JAVA开发(Spring Gateway 的原理和使用)
Posted 茅河野人
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JAVA开发(Spring Gateway 的原理和使用)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在springCloud的架构中,业务服务都是以微服务来划分的,每个服务可能都有自己的地址和端口。如果前端或者说是客户端直接去调用不同的微服务的话,就要配置不同的地址。其实这是一个解耦和去中心化出现的弊端。所以springCloud体系中,又将这一层的调用封装一层,使一切调用都经过网关,前端和客户端只需要和网关交互,而不需要关注每个微服务的地址,只需要知道微服务的名称就可以。当微服务的地址改变时,只需要修改网关就可以,前端和客户端不需要任何修改,这也方便了服务的扩容和分布式部署。这里的网关就是相当于一个队长的作用。外部的东西一切找队长,团队里自己的事情由队长和成员内部解决。
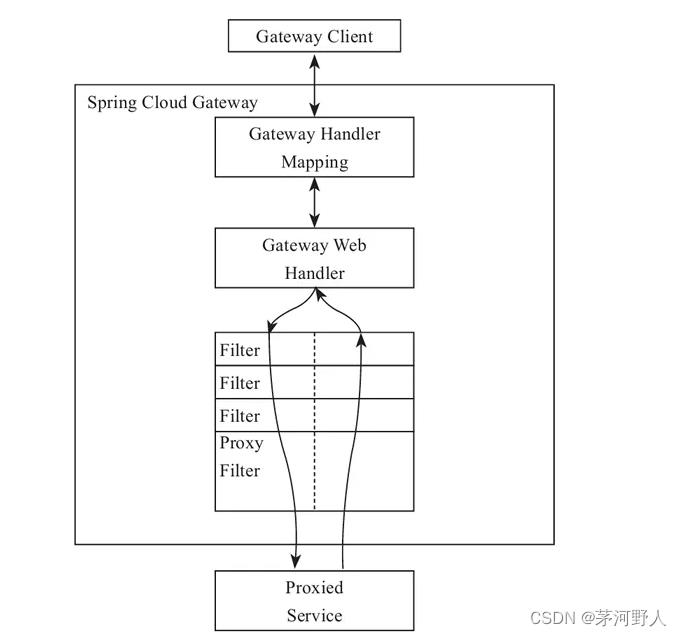
spring gateway的作用有点像封装了post和get的请求过程,增加不同微服务的路由断言判断访问哪个微服务,这里的微服务需要注册中心的协助,网关主要去找注册中心里注册的服务;
客户端向 Spring Cloud Gateway 发出请求,如果请求与网关程序定义的路由匹配,则该请求就会被发送到网关 Web 处理程序,此时处理程序运行特定的请求过滤器链。过滤器之间用虚线分开的原因是过滤器可能会在发送代理请求的前后执行逻辑。所有 pre 过滤器逻辑先执行,然后执行代理请求;代理请求完成后,执行 post 过滤器逻辑。
其原理架构如下:
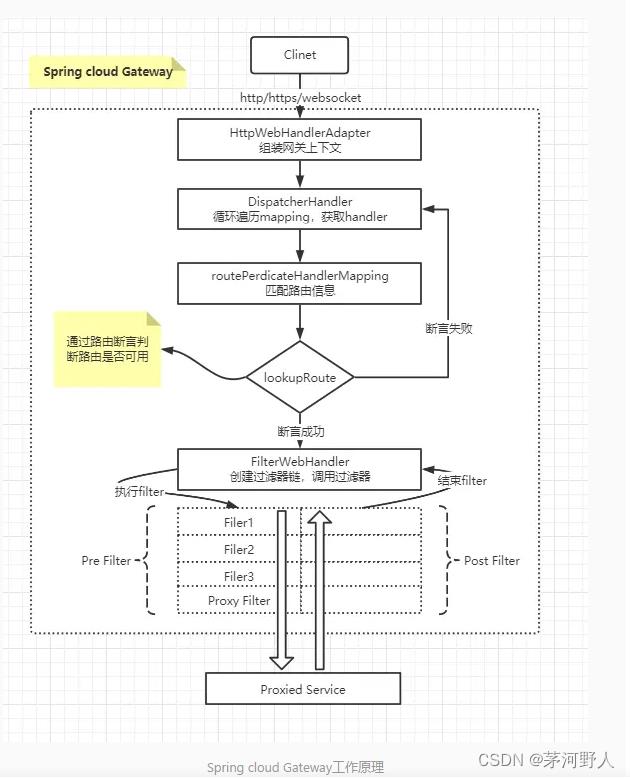
Gateway 接收客户端请求。客户端请求与路由信息进行匹配,匹配成功的才能够被发往相应的下游服务。请求经过 Filter 过滤器链,执行 pre 处理逻辑,如修改请求头信息等。请求被转发至下游服务并返回响应。响应经过 Filter 过滤器链,执行 post 处理逻辑。向客户端响应应答。
API 网关也存在不足之处,在微服务这种去中心化的架构中,网关又成了一个中心点,它增加了一个我们必须开发、部署和维护的高可用组件。正是由于这个原因,在网关设计时必须考虑即使 API 网关宕机也不要影响到服务的调用和运行,所以需要对网关的响应结果有数据缓存能力,通过返回缓存数据或默认数据屏蔽后端服务的失败。
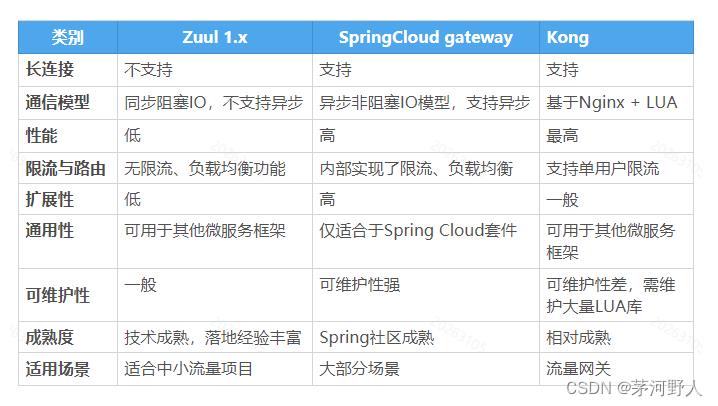
主要网关对比选型:
网关的作用:
性能:API高可用,负载均衡,容错机制。
安全:权限身份认证、脱敏,流量清洗,后端签名(保证全链路可信调用),黑名单(非法调用的限制)。
限流:流量控制,错峰流控,可以定义多种限流规则。
缓存:数据缓存。
日志:日志记录,一旦涉及分布式,全链路跟踪必不可少。
监控:记录请求响应数据,api耗时分析,性能监控。
网关的使用,配置
pom文件:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
<version>3.0.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>com.thoughtworks.xstream</groupId>
<artifactId>xstream</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.thoughtworks.xstream</groupId>
<artifactId>xstream</artifactId>
<version>$xstream.version</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>$fastjson.version</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.ctrip.framework.apollo</groupId>
<artifactId>apollo-client</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 健康检查 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
<version>2.6.3</version>
</dependency>yml文件配置详解:
#应用ID
app:
id: cn-maoheyeren-plat
#端口
server:
port: 8300
#应用版本
deploy:
version: -v1
#服务名称
spring:
application:
name: base-gateway
cloud:
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: false # 这个配置是默认给每个服务创建一个router,设置为false防止请求默认转发到url中包含的微服务名上
#例:/auth/**会默认转发到服务auth下,而不是转发到配置的uri
lower-case-service-id: true # 微服务名称以小写形式呈现
routes:
- id: base-admin #微服务路由规则
uri: lb://base-admin #负载均衡,将请求转发到注册中心的base-admin
predicates: #断言,如果前端请求包含/base-admin/,则走这条规则
- Path=/base-admin/**
filters: # 过滤器 /base-admin/** 转发到 uri/**
- StripPrefix=1
- id: maoheyeren-business
uri: lb://maoheyeren-business
predicates:
- Path=/maoheyeren-business/**
filters: # /maoheyeren-business/** 转发到 uri/**
- StripPrefix=1
- id: maoheyeren-cockpit
uri: lb://maoheyeren-cockpit
predicates:
- Path=/maoheyeren-cockpit/**
filters: # /maoheyeren-cockpit/** 转发到 uri/**
- StripPrefix=1
- id: maoheyeren-data
uri: lb://maoheyeren-data
predicates:
- Path=/maoheyeren-data/**
filters: # /maoheyeren-data/** 转发到 uri/**
- StripPrefix=1网关中过滤器的编写使用:
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilter;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GatewayFilterChain;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class PermissionGatewayFilter implements GatewayFilter, Ordered
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain)
log.info("执行了自定义的全局过滤器");
//1.获取请求参数access-token
String token = exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().getFirst("access-token");
//2.判断是否存在
if(token == null)
//3.如果不存在 : 认证失败
log.info("没有获取到token");
exchange.getResponse().setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
return exchange.getResponse().setComplete(); //请求结束
//4.如果存在,继续执行
return chain.filter(exchange); //继续向下执行
@Override
public int getOrder()
return 0;
spring gateway 实现限流
/**
* 自定义过滤器
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
@Order(-1)
public class RequestRateLimitFilter implements GlobalFilter
private static final Cache<String, RateLimiter> RATE_LIMITER_CACHE = CacheBuilder
.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000)
.expireAfterAccess(1, TimeUnit.HOURS)
.build();
private static final double DEFAULT_PERMITS_PER_SECOND = 1; // 令牌桶每秒填充速率
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain)
String remoteAddr = Objects.requireNonNull(exchange.getRequest().getRemoteAddress()).getAddress().getHostAddress();
RateLimiter rateLimiter = RATE_LIMITER_CACHE.get(remoteAddr, () -> RateLimiter.create(DEFAULT_PERMITS_PER_SECOND));
if (rateLimiter.tryAcquire())
return chain.filter(exchange);
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.TOO_MANY_REQUESTS);
response.getHeaders().add("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8");
DataBuffer dataBuffer = response.bufferFactory().wrap("Too Many Request!!!".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
return response.writeWith(Mono.just(dataBuffer));
/**
* 自定义局部限流
*
*/
@Component
public class CustomRequestRateLimitGatewayFilterFactory extends AbstractGatewayFilterFactory<CustomRequestRateLimitGatewayFilterFactory.Config>
public CustomRequestRateLimitGatewayFilterFactory()
super(Config.class);
private static final Cache<String, RateLimiter> RATE_LIMITER_CACHE = CacheBuilder
.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(1000)
.expireAfterAccess(1, TimeUnit.HOURS)
.build();
@Override
public GatewayFilter apply(Config config)
return new GatewayFilter()
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain)
String remoteAddr = Objects.requireNonNull(exchange.getRequest().getRemoteAddress()).getAddress().getHostAddress();
RateLimiter rateLimiter = RATE_LIMITER_CACHE.get(remoteAddr, () ->
RateLimiter.create(Double.parseDouble(config.getPermitsPerSecond())));
if (rateLimiter.tryAcquire())
return chain.filter(exchange);
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.TOO_MANY_REQUESTS);
response.getHeaders().add("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8");
DataBuffer dataBuffer = response.bufferFactory().wrap("Too Many Request!!!".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
return response.writeWith(Mono.just(dataBuffer));
;
@Override
public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder()
return Collections.singletonList("permitsPerSecond");
@Data
public static class Config
private String permitsPerSecond; // 令牌桶每秒填充速率
深入浅出SpringCloud原理及实战「SpringCloud-Gateway系列」微服务API网关服务的Gateway全流程开发实践指南(入门篇)
开发指南须知
本次实践主要在项目提供了构建在Spring生态系统之上API网关。
Spring Cloud Gateway的介绍
Spring Cloud Gateway目标是用一个简单、有效的方式路由到API,并且提供横切的一些关注点,例如:安全、监控、系统性能和弹性等。
API网关介绍
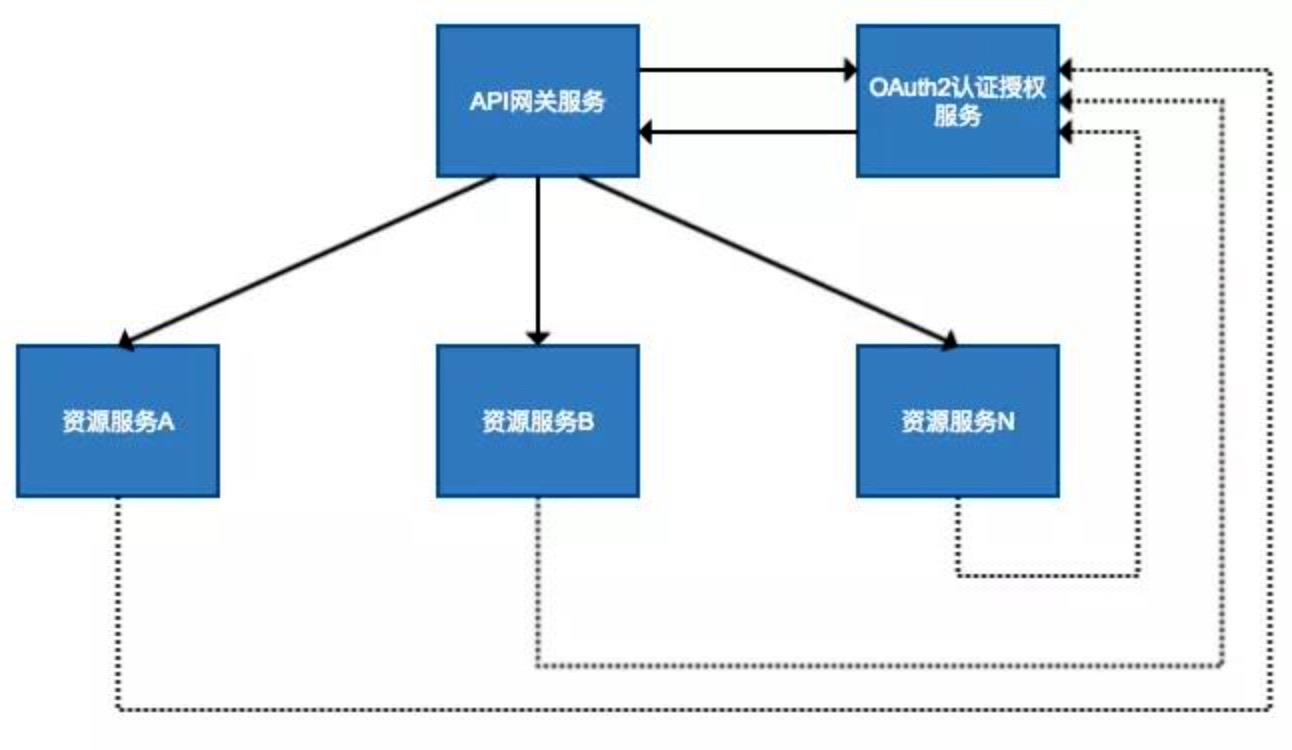
API 网关出现的原因是微服务架构的出现,不同的微服务一般会有不同的网络地址,而外部客户端可能需要调用多个服务的接口才能完成一个业务需求,如果让客户端直接与各个微服务通信,会有以下的问题:
- 客户端会多次请求不同的微服务,增加了客户端的复杂性。
- 存在跨域请求,在一定场景下处理相对复杂。
- 认证复杂,每个服务都需要独立认证。
- 难以重构,随着项目的迭代,可能需要重新划分微服务。
- 例如,可能将多个服务合并成一个或者将一个服务拆分成多个。如果客户端直接与微服务通信,那么重构将会很难实施。
- 某些微服务可能使用了防火墙 / 浏览器不友好的协议,直接访问会有一定的困难。
以上这些问题可以借助 API 网关解决。API 网关是介于客户端和服务器端之间的中间层,所有的外部请求都会先经过 API 网关这一层。也就是说,API 的实现方面更多的考虑业务逻辑,而安全、性能、监控可以交由 API 网关来做,这样既提高业务灵活性又不缺安全性。
SpringCloud Gateway技术基础
它是基于spring官方Spring 5.0、Spring Boot2.0和Project Reactor等技术开发的网关,Spring Cloud Gateway旨在为微服务架构提供简单、有效和统一的API路由管理方式,Spring Cloud Gateway作为Spring Cloud生态系统中的网关,目标是替代Netflix Zuul,其不仅提供统一的路由方式,并且还基于Filer链的方式提供了网关基本的功能,例如:安全、监控/埋点、限流等。
如何引用Spring Cloud Gateway
maven坐标为:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
有关使用当前Spring Cloud构建系统的详细信息,如果你引入了starter,但不想开启gateway,可以设置:
spring.cloud.gateway.enabled=false。
注意
-
Spring Cloud Gateway 构建在 Spring Boot 2.0, Spring WebFlux, and Project Reactor之上,因此,许多熟悉的同步库(例如:Spring Data 、Spring Security)或模式不适用于Spring Cloud Gateway。
-
Spring Cloud Gateway需要SpringBoot和SpringWebFlux提供的netty运行时,它不再运行于传统的Servlet容器或一个WAR包。
Route
网关基本构件块,也是网关最基础的部分,路由信息有一个ID、一个目的URL、一组断言predicates和一组filters组成。如果聚合断言为真,则匹配路由,说明请求的URL和配置。
Predicate
Java8中的断言函数。Spring Cloud Gateway中的断言函数输入类型是Spring5.0框架中的ServerWebExchange。Spring Cloud Gateway中的断言函数允许开发者去定义匹配来自于http request中的任何信息,比如请求头和参数等。
Java 8 Function Predicate. 输入类型是SpringFramework ServerWebExchange. 这允许开发人员匹配来自HTTP请求的任何内容,例如头或参数。
Filter
使用特定工厂构造的 Spring Framework GatewayFilter 实例。在这里,可以在发送downstream 请求之前或之后修改requests和responses。
一个标准的Spring webFilter。Spring cloud gateway中的filter分为两种类型的Filter,分别是Gateway Filter和Global Filter。过滤器Filter将会对请求和响应进行修改处理。
理解:
- 断言(Predicate):请求匹配;
- 过滤器(Filter):对请求或者返回进行过滤增强。
网关提供API全托管服务,丰富的API管理功能,辅助企业管理大规模的API,以降低管理成本和安全风险,包括协议适配、协议转发、安全策略、防刷、流量、监控日志等功能。一般来说网关对外暴露的URL或者接口信息,我们统称为路由信息。
Spring Cloud Gateway的工作原理
GatewayClient请求 Spring Cloud Gateway,如果Gateway Handler Mapping 确定请求与路由匹配,该请求被发送到Gateway Web Handler。此Handler运行时发送请求到具体的请求,其中通过过滤器链。

过滤器链被虚线分隔的原因是过滤器可以在发送代理请求之前或之后执行逻辑。执行所有“预”过滤逻辑,然后发出代理请求。在发出代理请求后,将执行“post”过滤器逻辑。URIs 在路由中没有设置端口,则按照HTTP和HTTPS默认端口设置为80和443。
Spring cloud Gateway发出请求。然后再由Gateway Handler Mapping中找到与请求相匹配的路由,将其发送到Gateway web handler。Handler再通过指定的过滤器链将请求发送到我们实际的服务执行业务逻辑,然后返回。
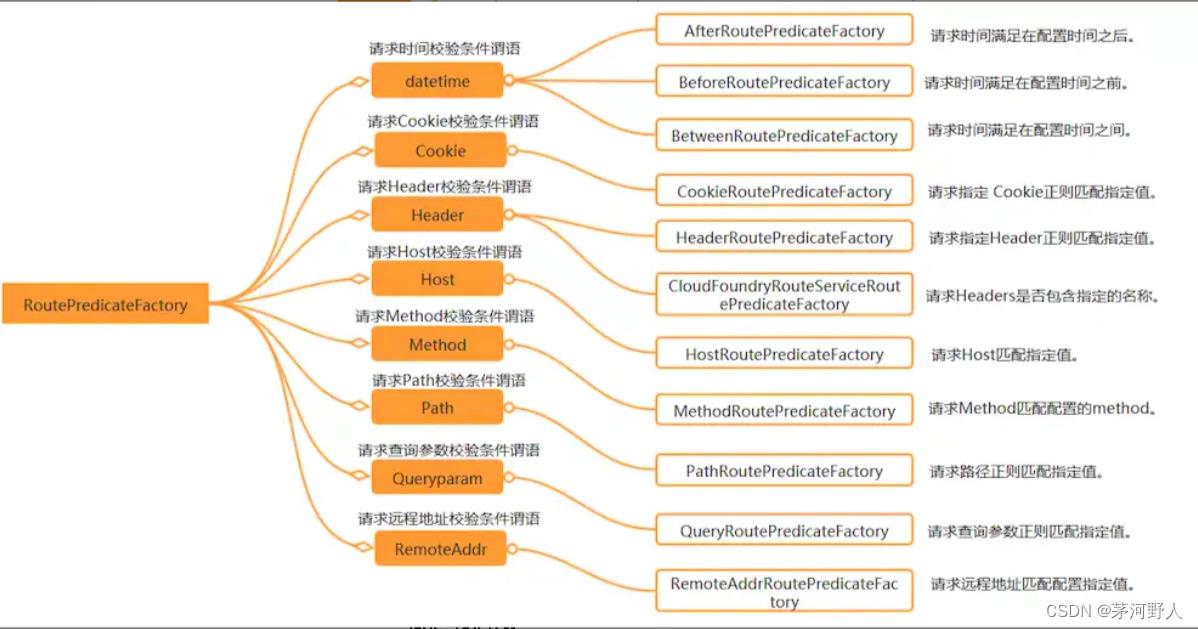
Spring Cloud Gateway-路由断言工厂
Spring Cloud Gateway匹配路由作为SpringWebFlux HandlerMapping基础设施的一部分。Spring Cloud Gateway包含许多内置的路由断言工厂,这些断言匹配不同属性的HTTP请求,可以组合多个路由断言工厂,并通过逻辑组合。
Before Route Predicate Factory
Before Route Predicate Factory 有一个时间参数,此断言匹配发生在该时间参数之前的请求。

这个路由匹配发生在 Jan 20, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver)之前的请求。
After Route Predicate Factory
After Route Predicate Factory有一个时间参数,此断言匹配发生在该时间参数之后的请求。

这个路由匹配发生在 Jan 20, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver)之后的请求。
Between Route Predicate Factory
Between Route Predicate Factory 有两个时间参数。此断言匹配发生在这两个时间之间的请求。
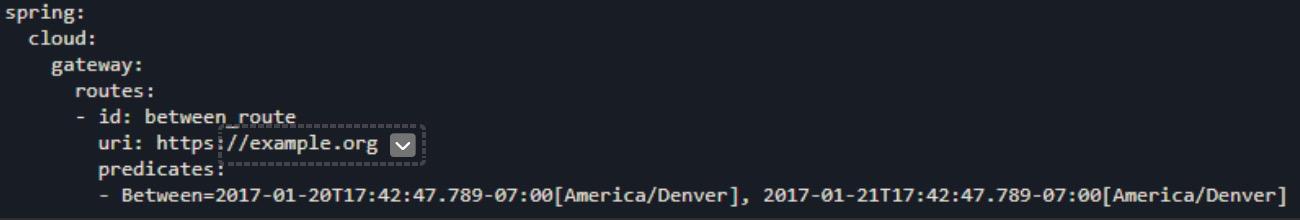
这个路由匹配发生在 Jan 20, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver)与Jan 21, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver)之间的请求。可应用于维护窗口。
Cookie Route Predicate Factory
Cookie Route Predicate Factory 有两个参数,包括cookie名称和正则表达式。此断言匹配cookies包括给定的名称和符合正则表达式的值。

此路由匹配cookie名称为chocolate ,cookie值为ch.p正则表达式,匹配chap,chbp等。
Header Route Predicate Factory
Header Route Predicate Factory 包括两个参数包括头名称和值的正则表达式。此断言匹配一个头信息包括该名称和符合该正则表达式值得请求。
此路由匹配头名称为X-Request-Id且值匹配\\d+ 表达式(包含一个或多个数字)。

Host Route Predicate Factory
Host Route Predicate Factory包括一个参数host 名称模式列表。此模式是一种 Ant 风格模式,以 “.” 作为分隔符。此断言匹配Host头。另外Host头来源有两种:第一种是请求地址;第二种是自己在http的header头中放入Host变量值。
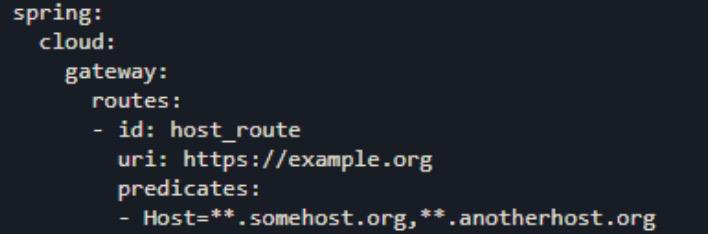
URI 模板变量也支持这种格式 sub.myhost.org。
此路由匹配头文件中的Host值www.somehost.org,beta.somehost.org 或 www.anotherhost.org。此示例均为默认端口80,如果为其他端口,需要在表达式中定义。
此断言提取URI模板变量(如上面示例中定义的子变量)作为名称和值的映射,并将其放置在ServerWebExchange.getAttributes()中,其键在ServerWebExchangeUtils.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE属性中定义。
在过滤其中加入如下代码示例:
Map uri_template_variables_attribute=exchange.getAttribute(ServerWebExchangeUtils.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE);
// Map variables=ServerWebExchangeUtils.getUriTemplateVariables(exchange);
uri_template_variables_attribute.forEach((K,V)->
System.out.println("K:"+K+"--V:"+V);
);
- 访问Host为:www.myhost.org
- 输出结果: K:sub–V:www
Filter规律器
Global Filter接口与GatewayFilter具有相同的签名。这些是有条件地应用于所有路由的特殊过滤器。
Combined Global Filter and GatewayFilter Ordering
-
当请求进入(并匹配路由)时,Filtering Web Handler会将GlobalFilter的所有实例和GatewayFilter的所有路由特定实例添加到过滤器链。
-
此组合过滤器链通过org.springframework.core.Ordered接口进行排序。可以通过实现getOrder()方法或者使用@Order注解。
Spring Cloud Gateway区分了过滤器逻辑执行的“请求”和“响应”阶段,具有最高优先级的过滤器将是“请求”阶段的第一个和“响应”阶段的最后一个 。

ANT通配符有三种:
而上面多数的匹配规则运算符号都是有AntPathMatcher对象进行实现的
private AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
- ?:匹配任意一个单个字符
-
- :匹配0或者任意数量的字符
- ** :匹配0和或者更多目录的字符
@Component
public class AuthGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered
private AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain)
ServerHttpRequest request = exchange.getRequest();
String path = request.getURI().getPath();
//商城api接口,校验用户必须登录
if(antPathMatcher.match("/api/**/auth/**", path))
List<String> tokenList = request.getHeaders().get("token");
if(null == tokenList)
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
return out(response);
else
// Boolean isCheck = JwtUtils.checkToken(tokenList.get(0));
// if(!isCheck)
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
return out(response);
//
//内部服务接口,不允许外部访问
if(antPathMatcher.match("/**/inner/**", path))
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
return out(response);
return chain.filter(exchange);
@Override
public int getOrder()
return 0;
private Mono<Void> out(ServerHttpResponse response)
JsonObject message = new JsonObject();
message.addProperty("success", false);
message.addProperty("code", 28004);
message.addProperty("data", "鉴权失败");
byte[] bits = message.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
DataBuffer buffer = response.bufferFactory().wrap(bits);
//response.setStatusCode(HttpStatus.UNAUTHORIZED);
//指定编码,否则在浏览器中会中文乱码
response.getHeaders().add("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8");
return response.writeWith(Mono.just(buffer));
自定义异常处理
服务网关调用服务时可能会有一些异常或服务不可用,它返回错误信息不友好,需要我们覆盖处理。
ErrorHandlerConfig
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class)
public class ErrorHandlerConfig
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
private final ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
private final List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
private final ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer;
public ErrorHandlerConfig(ServerProperties serverProperties,
ResourceProperties resourceProperties,
ObjectProvider<List<ViewResolver>> viewResolversProvider,
ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer,
ApplicationContext applicationContext)
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
this.viewResolvers = viewResolversProvider.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList);
this.serverCodecConfigurer = serverCodecConfigurer;
@Bean
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public ErrorWebExceptionHandler errorWebExceptionHandler(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes)
JsonExceptionHandler exceptionHandler = new JsonExceptionHandler(
errorAttributes,
this.resourceProperties,
this.serverProperties.getError(),
this.applicationContext);
exceptionHandler.setViewResolvers(this.viewResolvers);
exceptionHandler.setMessageWriters(this.serverCodecConfigurer.getWriters());
exceptionHandler.setMessageReaders(this.serverCodecConfigurer.getReaders());
return exceptionHandler;
参考资料
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37989738/article/details/107205863
以上是关于JAVA开发(Spring Gateway 的原理和使用)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章