1.头文件:#include<sstream>
2.stringstream是C++提供的串流(stream)物件,其中:
clear()重置流的标志状态;str()清空流的内存缓冲,重复使用内存消耗不再增加!
在使用stringstream时遇到的问题:
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
stringstream stream;
int a,b;
stream<<"80";
stream>>a;
stream<<"90";
stream>>b;
cout<<a<<endl;
cout<<b<<endl;
system("PAUSE ");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
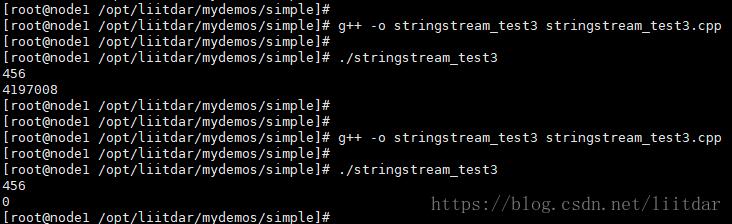
运行结果:
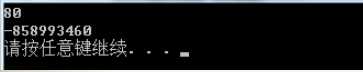
预期b为90,但是出现-858993460,这是由于stringstream重复使用时,没有清空导致的。
修改之后:
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
stringstream stream;
int a,b;
stream<<"80";
stream>>a;
stream.clear();
stream<<"90";
stream>>b;
cout<<a<<endl;
cout<<b<<endl;
system("PAUSE ");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
运行结果:
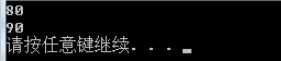
但是clear()仅仅清空标志位,并没有释放内存。
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
stringstream stream;
int a,b;
stream<<"80";
stream>>a;
stream.clear();
cout<<"Size of stream = "<<stream.str().length()<<endl;
stream<<"90";
stream>>b;
cout<<"Size of stream = "<<stream.str().length()<<endl;
cout<<a<<endl;
cout<<b<<endl;
system("PAUSE ");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
clear()之后,虽然结果正确了,但是stream占用的内存却没有释放!在实际的应用中,要是多次使用stringstream,每次都增加占用的内存。
可以利用stringstream.str("")来清空stringstream。
void str ( const string & s ); // copies the content of string s to the string object associated with the string stream buffer. The function effectivelly calls rdbuf()->str(). Notice that setting a new string does not clear the error flags currently set in the stream object unless the member function clear is explicitly called.
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
stringstream stream;
int a,b;
stream<<"80";
stream>>a;
cout<<"Size of stream = "<<stream.str().length()<<endl;
stream.clear();
stream.str("");
cout<<"Size of stream = "<<stream.str().length()<<endl;
stream<<"90";
stream>>b;
cout<<"Size of stream = "<<stream.str().length()<<endl;
cout<<a<<endl;
cout<<b<<endl;
system("PAUSE ");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
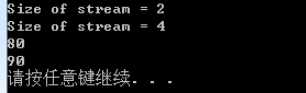
运行结果:
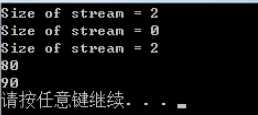
stringstream默认空格会直接分词!
題目:输入的第一行有一个数字 N 代表接下來有 N 行数字,每一行数字里有不固定个数的整数,打印每一行的总和。
输入:
3
1 2 3
20 17 23 54 77 60
111 222 333 444 555 666 777 888 999
输出:
6
251
4995
string s;
stringstream ss;
int n, i, sum, a;
cin >> n;
getline(cin, s); // 换行读取
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
getline(cin, s);
ss.clear();
ss.str(s);
sum=0;
while (1)
{
ss >> a;
if ( ss.fail() )
break;
sum+=a;
}
cout << sum << endl;
}
本文主要介绍 C++ 中 stringstream 类的常见用法。
1 概述
<sstream> 定义了三个类:istringstream、ostringstream 和 stringstream,分别用来进行流的输入、输出和输入输出操作。本文以 stringstream 为主,介绍流的输入和输出操作。
<sstream> 主要用来进行数据类型转换,由于 <sstream> 使用 string 对象来代替字符数组(snprintf方式),就避免缓冲区溢出的危险;而且,因为传入参数和目标对象的类型会被自动推导出来,所以不存在错误的格式化符的问题。简单说,相比c库的数据类型转换而言,<sstream> 更加安全、自动和直接。
2 代码示例
2.1 数据类型转换
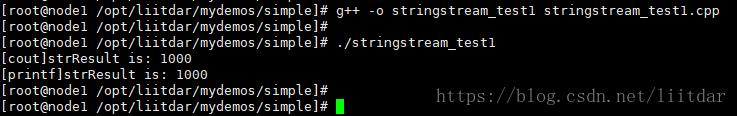
这里展示一个代码示例,该示例介绍了将 int 类型转换为 string 类型的过程。示例代码(stringstream_test1.cpp)如下:
#include <string> #include <sstream> #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> using namespace std; int main() { stringstream sstream; string strResult; int nValue = 1000; // 将int类型的值放入输入流中 sstream << nValue; // 从sstream中抽取前面插入的int类型的值,赋给string类型 sstream >> strResult; cout << "[cout]strResult is: " << strResult << endl; printf("[printf]strResult is: %s ", strResult.c_str()); return 0; }
编译并执行上述代码,结果如下:
2.2 多个字符串拼接
本示例介绍在 stringstream 中存放多个字符串,实现多个字符串拼接的目的(其实完全可以使用 string 类实现),同时,介绍 stringstream 的清空方法。
示例代码(stringstream_test2.cpp)如下:
#include <string> #include <sstream> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { stringstream sstream; // 将多个字符串放入 sstream 中 sstream << "first" << " " << "string,"; sstream << " second string"; cout << "strResult is: " << sstream.str() << endl; // 清空 sstream sstream.str(""); sstream << "third string"; cout << "After clear, strResult is: " << sstream.str() << endl; return 0; }
编译并执行上述代码,结果如下:
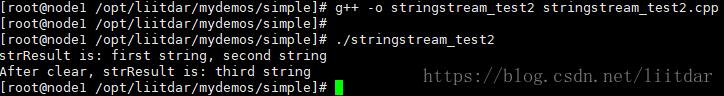
从上述代码执行结果能够知道:
- 可以使用 str() 方法,将 stringstream 类型转换为 string 类型;
- 可以将多个字符串放入 stringstream 中,实现字符串的拼接目的;
- 如果想清空 stringstream,必须使用 sstream.str(""); 方式;clear() 方法适用于进行多次数据类型转换的场景。详见示例2.3。
2.3 stringstream的清空
清空 stringstream 有两种方法:clear() 方法以及 str("") 方法,这两种方法有不同的使用场景。str("") 方法的使用场景,在上面的示例中已经介绍了,这里介绍 clear() 方法的使用场景。示例代码(stringstream_test3.cpp)如下:
#include <sstream> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { stringstream sstream; int first, second; // 插入字符串 sstream << "456"; // 转换为int类型 sstream >> first; cout << first << endl; // 在进行多次类型转换前,必须先运行clear() sstream.clear(); // 插入bool值 sstream << true; // 转换为int类型 sstream >> second; cout << second << endl; return 0; }
编译并执行上述代码,结果如下:
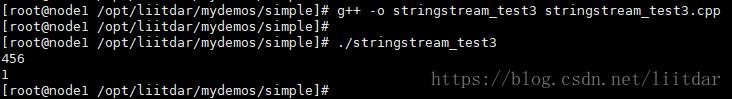
注意:在本示例涉及的场景下(多次数据类型转换),必须使用 clear() 方法清空 stringstream,不使用 clear() 方法或使用 str("") 方法,都不能得到数据类型转换的正确结果。下图分别是未使用 clear() 方法、使用 str("") 方法时的运行结果: