SQL四种语言:DDL,DML,DCL,TCL
介绍参见:http://www.cnblogs.com/henryhappier/archive/2010/07/05/1771295.html
DDL(Data Definition Language)数据库定义语言
一、创建数据库
例:create database 库名称;
二、创建数据表
例:create table 表名称
(
列名称1 数据类型 约束,
列名称2 数据类型 约束1 约束2,
列名称3 数据类型,
...
)
三、constraint约束,用于限制加入表的数据的类型
1、not null
2、unique
例1:-- 以下为mysql实现,sql server和Oracle实现为在数据类型后直接加unique
create table 表名称
(
列名称1 数据类型,
列名称2 数据类型,
列名称3 数据类型,
unique (列名称1)
)
例2:需要命名 unique 约束,以及为多个列定义 unique 约束,请使用下面的 SQL 语法
create table 表名称
(
列名称1 数据类型,
列名称2 数据类型,
列名称3 数据类型,
constraint uc_约束名 unique (列名称1,列名称2)
)
3、primary key,拥有自动定义的 unique 约束
例子参考unique
4、foreign key,预防破坏表之间连接的动作,也能防止非法数据插入外键列,因为它必须是它指向的那个表中的值之一
例1:-- 以下为MySQL实现,sql server和Oracle实现为在数据类型后直接加约束
create table 表名称1
(
列名称1 数据类型,
列名称2 数据类型,
列名称3 数据类型,
foreign key(列名称1) references 表名称2(主键列名称)
)
例2:需要命名 foreign key 约束,以及为多个列定义 foreign key 约束,请使用下面的 SQL 语法
create table 表名称
(
列名称1 数据类型,
列名称2 数据类型,
列名称3 数据类型,
constraint fk_约束名 foreign key(列名称1) references 表名称2(主键列名称)
)
5、check,用于限制列中的值的范围
例子参考unique,check (列名称 > 值)
6、default
(1)建表时,数据类型后面加 default ‘值‘
(2)通过使用类似 GETDATE() 这样的函数,DEFAULT 约束也可以用于插入系统值。建表时在数据类型后加 default getdate()
7、increment字段,每次插入新记录时,自动地创建主键字段的值
(1)MySQL中是increment,SQL Server中是identity,oracle比较复杂
(2)increment=10,指定从10开始,每增加一条新记录自动加1
(3)identity(20,10),以 20 起始且递增 10
四、create index语句,在不读取整个表的情况下,索引使数据库应用程序可以更快地查找数据
例1:create index index_索引名 on 表名称(列名称1,列名称2,...); -- 列名称,规定需要索引的列
例2:create index index_索引名 on 表名称(列名称 desc); -- 以降序索引某个列中的值
例3:create unique index index_索引名 on 表名称(列名称); -- 创建一个唯一的索引。唯一的索引意味着两个行不能拥有相同的索引值
五、drop语句,删除数据库、数据表、索引
1、删除数据库
例:drop database 数据库名;
2、删除数据表
例1:drop table 表名称; -- 表的结构、属性以及索引也会被删除
例2:truncate table 表名称; -- 仅删除表内的数据,但并不删除表本身
3、删除索引
例1:alter table 表名称 drop index 索引名; -- MySQL
例2:drop index 索引名; -- Oracle
例3:drop index 表名称.索引名; -- SQL Server
六、alter table 语句,用于在已有的表中添加、修改或删除列(包括数据类型和增删约束)
1、添加列
例:alter table 表名称 add 列名称 数据类型;
2、删除列
例:alter table 表名称 drop 列名称 数据类型; --某些数据库系统不允许这种在数据库表中删除列的方式
3、修改列的数据类型
例:alter table 表名称
alter column 列名称 数据类型;
4、修改约束
例1:alter table 表名称 add constraint chk_约束名 check (列名称 = 值); -- 增加check约束
例2:alter table 表名称 alter column 列名称 set default ‘值‘; -- 增加default约束
例3:alter table 表名称 drop foreign key fk_约束名; -- 撤销外键约束
例2:alter table 表名称 alter column 列名称 drop default; -- 撤销default约束
select into 语句可用于创建表的备份复件
例:select 列1,列2,... into 表back_up from 表名称1;
DML(Data Manipulation Language)数据操纵语言
一、增删查改
select * from 表名称;
insert into 表名称 value (值1,值2,...); 或者:insert into 表名称(列1,列2,...) value (值1,值2,...);
删除某些行:delete from 表名称 where 列名称 = 值;
删除所有行:delete from 表名称; 或者:delete * from 表名称;
update 表名称 set 列1 = 新值1, 列2 = 新值2,... where 列名称 = 值;
二、其他关键字、语句
1、distinct关键字,用于返回唯一不同的值
例:select distinct 列1 from 表名称; -- 返回列1中不同的值
2、order by语句,用于对返回结果按照某列进行排序
例1:select 列1 from 表名称 order by 列2 desc; -- 返回的列1的记录按照列2降序排序
例2:select 列1 from 表名称 order by 列2 desc; -- 返回的列1的记录按照列2升序排序
3、group by语句,用于结合合计函数,根据一个或多个列对结果集进行分组
例:select 列1,sum(列2) from 表名称 group by 列1; -- 根据列1分组显示对应的列2的总数
4、having子句,因为where关键字无法与合计函数一起使用,所以增加having,与group by一起使用。
例:select 列1,avg(列2) from 表名称 group by 列1 having avg(列2)>60;
注:WHERE语句在GROUP BY语句之前;SQL会在分组之前计算WHERE语句。
HAVING语句在GROUP BY语句之后;SQL会在分组之后计算HAVING语句。
5、top子句,规定要返回的记录的数目
例1:select top 2 from 表名称 where 列名称 = 值; -- 查询前两行记录
MySQL也可用limit:select * from 表名称 limit=2; -- limit2,4返回2-4行记录
oracle也可用rownum或colnum:select * from 表名称 where rownum<=2;
例2:select top 20 percent from 表名称 where 列名称 = 值; -- 查询20%的记录
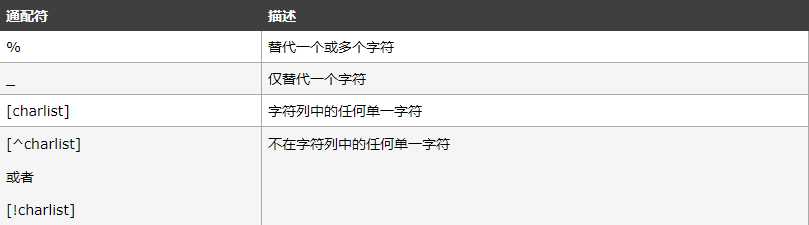
6、like运算符,在where子句中查找指定的模式,通配符必须和like一起使用
例:select * from 表名称 where 列名称 like ‘值%‘;
7、in和between操作符
例1:select * from 表名称 where 列名称 in (‘值1‘,‘值2‘,...); -- 在where子句中规定多个值,可与not一起使用
例2:select * from 表名称 where 列名称 between ‘值1‘ and ‘值2‘; -- 在where子句中规定值的范围,可与not一起使用
8、join关键字
例:select A.列1,B.列2 from 表名称 A left join 表名称 B on A.列C=B.列D;
注:JOIN: 如果表中有至少一个匹配,则返回行
LEFT JOIN: 即使右表中没有匹配,也从左表返回所有的行
RIGHT JOIN: 即使左表中没有匹配,也从右表返回所有的行
FULL JOIN: 只要其中一个表中存在匹配,就返回行
9、union操作符
例:select 列1,列2 from 表名称1
union
select 列1,列2 from 表名称2;
注:UNION 内部的 SELECT 语句必须拥有相同数量的列。列也必须拥有相似的数据类型。
默认地,UNION 操作符选取不同的值。如果允许重复的值,请使用 UNION ALL。