MyBatis 源码解析
Posted 柚几哥哥
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MyBatis 源码解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
- 1、工作原理
- 2、MyBatis中的缓存
- 3、如何扩展MyBatis中的缓存
- 4、MyBatis中的涉及的设计模式
- 5、谈谈你对SqlSessionFactory的理解
- 6、谈谈你读SqlSession的理解
- 7、谈谈你对MyBatis的理解
- 8、谈谈MyBatis中分页的理解
- 9、谈谈MyBatis中的插件原理
- 10、不同Mapper中的id是否可以相同?
- 11、谈谈对MyBatis架构设计的理解
- 12、谈谈对传统JDBC开发的不足
- 13、MyBatis中数据源模块的设计
- 14、MyBatis中事务模块的设计
- 15、谈谈你对Mapper接口的设计理解
- 16、谈谈你对Reflector模块的理解
- 17、MyBatis的类型转换模块
- 18、整合MyBatis
1、工作原理
1.1 初始化
1.1.1 系统启动的时候,加载解析全局配置文件和相应的映射文件
// 1.获取配置文件
InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
全局配置文件:mybatis-config.xml
映射文件:mapper/*.xml
// 2.加载解析配置文件并获取 SqlSessionFactory 对象
// SqlSessionFactory 的实例我们没有通过 DefaulSqlSessionFactory 直接来获取
// 而是通过一个 Builder 对象来建造的
// SqlSessionFactory 生产 SqlSession 对象的 SqlSessionFactory 应该是单例
// 全局配置文件和映射文件 也只需要在 系统启动的时候完成加载操作
// 通过建造者模式来 构建复杂的对象: 1.完成配置文件的加载解析 2.完成 SqlSessionFactory 的创建
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(in);
加载解析的相关信息存储在SqlSessionFactory对象的Configuration属性里,
1.1.2 建造者模式帮助我们解决复杂对象的创建:
- 完成配置文件的加载解析
- 完成 SqlSessionFactory 的创建
1.2 处理SQL请求的流程
通过工厂得到SqlSession对象
// 3.根据 SqlSessionFactory 对象获取 SqlSession 对象
SqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();
1.2.1 通过sqlSession中提供的API方法来操作数据库
// 4.通过sqlSession中提供的API方法来操作数据库
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("com.boge.mapper.UserMapper.selectUserList");
1.2.2 获取接口的代码对象-得到的其实是 通过JDBC代理模式获取的一个代理对象
// 获取接口的代码对象-得到的其实是 通过JDBC代理模式获取的一个代理对象
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
1.2.3 处理完请求之后,需要关闭会话SqlSession
//5.关闭会话
sqlSession.close();//关闭session 清空一级缓存
1.3 底层
全局配置文件的加载解析:Configuration
映射文件的加载解析:Configuration.mappedStatements
/**
* MappedStatement 映射
*
* KEY:`$namespace.$id`
*/
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<>("Mapped Statements collection");
生产了DefaultSqlsession实例对象,完成了Executor对象的创建,以及二级缓存CachingExecutor的装饰,同时完成了插件逻辑的植入。
selectOne():二级缓存->一级缓存->数据库插入
// 1. 读取配置文件,读成字节输入流,注意:现在还没解析
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
// 2. 解析配置文件,封装Configuration对象 创建DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
// 3. 生产了DefaultSqlsession实例对象 设置了事务不自动提交 完成了executor对象的创建
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 4.(1)根据statementid来从Configuration中map集合中获取到了指定的MappedStatement对象
//(2)将查询任务委派了executor执行器
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("com.lagou.mapper.IUserMapper.findById",1);
System.out.println(user);
User user2 = sqlSession.selectOne("com.lagou.mapper.IUserMapper.findById",1);
System.out.println(user2);
// 5.释放资源
sqlSession.close();
1.3.1 原理图:

1.3.2 源码结构:

2、MyBatis中的缓存
2.1 缓存的作用
降低数据源的访问频率,从而提高数据源的处理能力,提高服务器的响应速度。
2.2 缓存的设计
2.2.1 架构设计

通过装饰者模式对Cache接口的工作做增强

| 装饰者 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| BlockingCache | 阻塞的 Cache 实现类 |
| FifoCache | 基于先进先出的淘汰机制的 Cache 实现类 |
| LoggingCache | 支持打印日志的 Cache 实现类 |
| LruCache | 基于最少使用的淘汰机制的 Cache 实现类 |
| ScheduledCache | 定时清空整个容器的 Cache 实现类 |
| SerializedCache | 支持序列化值的 Cache 实现类 |
| SoftCache | 软引用缓存装饰器 |
| SynchronizedCache | 同步的 Cache 实现类 |
| TransactionalCache | 支持事务的 Cache 实现类,主要用于二级缓存中 |
| WeakCache | 弱引用缓存装饰器 |
2.2.2 一级缓存和二级缓存
一级缓存:session级别,默认开启
<!-- STATEMENT级别的缓存,使一级缓存,只针对当前执行的这一statement有效 -->
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="STATEMENT"/>
二级缓存:SqlSessionFactory级别(工厂/进程级别)
开启二级缓存:
-
在mybatis配置文件中配置cacheEnabled为true
<!-- 控制全局二级缓存,默认ture--> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> <!-- 延迟加载的全局开关。开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载。默认false --> <setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/> -
在映射文件中添加cache标签,可以在cache标签中更细致的增加配置
<!--二级缓存开启--> <cache /> -
命名空间下的所有标签放开二级缓存
-
可以通过在标签中添加 useCache=false 指定api不走二级缓存
mybatis-config.xml

2.2.3 缓存的处理顺序
- 获取mapper映射文件中cache标签里的配置MappedStatement.getCache()
- 如果cache配置不为空,从二级缓存中查找(List) TransactionalCacheManager.getObject(cache, key);
- 如果没有值,则执行查询, Executor.query()这个查询实际也是先走一级缓存查询,
- 一级缓存也没有的话,则进行DB查询
- 先将查询到的结果放入缓存TransactionalCacheManager.putObject(cache, key, list),再返回结果
2.2.3.1 先在二级缓存中查找
原因:找到概率更高,性能角度。
| 一级缓存 | 二级缓存 | |
|---|---|---|
| 作用域 | SqlSession级别 | SqlSessionFactory级别 |
| 找到概率 | 5% | 90% |
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException
// 从 MappedStatement 中获取 Cache,注意这里的 Cache 是从MappedStatement中获取的
// 也就是我们上面解析Mapper中<cache/>标签中创建的,它保存在Configration中
// 我们在初始化解析xml时分析过每一个MappedStatement都有一个Cache对象,就是这里
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 如果配置文件中没有配置 <cache>,则 cache 为空
if (cache != null)
//如果需要刷新缓存的话就刷新:flushCache="true"
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null)
// 暂时忽略,存储过程相关
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 从二级缓存中,获取结果
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null)
// 如果没有值,则执行查询,这个查询实际也是先走一级缓存查询,一级缓存也没有的话,则进行DB查询
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// 缓存查询结果
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
// 如果存在,则直接返回结果
return list;
// 不使用缓存,则从数据库中查询(会查一级缓存)
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
2.2.3.2 Executor.query()先走一级缓存查询,一级缓存也没有的话,则进行DB查询
/**
* 记录嵌套查询的层级
*/
protected int queryStack;
/**
* 本地缓存,即一级缓存
*/
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
// 已经关闭,则抛出 ExecutorException 异常
if (closed)
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
// 清空本地缓存,如果 queryStack 为零,并且要求清空本地缓存。
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired())
clearLocalCache();
List<E> list;
try
// queryStack + 1
queryStack++;
// 从一级缓存中,获取查询结果
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
// 获取到,则进行处理
if (list != null)
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
// 获得不到,则从数据库中查询
else
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
finally
// queryStack - 1
queryStack--;
if (queryStack == 0)
// 执行延迟加载
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads)
deferredLoad.load();
// issue #601
// 清空 deferredLoads
deferredLoads.clear();
// 如果缓存级别是 LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT ,则进行清理
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT)
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
return list;
3、如何扩展MyBatis中的缓存
3.1 架构理解
3.2 实际开发
/**
* 永不过期的 Cache 实现类,基于 HashMap 实现类
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class PerpetualCache implements Cache
/**
* 缓存容器
*/
private Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value)
cache.put(key, value);
3.2.1 自定义三级缓存
创建Cache接口的实现,重写putObject和getObject方法
在mapper映射文件中的cache标签里增加type属性,关联自定义的Cache接口的实现
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache" />
如果未添加type,会默认读取 PERETUAL (二级缓存)
4、MyBatis中的涉及的设计模式
4.1 从整体架构设计分析
4.1.1 基础模块:
cache缓存模块:装饰器模式
Cache接口 定义了缓存的基本行为
PerpetualCache基于Cache实现,针对于缓存的功能 1.缓存数据淘汰;2.缓存数据的存放机制;3.缓存数据添加是否同步【阻塞】;4.缓存对象是否同步处理…做了增强处理–>代理模式
以及很多装饰类,灵活增强出适用于不同业务场景的Cache实现
logging日志模块:适配器模式、策略模式、代理模式
帮助我们适配不同的日志框架
Log接口针对不同日志框架,有不同的实现类,做增强处理
reflection反射模块:工程模式、装饰器模式
datasource数据源:工程模式
transaction事务模块:工厂模式
SqlSessionFactory:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder建造者模式
5、谈谈你对SqlSessionFactory的理解
- 目的:创建SqlSession对象
- 单例,在应用程序(服务)中只保存唯一的一份
- SqlSessionFactory对象的创建是通过SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,
- 同时也完成了全局配置文件Configuration和相关映射文件Mapper的加载和解析操作。
- 涉及到了工厂模式和建造者模式
/**
* 构造 SqlSessionFactory 对象
*
* @param reader Reader 对象
* @param environment 环境
* @param properties Properties 变量
* @return SqlSessionFactory 对象
*/
@SuppressWarnings("Duplicates")
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties)
try
// 创建 XMLConfigBuilder 对象
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
// 执行 XML 解析
// 创建 DefaultSqlSessionFactory 对象
return build(parser.parse());
catch (Exception e)
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
finally
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try
reader.close();
catch (IOException e)
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
/**
* 1.我们最初调用的build
*/
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream)
//调用了重载方法
return build(inputStream, null, null);
/**
* 解析 XML
*
* 具体 MyBatis 有哪些 XML 标签,参见 《XML 映射配置文件》http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html
*
* @param root 根节点
*/
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root)
try
//issue #117 read properties first
// 解析 <properties /> 标签
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
// 解析 <settings /> 标签
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
// 加载自定义的 VFS 实现类
loadCustomVfs(settings);
// 解析 <typeAliases /> 标签
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
// 解析 <plugins /> 标签
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
// 解析 <objectFactory /> 标签
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
// 解析 <objectWrapperFactory /> 标签
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
// 解析 <reflectorFactory /> 标签
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
// 赋值 <settings /> 到 Configuration 属性
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
// 解析 <environments /> 标签
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
// 解析 <databaseIdProvider /> 标签
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
// 解析 <typeHandlers /> 标签
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 解析 <mappers /> 标签
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
catch (Exception e)
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
6、谈谈你读SqlSession的理解
6.1 SqlSession
-
作用:通过相关API来实现对应的数据的操作
-
SqlSession对象的获取需要通SqlSessionFactory来实现,
-
作用域是会话级别,当一个新的会话到来的时候,需要新建一个SqlSession对象;当一个会话结束后,需要关闭相关会话资源
-
处理请求的方式:
1.通过相关crud的API直接处理
2.通过getMapper(xx.xml)来获取相关mapper接口的代理对象来处理
6.2 SqlSession的安全问题
6.2.1 非线程安全:
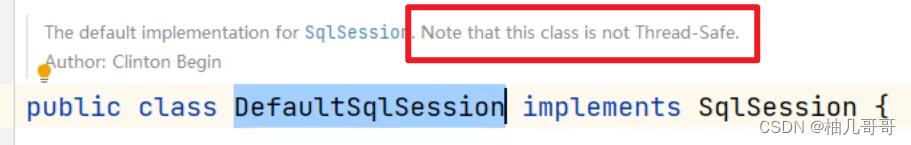
6.2.2 Spring中是如何解决DefaultSqlSession的数据安全问题?
- DefaultSqlSession是非线程安全的,也就意味着我们不能把DefaultSqlSession声明在成员变量中。
- 每个线程都应该有自己的SqlSession实例。
- 最佳作用域是请求或方法作用域
- 决不能将SqlSession实例引用放在一个类的静态域,甚至一个类的实例变量也不行。
- 应该将SqlSession放在一个和HTTP请求相似的作用域中,每次请求打开一个SqlSession,返回一个响应后就关闭他,关闭操作放在finally块中。

- Spring中提供了SqlSessionTemplate来实现SqlSession的相关定义。
- 其中每一个方法都通过SqlSessionProxy来操作,这是一个动态代理对象。
- 在动态代理对象中通过方法级别的DefaultSqlSession来实现相关的数据库操作。
7、谈谈你对MyBatis的理解
- 使用频率最高的ORM框架、持久层框架
- 提供了非常方便的API实现CRUD
- 支持灵活的缓存处理方案,一级缓存、二级缓存、三级缓存
- 支持相关的延迟数据加载处理
- 还提供了非常多的灵活标签,来实现复杂的业务处理,if forech where trim set bind…
- 相比Hibernate(全自动化)会更加灵活
8、谈谈MyBatis中分页的理解
8.1 谈谈分页的理解:
-
数据库层面SQL:
mysql:LIMIT
Oracle:rowid
8.2 分页的实现
8.2.1 逻辑分页:RowBounds
8.2.2 物理分页:拦截器实现,执行分页语句的组装

9、谈谈MyBatis中的插件原理
9.1 插件设计的目的:
方便开发人员实现对MyBatis功能的增强
设计中MyBatis允许映射语句执行过程中的某一点进行拦截调用,允许使用插件拦截的方法包括:

9.2 实现原理:
9.2.1 创建自定义Java类,通过@Interceptor注解来定义相关的方法签名
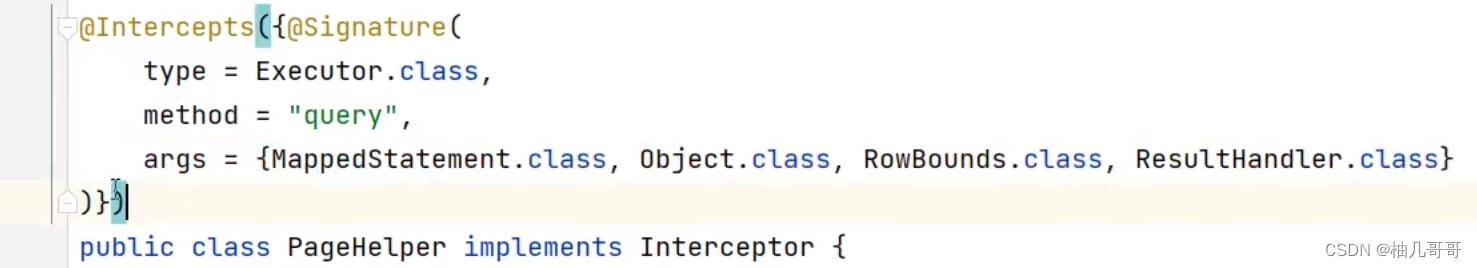
9.2.2 在对应的配置文件中通过plugin来注册自定义的拦截器
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper">
<property name="dialect" value="mysql"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
9.2.3 拦截器的作用
- 检查执行的SQL
- 对执行SQL的参数做处理
- 对查询的结果做装饰处理
- 对查询SQL做分表处理
10、不同Mapper中的id是否可以相同?
可以相同,每一个映射文件的namespace都会设置为对应的mapper接口的全类路径名称
保证了每个Mapper映射文件的namespace是唯一的。
11、谈谈对MyBatis架构设计的理解
11.1 接口层
面向开发者,提供相关API
11.2 核心层
核心功能的实现:增删改查操作
11.3 基础模块
支撑核心层来完成核心的功能

本文:12006字,阅读时长:10分15秒
前面已经发过Mybatis源码解析的文章了,本文是对前面文章进行精简以及部分调整优化,总结出来的一篇万字Mybatis源码分析。
主要内容
我们从一个简单案例入手,接着就是一步一步的剥开Mybatis的源码,大量的图文结合。
Mybatis使用案例
添加mybatis和MySQL相关pom依赖。
<!-- Mybatis依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.16</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
本地创建数据库,创建一张表。同时可以初始化几条数据,方便后面debug。
CREATE TABLE `t_user` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`pwd` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`gender` int DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
实体类(entity):
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String userName;
private Integer age;
private Integer gender;
//省略.....
}
创建UserMapper.java接口:
public interface UserMapper {
User selectById(Integer id);
}
创建UserMapper.xml配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tian.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="User" type="com.tian.mybatis.entity.User">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="userName"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectById" resultMap="User">
select * from t_user
<where>
<if test="id != null">
id = #{id}
</if>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>
创建mybatis-config.xml配置文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tian?useUnicode=true"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
使用案例:
public class MybatisApplication {
public static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mblog?useUnicode=true";
public static final String USER = "root";
public static final String PASSWORD = "123456";
public static void main(String[] args) {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
//读取mybatis-config.xml
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//解析mybatis-config.xml配置文件,创建sqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//创建sqlSession
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//创建userMapper对象(UserMapper并没有实现类)
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//调用userMapper对象的方法
User user = userMapper.selectById(1);
System.out.println(user);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
sqlSession.close();
}
}
}
运行输出:
User{id=1, userName='田维常', age=23, gender=1}
就这么简单的搞定了,下面我们来详细的分析这个案例背后的设计原理。
猜想Mybatis是如何设计的
从上面的案例中,我们可以大致可以猜测到Mybatis一共做了哪些步骤。
1.定位到mybatis-config.xml并读取装载。获取输入流InputStream。
2.解析输入流InputStream,把mybatis-config.xml配置文件中相关配置项解析,校验,保存起来。
3.创建sqlSessionFactory对象,在我们的印象里,session就是一次会话,所以我们可以理解sqlSessionFactory就是个工厂类,就专门创建sqlSession对象,并且这个sqlSessionFactory工厂类是唯一不变的(单例)。
4.创建sqlSession,SqlSession中肯定保存了配置文件内容信息和执行数据库相关的操作。
5.获取userMapper对象,但是UserMapper是接口,并且没有实现类。怎么就可以调用其方法呢?这里猜想可能用到了动态代理。
6.userMapper接口中的方法是如何关联到SQL的,这个猜想可能是有个专门映射的类,另外,肯定使用到了接口全路径名+方法名称,这个才能确保方法和SQL关联(主要是使用的时候,都是方法名必须和SQL中statementId一致,由此猜想的)。
7.最后底层使用JDBC去操作数据库。
8.作为一个持久化框架,很有可能会使用到缓存,用来存储每次查询数据。
仅仅是个人假设不清楚源码的情况,仅仅从这个简单的案例出发的,案例中没有差距、缓存,但是下面源码分析中是有的。
面试中遇到,让你来设计一个Mybatis如何设计?
配置文件解析,并保存于Configuration中
因为第一步是读取mybatis-config.xml配置文件,这里我们就没必要阅读这部分源码了,这里得到是InputStream输入流。接下来就是基于这个输入流进行一系列牛逼的操作。
我们将从下面这行代码开始:
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSessionFactory没有构造方法,那么这里使用的就是默认无参构造方法,所以我们直接进去build方法。
//这个方法啥也没干
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
//调用的是另外一个build方法
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
//创建一个XMLConfigBuilder对象
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
该类中的build重载的方法如下:
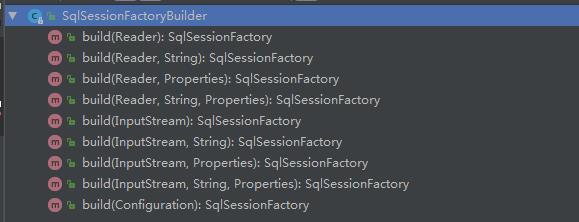
SqlSessionFactory中提供了三种读取配置信息的方法后:字节流、字符流和Configuration配置类。
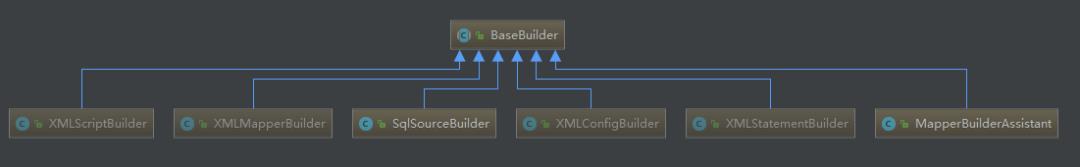
创建XMLConfigBuilder对象,这个类是BaseBuilder的子类,BaseBuilder类图:
看到这些子类基本上都是以Builder结尾,所以这里使用的是建造者设计模式。
这个类名可以猜出给类就是解析xml配置文件的。然后我们继续进入
public XMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props) {
this(new XPathParser(inputStream,...);
}
Mybatis对应解析包org.apache.ibatis.parsing:
XPathParser基于 Java XPath 解析器,用于解析 MyBatis中
-
mybatis-config.xml -
mapper.xml
等 XML 配置文件 。
XPathParser主要内容:

继续上面的源码分析:
private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) {
super(new Configuration());
ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration");
this.configuration.setVariables(props);
this.parsed = false;
this.environment = environment;
this.parser = parser;
}
构造一个XMLConfigBuilder对象,给属性设置相应值。
然后我们再回到SqlSessionFactoryBuilder中的build方法里:
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
build(parser.parse());
先看parser.parse()方法:
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
//mybatis-config.xml的一级标签
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
继续parseConfiguration()方法:
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
结合 mybatis-config.xml配置文件和解析方法,可以得出如何关联:
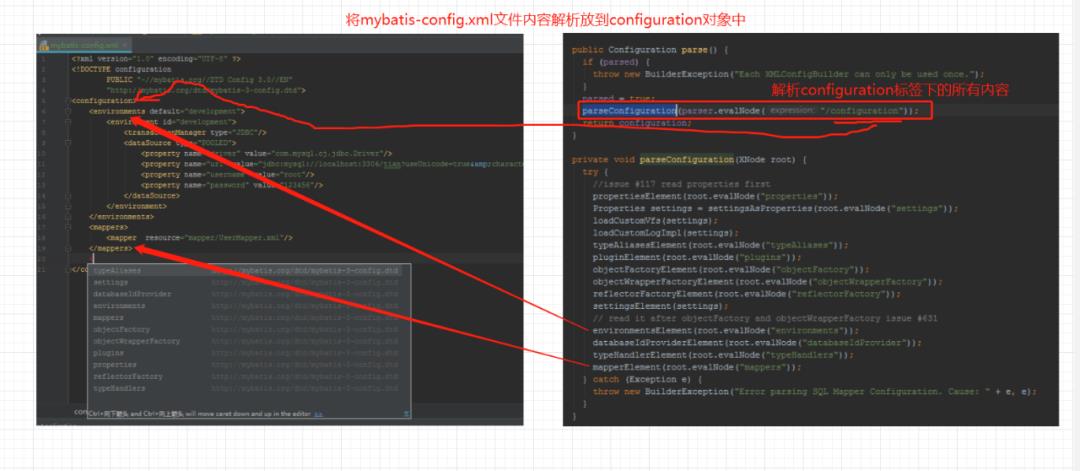
mybatis-config.xml中如果把
在org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml下的mybatis-3-config.dtd中已经定义了
<!ELEMENT configuration (properties?, settings?, typeAliases?, typeHandlers?, objectFactory?, objectWrapperFactory?, reflectorFactory?, plugins?, environments?, databaseIdProvider?, mappers?)>
与之对应的mybatis-config.xsd中
<xs:element name="configuration">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="properties"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="settings"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="typeAliases"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="typeHandlers"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="objectFactory"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="objectWrapperFactory"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="reflectorFactory"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="plugins"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="environments"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="databaseIdProvider"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="mappers"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
同理,我们最关心的Mapper.xml中能定义哪些标签,也在mybatis-3-mapper.dtd中也定义了,另外也有与之对应的
mybatis-mapper.xsd文件中也能找到:
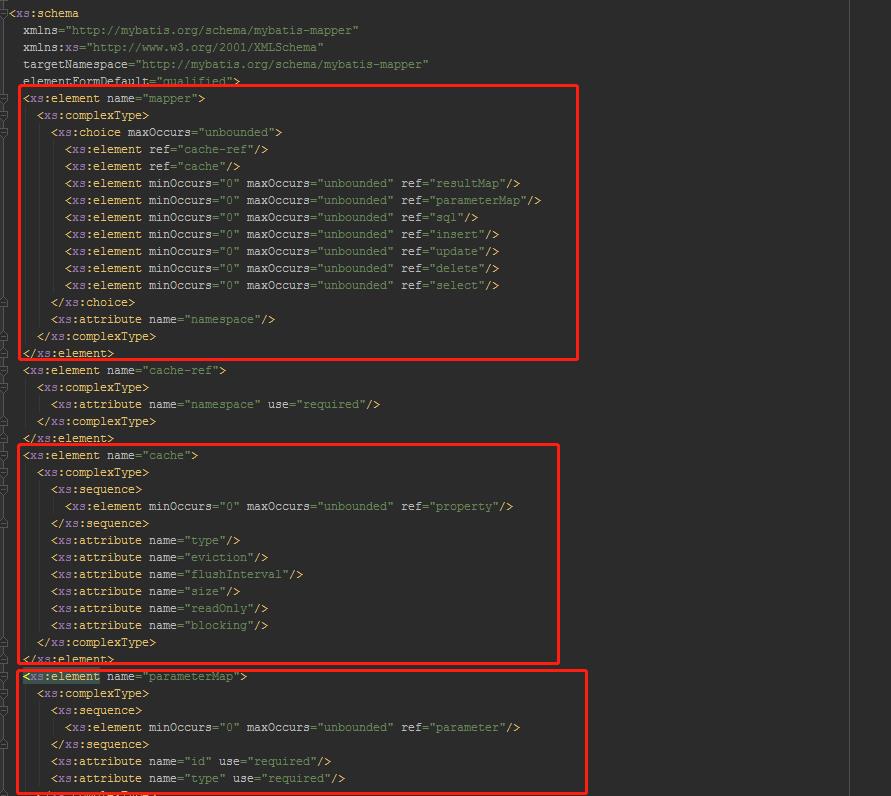
关于Mybatis中标签相关就介绍到此。关于Mybatis配置文件中有哪些标签现在是不是觉得很轻松就能找到了?其实在IDEA中也会提示的。
下面我们来看看这些标签内容是如何存入configuration对象中?(这里例举部分,挑几个相对重要的)。
propertiesElement()方法:
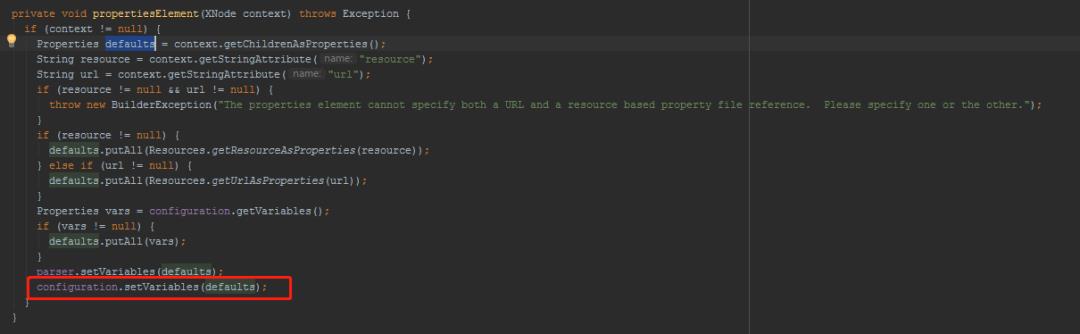
typeAliasesElement()方法:
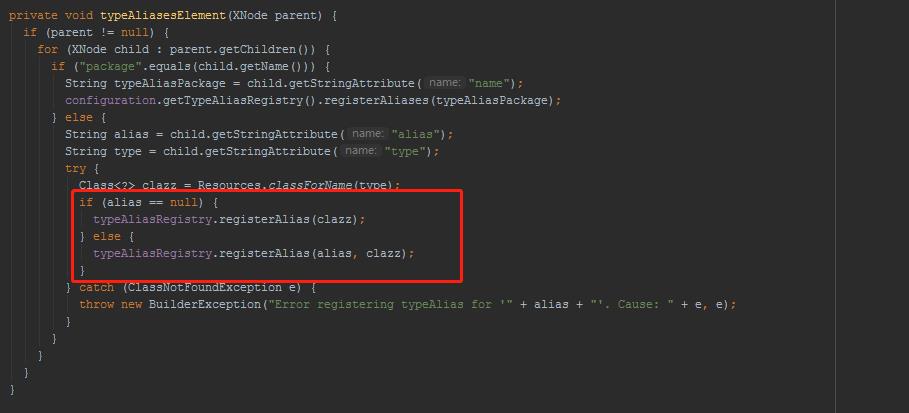
插件plugins解析
pluginElement()方法:
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
//可以定义多个插件
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
Configuration中interceptorChain用来存储所有定义的插件。
//interceptorChain中有个List<Interceptor> interceptors
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
//存入interceptors中
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
InterceptorChain插件链(连接链),责任链模式。
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
}
我们继续看看Mapper.xml是如何解析的。
mapper.xml解析
我们的Mapper.xml在mybatis-config.xml中的配置是这样的:
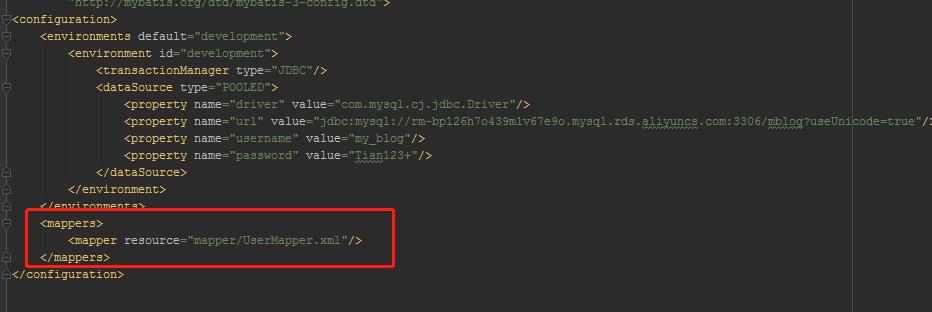
<--! 1使用类路径 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/BlogMapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="org/mybatis/builder/PostMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
<--! 2使用绝对url路径 -->
<mappers>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/AuthorMapper.xml"/>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/BlogMapper.xml"/>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/PostMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
<--! 3使用java类名 -->
<mappers>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.AuthorMapper"/>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.BlogMapper"/>
<mapper class="org.mybatis.builder.PostMapper"/>
</mappers>
<--! 4自动扫描包下所有映射器 -->
<mappers>
<package name="org.mybatis.builder"/>
</mappers>
源码分析:
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
//自动扫描包下所有映射器
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
//放到配置对象configuration中
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
//使用java类名
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
//根据文件存放目录,读取XxxMapper.xml
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//映射器比较复杂,调用XMLMapperBuilder
//注意在for循环里每个mapper都重新new一个XMLMapperBuilder,来解析
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
//使用绝对url路径
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
//映射器比较复杂,调用XMLMapperBuilder
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
//使用类路径
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
//直接把这个映射加入配置
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry();
this.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
}
private XMLMapperBuilder(.....) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.parser = parser;
this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments;
this.resource = resource;
}
把这些UserMapper类似接口保存到configuration对象中。
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
到这里,配置文件mybatis-config.xml和我们定义映射文件XxxMapper.xml就全部解析完成。
关于其他配置项,解析方式类似,最终都保存到了一个Configuration大对象中。
Configuration对象类似于单例模式,就是整个Mybatis中只有一个Configuration对象。
回到SqlSessionFactoryBuilder类
前面讲到了XMLConfigBuilder中的parse方法,并返回了一个Configuration对象。
build(parser.parse());
这个build方法就是传入一个Configuration对象,然后构建一个DefaultSqlSession对象。
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
继续回到我们的demo代码中这一行代码里。
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
这一行代码就相当于:
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new new DefaultSqlSessionFactory();
到此。配置文件解析完毕。
配置文件解析流程
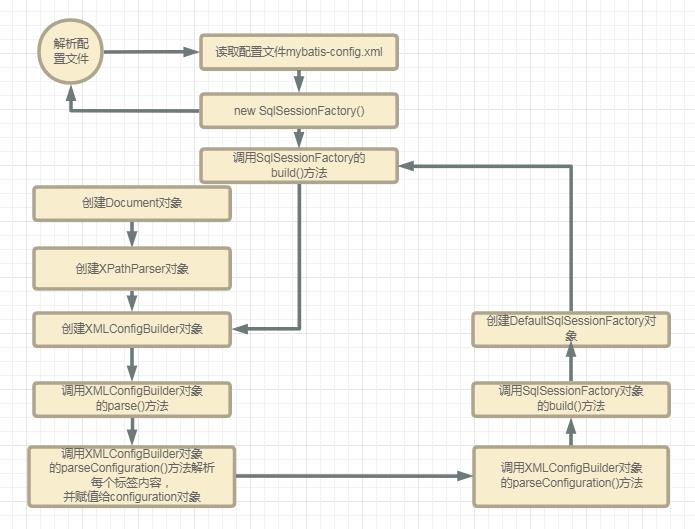
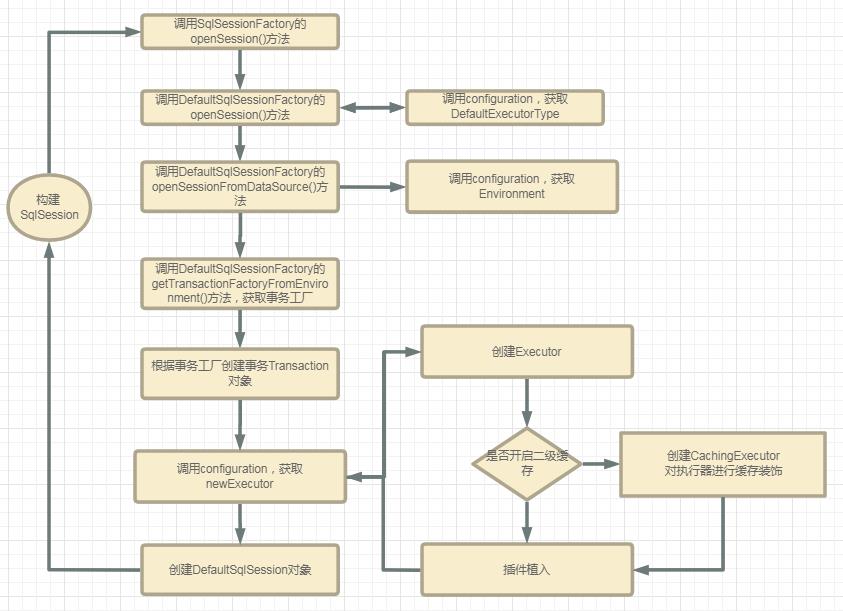
既然已经获取到了SqlSessionFactory,那么我们就可以构建SqlSession了。下面我们来看看构建SqlSession的整个过程。
构建SqlSession
前面已经做了配置文件的解析,那么现在我们来构建SqlSession。
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
前面已经分析了,这里的sqlSessionFactory是DefaultSqlSessionFactory。那么此时调用的openSession()方法为DefaultSqlSessionFactory中的方法。
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
//配置文件所有内容
private final Configuration configuration;
//创建session
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
//调用的是另外一个openSessionFromDataSource方法
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
//其实是调用这个方法
//protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//对应xml标签<environments> ,这个在配置文件解析的时候就已经存放到configuration中了。
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//构建事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
//构建一个失误对象对象
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//创建一个executor来执行SQL
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//创建一个DefaultSqlSession对象并返回
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
private TransactionFactory getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(Environment environment) {
if (environment == null || environment.getTransactionFactory() == null) {
return new ManagedTransactionFactory();
}
return environment.getTransactionFactory();
}
创建事务Transaction
Transaction类图:
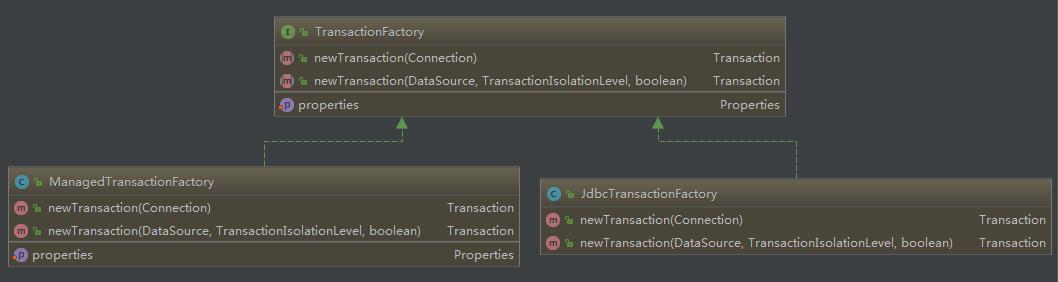
事务工厂类型可以配置为JDBC类型或者MANAGED类型。
-
JdbcTransactionFactory生产JdbcTransaction。
-
ManagedTransactionFactory生产ManagedTransaction。
如果配置的JDBC,则会使用Connection对象的commit()、rollback()、close()方法来管理事务。
如果我们配置的是MANAGED,会把事务交给容器来管理,比如JBOSS,Weblogic。因为我们是本地跑的程序,如果配置成MANAGED就会不有任何事务。
但是,如果是Spring+Mybatis,则没有必要配置,因为我们会直接在applicationContext.xml里配置数据源和事务管理器,从而覆盖Mybatis的配置。
把事务传给newExecutor()方法创建执行器Executor对象。
configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType)
创建Executor
调用configuration的newExecutor方法创建Executor。
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//Configuration中
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//第一步
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//第二步
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//第三步
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
此方法分三个步骤。
第一步:创建执行器
Executor的基本类型有三种:SIMPLE为默认类型。
public enum ExecutorType {
SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH
}
Executor类图:
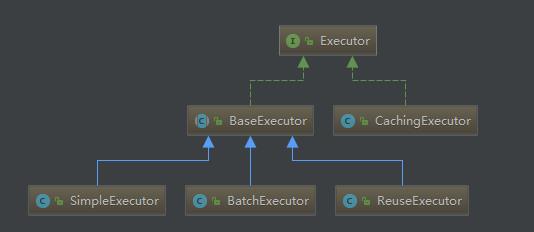
为什么要让抽象类BaseExecutor实现Executor接口,然后让具体实现类继承抽象类呢?
这就是模板方法模式的实现。
模板方法模式就是定义一个算法骨架,并允许子类为一个或者多个步骤提供实现。模板方法是得子类可以再不改变算法结构的情况下,重新定义算法的某些步骤。
抽象方法是在子类汇总实现的,每种执行器自己实现自己的逻辑,BaseExecutor最终会调用到具体的子类。
抽象方法
protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
protected abstract List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException;
protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
protected abstract <E> Cursor<E> doQueryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
第二步:缓存装饰
在上面代码中的第二步
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
如果cacheEnabled=true,会用装饰器设计模式对Executor进行装饰。
第三步:插件代理
缓存装饰完后,就会执行
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
这里会对Executor植入插件逻辑。
关于插件:
比如:分页插件中就需要把插件植入的Executor
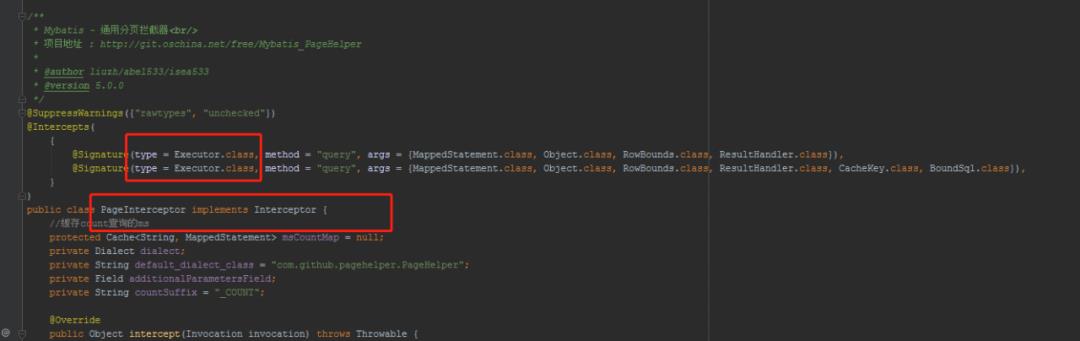
好了,到此,执行器创建的就搞定了。
Executor创建完毕后,就该创建DefaultSqlSession了,请看代码:
//创建一个DefaultSqlSession对象并返回
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
进入DefaultSqlSession的构造方法中:
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final Executor executor;
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
}
DefaultSqlSession中包含两个重要属性:
自此,SqlSession对象构建完毕。
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
这里的sqlSession就是:
sqlSession = new DefaultSqlSession();
整个构建过程:
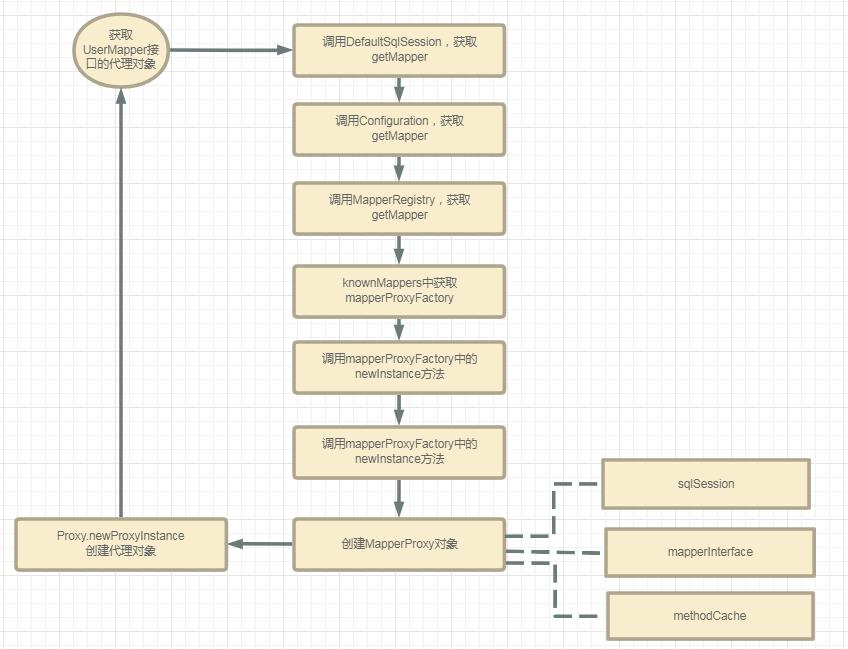
获取UserMapper接口的代理对象
前面我们已经Mybatis配置文件解析到获取SqlSession,下面我们来分析从SqlSession到userMapper:
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
我们已经知道了这里的sqlSession使用的是默认实现类DefaultSqlSession。
所以,我们的故事就从这个类开始,直接进入DefaultSqlSession的getMapper方法。
//DefaultSqlSession中
private final Configuration configuration;
//type=UserMapper.class
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
三个疑问:

问题1:getMapper返回的是个什么对象?
上面可以看出,getMapper方法调用的是Configuration中的getMapper方法。然后我们进入Configuration中
//Configuration中
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
////type=UserMapper.class
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
这里也没做什么,继续调用MapperRegistry中的getMapper:
//MapperRegistry中
public class MapperRegistry {
//主要是存放配置信息
private final Configuration config;
//MapperProxyFactory 的映射
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
//获得 Mapper Proxy 对象
//type=UserMapper.class,session为当前会话
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//这里是get,那就有add或者put
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
//创建实例
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
//解析配置文件的时候就会调用这个方法,
//type=UserMapper.class
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 判断 type 必须是接口,也就是说 Mapper 接口。
if (type.isInterface()) {
//已经添加过,则抛出 BindingException 异常
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
//添加到 knownMappers 中
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
//创建 MapperAnnotationBuilder 对象,解析 Mapper 的注解配置
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
//标记加载完成
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
//若加载未完成,从 knownMappers 中移除
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
}
MapperProxyFactory对象里保存了mapper接口的class对象,就是一个普通的类,没有什么逻辑。
在这个类里可以理解使用了单例模式methodCache(注册式单例模式),和工厂模式getMapper()。
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
//创建MapperProxy对象
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
//最终以JDK动态代理创建对象并返回
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
}
继续看这行重点代码:
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
newInstance()方法:
依然是稳稳的基于 JDK Proxy 实现,而 InvocationHandler 参数是 MapperProxy 对象。
//UserMapper 的类加载器
//接口是UserMapper
//h是mapperProxy对象
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h){
}
问题2:为什么就可以调用他的方法?
上面调用newInstance方法时候创建了MapperProxy对象,并且是当做newProxyInstance的第三个参数,所以MapperProxy类肯定实现了InvocationHandler。
进入MapperProxy类中:
//果然实现了InvocationHandler接口
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
//调用userMapper.selectById()实质上是调用这个invoke方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//如果是Object的方法toString()、hashCode()等方法
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (method.isDefault()) {
//JDK8以后的接口默认实现方法
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
//创建MapperMethod对象
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//下一篇再聊
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
也就是说,getMapper方法返回的是一个JDK动态代理对象(类型是$Proxy+数字)。这个代理对象会继承Proxy类,实现被代理的接口UserMpper,里面持有了一个MapperProxy类型的触发管理类。
当我们调用UserMpper的方法时候,实质上调用的是MapperProxy的invoke方法。
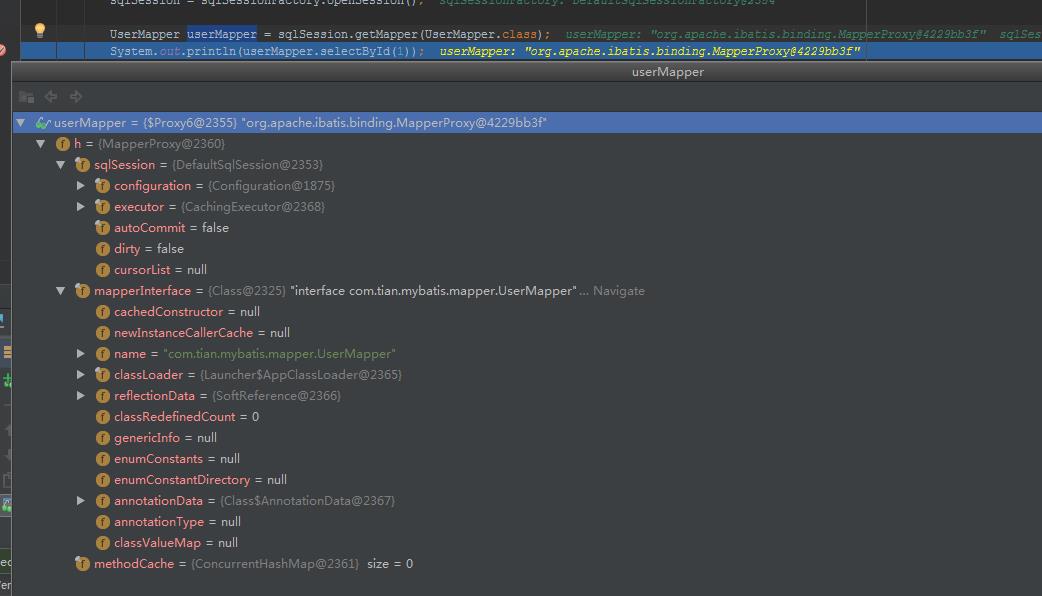
userMapper=$Proxy6@2355。
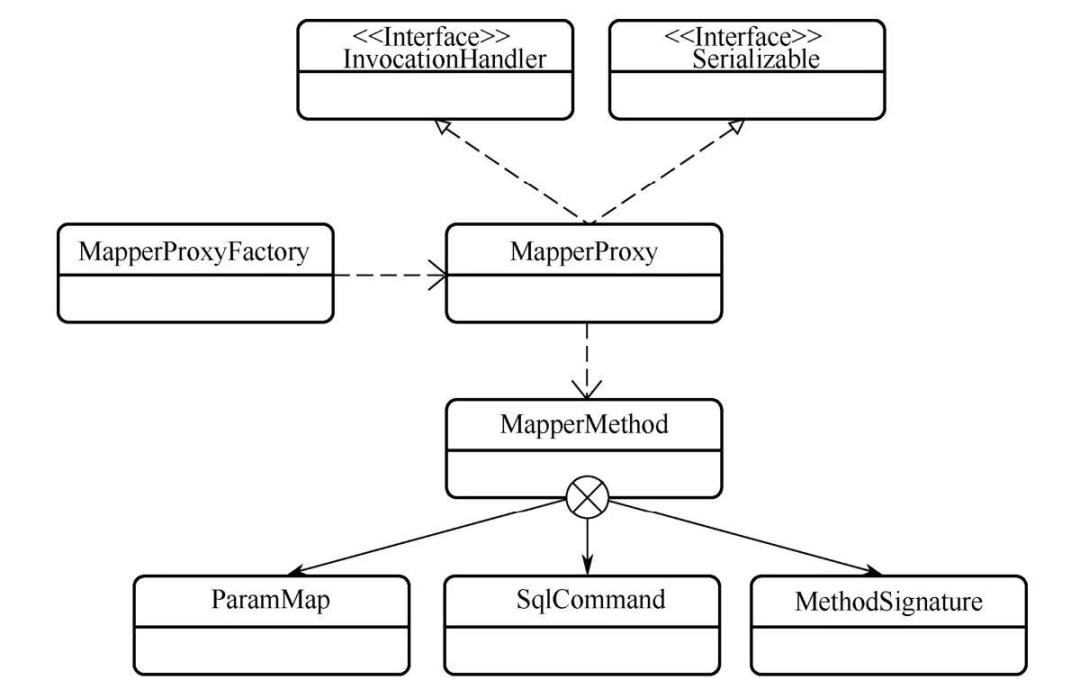
现在我们回答前面的问题:
为什么要在MapperRegistry中保存一个工厂类,原来他是用来创建并返回代理类的。这里是代理模式的一个非常经典的应用。
MapperProxy如何实现对接口的代理?
我们知道,JDK动态代理有三个核心角色:
-
被代理类(即就是实现类) -
接口 -
实现了InvocationHanndler的触发管理类,用来生成代理对象。
被代理类必须实现接口,因为要通过接口获取方法,而且代理类也要实现这个接口。
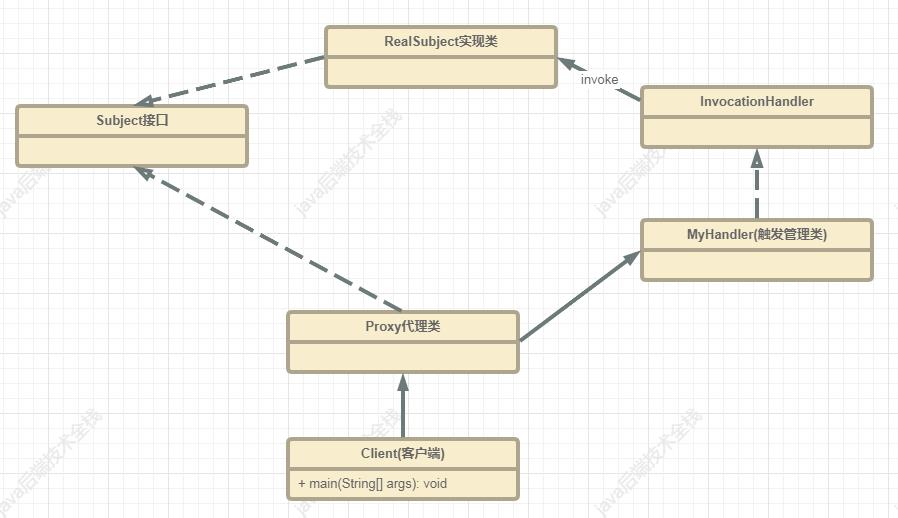
而Mybatis中并没有Mapper接口的实现类,怎么被代理呢?它忽略了实现类,直接对Mapper接口进行代理。
MyBatis动态代理:
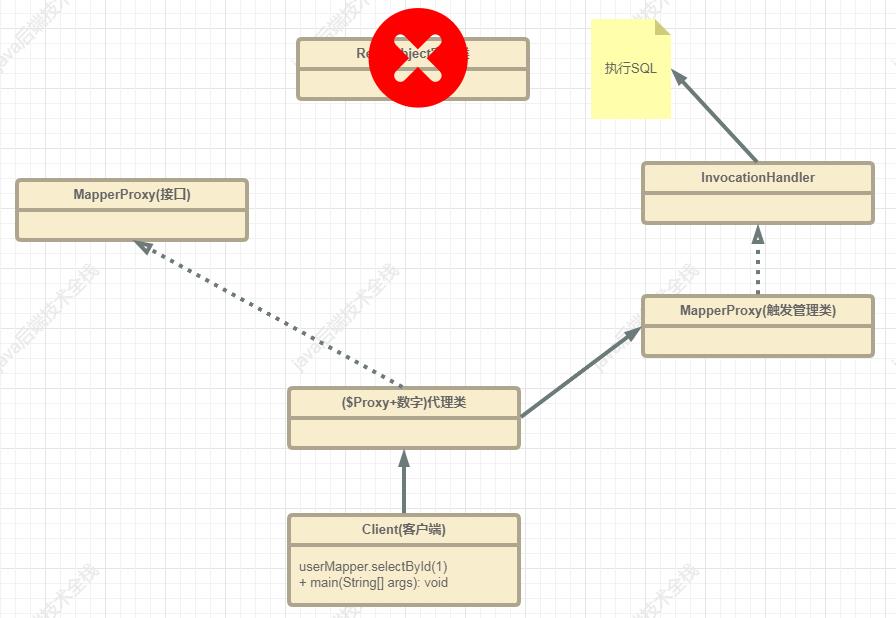
在Mybatis中,JDK动态代理为什么不需要实现类呢?
这里我们的目的其实就是根据一个可以执行的方法,直接找到Mapper.xml中statement ID ,方便调用。
最后返回的userMapper就是MapperProxyFactory的创建的代理对象,然后这个对象中包含了MapperProxy对象,
问题3:到底是怎么根据Mapper.java找到Mapper.xml的?
最后我们调用userMapper.selectUserById(),本质上调用的是MapperProxy的invoke()方法。
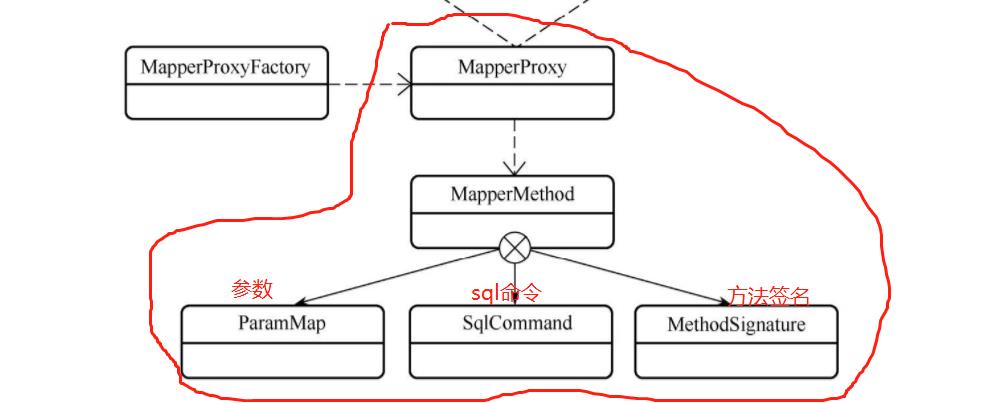
如果根据(接口+方法名找到Statement ID ),这个逻辑在InvocationHandler子类(MapperProxy类)中就可以完成了,其实也就没有必要在用实现类了。
自此上面三个问题已经全部解决。
整个流程
自此,我们已经拿到了UserMapper接口的代理对象。接下来我们就去调用这个代理对象的方法。
UserMapp中的方法和SQL关联
加油坚持,我们已经到从这一行代码开始:
User user = userMapper.selectById(1));
这一行代码搞完,也就代表着我们Mybatis源码第一遍搞完。想想就很开心,嘿嘿~,加油
继续开撸。
通过前面的分析,我们已经知道了userMapper是通过动态代理生成的代理对象,所以调用这个代理对象的任意方法都是执行触发管理类MapperProxy的invoke()方法。
分为两部分,
1- MapperProxy.invoke()到Executor.query(方法和SQL关联)。2- Executor.query到JDBC中的SQL执行
第一部分流程图:
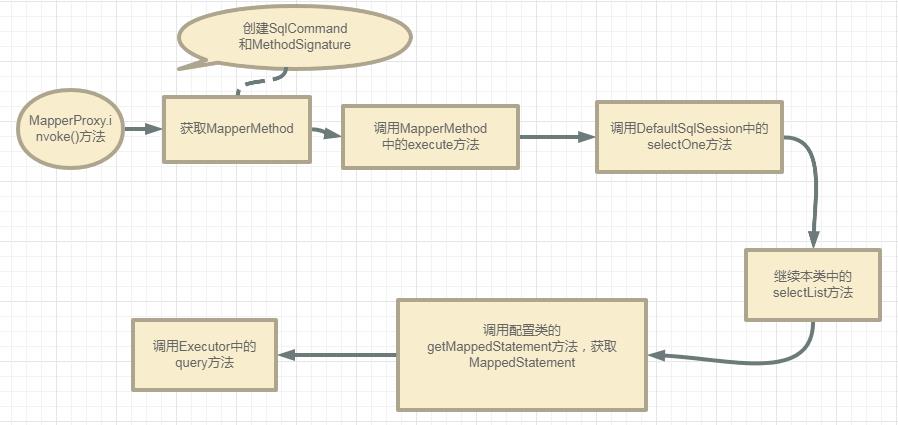
MapperProxy.invoke()
先来看看这个invoke()方法里有些什么逻辑。
//MapperProxy类
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//首先判断是否为Object本身的方法,是则不需要去执行SQL,
//比如:toString()、hashCode()等方法。
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (method.isDefault()) {
//判断是否JDK8以后的接口默认实现方法。
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
//<3>
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//<4>
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
从缓存获取MapperMethod,这里加入了缓存主要是为了提升MapperMethod的获取速度。这个设计非常的有意思,缓存的使用在Mybatis中也是非常之多。
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, k -> new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
Map的computeIfAbsent方法:根据key获取值,如果值为null,则把后面的Object的值付给key。
继续看MapperMethod这个类,定义了两个属性command和method,以及两个静态内部类。
public class MapperMethod {
private final SqlCommand command;
private final MethodSignature method;
public static class SqlCommand {
private final String name;
private final SqlCommandType type;
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
final String methodName = method.getName();
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
//获得 MappedStatement 对象
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
// <2> 找不到 MappedStatement
if (ms == null) {
// 如果有 @Flush 注解,则标记为 FLUSH 类型
if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {
name = null;
type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;
} else {
// 抛出 BindingException 异常,如果找不到 MappedStatement
//(开发中容易见到的错误)说明该方法上,没有对应的 SQL 声明。
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "
+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);
}
//找到 MappedStatement
} else {
// 获得 name
//id=com.tian.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.selectById
name = ms.getId();
// 获得 type=SELECT
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
//如果type=UNKNOWN
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) { // 抛出 BindingException 异常,如果是 UNKNOWN 类型
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}
private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName,
Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {
// 获得编号
//com.tian.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.selectById
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;
//如果有,获得 MappedStatement 对象,并返回
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {
//mappedStatements.get(statementId);
//解析配置文件时候创建并保存Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements中
return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
// 如果没有,并且当前方法就是 declaringClass 声明的,则说明真的找不到
} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {
return null;
}
// 遍历父接口,继续获得 MappedStatement 对象
for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {
if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,
declaringClass, configuration);
if (ms != null) {
return ms;
}
}
}
// 真的找不到,返回 null
return null;
}
//....
}
public static class MethodSignature {
private final boolean returnsMap;
private final Class<?> returnType;
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
//....
}
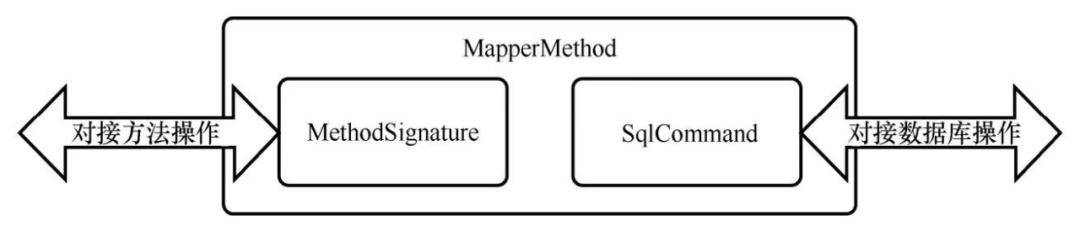
SqlCommand封装了statement ID,比如说:
com.tian.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.selectById
和SQL类型。
public enum SqlCommandType {
UNKNOWN, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH;
}
另外还有个属性MethodSignature,主要是封装的是返回值的类型和方法入参。这里我们debug看看这个MapperMethod对象返回的内容和我们案例中代码的关联。
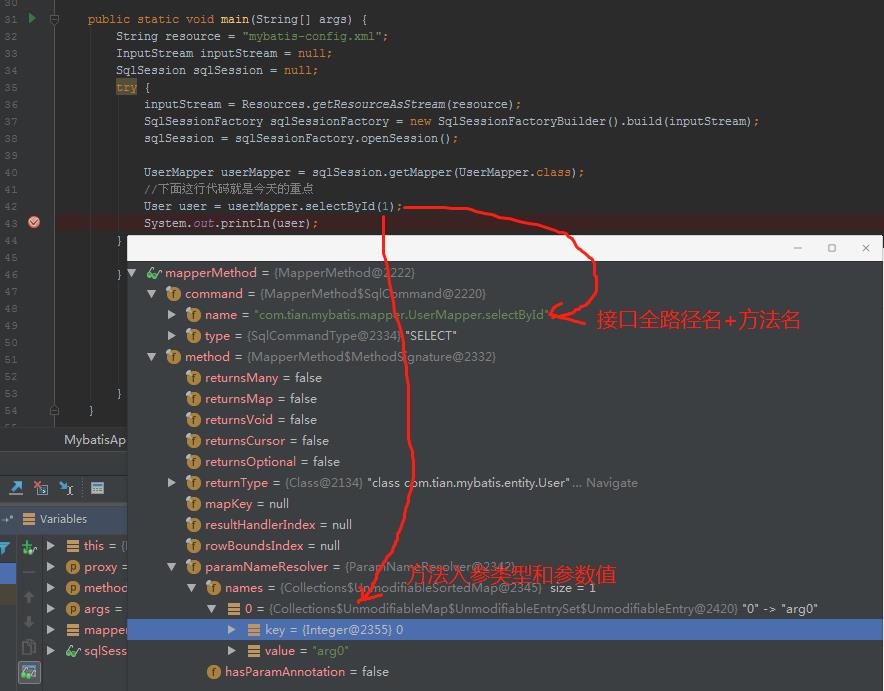
妥妥的,故事继续,我们接着看MapperMethod中execute方法。
MapperMethod.execute
先来看看这个方法的整体逻辑:
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case SELECT:
//部分代码省略
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//本次是QUERY类型,所以这里是重点
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
return result;
}
这个方法中,根据我们上面获得的不同的type(INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE、SELECT)和返回类型:
1.调用convertArgsToSqlCommandParam()将方法参数转换为SQL的参数。2.调用sqlSession的insert()、update()、dalete()、selectOne()方法。我们这个案例是查询,这里回到了DefaultSqlSession中selectOne方法中。
SqlSession.selectOne方法
继续DefaultSqlSession中的selectOne()方法:
//DefaultSqlSession中
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
//这是一种好的设计方法
//不管是执行多条查询还是单条查询,都走selectList方法(重点)
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
//如果只有一条就返回第一条
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
//(开发中常见错误)方法定义的是返回一条数据,结果查出了多条数据,就会报这个异常
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
//数据库中没有数据就返回null
return null;
}
}
这里调用的是selectList方法。
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//从configuration获取MappedStatement
//此时的statement=com.tian.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.selectById
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//调用执行器中的query方法
return executor.query(...);
} catch (Exception e) {
//.....
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
在这个方法里是根据statement从configuration对象中获取MappedStatement。
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
在configuration中getMappedStatement方法:
//存放在一个map中的
//key是statement=com.tian.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.selectById,value是MappedStatement
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>();
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id) {
return this.getMappedStatement(id, true);
}
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id, boolean validateIncompleteStatements) {
return mappedStatements.get(id);
}
而MappedStatement里面有xml中增删改查标签配置的所有属性,包括id、statementType、sqlSource、入参、返回值等。
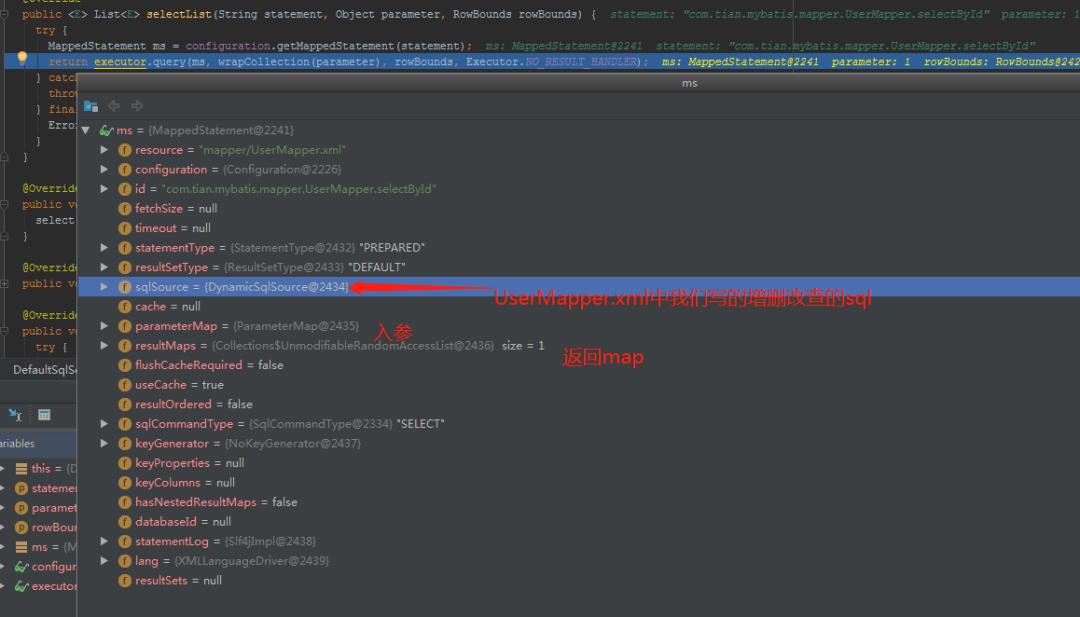
到此,我们UserMapper类中的方法已经和UserMapper.xml中的sql给彻底关联起来了。继续
executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
这里执行的是执行器Executor中的query()方法。
Executor.query()方法
这里的Executor对象是在调用openSession方法的时候创建的。
下面来看看调用执行器的query()放的整个流程(第二部分流程):
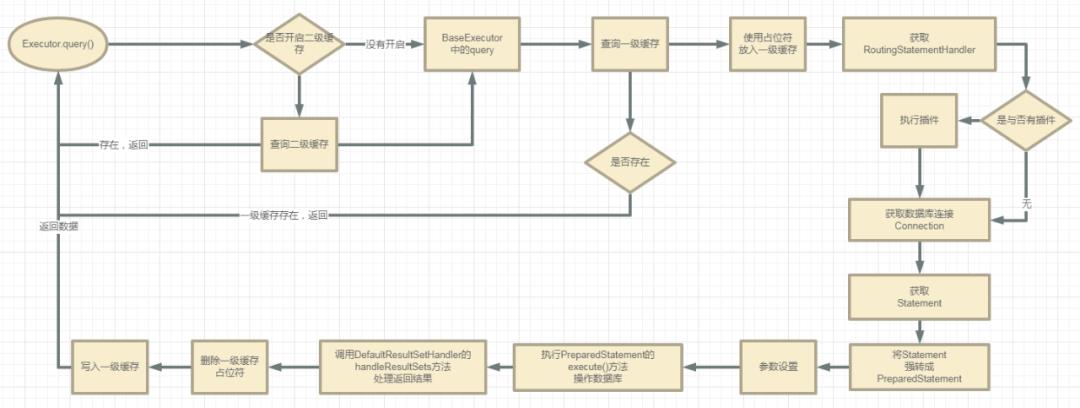
下面我们看看具体源码是如何实现的。
CachingExecutor.query()
在CachingExecutor中
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
BoundSql中主要是SQL和参数:
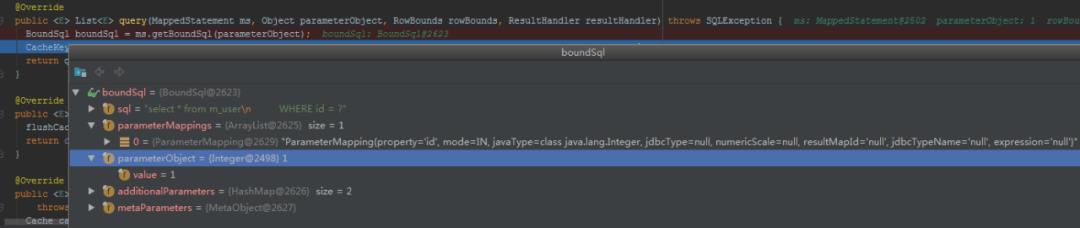
既然是缓存,我们肯定想到key-value数据结构。
下面来看看这个key生成规则:
这个二级缓存是怎么构成的呢?并且还要保证在查询的时候必须是唯一。
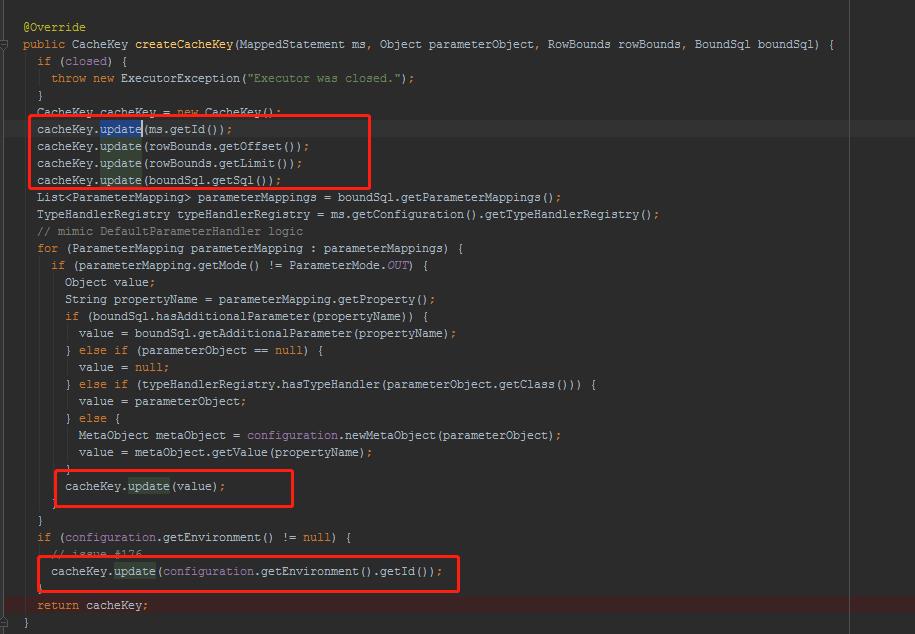
也就说,构成key主要有:
方法相同、翻页偏移量相同、SQL相同、参数相同、数据源环境相同才会被认为是同一个查询。
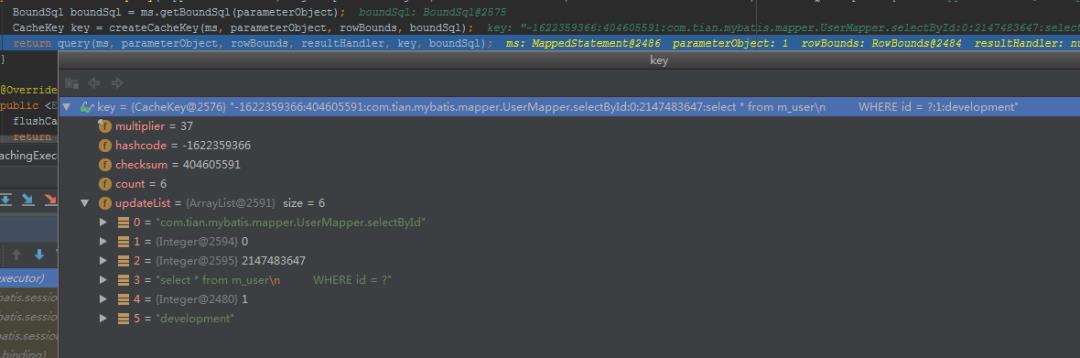
这里大家知道这个层面就已经阔以了。如果向更深入的搞,就得把hashCode这些扯进来了,请看上面这个张图里前面的几个属性。
处理二级缓存
首先是从ms中取出cache对象,判断cache对象是否为null,如果为null,则没有查询二级缓存和写入二级缓存的流程。
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
//判断是否有二级缓存
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
那么这个Cache对象是什么创建的呢?
二级缓存如何开启?
配置项:
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true|false" />
</settings>
</configuration>
cacheEnabled=true表示二级缓存可用,但是要开启话,需要在Mapper.xml内配置。
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
<!--或者 简单方式-->
<cache/>
对配置项属性说明:
-
flushInterval="60000",间隔60秒清空缓存,这个间隔60秒,是被动触发的,而不是定时器轮询的。 -
size=512,表示队列最大512个长度,大于则移除队列最前面的元素,这里的长度指的是CacheKey的个数,默认为1024。 -
readOnly="true",表示任何获取对象的操作,都将返回同一实例对象。如果readOnly="false",则每次返回该对象的拷贝对象,简单说就是序列化复制一份返回。 -
eviction:缓存会使用默认的Least Recently Used(LRU,最近最少使用的)算法来收回。FIFO:First In First Out先进先出队列。
在解析Mapper.xml的XMLMapperBuilder类中的cacheElement()方法里。
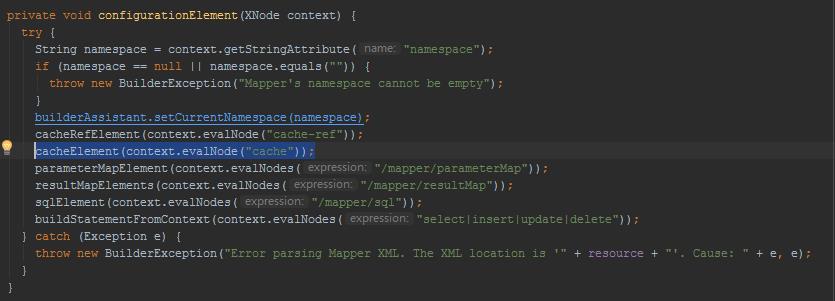
解析二级缓存中的标签:
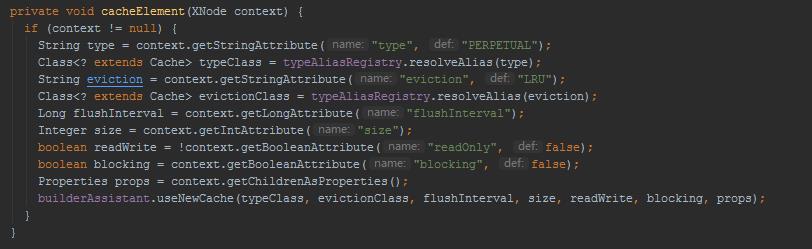
创建Cache对象:
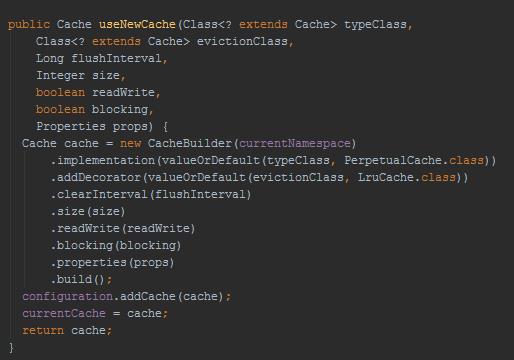
二级缓存处理完了,就来到BaseExecutor的query方法中。
BaseExecutor.query()
第一步,清空缓存
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
queryStack用于记录查询栈,防止地柜查询重复处理缓存。
flushCache=true的时候,会先清理本地缓存(一级缓存)。
如果没有缓存会从数据库中查询
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
在看看这个方法的逻辑:
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(...) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
//使用占位符的方式,先抢占一级缓存。
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
//删除上面抢占的占位符
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
//放入一级缓存中
localCache.putObject(key, list);
return list;
}
先在缓存使用占位符占位,然后查询,移除占位符,将数据放入一级缓存中。
执行Executor的doQuery()方法,默认使用SimpleExecutor。
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
下面就来到了SimpleExecutor中的doQuery方法。
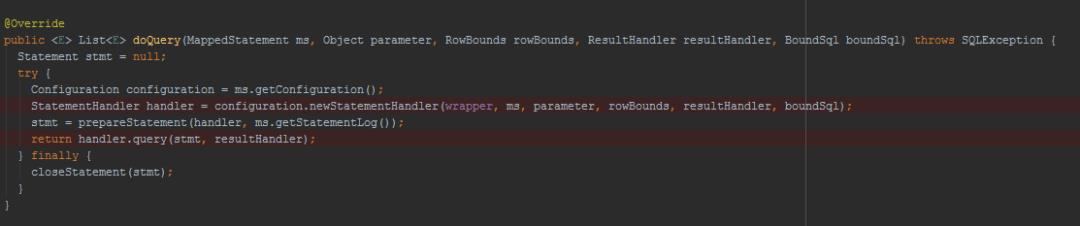
SimpleExecutor.doQuery
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(....) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
//获取配置文件信息
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//获取handler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(....);
//获取Statement
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
//执行RoutingStatementHandler的query方法
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
创建StatementHandler
在configuration中newStatementHandler()里,创建了一个StatementHandler,先得到RoutingStatementHandler(路由)。
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler() {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler
//执行StatementHandler类型的插件
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
RoutingStatementHandler创建的时候是用来创建基本的StatementHandler的。这里会根据MapperStament里面的statementType决定StatementHandler类型。
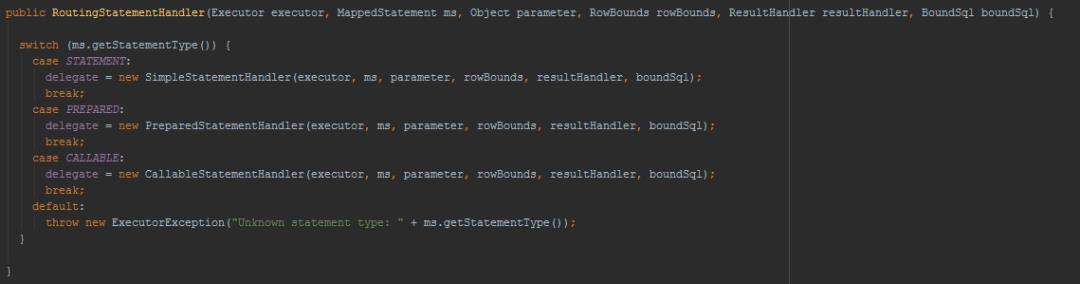
默认是PREPARED。
StatementHandler里面包含了处理参数的ParameterHandler和处理结果集的ResultHandler。
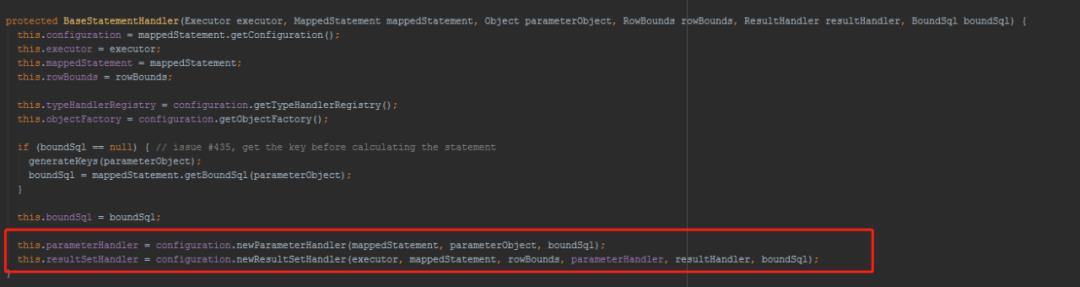
上面说的这几个对象正式被插件拦截的四大对象,所以在创建的时都要用拦截器进行包装的方法。
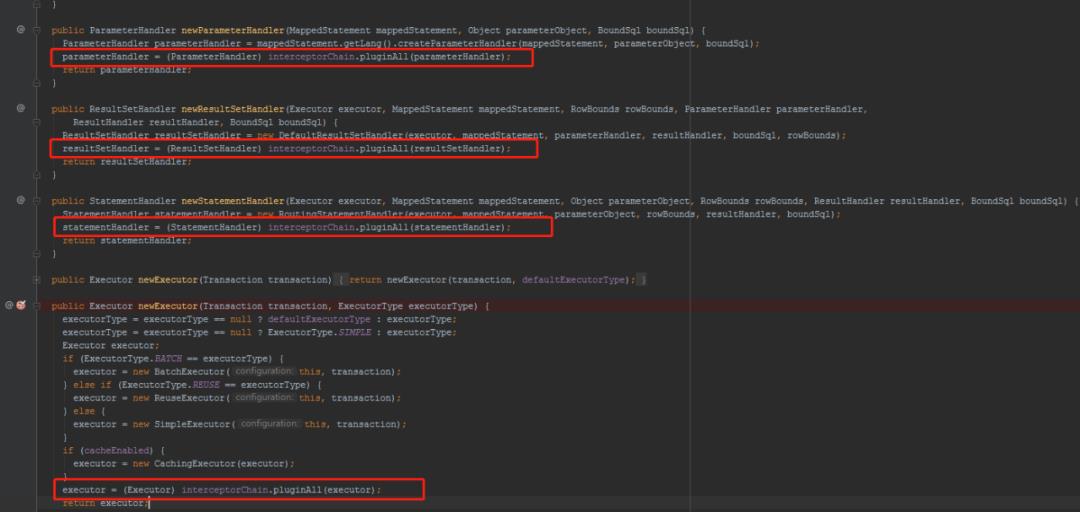
对于插件相关的,请看前面发的插件的文章。
创建Statement
创建对象后就会执行RoutingStatementHandler的query方法。
//RoutingStatementHandler中
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//委派delegate=PreparedStatementHandler
return delegate.query(statement, resultHandler);
}
这里设计很有意思,所有的处理都要使用RoutingStatementHandler来路由,全部通过委托的方式进行调用。
然后执行到PreparedStatementHandler中的query方法。
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
//JDBC的流程了
ps.execute();
//处理结果集,如果有插件代理ResultHandler,会先走到被拦截的业务逻辑中
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
看到了ps.execute();表示已经到JDBC层面了,这时候SQL就已经执行了。后面就是调用DefaultResultSetHandler类进行处理。
到这里,SQL语句就执行完毕,并将结果集赋值并返回了。
整个流程
从调用userMapper的selectById()方法开始,到JDBC中SQL执行的整个流程图。
感兴趣的小伙伴,可以对照着这张流程图就行一步一步的debug。
总结
本文从一个案例代码出发,到解析Mybatis的配置文件,到创建SqlSession对象,到获取UserMapper接口的代理对象,到调用代理对象方法,再到让方法和SQL关联起来,最后执行SQL,返回结果集。
涉及到的设计模式:单例模式、建造者设计模式、模板方法模式、代理模式、装饰器模式等。
技术难点:动态代理。
推荐阅读
以上是关于MyBatis 源码解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章