StringBuilder 你不知道的骚操作
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了StringBuilder 你不知道的骚操作相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 在 String你还需要知道这些细节 中提到过,由于String被设计成immutable,所以才有了StringBuilder和StringBuffer这2个类来帮助我们操作字符串,StringBuilder线程不安全,StringBuffer线程安全,在我们大多数日常使用场景,都是单线程操作字符串,所以StringBuidler用的会多一些,而且编译器也会默认帮我们将+号字符串拼接转化为StringBuidler append,这篇文章我会跟大家分享我知道的StringBuilder使用的一些骚操作。这个问题只要看下Jdk的源码就能清楚
底层数据结构很简单,就是一个char[] value 和大小字段 count,构造器生成的char[] 默认capacity大小是16,如果很明确插入的字符串很长,应该将capacity设置大一些,避免频繁拷贝数组扩容。
接下来,我们看下StringBuilder 插入删除的实现
可以看到,由于是基于数组实现的,所以插入删除的效率都不会太高,毕竟都要进行数组的拷贝,但是也不必太过担心,System.arrayCopy的速度还是很快的。
这里我想提一点,append和insert方法都能增长字符串,该如何选择,看上面的源码可以看到,insert不论字符串插入的位置是在中间还是最后,都会进行数组拷贝,而append则会根据当前数组的长度来判断是否需要拷贝扩容,所以如果需要在尾部增加字符串使用append,其他位置使用insert。
我们看一下StringBuilder append方法
可以看到,在字符数组大小不足够容纳新的字符的时候,会进行扩容,而扩容后的大小是原来数组的大小+新字符串的长度,所以这里的扩容策略是非常保守的,只能够容纳这一次的append操作,所以如果我们要在循环内频繁进行append操作,可以将StringBuilder初始大小capacity设置大一些,避免频繁扩容数组拷贝
平常我们使用的Jdk集合类,如ArrayList,HashMap等都会有clear方法来清空数据,但是StringBuilder没有提供这个方法,那我们如何清空StringBuilder中的数据呢,难道非要循环去调用delete?当然不用,StringBuilder另外给我们提供了setLength方法,参数传0,就达到了清空数据的作用。
通过源码可以看到,setLength方法,当传入的新length小于原来的count时,只是简单的将count设为新length,并不会去动原来的字符数组value,相当于count是一个指针,只是在移动指针,避免了数组拷贝,效率比较高。这个又引出了一个新问题,既然setLength不会去改变value数组,那value占用的内存怎么释放呢?
StringBuilder 提供了trimToSize方法
以上(安排的很明白),水平有限,各位大佬轻点喷😆
除了try{}catch{},你究竟还知道多少避免空指针异常的骚操作?
你究竟还知道多少避免空指针异常的那些骚操作?
一个有趣的bug总能找到一个有趣的java8特性!当我们遇到空指针异常时,你还在使用try...catch吗?那就太out啦!这里教你一招使用java8特性来避免空指针异常。
小伙伴知直呼——装到啦!
目录
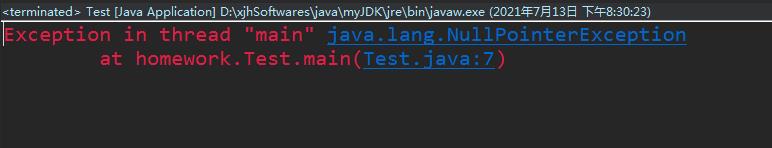
我们从一个staff案例开始,这里的类结构我们为了演示暂时随便写(不要介意),在构建的Test类中实例化这个Staff,并依次调用方法,获取员工的地址编码!
public class Test
public static void main(String[] args)
Staff staff=new Staff();
String code=staff.getAdd().getCity().getCode().getCodeMsg();
System.out.println(code);
但是run后发现他报错了,太正常了!
class Staff
int uid;
String uname;
Address add;
public Staff(int uid, String uname, Address add)
super();
this.uid = uid;
this.uname = uname;
this.add = add;
public Staff()
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
/**
* @return the uid
*/
public int getUid()
return uid;
/**
* @param uid the uid to set
*/
public void setUid(int uid)
this.uid = uid;
/**
* @return the uname
*/
public String getUname()
return uname;
/**
* @param uname the uname to set
*/
public void setUname(String uname)
this.uname = uname;
/**
* @return the add
*/
public Address getAdd()
return add;
/**
* @param add the add to set
*/
public void setAdd(Address add)
this.add = add;
class Address
int id;
City city;
public Address()
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
public Address(int id, City city)
super();
this.id = id;
this.city = city;
/**
* @return the id
*/
public int getId()
return id;
/**
* @param id the id to set
*/
public void setId(int id)
this.id = id;
/**
* @return the city
*/
public City getCity()
return city;
/**
* @param city the city to set
*/
public void setCity(City city)
this.city = city;
class City
Code code;
String name;
public City()
super();
public City(Code code, String name)
super();
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
public Code getCode()
return code;
public void setCode(Code code)
this.code = code;
public String getName()
return name;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
class Code
int id;
String codeMsg;
public Code()
public Code(int id, String code)
super();
this.id = id;
this.codeMsg = code;
/**
* @return the id
*/
public int getId()
return id;
/**
* @param id the id to set
*/
public void setId(int id)
this.id = id;
/**
* @return the code
*/
public String getCodeMsg()
return codeMsg;
/**
* @param code the code to set
*/
public void setCodeMsg(String code)
this.codeMsg = code;
1. 错误分析
main方法在staff调用过程链中的每个环节中都存在空对象!
2. 第一步解决方案
2.1 解决过程
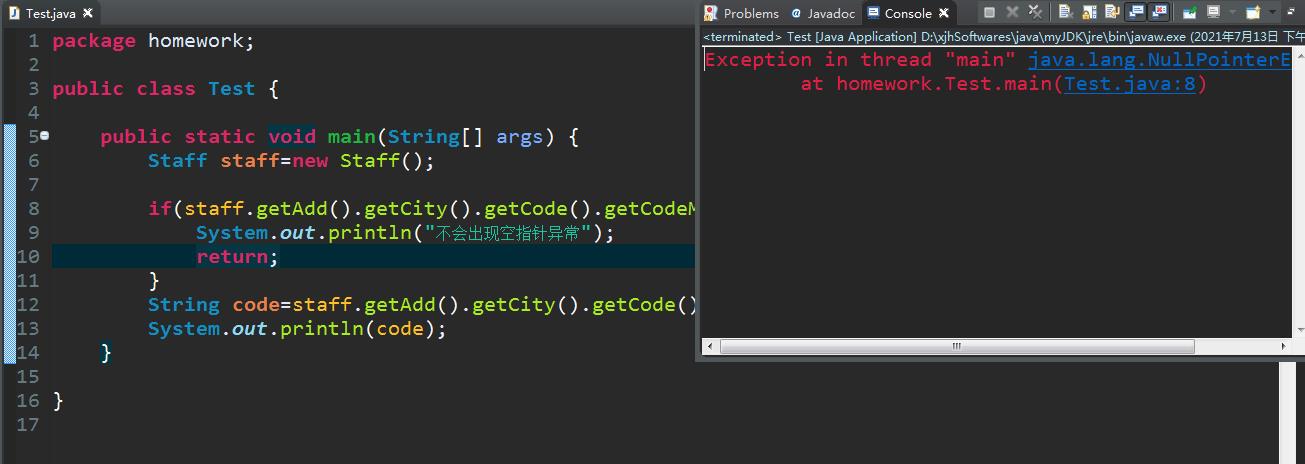
main方法中,在调用方法前对调用链中的环节进行判断。
public static void main(String[] args)
Staff staff=new Staff();
if(staff.getAdd().getCity().getCode().getCodeMsg() == null)
return;
String code=staff.getAdd().getCity().getCode().getCodeMsg();
System.out.println(code);
运行结果仍然出错了:
2.1 过程分析
显而易见,这样是错误的,调用链中,如:
- staff可能为空
- staff.getAdd()可能为空
- staff.getAdd().getCity().getCode()也可能为空
所以这样的判断条件是不充分的,仍然存在空指针异常。
3. 第二步解决方案
2.1 解决过程
根据第一步解决办法我们进行完善判断条件得到第二步解决办法:
public static void main(String[] args)
Staff staff=new Staff();
if(staff==null ||
staff.getAdd() == null ||
staff.getAdd().getCity() == null ||
staff.getAdd().getCity().getCode() == null ||
staff.getAdd().getCity().getCode().getCodeMsg() == null)
System.out.println("不会出现空指针异常");
return;
String code=staff.getAdd().getCity().getCode().getCodeMsg();
System.out.println(code);
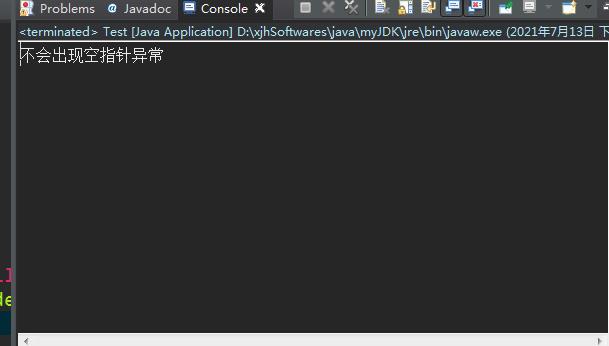
运行结果:
2.1 过程分析
明显,运行后并没有出现新的空指针异常了,但是这个判断过程实在是比较繁琐,好多同学反映这样不太友好,他说:“如果这个调用链好长怎么办?写这么多判断条件不友好啊!”
4. 使用java8特性后
根据同学们的反馈,我们直接来使用java8为我们提供的避免空指针异常的新特性:
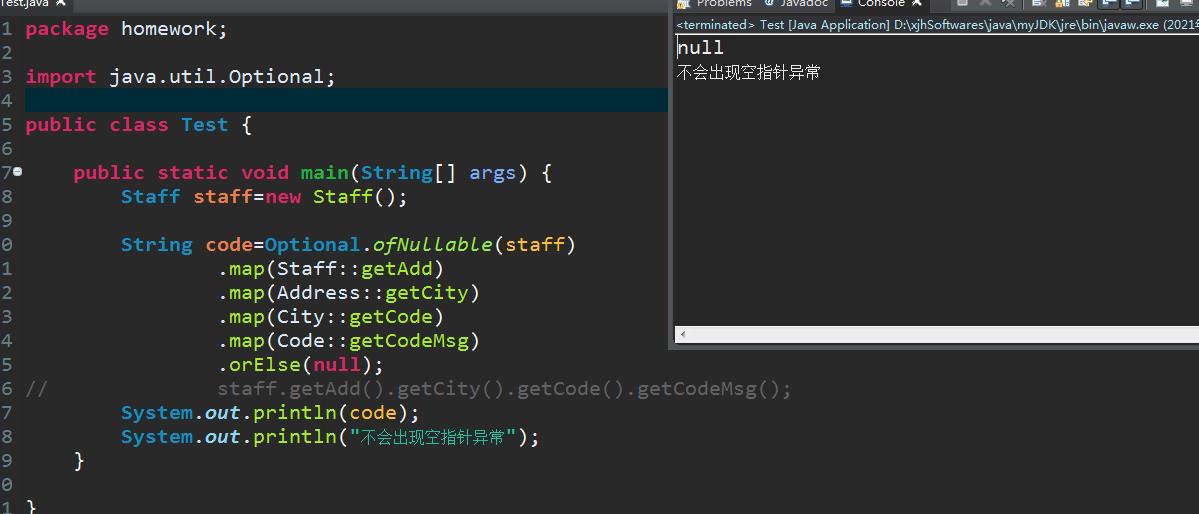
public static void main(String[] args)
Staff staff=new Staff();
String code=Optional.ofNullable(staff)
.map(Staff::getAdd)
.map(Address::getCity)
.map(City::getCode)
.map(Code::getCodeMsg)
.orElse(null);
// staff.getAdd().getCity().getCode().getCodeMsg();
System.out.println(code);
运行结果,发现是不会出现空指针异常的:
5. 总结
其实,在日常工作学习中不断地探索和发现一些Java8特性是一个非常有意义的过程!
但是我们不可不知的是,无论在什么情况下,一个空指针异常或许是一件不能去避免的过程,如果强行掩盖一个这样的问题,那么迎接的问题可能会更加严重,一句老话说得好,叫“丢了西瓜,捡了芝麻”,敲代码就是不断发现错误和解决错误的一个过程,有时候使用某些方法就行这里一样去避免这种空指针异常一样,我们需要一个工具来避免异常的发生。

以上是关于StringBuilder 你不知道的骚操作的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
除了try{}catch{},你究竟还知道多少避免空指针异常的骚操作?
除了try{}catch{},你究竟还知道多少避免空指针异常的骚操作?