mysql数据库查询
Posted 巴蜀秀才
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mysql数据库查询相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
建立联系表:
学院表:
create table `department`(
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`name` varchar(20) not null
);
学生表:
create table `student`(
`s_id` int primary key auto_increment,
`name` varchar(20) not null,
`dep_id` int,
foreign key(`dep_id`) references `department`(`id`)
);
学生信息表:
create table `stu_details`(
`s_id` int primary key,
`age` int,
`sex` char(1),
foreign key(`s_id`) references `student` (`s_id`)
);
课程表:
create table `course`(
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`name` varchar(20) not null
);
创建中间表:
create table `course_details`(
`s_id` int,
`c_id` int,
primary key (s_id,c_id),
foreign key (`s_id`) references `student`(`s_id`),
foreign key (`c_id`) references `course`(`id`)
);
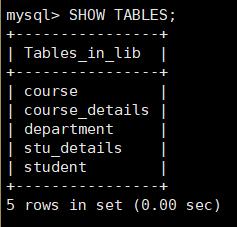
查看创建的五张表:
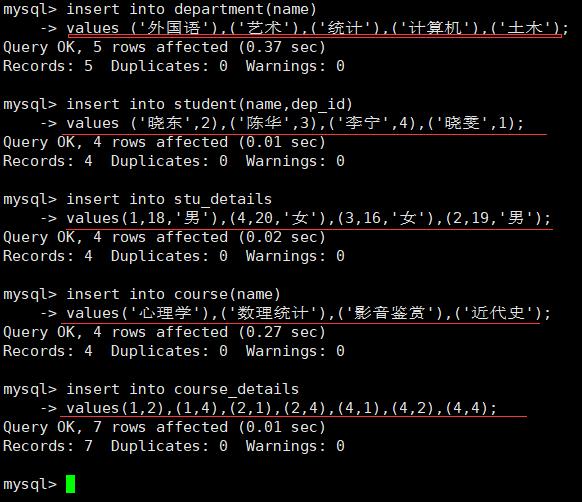
给每个表插入数据:
表的查询操作
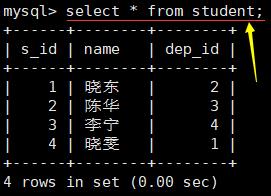
查询所有记录:
select * from [表名];
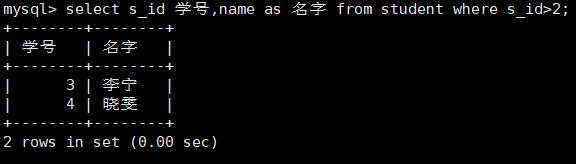
查询某列或者某些列的记录:将*号换成列名字[col_name],多个列用\',\'号隔开;

模糊查询:


#逻辑运算符 or and


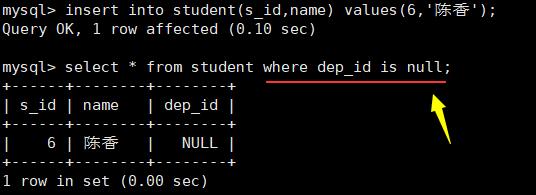
判断是否为null 不能用等于符合,要用is来判断:
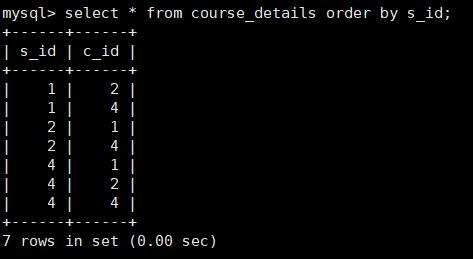
排序 order by:
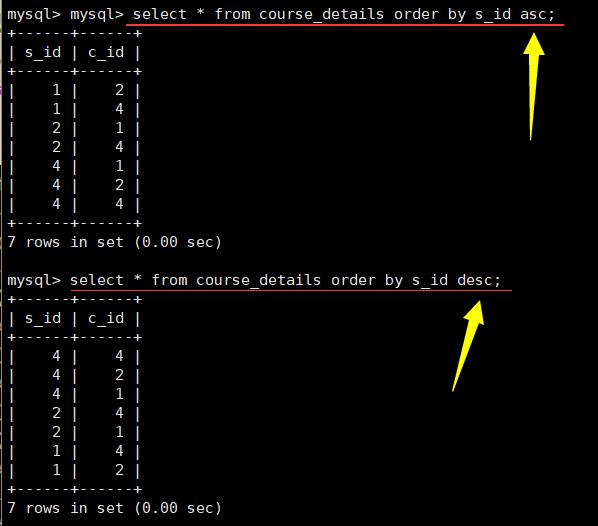
asc升序; desc降序
按学号升序排列输出:select * from course_details order by s_id;
不加是默认升序,加desc就是降序:
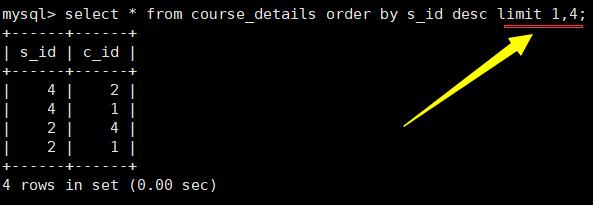
限制显示数据的数量 limit
limit后接一个数时,默认从0号位开始取对应的个数;两个参数,如3,4表示从3号位开始取4个数。
这个功能可以用于分页。
***分组查询
一般跟聚合函数一起使用:
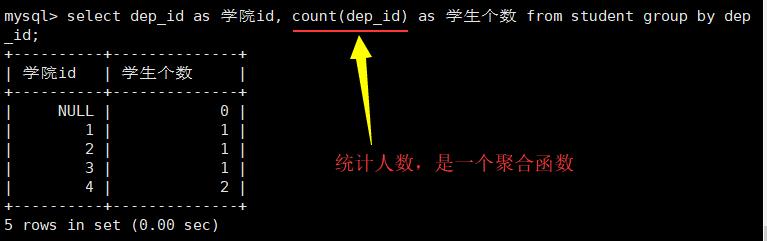
select dep_id as 学院id, count(dep_id) as 学生个数 from student group by dep_id;
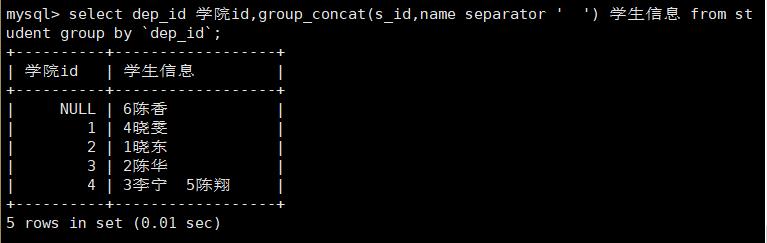
select dep_id 学院id,group_concat(s_id,name separator \' \') 学生信息 from student group by `dep_id`;
having条件
select dep_id 学院id,count(dep_id) 学生个数 from student group by dep_id having 学生个数>1;

having是在selecct返回的内容里面筛选,而where是在表中直接筛选。
子查询:出现在其他SQL语句内的SELECT字句。
嵌套在查询内部;
必须始终出现在圆括号内;
可以包含多个关键字或条件。
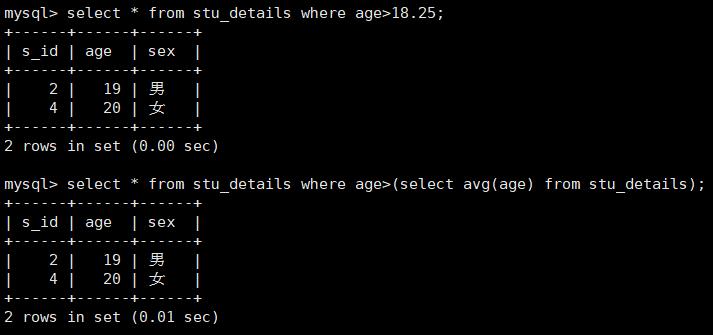
select * from stu_details where age>18.25;
select * from stu_details where age>(select avg(age) from stu_details);
select * from student where dep_id in (select id from department where name in (\'计算机\',\'外国语\'));

***联表查询***
内连接 inner join
有条件内连接:在无条件的内连接基础上,加上一个ON子句,当连接的时候,筛选出那些有实际意义的记录行来进行拼接。
在写条件时注意两张表的列名是否一样,如果时一样的则要在前面加上表名,tb_name.colname这种形式存在。
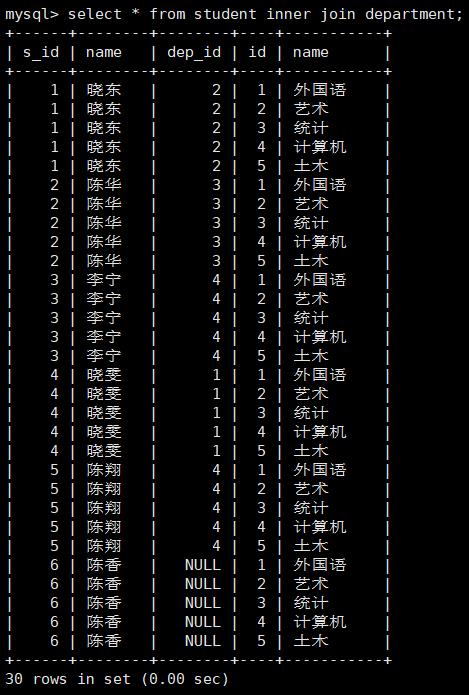
select * from student inner join department; 无条件内连接
select * from student inner join department on dep_id=id; 有条件内连接
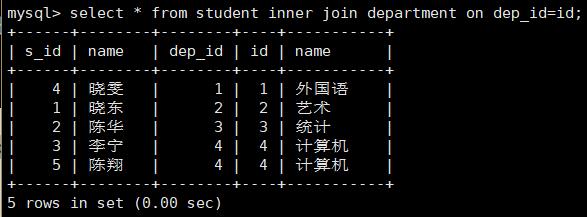
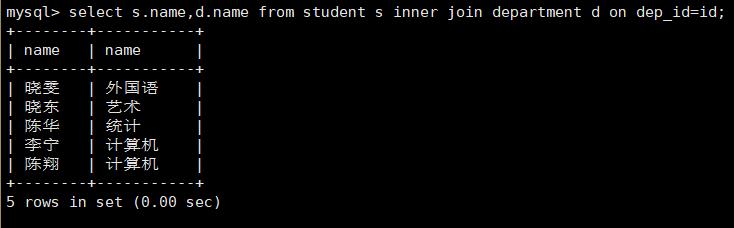
select s.name,d.name from student s inner join department d on dep_id=id;
查询学生姓名和对应的学院名字:
外连接 left join; right join;
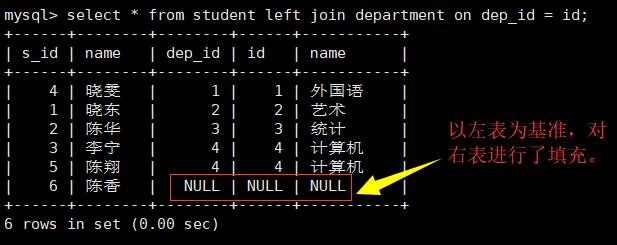
右外连接: (以右表为基准)对两张表做连接的时候,在连接条件不匹配的时候,留下右表中的数据,而左表中的数据以NULL填充
select * from student left join department on dep_id = id;
select * from student right join department on dep_id = id;

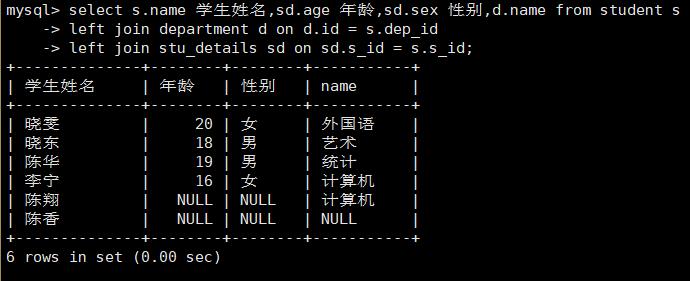
#需求: 作为宿管, 学生的 ( 姓名, 年龄,性别,所属学院)
事物 是数据库运行中的一个逻辑工作单位。
原子性:
事务必须是原子工作单元;对于其数据修改,要么全都执行,要么全都不执行。
一致性:
事务在完成时,必须使所有的数据都保持一致状态。
隔离性:
由并发事务所作的修改必须与任何其它并发事务所作的修改隔离。
案例:假设现在用户小明在商店买了500元东西,现在要转账给商店,那么就需要从小明的账户上减去500,然后在商店的用户上加
上500,但是如果在减500的过程中出现了系统故障,再重新启动后发现小明的钱扣了,但商店却没有收到,这时候就会出现数据变动不
一致。对于这种数据的修改我们需要的就是要么同时修改成功,要么同时修改失败,所以这就需要用事务来进行出来。
start transaction:开始一个新的事务
commit:提交当前事务,做出永久改变
rollback:回滚当前事务,放弃修改
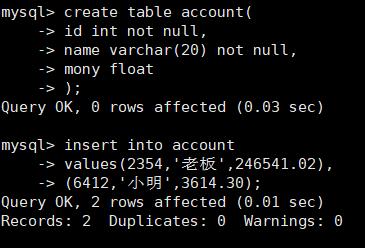
先给小明和店户创建一个银行账户:
create table account(
id int not null,
name varchar(20) not null,
mony float
);
给老板和小明的账户插值,初始化账户,然后执行转账的操作:
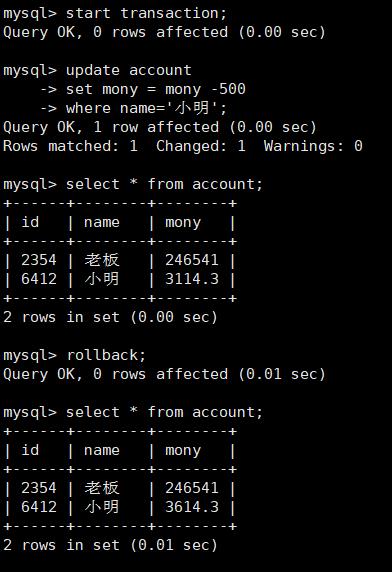
如果转账后系统崩溃,老板没有收到钱,则用rollback还原数据:
正确的执行如下:
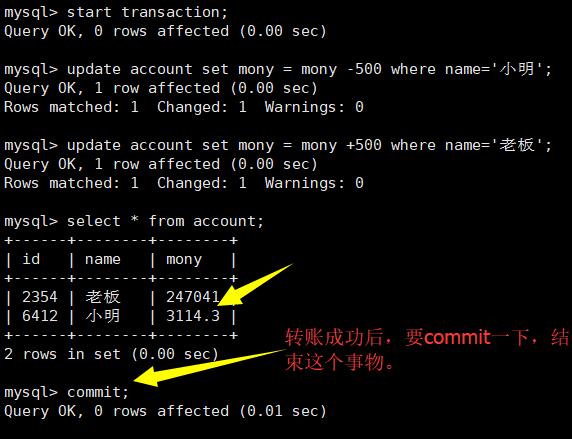
commit之后再rollback是没有作用的,但是不会报错!
以上是关于mysql数据库查询的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章