引的版本号。默认的索引版本取决于mongod创建索引时运行的版本。 |
| weights | document | 索引权重值,数值在 1 到 99,999 之间,表示该索引相对于其他索引字段的得分权重。 |
| default_language | string | 对于文本索引,该参数决定了停用词及词干和词器的规则的列表。 默认为英语 |
| language_override | string | 对于文本索引,该参数指定了包含在文档中的字段名,语言覆盖默认的language,默认值为 language. |
后台创建索引
db.values.ensureIndex({open: 1, close: 1}, {background: true})通过在创建索引时加background:true 的选项,让创建工作在后台执行
创建TTL索引
> db.indexes.getIndexes()
[ ]
> db.indexes.ensureIndex({ time:1 },{ expireAfterSeconds:30 })
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : true,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.indexes.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"time" : 1
},
"name" : "time_1",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes",
"expireAfterSeconds" : 30
}
]
> new Date()
ISODate("2018-02-07T12:48:54.955Z")
> db.indexes.insert({ time: new Date() });
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.indexes.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a7af5e8bba5630ed0ccc0cf"), "time" : ISODate("2018-02-07T12:49:44.309Z") }
> db.indexes.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a7af5e8bba5630ed0ccc0cf"), "time" : ISODate("2018-02-07T12:49:44.309Z") }
> new Date()
ISODate("2018-02-07T12:51:10.233Z")
> db.indexes.find()
>在索引过期后,相应的数据会删除(不仅仅是索引删除,还有数据)
适用场景:在一段时间之后会时效的数据,比如用户的登陆信息、存储的日志
存储在过期索引字段的值必须是指定的时间类型
说明:必须是ISOData或者ISOData数组,不能使用时间戳,否则不能自动删除
如果指定的是ISOData数组,则按照数组中最小的数值计算删除
过期索引不能是复合索引
删除时间不是精确,在文档不多时无论设置多长时间都是60秒内删除
命名索引
MongoDB会自动的创建,规则是
- key_1 或者 key_-1 1或者-1代表排序方向,一般影响不大,
- 全文索引可能为key_text
- 长度一般有限制125字节
为了见名知意我们可以自己来命名
> db.articles.getIndexes()
[
...
"name" : "article_text",
...
]
> db.articles.dropIndex("article_text")
{ "nIndexesWas" : 2, "ok" : 1 }
> db.articles.ensureIndex( { "article":"text" },{ name: "atext" })
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.articles.getIndexes()
[
...
"name" : "atext",
...
]
>唯一索引
建立索引时不允许存在相同的键值
> db.uniqueTest.find({},{ _id:0, x:1, y:1, z:1 })
{ "x" : 3, "y" : 4, "z" : 5 }
{ "x" : 3, "y" : 4 }
{ "x" : 3 }
> db.uniqueTest.ensureIndex({ x:1 },{ unique:true })
{
"ok" : 0,
"errmsg" : "E11000 duplicate key error collection: whoami.uniqueTest index: x_1 dup key: { : 3.0 }",
"code" : 11000,
"codeName" : "DuplicateKey"
}
> db.uniqueTest.remove({ x:3, y:4, z:5 })
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 })
> db.uniqueTest.remove({ x:3, y:4 })
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 })
> db.uniqueTest.ensureIndex({ x:1 },{ unique:true })
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.uniqueTest.insert({ x:6, y:8, z:10 })
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
>稀疏索引
> db.sparseTest.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a7b94aa940ce42ef05591f6"), "m" : 1 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a7b94b9940ce42ef05591f7"), "n" : 1 }通过$exists可以判断字段是否存在,如
> db.sparseTest.find({ m:{ $exists:true } })
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a7b94aa940ce42ef05591f6"), "m" : 1 }创建一个稀疏索引
> db.sparseTest.ensureIndex({ m:1 },{ sparse:true })
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
>第二条文档不存在m字段,所以不会创建这个索引,如果使用稀疏索引查找不存在稀疏索引字段的文档,mongodb则不会使用这个索引查找
例如:
> db.sparseTest.find({ m:{ $exists:false } })
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5a7b94b9940ce42ef05591f7"), "n" : 1 }但如果我们通过hint强制使用索引,就不会查到数据了
> db.sparseTest.getIndexes()
[
...
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"m" : 1
},
...
]
> db.sparseTest.find({m:{$exists:false}}).hint("m_1")
>_id索引
MongoDB在创建集合时在 _id 字段上创建一个惟一的索引。_id索引阻止客户机插入两个具有相同值的 _id 字段的文档。不能在 _id 字段上删除该索引。
在分片集群中,如果您不使用_id字段作为分片键,那么您的应用程序必须确保_id字段中值的惟一性,以防止出现错误。这通常是使用标准自动生成的ObjectId完成的。
> db.indexes.insert({ x:1 })
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.indexes.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
}
]
>单键索引(Single Field)
除了MongoDB定义的_id索引之外,MongoDB还支持在文档的单个字段上创建用户定义的提升/下降索引。
特点:
- 单键索引是最普通的索引
- 与_id索引不同,单键索引不会自动创建
> for(i = 0; i < 100; i++)db.indexes.insert({x:i})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.indexes.ensureIndex({ x:1 })
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.indexes.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"x" : 1
},
"name" : "x_1",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
}
]
> db.indexes.ensureIndex({ x:-1 })
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 2,
"numIndexesAfter" : 3,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.indexes.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"x" : 1
},
"name" : "x_1",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"x" : -1
},
"name" : "x_-1",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
}
]
> db.indexes.ensureIndex({ x:-1 })
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 3,
"numIndexesAfter" : 3,
"note" : "all indexes already exist",
"ok" : 1
}
> db.indexes.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"x" : 1
},
"name" : "x_1",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"x" : -1
},
"name" : "x_-1",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
}
]
> 可见对于同一个字段所创建的dec与asc索引也是不一样的.也可以重复创建索引,不会报错.
多键索引(Multikey Index)
MongoDB使用多索引索引来索引存储在数组中的内容。如果索引一个包含数组值的字段,MongoDB将为数组的每个元素创建单独的索引条目。这些多键索引允许查询通过匹配数组的元素或元素来选择包含数组的文档。MongoDB自动决定是否创建索引域包含数组值的multikey索引;不需要显式地指定多键类型。与单键索引创建形式相同,区别在于字段的值
- 单键索引:值为一个单一的值,例如字符串,数字或者日期
- 多键索引:值具有多个记录,例如数组
使用语句插入数组时系统默认创建多键索引
> db.indexes.insert({x:[1,2,3,4,5]});这样的多键索引是看不到的
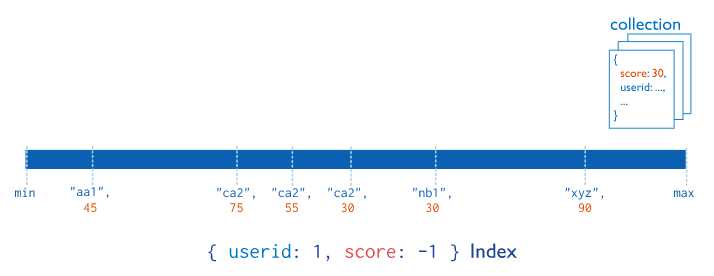
复合索引(Compound Index)
MongoDB还支持多个字段的用户定义索引,即复合索引。
复合索引中列出的字段顺序具有重要意义。例如,如果一个复合索引包含{userid: 1, score: -1},索引排序首先是userid,然后在每个userid值中按分数排序。
> db.indexes.insert({ x:[1,2,3,4,5], y:66 });
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.indexes.ensureIndex({ x:-1, y:1 })
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 2,
"numIndexesAfter" : 3,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.indexes.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"x" : -1
},
"name" : "x_-1",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"x" : -1,
"y" : 1
},
"name" : "x_-1_y_1",
"ns" : "whoami.indexes"
}
]
> 全文索引(Text Indexes)
MongoDB提供了一个文本索引类型,支持在集合中搜索字符串内容。这些文本索引不存储特定于语言的stop单词(例如,“the”、“a”、“or”),并将这些单词放在一个集合中,只存储根单词。
支持的语言在这里
全文索引创建方法:与创建单键索引,复合索引类似。value换成‘text‘,$**匹配集合下所有
db.articles.ensureIndex({key:"text"}) # 设置单键的全文索引
db.articles.ensureIndex({key_1:"text"},{key_2:"text"}) # 设置多键全文索引索引
db.articles.ensureIndex({"$**":"text"}) # 为所有的字段设置全文索引实践如下
> use whoami
switched to db whoami
> db.articles.ensureIndex({"article":"text"})
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : true,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.articles.insert({"article":"aa bb cc rr hh asdfasdf dd"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.articles.insert({"article":"cc"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.articles.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "whoami.articles"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_fts" : "text",
"_ftsx" : 1
},
"name" : "article_text",
"ns" : "whoami.articles",
"weights" : {
"article" : 1
},
"default_language" : "english",
"language_override" : "language",
"textIndexVersion" : 3
}
]
>相应的查询
//只有一个全文索引,或查询
> db.articles.find({$text:{$search:"aa bb cc"}})
{ "_id" : xxx, "article" : "cc" }
{ "_id" : xxx, "article" : "aa bb cc rr hh asdfasdf dd" }
> db.articles.find({$text:{$search:"cc"}})
{ "_id" : xxx, "article" : "aa bb cc rr hh asdfasdf dd" }
{ "_id" : xxx, "article" : "cc" }
// - 代表不包含 cc 字符串
> db.articles.find({$text:{$search:"-cc aa"}})
>
//与查询要将查找值用双引号包含起来,\\对引号转义
> db.articles.insert({"article":"\\"aa\\" bb cc rr hh asdfasdf dd"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.articles.find({$text:{$search:" \\"aa\\" \\"cc\\" \\"bb\\" "}})
{ "_id" : xxx, "article" : "aa bb cc rr hh asdfasdf dd" }
{ "_id" : xxx, "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc rr hh asdfasdf dd" }全文索引相似度
$meta操作符:{score:{$meta:"textScore"}}查询条件之后可以返回返回结果的相似度,与 sort 一起使用可以达到很好的使用效果.为了达到在搜索后能够根据内容与搜索条件的相似度进行排序,越相似越前,可以在建立全文索引后使用$meta操作符:
> db.articles.find({},{ _id:0,article:1 })
{ "article" : "aa bb cc rr hh asdfasdf dd" }
{ "article" : "cc" }
{ "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc rr hh asdfasdf dd" }
{ "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc rr hh asdfasdf" }
{ "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc rr hh" }
{ "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc rr" }
{ "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc" }
{ "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb" }
{ "article" : "\\"aa\\"" }
> db.articles.find(
... {$text:{$search:"aa bb"}},
... {score:{$meta:"textScore"}}
... ).sort({score:{$meta:"textScore"}});
{ xxx, "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb", "score" : 1.5 }
{ xxx, "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc", "score" : 1.3333333333333333 }
{ xxx, "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc rr", "score" : 1.25 }
{ xxx, "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc rr hh", "score" : 1.2 }
{ xxx, "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc rr hh asdfasdf", "score" : 1.1666666666666667 }
{ xxx, "article" : "aa bb cc rr hh asdfasdf dd", "score" : 1.1428571428571428 }
{ xxx, "article" : "\\"aa\\" bb cc rr hh asdfasdf dd", "score" : 1.1428571428571428 }
{ xxx, "article" : "\\"aa\\"", "score" : 1 }
全局索引的限制:
- 每次查询,只能指定一个$text查询
- $text查询不能出现在$nor查询中
- 查询中如果包含了$text, hint不再起作用
- MongoDB全文索引还不支持中文
- 全文索引一个集合里面只能有一个
地理位置索引(Geospatial Inde)
为了支持地理空间坐标数据的高效查询,MongoDB提供了两个特殊的索引:在返回结果时使用平面几何的2d索引和使用球面几何返回结果的2dsphere索引。
数据范围
- 位置表示方式:经纬度[经度,纬度]
- 取值范围:经度[-180,180],纬度[-90,90]
- 超过经度一般会报错,而纬度可能不会,但是带来查询上的不方便.
2d
用于存储和查找平面上的点
格式:
db.mycoll.ensureIndex({w:"2d"})查找方式:
- 查找距离某个点一定一定距离内的点
- 查找包含在某个区域内的点
查询方式:
- $near: 查询距离某个点最近的点
- $goWithin: 查询某个形状内的点
$near查询
形状的表示
- $box:矩形,使用
{$box:[[<x1>,<y1>],[<x2>,<y2>]]}- $center:圆形,使用
{$center:[[<x1>,<y1>],r]}- $polygon:多边形,使用
{$polygon:[[<x1>,<y1>],[<x2>,<y2>],[<x3>,<y3>]]}例子:
db.mycoll.find({w:{$near:[1,1]}})
查找距离[1,1]最大距离为10的点
db.mycoll.find({w:{$near:[1,1], $maxDistance:10}})
查找在矩形[0,0][3,3]范围内的点
db.mycoll.find({w:{$geoWithin:{$box:[[0,0],[3,3]]}}})
查找以[0,0]为圆心半径为5的园内的点
db.mycoll.find({w:{$geoWithin:{$center:[[0,0],5]}}})
查找以[0,0],[1,1],[4,5],[6,6]为多边形内的点
db.mycoll.find({w:{$geoWithin:{$polygon:[[0,0],[1,1],[4,5],[6,6]]}}}) 实例
> db.locations.ensureIndex({ w:'2d' })
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : true,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.locations.insert({ w:[1,1] })
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.locations.insert({ w:[1,2] })
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.locations.insert({ w:[3,2] })
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.locations.insert({ w:[3,4] })
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.locations.insert({ w:[5,4] })
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.locations.insert({ w:[100,4] })
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.locations.insert({ w:[100,100] })
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.locations.insert({ w:[200,100] })
WriteResult({
"nInserted" : 0,
"writeError" : {
"code" : 13027,
"errmsg" : "point not in interval of [ -180, 180 ] :: caused by :: { _id: ObjectId('5a7b162cbba5630ed0ccc0d7'), w: [ 200.0, 100.0 ] }"
}
})
>$geoNear查询
格式
db.runCommand({
geoNear:mycoll,
near:[x, y],
minDistance: (对2d索引无效)
maxDistance:
num:
})查询返回结果
{
"results":[ //查询的结果
{
"dis": //查找到的数据与所指定查找的数据之间的距离
"obj":{} //查找到的数据
}
],
"stats":{ //查询的参数
"nscanned": //扫描了哪些数据
"objectsloaded":
"avgDistance": //平均距离
"maxDistance": //最大的距离
"time": //花费的时间
},
"ok":
}2dsphere
格式:
db.mycoll.ensureIndex({w:"2dsphere"})位置表示方式:
GeoJSON:描述一个点,一条直线,多边形等形状。
格式:
{type:'', coordinates:[list]}GeoJSON查询可支持多边形交叉点等,支持MaxDistance 和 MinDistance
MongoDB 索引限制
额外开销
每个索引占据一定的存储空间,在进行插入,更新和删除操作时也需要对索引进行操作。所以,如果你很少对集合进行读取操作,建议不使用索引。
内存(RAM)使用
由于索引是存储在内存(RAM)中,你应该确保该索引的大小不超过内存的限制。
如果索引的大小大于内存的限制,MongoDB会删除一些索引,这将导致性能下降。
查询限制
索引不能被以下的查询使用:
- 正则表达式及非操作符,如 $nin, $not, 等。
- 算术运算符,如 $mod, 等。
- $where 子句
所以,检测你的语句是否使用索引是一个好的习惯,可以用explain来查看。
索引键限制
从2.6版本开始,如果现有的索引字段的值超过索引键的限制,MongoDB中不会创建索引。
插入文档超过索引键限制
如果文档的索引字段值超过了索引键的限制,MongoDB不会将任何文档转换成索引的集合。与mongorestore和mongoimport工具类似。
最大范围
- 集合中索引不能超过64个
- 索引名的长度不能超过128个字符
- 一个复合索引最多可以有31个字段
索引构建情况分析
mongostat工具
输出部分字段的含义
| 字段 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| inserts/query/update/delete | 分别指当前mongodb插入、查询、更新、删除 数量,以每秒计; |
| getmore | MongoDB返回结果时,每次只会返回一定量;当我们继续用find()查询更多数据时,系统就会自动用getmore来获取之后的数据; |
| command | 执行的命令数量 |
| flushes | MongoDB使用虚拟内存映射的方式管理数据,我们在向MongoDB写入或查询数据时,MongoDB会做一次虚拟内存映射,有些数据其实是在硬盘上的;每隔一段时间,MongoDB会把我们写到内存的数据flush到硬盘上;这个数据大的话,会导致mongodb的性能较差 |
| mapped/vsize/res | 与磁盘空间大小有关,申请的内存大小 |
| faults | 如果我们查询的数据,没有提前被MongoDB加载到内存中,我们就必须到硬盘上读取,叫做“换页”;如果faults比较高,也会造成性能下降; |
| idx miss | 表示我们的查询没有命中索引的比率;如果很高,说明索引构建有问题,索引不合适或者索引数量不够 |
| qr|qw | 说明MongoDB的写队列或者读队列的情况。我们向MongoDB读写时,这些请求会被放到队列中等待。数量大(几百上千)说明MongoDB处理速度慢或者读写请求太多,性能会下降。 |
| ar|aw | 当前活跃的读写客户端的个数 |
profile集合
查看当前数据库的profile状态
> db.getProfilingStatus() { "was" : 0, "slowms" : 100 }- was--profile记录级别,0关闭,1记录所有慢查询,2记录所有操作
- slowms--慢查询阀值
设置当前数据库的profile记录级别
db.setProfilingLevel(0|1|2)查看profile文件
db.system.profile.find() { "op" : "query",--操作类型 "ns" : "dbname.system.profile", --查询的命名空间,;dbname.mycoll "query" : { "query" : { }, --查询条件 "orderby" : { "$natural" : -1 } }, --约束条件 "ntoreturn" : 1, --返回数据条目 "ntoskip" : 0, --跳过的条目 "nscanned" : 1, --扫描的数目含索引 "nscannedObjects" : 1, --扫描的数据数目 "keyUpdates" : 0, -- "numYield" : 0, --其他情况 "lockStats" : { --锁状态 "timeLockedMicros" : { --锁占用时间(毫秒) "r" : NumberLong(82), --读锁 "w" : NumberLong(0) --写锁 }, "timeAcquiringMicros" : { "r" : NumberLong(2), "w" : NumberLong(2) } }, "nreturned" : 1, "responseLength" : 651, --返回长度 "millis" : 0, --查询时间 }
日志
可以在服务启动文件指定选项vebose
verbose = vvvvv # v 代表一个等级explain分析
db.colltction.find({x:1}).explain()
{
"cursor" : "BasicCursor", --使用的游标
"isMultiKey" : false,
"n" : 1,
"nscannedObjects" : 100000, --扫描的数据量
"nscanned" : 100000, --包含索引的扫描量
"nscannedObjectsAllPlans" : 100000,
"nscannedAllPlans" : 100000,
"scanAndOrder" : false,
"indexOnly" : false,
"nYields" : 781,
"nChunkSkips" : 0,
"millis" : 25, --查询消耗时间(毫秒)可以比较一下索引建立前后的变化
"server" : "XXX",
"filterSet" : false
}