用KNN算法判断知识掌握程度高低
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了用KNN算法判断知识掌握程度高低相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A KNN算法既可以解决分类问题,也可以解决预测问题。
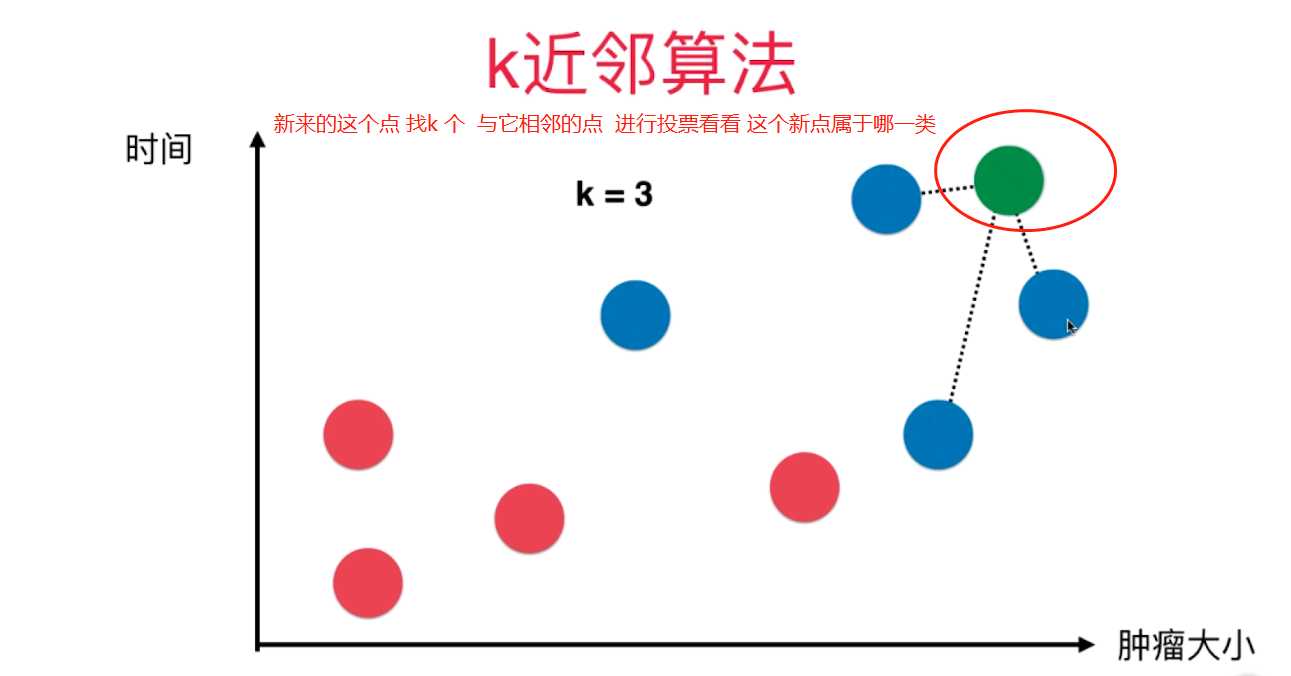
基础思想:通过计算每个训练样例到待分类样品的距离,取和待分类样品距离最近的K个训练样例,K个样品中哪个类别的训练样例占多数,则待分类样品就属于哪个类别。
对于离散型因变量,从k个最近的已知类别样本中挑选出频率最高的类别用于未知样本的判断;对于连续型因变量,将k个最近的已知样本均值用作未知样本的预测。
k值过小,模型过拟合,例如k=1,未知样本的类别将由最近的1个已知样本点来决定,对于训练数据来说,训练误差几乎为0,对于测试数据来说,训练误差可能会很大,因为距离最近的1个已知样本点可以是异常观测值,也可以是正常观测值。
k值过大,模型欠拟合,例如k=N,未知样本的类别将由所有已知样本中频数最高的类别决定,不管是训练集还是测试集被判为一种类别,易欠拟合。
一般利用多重交叉验证得到平均误差最小的k值。还有一种方法是设置k近邻样本的投票权重,对已知样本距离较远的设置权重低一些,较近的设置权重高一些,通常将权重设置为距离的倒数。
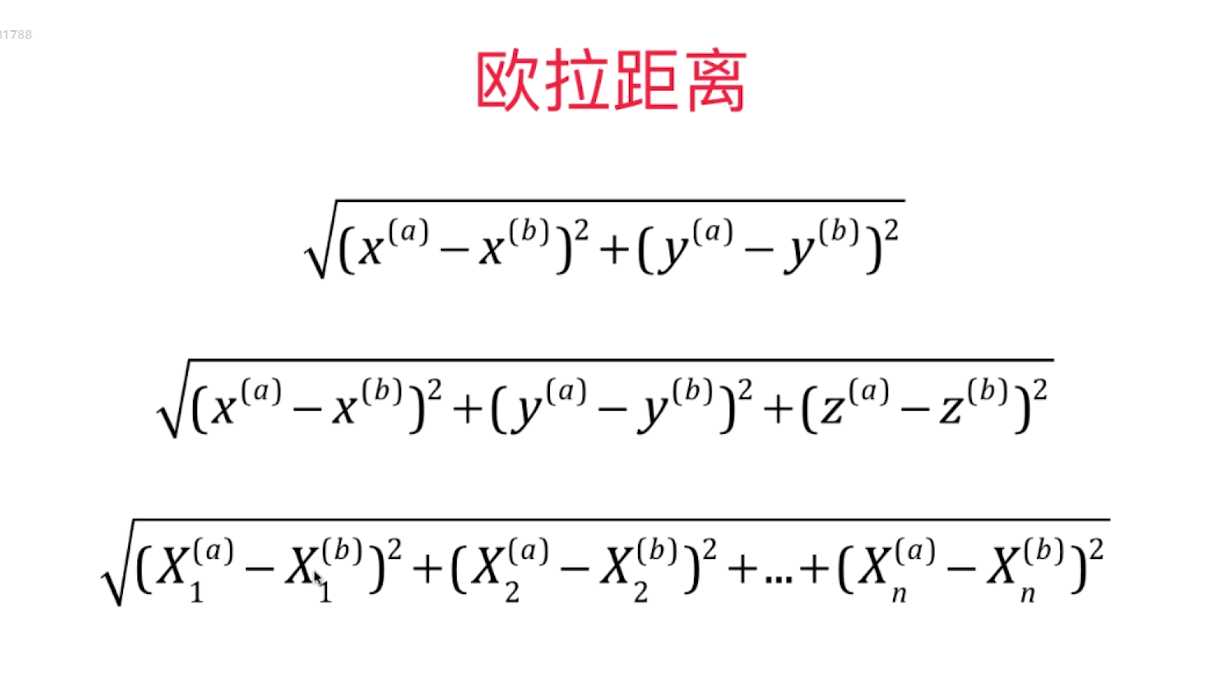
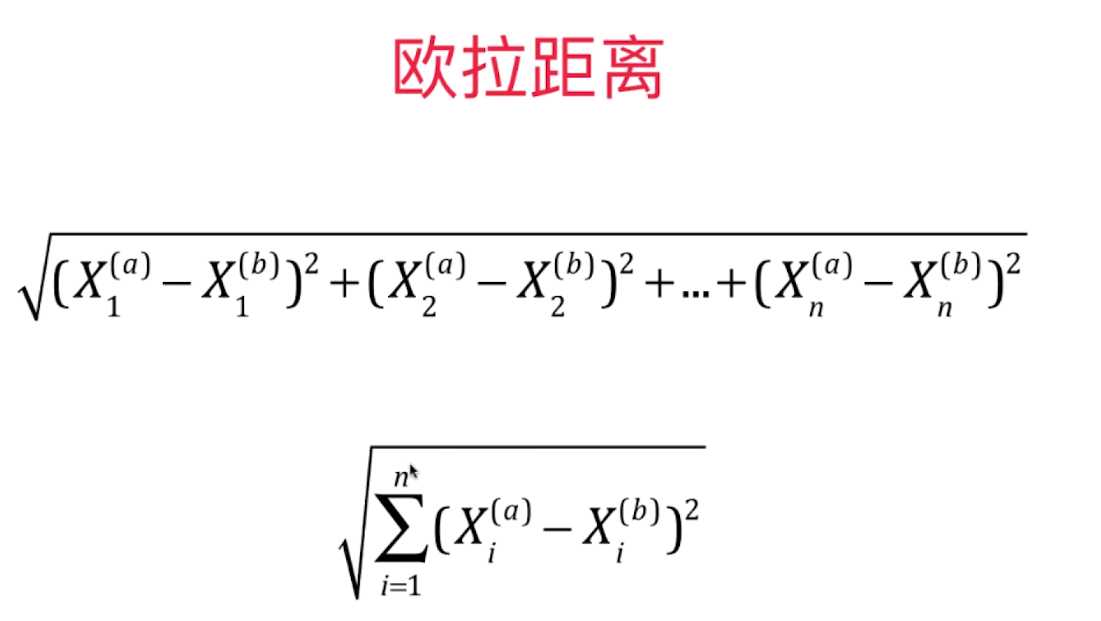
点与点之间的距离即相似性,一般用欧氏距离,即L2范数
或者曼哈顿距离,即L1范数
或者余弦相似度cosα
或者杰卡德相似系数,即J=|A∩B|/|A∪B|
在使用距离方法来度量相似性时,要使所有变量数值化(通过哑变量或者重编码为0,1,2),而且采用标准化方法进行归一化,防止数值变量的量纲影响
近邻搜寻方法包括:暴力搜寻法(全表扫描),kd树(k为训练集中包含的变量个数,而非KNN中的k个邻近样本,先用所有已知类别的样本点构造一棵树,再将未知类别应用在树上),球树搜寻(将kd树中的超矩形体换成了超球体)。
优点:
精度高,对异常值不敏感,无数据输入假定;
KNN 是一种在线技术,新数据可以直接加入数据集而不必进行重新训练;
KNN 理论简单,容易实现。
缺点:
对于样本容量大的数据集计算量比较大,即计算复杂度高;
必须保存全部数据集,即空间复杂度高;
KNN 每一次分类都会重新进行一次全局运算;
样本不平衡时,预测偏差比较大。如:某一类的样本比较少,而其它类样本比较多;
K 值大小的选择;
KNN 无法给出基础结构信息,无法知晓平均实例样本与典型实例样本具有什么特征,即无法给出数据的内在含义。
应用领域:
文本分类;模式识别;聚类分析;多分类领域。
行表示每一个被观测的学生,
STG:在目标学科上的学习时长,
SCG:重复次数
STR:相关科目的学习时长
LPR:相关科目的考试成绩
PEG:目标科目的考试成绩
(以上指标均已标准化)
UNG:对知识的掌握程度高低
利用多重交叉验证获取符合数据的理想k值
经过10重交叉验证,最佳的近邻个数为6
weights=uniform,表示投票权重一样
=distance,表示投票权重与距离成反比
从主对角线看,绝大多数样本被正确分类
通过热力图可视化混淆矩阵
行代表真实地,列代表预测的,主对角线上的颜色比较深,说明绝大多数样本是被正确分类的。
下面得到模型在测试集上的预测准确率:
整体预测准确率为91.09%,要得到每个类别的准确率:
第一列为预测精度,即”预测正确的类别个数/该类别预测的所有个数"
第二列为预测覆盖率,即”预测正确的类别个数/该类别实际的所有个数"
第三列为前两列的加权结果
第四列为类别实际的样本个数
对于预测问题的解决同决策树中一样,用MSE衡量
机器学习 分类算法--K近邻算法 KNN
一、K近邻算法基础
KNN------- K近邻算法--------K-Nearest Neighbors
思想极度简单
应用数学知识少 (近乎为零)
效果好(缺点?)
可以解释机器学习算法使用过程中很多细节问题
更完整的刻画机器学习应用的流程
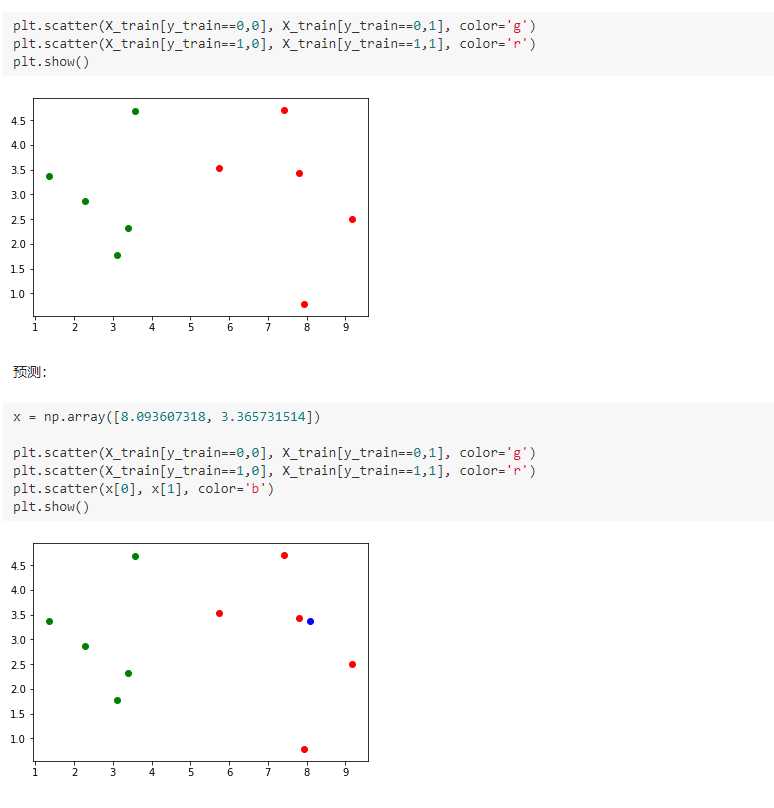
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 实现我们自己的 kNN 创建简单测试用例 raw_data_X = [[3.393533211, 2.331273381], [3.110073483, 1.781539638], [1.343808831, 3.368360954], [3.582294042, 4.679179110], [2.280362439, 2.866990263], [7.423436942, 4.696522875], [5.745051997, 3.533989803], [9.172168622, 2.511101045], [7.792783481, 3.424088941], [7.939820817, 0.791637231] ] raw_data_y = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1] X_train = np.array(raw_data_X) y_train = np.array(raw_data_y) X_train array([[ 3.39353321, 2.33127338], [ 3.11007348, 1.78153964], [ 1.34380883, 3.36836095], [ 3.58229404, 4.67917911], [ 2.28036244, 2.86699026], [ 7.42343694, 4.69652288], [ 5.745052 , 3.5339898 ], [ 9.17216862, 2.51110105], [ 7.79278348, 3.42408894], [ 7.93982082, 0.79163723]]) y_train array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])
kNN的过程
from math import sqrt distances = [] for x_train in X_train: d = sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x)**2)) distances.append(d) distances [4.812566907609877, 5.229270827235305, 6.749798999160064, 4.6986266144110695, 5.83460014556857, 1.4900114024329525, 2.354574897431513, 1.3761132675144652, 0.3064319992975, 2.5786840957478887] distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x)**2)) for x_train in X_train] distances [4.812566907609877, 5.229270827235305, 6.749798999160064, 4.6986266144110695, 5.83460014556857, 1.4900114024329525, 2.354574897431513, 1.3761132675144652, 0.3064319992975, 2.5786840957478887] np.argsort(distances) array([8, 7, 5, 6, 9, 3, 0, 1, 4, 2]) nearest = np.argsort(distances) k = 6 topK_y = [y_train[neighbor] for neighbor in nearest[:k]] topK_y [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0] from collections import Counter votes = Counter(topK_y) votes Counter({0: 1, 1: 5}) votes.most_common(1) [(1, 5)] predict_y = votes.most_common(1)[0][0] predict_y 1
二、scikit-learn 中的机器学习算法封装
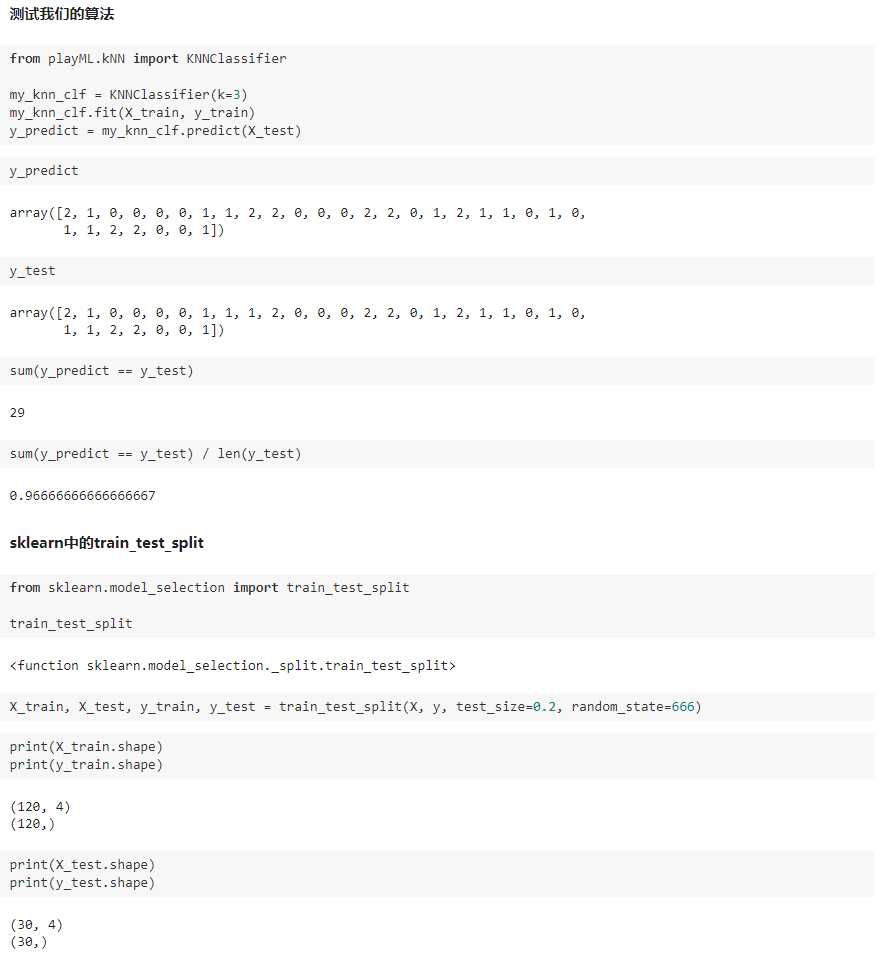
KNN/KNNN.py
import numpy as np from math import sqrt from collections import Counter class KNNClassifier: def __init__(self, k): """初始化kNN分类器""" assert k >= 1, "k must be valid" self.k = k self._X_train = None self._y_train = None def fit(self, X_train, y_train): """根据训练数据集X_train和y_train训练kNN分类器""" assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], "the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train" assert self.k <= X_train.shape[0], "the size of X_train must be at least k." self._X_train = X_train self._y_train = y_train return self def predict(self, X_predict): """给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量""" assert self._X_train is not None and self._y_train is not None, "must fit before predict!" assert X_predict.shape[1] == self._X_train.shape[1], "the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train" y_predict = [self._predict(x) for x in X_predict] return np.array(y_predict) def _predict(self, x): """给定单个待预测数据x,返回x的预测结果值""" assert x.shape[0] == self._X_train.shape[1], "the feature number of x must be equal to X_train" distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2)) for x_train in self._X_train] nearest = np.argsort(distances) topK_y = [self._y_train[i] for i in nearest[:self.k]] votes = Counter(topK_y) return votes.most_common(1)[0][0] def __repr__(self): return "KNN(k=%d)" % self.k
kNN_function/KNN.py
import numpy as np from math import sqrt from collections import Counter def kNN_classify(k, X_train, y_train, x): assert 1 <= k <= X_train.shape[0], "k must be valid" assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], "the size of X_train must equal to the size of y_train" assert X_train.shape[1] == x.shape[0], "the feature number of x must be equal to X_train" distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x)**2)) for x_train in X_train] nearest = np.argsort(distances) topK_y = [y_train[i] for i in nearest[:k]] votes = Counter(topK_y) return votes.most_common(1)[0][0]

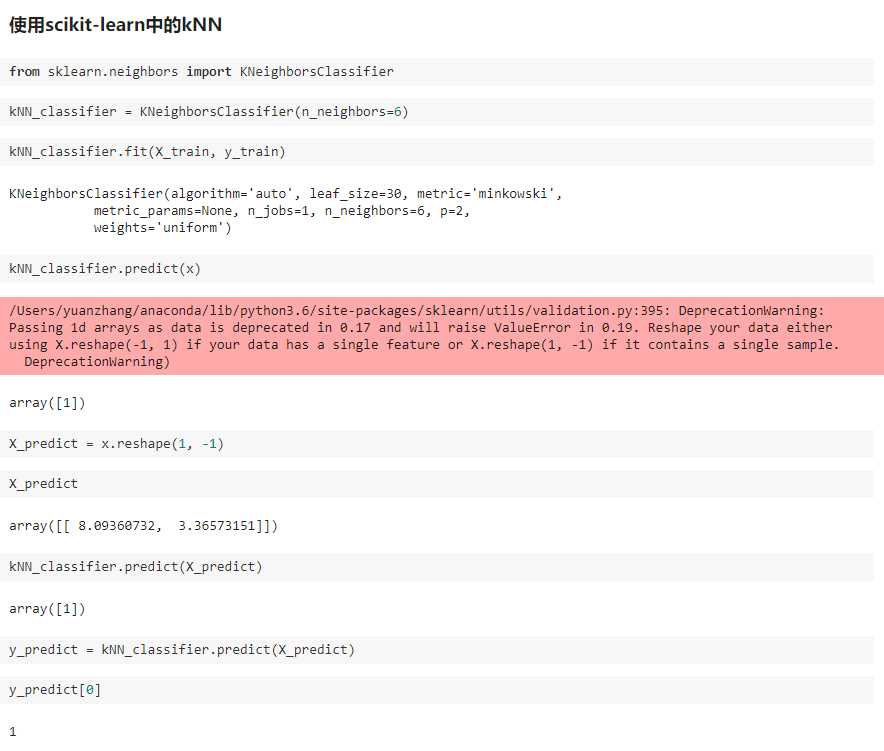
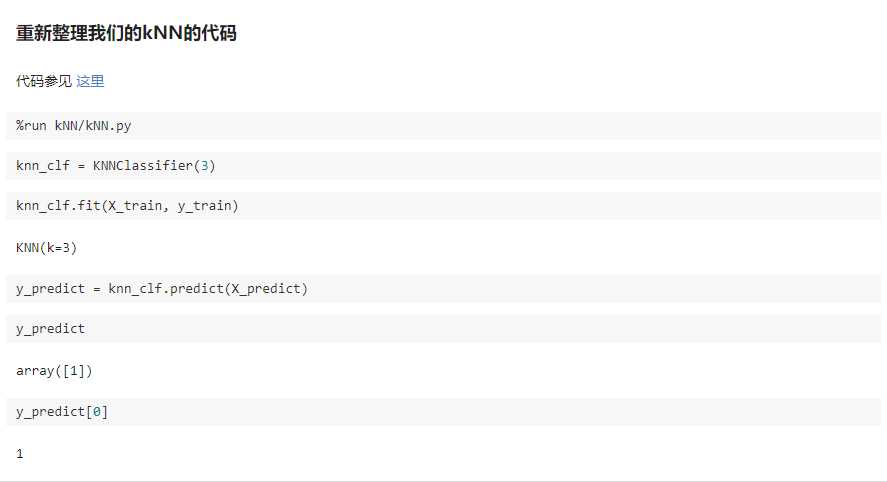
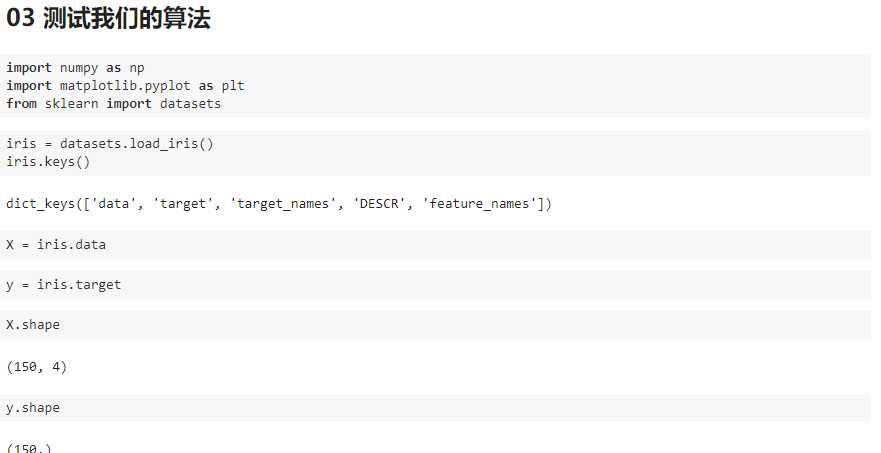
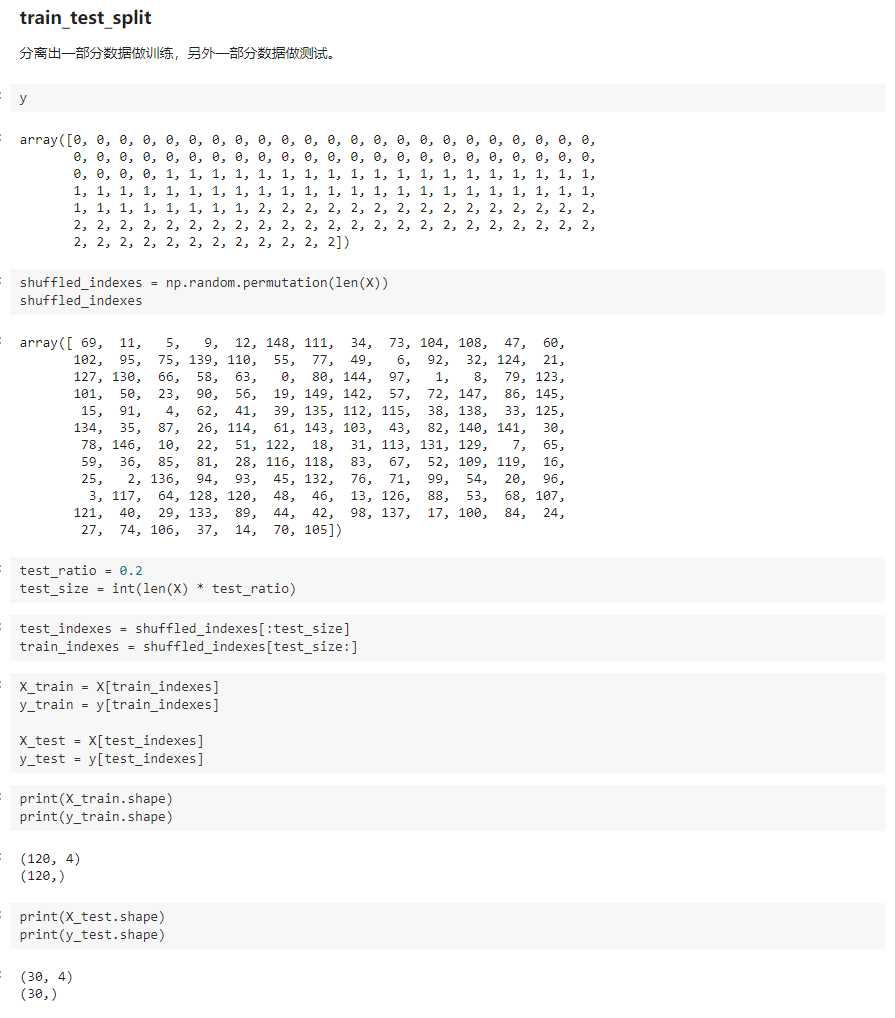
三、训练数据集、测试数据集
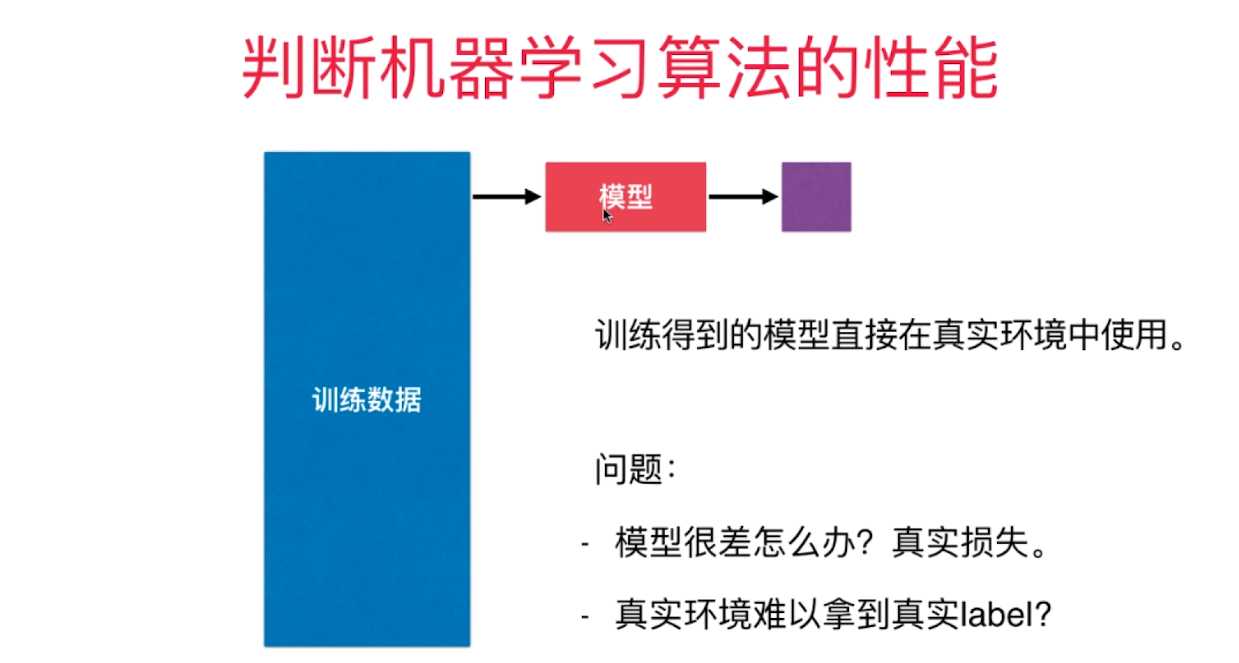
判断机器学习算法的性能
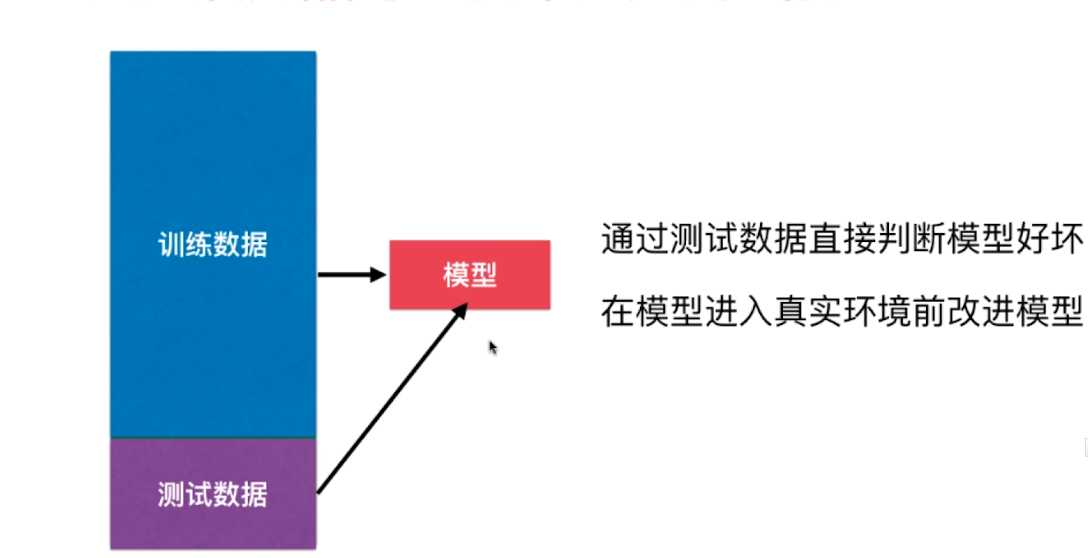
playML/KNN.py
import numpy as np from math import sqrt from collections import Counter class KNNClassifier: def __init__(self, k): """初始化kNN分类器""" assert k >= 1, "k must be valid" self.k = k self._X_train = None self._y_train = None def fit(self, X_train, y_train): """根据训练数据集X_train和y_train训练kNN分类器""" assert X_train.shape[0] == y_train.shape[0], "the size of X_train must be equal to the size of y_train" assert self.k <= X_train.shape[0], "the size of X_train must be at least k." self._X_train = X_train self._y_train = y_train return self def predict(self, X_predict): """给定待预测数据集X_predict,返回表示X_predict的结果向量""" assert self._X_train is not None and self._y_train is not None, "must fit before predict!" assert X_predict.shape[1] == self._X_train.shape[1], "the feature number of X_predict must be equal to X_train" y_predict = [self._predict(x) for x in X_predict] return np.array(y_predict) def _predict(self, x): """给定单个待预测数据x,返回x的预测结果值""" assert x.shape[0] == self._X_train.shape[1], "the feature number of x must be equal to X_train" distances = [sqrt(np.sum((x_train - x) ** 2)) for x_train in self._X_train] nearest = np.argsort(distances) topK_y = [self._y_train[i] for i in nearest[:self.k]] votes = Counter(topK_y) return votes.most_common(1)[0][0] def __repr__(self): return "KNN(k=%d)" % self.k
playML/model_selection.py
import numpy as np def train_test_split(X, y, test_ratio=0.2, seed=None): """将数据 X 和 y 按照test_ratio分割成X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test""" assert X.shape[0] == y.shape[0], "the size of X must be equal to the size of y" assert 0.0 <= test_ratio <= 1.0, "test_ration must be valid" if seed: np.random.seed(seed) shuffled_indexes = np.random.permutation(len(X)) test_size = int(len(X) * test_ratio) test_indexes = shuffled_indexes[:test_size] train_indexes = shuffled_indexes[test_size:] X_train = X[train_indexes] y_train = y[train_indexes] X_test = X[test_indexes] y_test = y[test_indexes] return X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test
playML/__init__.py

以上是关于用KNN算法判断知识掌握程度高低的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章