FFmpeg简单使用:视频编码 ---- YUV转H264
Posted huabiaochen
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了FFmpeg简单使用:视频编码 ---- YUV转H264相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
基本流程
从本地读取YUV数据编码为h264格式的数据,然后再存⼊到本地,编码后的数据有带startcode。
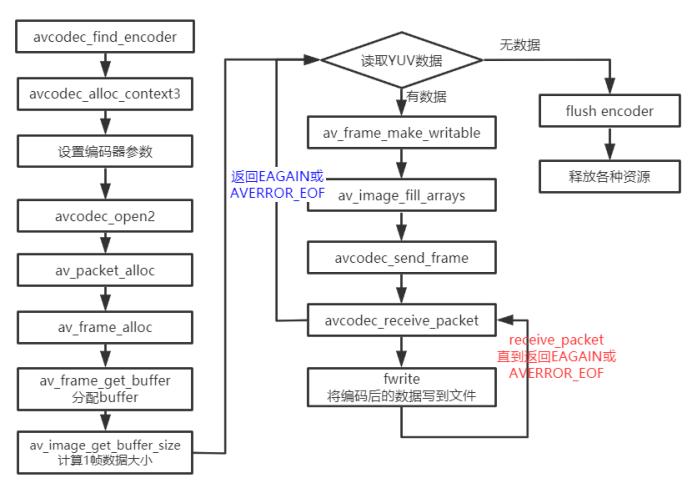
与FFmpeg 示例⾳频编码的流程基本⼀致。
函数说明:
avcodec_find_encoder_by_name:根据指定的编码器名称查找注册的编码器。
avcodec_alloc_context3:为AVCodecContext分配内存。
avcodec_open2:打开编解码器。
avcodec_send_frame:将AVFrame⾮压缩数据给编码器。
avcodec_receive_packet:获取到编码后的AVPacket数据。
av_frame_get_buffer: 为⾳频或视频数据分配新的buffer。在调⽤这个函数之前,必须在AVFame上设置好以下属性:format(视频为像素格式,⾳频为样本格式)、nb_samples(样本个数,针对⾳频)、channel_layout(通道类型,针对⾳频)、width/height(宽⾼,针对视频)。
av_frame_make_writable:确保AVFrame是可写的,尽可能避免数据的复制。如果AVFrame不是是可写的,将分配新的buffer和复制数据。
av_image_fill_arrays: 存储⼀帧像素数据存储到AVFrame对应的data buffer。
编码:
/**
* @projectName 08-02-encode_video
* @brief 视频编码,从本地读取YUV数据进行H264编码
* @author Liao Qingfu
* @date 2020-04-16
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>
#include <libavutil/time.h>
#include <libavutil/opt.h>
#include <libavutil/imgutils.h>
int64_t get_time()
return av_gettime_relative() / 1000; // 换算成毫秒
static int encode(AVCodecContext *enc_ctx, AVFrame *frame, AVPacket *pkt,
FILE *outfile)
int ret;
/* send the frame to the encoder */
if (frame)
printf("Send frame %3"PRId64"\\n", frame->pts);
/* 通过查阅代码,使用x264进行编码时,具体缓存帧是在x264源码进行,
* 不会增加avframe对应buffer的reference*/
ret = avcodec_send_frame(enc_ctx, frame);
if (ret < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Error sending a frame for encoding\\n");
return -1;
while (ret >= 0)
ret = avcodec_receive_packet(enc_ctx, pkt);
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF)
return 0;
else if (ret < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Error encoding audio frame\\n");
return -1;
if(pkt->flags & AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY)
printf("Write packet flags:%d pts:%3"PRId64" dts:%3"PRId64" (size:%5d)\\n",
pkt->flags, pkt->pts, pkt->dts, pkt->size);
if(!pkt->flags)
printf("Write packet flags:%d pts:%3"PRId64" dts:%3"PRId64" (size:%5d)\\n",
pkt->flags, pkt->pts, pkt->dts, pkt->size);
fwrite(pkt->data, 1, pkt->size, outfile);
return 0;
/**
* @brief 提取测试文件:ffmpeg -i test_1280x720.flv -t 5 -r 25 -pix_fmt yuv420p yuv420p_1280x720.yuv
* 参数输入: yuv420p_1280x720.yuv yuv420p_1280x720.h264 libx264
* @param argc
* @param argv
* @return
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
int ret = 0;
const char *in_yuv_file = "yuv420p_1280x720.yuv"; // 输入YUV文件
const char *out_h264_file = "yuv420p_1280x720.h264";
const char *codec_name = "libx264";
// 1.查找编码器
const AVCodec *codec = avcodec_find_encoder_by_name(codec_name);
if (!codec)
fprintf(stderr, "Codec '%s' not found\\n", codec_name);
exit(1);
// 2.分配内存
AVCodecContext *codec_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);
if (!codec_ctx)
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video codec context\\n");
exit(1);
// 3.设置编码参数
/* 设置分辨率*/
codec_ctx->width = 1280;
codec_ctx->height = 720;
/* 设置time base */
codec_ctx->time_base = (AVRational)1, 25;
codec_ctx->framerate = (AVRational)25, 1;
/* 设置I帧间隔
* 如果frame->pict_type设置为AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I, 则忽略gop_size的设置,一直当做I帧进行编码
*/
codec_ctx->gop_size = 25; // I帧间隔
codec_ctx->max_b_frames = 2; // 如果不想包含B帧则设置为0
codec_ctx->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P;
//
if (codec->id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264)
// 相关的参数可以参考libx264.c的 AVOption options
ret = av_opt_set(codec_ctx->priv_data, "preset", "medium", 0);
if(ret != 0)
printf("av_opt_set preset failed\\n");
ret = av_opt_set(codec_ctx->priv_data, "profile", "main", 0); // 默认是high
if(ret != 0)
printf("av_opt_set profile failed\\n");
ret = av_opt_set(codec_ctx->priv_data, "tune","zerolatency",0); // 直播是才使用该设置
// ret = av_opt_set(codec_ctx->priv_data, "tune","film",0); // 画质film
if(ret != 0)
printf("av_opt_set tune failed\\n");
/* 设置bitrate */
codec_ctx->bit_rate = 3000000;
// codec_ctx->rc_max_rate = 3000000;
// codec_ctx->rc_min_rate = 3000000;
// codec_ctx->rc_buffer_size = 2000000;
// codec_ctx->thread_count = 4; // 开了多线程后也会导致帧输出延迟, 需要缓存thread_count帧后再编程。
// codec_ctx->thread_type = FF_THREAD_FRAME; // 并 设置为FF_THREAD_FRAME
//对于H264 AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER 设置则只包含I帧,此时sps pps需要从codec_ctx->extradata读取 不设置则每个I帧都带 sps pps sei
//codec_ctx->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER; // 存本地文件时不要去设置
// 4.将codec_ctx和codec进行绑定
ret = avcodec_open2(codec_ctx, codec, NULL);
if (ret < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open codec: %s\\n", av_err2str(ret));
exit(1);
printf("thread_count: %d, thread_type:%d\\n", codec_ctx->thread_count, codec_ctx->thread_type);
// 5.打开输入和输出文件
FILE *infile = fopen(in_yuv_file, "rb");
if (!infile)
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open %s\\n", in_yuv_file);
exit(1);
FILE *outfile = fopen(out_h264_file, "wb");
if (!outfile)
fprintf(stderr, "Could not open %s\\n", out_h264_file);
exit(1);
// 6.分配pkt和frame
AVPacket *pkt = av_packet_alloc();
if (!pkt)
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video frame\\n");
exit(1);
AVFrame *frame = av_frame_alloc();
if (!frame)
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video frame\\n");
exit(1);
// 7.为frame分配buffer
frame->format = codec_ctx->pix_fmt;
frame->width = codec_ctx->width;
frame->height = codec_ctx->height;
ret = av_frame_get_buffer(frame, 0);
if (ret < 0)
fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate the video frame data\\n");
exit(1);
// 计算出每一帧的数据 像素格式 * 宽 * 高
// 1382400
int frame_bytes = av_image_get_buffer_size(frame->format, frame->width,
frame->height, 1);
printf("frame_bytes %d\\n", frame_bytes);
uint8_t *yuv_buf = (uint8_t *)malloc(frame_bytes);
if(!yuv_buf)
printf("yuv_buf malloc failed\\n");
return 1;
int64_t begin_time = get_time();
int64_t end_time = begin_time;
int64_t all_begin_time = get_time();
int64_t all_end_time = all_begin_time;
int64_t pts = 0;
// 8.循环读取数据
printf("start enode\\n");
for (;;)
memset(yuv_buf, 0, frame_bytes);
size_t read_bytes = fread(yuv_buf, 1, frame_bytes, infile);
if(read_bytes <= 0)
printf("read file finish\\n");
break;
/* 确保该frame可写, 如果编码器内部保持了内存参考计数,则需要重新拷贝一个备份
目的是新写入的数据和编码器保存的数据不能产生冲突
*/
int frame_is_writable = 1;
if(av_frame_is_writable(frame) == 0) // 这里只是用来测试
printf("the frame can't write, buf:%p\\n", frame->buf[0]);
if(frame->buf && frame->buf[0]) // 打印referenc-counted,必须保证传入的是有效指针
printf("ref_count1(frame) = %d\\n", av_buffer_get_ref_count(frame->buf[0]));
frame_is_writable = 0;
ret = av_frame_make_writable(frame);
if(frame_is_writable == 0) // 这里只是用来测试
printf("av_frame_make_writable, buf:%p\\n", frame->buf[0]);
if(frame->buf && frame->buf[0]) // 打印referenc-counted,必须保证传入的是有效指针
printf("ref_count2(frame) = %d\\n", av_buffer_get_ref_count(frame->buf[0]));
if(ret != 0)
printf("av_frame_make_writable failed, ret = %d\\n", ret);
break;
int need_size = av_image_fill_arrays(frame->data, frame->linesize, yuv_buf,
frame->format,
frame->width, frame->height, 1);
if(need_size != frame_bytes)
printf("av_image_fill_arrays failed, need_size:%d, frame_bytes:%d\\n",
need_size, frame_bytes);
break;
pts += 40;
// 设置pts
frame->pts = pts; // 使用采样率作为pts的单位,具体换算成秒 pts*1/采样率
begin_time = get_time();
ret = encode(codec_ctx, frame, pkt, outfile);
end_time = get_time();
printf("encode time:%lldms\\n", end_time - begin_time);
if(ret < 0)
printf("encode failed\\n");
break;
// 9.冲刷编码器
encode(codec_ctx, NULL, pkt, outfile);
all_end_time = get_time();
printf("all encode time:%lldms\\n", all_end_time - all_begin_time);
// 10.结束
fclose(infile);
fclose(outfile);
// 释放内存
if(yuv_buf)
free(yuv_buf);
av_frame_free(&frame);
av_packet_free(&pkt);
avcodec_free_context(&codec_ctx);
printf("main finish, please enter Enter and exit\\n");
getchar();
return 0;
preset设置 预设是⼀系列参数的集合,这个集合能够在编码速度和压缩率之间做出⼀个权衡。⼀个编码速度稍慢的预设会提供更⾼的压缩效率(压缩效率是以⽂件⼤⼩来衡量的)。 这就是说,假如你想得到⼀个指定⼤⼩的⽂件或者采⽤恒定⽐特率编码模式,你可以采⽤⼀个较慢的预设来获得更好的质量。同样的,对于恒定质量编码模式,你可以 通过选择⼀个较慢的预设轻松地节省⽐特率。如果你很有耐⼼,通常的建议是使⽤最慢的预设。⽬前所有的预设按照编码速度降序排列为: 常用设置:
- ultrafast
- superfast
- veryfast
- faster
- fast
- medium – default preset
- slow
- slower
- veryslow
设置为ultrafa

设置为slower,明显编码时间慢了很多,码率会低一点

tune设置
tune是x264中重要性仅次于preset的选项,它是视觉优化的参数,tune可以理解为视频偏好(或者视频类型),tune不是⼀个单⼀的参数,⽽是由⼀组参数构成-tune来改变参数设置。当前的 tune包括:
film:电影类型,对视频的质量⾮常严格时使⽤该选项
animation:动画⽚,压缩的视频是动画⽚时使⽤该选项
grain:颗粒物很重,该选项适⽤于颗粒感很重的视频
stillimage:静态图像,该选项主要⽤于静⽌画⾯⽐较多的视频
psnr:提⾼psnr,该选项编码出来的视频psnr⽐较⾼
02 使用FFmpeg库, YUV420转H264编码
演示环境:CentOS 7
FFmpeg的H264编码,需要x264库支持
[[email protected] ~]# wget ftp://ftp.videolan.org/pub/x264/snapshots/last_x264.tar.bz2 [[email protected] ~]# tar xf last_x264.tar.bz2 [[email protected] ~]# cd x264-snapshot-20171020-2245/ [[email protected] x264-snapshot-20171020-2245]# ./configure --prefix=/home/x264_dev --enable-shared --enable-static --disable-asm [[email protected] x264-snapshot-20171020-2245]# make && make install [[email protected] x264-snapshot-20171020-2245]# echo ‘/home/x264_dev/lib/‘ >> /etc/ld.so.conf && ldconfig -v #添加x264库到系统路路径
编译安装FFmpeg:
[[email protected] ~]# wget http://ffmpeg.org/releases/ffmpeg-3.4.tar.bz2 [[email protected] ~]# tar xf ffmpeg-3.4.tar.bz2 [[email protected] ~]# cd ffmpeg-3.4 [[email protected] ffmpeg-3.4]# export PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/home/x264_dev/lib/pkgconfig/:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH #根据PKG_CONFIG_PATH的值寻找x264库路径 [[email protected] ffmpeg-3.4]# ./configure --prefix=/home/ffmpeg_dev --enable-shared --enable-static --disable-optimizations --disable-x86asm --enable-libx264 --enable-gpl --disable-cuvid --disable-cuda [[email protected] ffmpeg-3.4]# make && make install [[email protected] ffmpeg-3.4]# echo ‘/home/ffmpeg_dev/lib/‘ >> /etc/ld.so.conf && ldconfig -v #添加FFmpeg的库到系统路路径 #说明:若需使用x264需要 安装x264库:--enable-libx264 --enable-gpl # 关闭GPU视频硬件加速的库: --disable-cuda --disable-cuvid # 生成静态库与动态库 --enable-shared --enable-static
下载测试视频,截取一段转为yuv格式(从第5秒,截取20秒)
[[email protected] ~]# cd /home/ [[email protected] home]# wget http://sh.yinyuetai.com/uploads/videos/common/0E3E014EBF3448D901AF3519C4A1D4E0.mp4 [[email protected] home]# /home/ffmpeg_dev/bin/ffmpeg -ss 5 -t 20 -i 0E3E014EBF3448D901AF3519C4A1D4E0.mp4 -s 1280x720 -pix_fmt yuv420p 1280x720_yuv420p.yuv [[email protected] home]# /home/ffmpeg_dev/bin/ffmpeg -ss 5 -t 20 -i 0E3E014EBF3448D901AF3519C4A1D4E0.mp4 -s 1280x720 -pix_fmt yuv422p 1280x720_yuv422p.yuv
FFmpeg 常见的结构体
YUV420转h264源程序:
[[email protected] ffmpeg_dev]# cat main.c #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "libavutil/imgutils.h" #include "libavutil/samplefmt.h" #include "libavutil/opt.h" #include "libavformat/avformat.h" const char *inputFileName = NULL; const char *outputFileName = NULL; int frameWidth = 0; int frameHeight = 0; int bitRate = 0; int frameTotal = 0; FILE *pFileInput = NULL; FILE *pFileOutput = NULL; AVCodec *codec = NULL; AVCodecContext *codecCtx = NULL; AVFrame *frame = NULL; AVPacket pkt; static int parse_input_paramaters(int argc, char **argv) { inputFileName = argv[1]; outputFileName = argv[2]; pFileInput = fopen(inputFileName, "rb"); if(NULL == pFileInput) { printf("open file ERR: [%s] \n", inputFileName); return -1; } pFileOutput = fopen(outputFileName, "wb+"); if(NULL == pFileInput) { printf("open file ERR: [%s] \n", outputFileName); return -1; } frameWidth = atoi(argv[3]); frameHeight = atoi(argv[4]); bitRate = atoi(argv[5]); frameTotal = atoi(argv[6]); return 0; } static int read_yuv_data(int color) { //color = 0 -> Y //color = 1 -> U //color = 2 -> V int color_height = color == 0 ? frameHeight : frameHeight / 2; int color_width = color == 0 ? frameWidth : frameWidth / 2; int color_size = color_height * color_width; int color_stride = frame->linesize[color]; if(color_width == color_stride) { //printf("color_width == color_stride,color=[%d],color_stride=[%d] \n", color, color_stride); fread(frame->data[color], color_size, 1, pFileInput); } //else //{ // printf("color_width != color_stride,color=[%d] \n", color); // int i; // for(i = 0; i < color_height; i++) // { // fread(frame->data[color] + i * color_stride, color_width, 1, pFileInput); // } //} return color_size; } int main(int argc, char **argv) { if(parse_input_paramaters(argc, argv) == 0) { printf("inputFile:%s \n", inputFileName); printf("outputFile:%s \n", outputFileName); printf("Frame resolution::[%d*%d] \n", frameWidth, frameHeight); printf("freamToEncode=%d\n", frameTotal); printf("rate:%d \n", bitRate); } else { printf("init ERROR\n"); return -1; } avcodec_register_all();//注册编解码组件 codec = avcodec_find_encoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);//查找编解码器 if(NULL == codec) { printf("find AV_CODEC_ID_H264 fail! \n"); return -1; } //分配AVCodecContex实例 codecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec); if(NULL == codecCtx) { printf("avcodec_alloc_context3 ERROR\n"); return -1; } //设置编解码器的参数 codecCtx->width = frameWidth;//帧高 codecCtx->height = frameHeight; codecCtx->bit_rate = bitRate;//比特率 AVRational r = {1, 25};//设置帧率 codecCtx->time_base = r;//设置帧率 codecCtx->gop_size =12; codecCtx->max_b_frames = 1; codecCtx->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P; av_opt_set(codecCtx->priv_data, "preset", "slow", 0); //打开编码器 if(avcodec_open2(codecCtx, codec, NULL) < 0) { printf("avcodec_open2 ERR\n"); } frame = av_frame_alloc(); if(NULL == frame) { printf("av_frame_alloc err \n"); return -1; } //分配AVframe及像素存储空间 frame->width = codecCtx->width; frame->height = codecCtx->height; frame->format = codecCtx->pix_fmt; if(av_image_alloc(frame->data, frame->linesize, frame->width, frame->height, frame->format, 32) < 0)//32 表示对齐 { printf("ERROR av_image_alloc\n"); } int i; for(i = 0; i < frameTotal; i++) { av_init_packet(&pkt); pkt.data = NULL; pkt.size = 0; read_yuv_data(0); read_yuv_data(1); read_yuv_data(2); frame->pts = i; int got_packet; //int avcodec_encode_video2(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVPacket *avpkt, const AVFrame *frame, int *got_packet_ptr); if(avcodec_encode_video2(codecCtx, &pkt, (const AVFrame *)frame, &got_packet) < 0) { printf("avcodec_encodec_video2 ERR \n"); return -1; } if(got_packet) { printf("Write packet of frame [%d], size=[%d] \n", i, pkt.size); //size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream); fwrite(pkt.data, 1, pkt.size, pFileOutput); av_packet_unref(&pkt); } } int got_packet = 1; while(got_packet) { if(avcodec_encode_video2(codecCtx, &pkt, NULL, &got_packet) < 0) { printf("avcodec_encodec_video2 ERR \n"); return -1; } if(got_packet) { printf("Write cache packet of frame [%d], size=[%d] \n", i, pkt.size); fwrite(pkt.data, 1, pkt.size, pFileOutput); av_packet_unref(&pkt); } } fclose(pFileInput); fclose(pFileOutput); avcodec_close(codecCtx); av_free(codecCtx); av_freep(&frame->data[0]); av_frame_free(&frame); return 0; } [[email protected] ffmpeg_dev]#
makefile文件
[[email protected] ffmpeg_dev]# cat makefile FLAGS = -Wall -g INCLUDEPATH = -I /home/ffmpeg_dev/include/ LIBPATH = -L /home/ffmpeg_dev/lib/ LIBS= -l avcodec -l pthread -l avutil -l m -l dl -l swresample exe=yuv2h264 $(exe): gcc main.c ${FLAGS} ${INCLUDEPATH} ${LIBPATH} ${LIBS} -o [email protected] clean: rm -rf ${exe} [[email protected] ffmpeg_dev]#
编译并运行,将YUV420文件转为H264
[[email protected] ffmpeg_dev]# cat auto.sh make clean make #提示 : Potplayer可以直接播放H264文件 #程序名: YUV420P文件名, H264输出文件名, YUV的宽与高, 压缩比特率, 需要编码多少帧(不要大于YUV文件的帧数) ./yuv2h264 1280x720_420P.yuv 1280x720.h264 1280 720 819200 250 [[email protected] ffmpeg_dev]#
播放器打开H264文件:
本文出自 “李春利” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://990487026.blog.51cto.com/10133282/1974942
以上是关于FFmpeg简单使用:视频编码 ---- YUV转H264的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章

