Redis 设计与实现(第十三章) -- 服务器
Posted qiezijiajia
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Redis 设计与实现(第十三章) -- 服务器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
概述
Redis服务器负责与客户端建立网络连接,之前的数据结构部分已经看过了,本章主要从下面三个方面讲解。
1.服务器执行命令的过程
2.serverCron函数的执行
3.服务器的初始化
服务器执行命令的过程
一个客户端请求命令的基本过程大致如下:
1.客户端发送请求命令给服务器,比如set key value;
2.服务器端接受命令并处理,在数据库中进行设置操作,并返回ok;
3.客户端接受服务器返回的ok,并将这个回复打印给用户看。
接下来会根据这个大致的流程来讲一些细节的处理:
1.发送命令请求:
当用户在客户端键入一个命令后,客户端会将这个命令转为相应的协议格式,并通过套接字,将命令请求的协议格式发送给服务器;
2.读取命令请求:
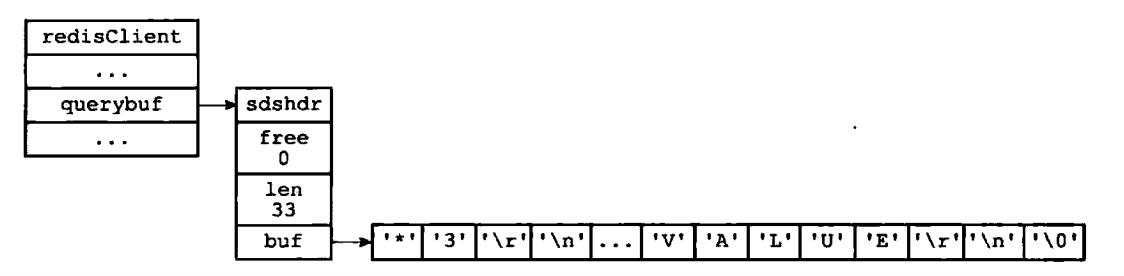
服务器接受到套接字发送来的协议请求后,将其保存在客户端状态的输入缓冲区中(之前的看过redisServer和client的数据结构可以知道),如下;
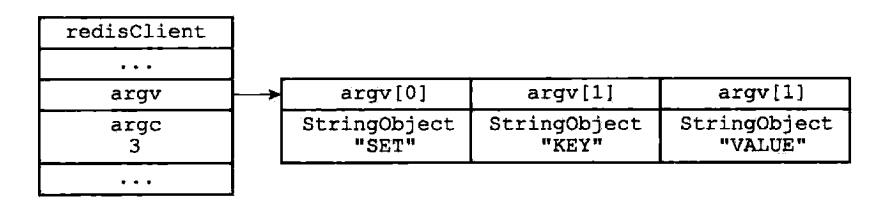
对输入缓冲区的协议格式进行解析,提前命令请求中的命令参数,以及参数的个数,分别将参数和参数个数保存到客户端状态的argv和argc属性中,如下;
调用命令执行器,执行客户端指定的命令。
命令执行器的执行
查找命令实现
命令执行器首先查找argv[0]的参数,并在命令表中查找所指定的指令,并将指令保存到客户端状态的cmd属性中。
命令表是一个字典,键为一个命令名字,比如set、get、del等,而字典的值则是一个redisCommand的数据结构,每个RedisCommand记录一个命令的实现信息,数据结构如下:
struct redisCommand { char *name; //命令的名字,比如set、get等 redisCommandProc *proc; //执行命令的实现函数 int arity; //命令参数的个数,用于校验命令请求的格式是否正确 char *sflags; /* Flags as string representation, one char per flag. ,记录命令的属性,比如是读还是写等*/ int flags; /* The actual flags, obtained from the \'sflags\' field.,对sflags的分析得出的二进制,服务器自动生成 */ /* Use a function to determine keys arguments in a command line. * Used for Redis Cluster redirect. */ redisGetKeysProc *getkeys_proc; // /* What keys should be loaded in background when calling this command? */ int firstkey; /* The first argument that\'s a key (0 = no keys) */ int lastkey; /* The last argument that\'s a key */ int keystep; /* The step between first and last key */ long long microseconds, calls; //服务器执行的总时长,和执行了多少次 };
下图分别用set和get展示了RedisCommand的结构:
set命令表示,name为set;参数arity未-3,表示接受三个或三个以上的参数;命令标识为\'wm\',表示这是一个写入命令,并且在执行前要先对服务器占用内存检查,因为这个命令可能占用大量内存。(命令的大小写不限制)
查找到命令表后,将redisClient中的cmd指针指向redisCommand对应的结构。
执行预备操作
服务器通过上述步骤,已经将执行命令所需函数、参数、参数个数都收集到了,在真正执行前,还需要执行一个进行一些预备操作,才能保证命令被正确执行,这些操作包括:
1.判断cmd的执行是否指向null,如果指向null,则说明命令不存在,这时给客户端返回错误信息;
2.根据artiy属性的值,判断argc中的参数个数是否正确,如果不正确,则返回错误;
3.检测客户端是否已经通过了认证,未通过认证的只能指向auth命令,如果未通过认证执行auth以为的命令会返回给客户端错误信息;
4.如果服务器打开了maxmemory命令,在命令执行前,先检查服务器的内存占用情况,并在有需要时进行回收,如果回收失败,则给客户端返回错误信息;
5.如果服务器上一次执行bgsave命令错误,并且服务器打开了stop-write-on-bgsave-error功能,如果此时执行的命令是写命令,那么则会返回错误;
6.如果当前客户端正在用subscribe命令订阅频道,或者正则用psubscribe命令订阅模式,那么服务器只会执行订阅有关的四个命令(subscribe,psubscribe,unsubscribe,punsubscribe),其他命令会被拒绝;
7.如果服务器正在执行数据载入,那么客户端发送的命令必须带有1标识(比如info,shutdown,publish等等)才能被服务器执行,其他命令会被拒绝;
8.如果服务器正在执行lua脚本而超时进入阻塞状态,那么服务器只会执行客户端发来的shutdown nosave和script kill命令,其他命令都会被拒绝;
9.如果客户端正在执行事务,那么服务器只会执行客户端发来的事务命令,exec,discard,multi,watch四个命令,其他命令都会被放入事务队列中;
10.如果服务器打开了监视器功能,那么服务器会将就要将执行的命令及参数发送给监视器。
上述步骤都完成后,就开始执行命令了(这里这讲了单机模式的,集群模式下还会有更多一些步骤)。
下面是commandProc的源码,上述步骤的判断与集群模式的处理都在里面:

/* If this function gets called we already read a whole * command, arguments are in the client argv/argc fields. * processCommand() execute the command or prepare the * server for a bulk read from the client. * * If 1 is returned the client is still alive and valid and * other operations can be performed by the caller. Otherwise * if 0 is returned the client was destroyed (i.e. after QUIT). */ int processCommand(redisClient *c) { /* The QUIT command is handled separately. Normal command procs will * go through checking for replication and QUIT will cause trouble * when FORCE_REPLICATION is enabled and would be implemented in * a regular command proc. */ if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[0]->ptr,"quit")) { addReply(c,shared.ok); c->flags |= REDIS_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY; return REDIS_ERR; } /* Now lookup the command and check ASAP about trivial error conditions * such as wrong arity, bad command name and so forth. */ c->cmd = c->lastcmd = lookupCommand(c->argv[0]->ptr); if (!c->cmd) { flagTransaction(c); addReplyErrorFormat(c,"unknown command \'%s\'", (char*)c->argv[0]->ptr); return REDIS_OK; } else if ((c->cmd->arity > 0 && c->cmd->arity != c->argc) || (c->argc < -c->cmd->arity)) { flagTransaction(c); addReplyErrorFormat(c,"wrong number of arguments for \'%s\' command", c->cmd->name); return REDIS_OK; } /* Check if the user is authenticated */ if (server.requirepass && !c->authenticated && c->cmd->proc != authCommand) { flagTransaction(c); addReply(c,shared.noautherr); return REDIS_OK; } /* If cluster is enabled perform the cluster redirection here. * However we don\'t perform the redirection if: * 1) The sender of this command is our master. * 2) The command has no key arguments. */ if (server.cluster_enabled && !(c->flags & REDIS_MASTER) && !(c->flags & REDIS_LUA_CLIENT && server.lua_caller->flags & REDIS_MASTER) && !(c->cmd->getkeys_proc == NULL && c->cmd->firstkey == 0)) { int hashslot; if (server.cluster->state != REDIS_CLUSTER_OK) { flagTransaction(c); clusterRedirectClient(c,NULL,0,REDIS_CLUSTER_REDIR_DOWN_STATE); return REDIS_OK; } else { int error_code; clusterNode *n = getNodeByQuery(c,c->cmd,c->argv,c->argc,&hashslot,&error_code); if (n == NULL || n != server.cluster->myself) { flagTransaction(c); clusterRedirectClient(c,n,hashslot,error_code); return REDIS_OK; } } } /* Handle the maxmemory directive. * * First we try to free some memory if possible (if there are volatile * keys in the dataset). If there are not the only thing we can do * is returning an error. */ if (server.maxmemory) { int retval = freeMemoryIfNeeded(); /* freeMemoryIfNeeded may flush slave output buffers. This may result * into a slave, that may be the active client, to be freed. */ if (server.current_client == NULL) return REDIS_ERR; /* It was impossible to free enough memory, and the command the client * is trying to execute is denied during OOM conditions? Error. */ if ((c->cmd->flags & REDIS_CMD_DENYOOM) && retval == REDIS_ERR) { flagTransaction(c); addReply(c, shared.oomerr); return REDIS_OK; } } /* Don\'t accept write commands if there are problems persisting on disk * and if this is a master instance. */ if (((server.stop_writes_on_bgsave_err && server.saveparamslen > 0 && server.lastbgsave_status == REDIS_ERR) || server.aof_last_write_status == REDIS_ERR) && server.masterhost == NULL && (c->cmd->flags & REDIS_CMD_WRITE || c->cmd->proc == pingCommand)) { flagTransaction(c); if (server.aof_last_write_status == REDIS_OK) addReply(c, shared.bgsaveerr); else addReplySds(c, sdscatprintf(sdsempty(), "-MISCONF Errors writing to the AOF file: %s\\r\\n", strerror(server.aof_last_write_errno))); return REDIS_OK; } /* Don\'t accept write commands if there are not enough good slaves and * user configured the min-slaves-to-write option. */ if (server.masterhost == NULL && server.repl_min_slaves_to_write && server.repl_min_slaves_max_lag && c->cmd->flags & REDIS_CMD_WRITE && server.repl_good_slaves_count < server.repl_min_slaves_to_write) { flagTransaction(c); addReply(c, shared.noreplicaserr); return REDIS_OK; } /* Don\'t accept write commands if this is a read only slave. But * accept write commands if this is our master. */ if (server.masterhost && server.repl_slave_ro && !(c->flags & REDIS_MASTER) && c->cmd->flags & REDIS_CMD_WRITE) { addReply(c, shared.roslaveerr); return REDIS_OK; } /* Only allow SUBSCRIBE and UNSUBSCRIBE in the context of Pub/Sub */ if (c->flags & REDIS_PUBSUB && c->cmd->proc != pingCommand && c->cmd->proc != subscribeCommand && c->cmd->proc != unsubscribeCommand && c->cmd->proc != psubscribeCommand && c->cmd->proc != punsubscribeCommand) { addReplyError(c,"only (P)SUBSCRIBE / (P)UNSUBSCRIBE / PING / QUIT allowed in this context"); return REDIS_OK; } /* Only allow INFO and SLAVEOF when slave-serve-stale-data is no and * we are a slave with a broken link with master. */ if (server.masterhost && server.repl_state != REDIS_REPL_CONNECTED && server.repl_serve_stale_data == 0 && !(c->cmd->flags & REDIS_CMD_STALE)) { flagTransaction(c); addReply(c, shared.masterdownerr); return REDIS_OK; } /* Loading DB? Return an error if the command has not the * REDIS_CMD_LOADING flag. */ if (server.loading && !(c->cmd->flags & REDIS_CMD_LOADING)) { addReply(c, shared.loadingerr); return REDIS_OK; } /* Lua script too slow? Only allow a limited number of commands. */ if (server.lua_timedout && c->cmd->proc != authCommand && c->cmd->proc != replconfCommand && !(c->cmd->proc == shutdownCommand && c->argc == 2 && tolower(((char*)c->argv[1]->ptr)[0]) == \'n\') && !(c->cmd->proc == scriptCommand && c->argc == 2 && tolower(((char*)c->argv[1]->ptr)[0]) == \'k\')) { flagTransaction(c); addReply(c, shared.slowscripterr); return REDIS_OK; } /* Exec the command */ if (c->flags & REDIS_MULTI && c->cmd->proc != execCommand && c->cmd->proc != discardCommand && c->cmd->proc != multiCommand && c->cmd->proc != watchCommand) { queueMultiCommand(c); addReply(c,shared.queued); } else { call(c,REDIS_CALL_FULL); c->woff = server.master_repl_offset; if (listLength(server.ready_keys)) handleClientsBlockedOnLists(); } return REDIS_OK; }
命令的执行
服务器将要执行的命令保存到了客户端状态的cmd属性中,且命令及参数个数保存到了argv和argc属性中,所以服务器执行的时候,只需要调用函数即可:
c->cmd->proc(c); //proc函数只需要c指针作为参数即可获取到所需要的数据,如下:

执行成功后,产生相应的回复,并将回复的内容放入到客户端状态的输出缓冲区中(buf和reply属性),之后函数还会为客户端的套接字关联回复处理器,回复处理器将命令返回给客户端,当执行set命令后,会返回一个ok,如下:
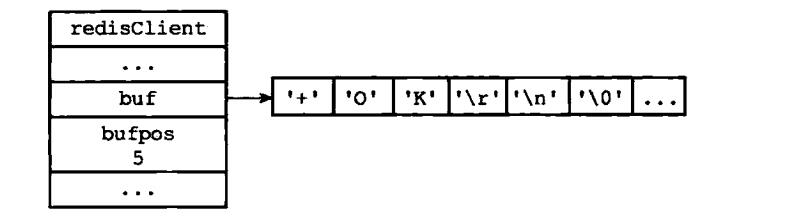
执行后续工作
在执行完命令后,服务器还需要一些后续工作:
1.如果服务器开启了慢查询日志,那么服务器会检查是否需要为刚才执行的命令产生一条慢查询日志;
2.根据刚才命令执行的耗时,更新被执行命令的rediscommand属性中的milliseconds属性,并将calls属性值+1;
3.如果服务器开启了AOF持久化,会将刚才执行的命令写入到AOF缓冲区;
4.如果有其他从服务器正在复制当前这个服务器,服务器会将刚才这个命令传播给所有从服务器;
到此,服务器的执行完毕,下面是call函数的实现:
/* Call() is the core of Redis execution of a command */ void call(redisClient *c, int flags) { long long dirty, start, duration; int client_old_flags = c->flags; /* Sent the command to clients in MONITOR mode, only if the commands are * not generated from reading an AOF. */ if (listLength(server.monitors) && !server.loading && !(c->cmd->flags & (REDIS_CMD_SKIP_MONITOR|REDIS_CMD_ADMIN))) { replicationFeedMonitors(c,server.monitors,c->db->id,c->argv,c->argc); } /* Call the command. */ c->flags &= ~(REDIS_FORCE_AOF|REDIS_FORCE_REPL); redisOpArrayInit(&server.also_propagate); dirty = server.dirty; start = ustime(); c->cmd->proc(c); duration = ustime()-start; dirty = server.dirty-dirty; if (dirty < 0) dirty = 0; /* When EVAL is called loading the AOF we don\'t want commands called * from Lua to go into the slowlog or to populate statistics. */ if (server.loading && c->flags & REDIS_LUA_CLIENT) flags &= ~(REDIS_CALL_SLOWLOG | REDIS_CALL_STATS); /* If the caller is Lua, we want to force the EVAL caller to propagate * the script if the command flag or client flag are forcing the * propagation. */ if (c->flags & REDIS_LUA_CLIENT && server.lua_caller) { if (c->flags & REDIS_FORCE_REPL) server.lua_caller->flags |= REDIS_FORCE_REPL; if (c->flags & REDIS_FORCE_AOF) server.lua_caller->flags |= REDIS_FORCE_AOF; } /* Log the command into the Slow log if needed, and populate the * per-command statistics that we show in INFO commandstats. */ if (flags & REDIS_CALL_SLOWLOG && c->cmd->proc != execCommand) { char *latency_event = (c->cmd->flags & REDIS_CMD_FAST) ? "fast-command" : "command"; latencyAddSampleIfNeeded(latency_event,duration/1000); slowlogPushEntryIfNeeded(c->argv,c->argc,duration); } if (flags & REDIS_CALL_STATS) { c->cmd->microseconds += duration; c->cmd->calls++; } /* Propagate the command into the AOF and replication link */ if (flags & REDIS_CALL_PROPAGATE) { int flags = REDIS_PROPAGATE_NONE; if (c->flags & REDIS_FORCE_REPL) flags |= REDIS_PROPAGATE_REPL; if (c->flags & REDIS_FORCE_AOF) flags |= REDIS_PROPAGATE_AOF; if (dirty) flags |= (REDIS_PROPAGATE_REPL | REDIS_PROPAGATE_AOF); if (flags != REDIS_PROPAGATE_NONE) propagate(c->cmd,c->db->id,c->argv,c->argc,flags); } /* Restore the old FORCE_AOF/REPL flags, since call can be executed * recursively. */ c->flags &= ~(REDIS_FORCE_AOF|REDIS_FORCE_REPL); c->flags |= client_old_flags & (REDIS_FORCE_AOF|REDIS_FORCE_REPL); /* Handle the alsoPropagate() API to handle commands that want to propagate * multiple separated commands. */ if (server.also_propagate.numops) { int j; redisOp *rop; for (j = 0; j < server.also_propagate.numops; j++) { rop = &server.also_propagate.ops[j]; propagate(rop->cmd, rop->dbid, rop->argv, rop->argc, rop->target); } redisOpArrayFree(&server.also_propagate); } server.stat_numcommands++; }
serverCron函数的执行
serverCron函数默认100ms执行一次,负责服务器资源的管理。主要操作如下:
1.更新服务器时间缓存
Redis服务器中有不少功能都需要调用系统时间,为了减少系统时间的调用次数,服务器状态中的unixtime和mstime属性保存了系统时间,即系统时间缓存;
time_t unixtime; /* Unix time sampled every cron cycle.秒级 */ long long mstime; /* Like \'unixtime\' but with milliseconds resolution. 毫秒级*/
因为serverCron每100毫秒执行一次,所以这两个属性记录的时间精确度并不高:
- 服务器只会在打印日志、更新服务器的LRU时钟、决定是否执行持久化、计算服务器上线时间这类对精确度要求不高的操作,才会调用缓存属性;
- 为键设置过期时间、为慢查询添加日志这些高精确度的计算上,会再次调用执行系统调用获取精确的时间。
/* Update the time cache. */ updateCachedTime(); void updateCachedTime(void) { server.unixtime = time(NULL); server.mstime = mstime(); }
2.更新LRU时钟
redisServer{
unsigned lruclock:REDIS_LRU_BITS; /* Clock for LRU eviction */
lruclock也是一个服务器时间缓存。默认10s更新一次,用于计算键的空转时长。
每个redis对象都有一个lru属性,记录了对象最后一次被命令访问的时间
typedef struct redisObject { unsigned type:4; unsigned encoding:4; unsigned lru:REDIS_LRU_BITS; /* lru time (relative to server.lruclock),需要与server的lruclock计算 */ int refcount; void *ptr; } robj;
服务器在计算空转时长,就将server的lruclock减去对象的lru,得到的值就是对象的空转时长。通过info server命令可以看到服务器的lruclock值
127.0.0.1:6379> info server
# Server
redis_version:3.2.1
hz:10
lru_clock:14359453
/* We have just REDIS_LRU_BITS bits per object for LRU information. * So we use an (eventually wrapping) LRU clock. * * Note that even if the counter wraps it\'s not a big problem, * everything will still work but some object will appear younger * to Redis. However for this to happen a given object should never be * touched for all the time needed to the counter to wrap, which is * not likely. * * Note that you can change the resolution altering the * REDIS_LRU_CLOCK_RESOLUTION define. */ server.lruclock = getLRUClock();
3.更新服务器每秒执行命令数
serverCron函数中的执行时,有个函数以100毫秒频率执行,采用抽样计算方式计算最近1s内服务器处理的命令请求数量,通过info stats命令可以查看到:
127.0.0.1:6379> info stats
# Stats
total_connections_received:8021544
total_commands_processed:89091769
instantaneous_ops_per_sec:7
run_with_period(100) { trackInstantaneousMetric(REDIS_METRIC_COMMAND,server.stat_numcommands); trackInstantaneousMetric(REDIS_METRIC_NET_INPUT, server.stat_net_input_bytes); trackInstantaneousMetric(REDIS_METRIC_NET_OUTPUT, server.stat_net_output_bytes); }
4.更新服务器的内存使用峰值
如果当前使用值大于峰值则更新
通过info memory可以看到峰值
127.0.0.1:6379> info memory
# Memory
used_memory:126646712
used_memory_human:120.78M
used_memory_rss:149495808
used_memory_rss_human:142.57M
used_memory_peak:302379288
used_memory_peak_human:288.37M
/* Record the max memory used since the server was started. */ if (zmalloc_used_memory() > server.stat_peak_memory) server.stat_peak_memory = zmalloc_used_memory();
5.处理sigterm信号
在启动服务器时,Redis会为服务器进程的SIGTERM信号关联sigshutdownHandler函数,这个函数负责在服务器接受到sigterm信号时,打开服务器的shutdown_asap标识:
每次serverCron执行时,会判断shutdown_asap属性值,决定是否需要关闭服务器。
struct redisServer { unsigned lruclock:REDIS_LRU_BITS; /* Clock for LRU eviction */ int shutdown_asap; /* SHUTDOWN needed ASAP */
static void sigShutdownHandler(int sig) { char *msg; switch (sig) { case SIGINT: msg = "Received SIGINT scheduling shutdown..."; break; case SIGTERM: msg = "Received SIGTERM scheduling shutdown..."; break; default: msg = "Received shutdown signal, scheduling shutdown..."; }; /* SIGINT is often delivered via Ctrl+C in an interactive session. * If we receive the signal the second time, we interpret this as * the user really wanting to quit ASAP without waiting to persist * on disk. */ if (server.shutdown_asap && sig == SIGINT) { redisLogFromHandler(REDIS_WARNING, "You insist... exiting now."); rdbRemoveTempFile(getpid()); exit(1); /* Exit with an error since this was not a clean shutdown. */ } else if (server.loading) { exit(0); } redisLogFromHandler(REDIS_WARNING, msg); server.shutdown_asap = 1;
/* We received a SIGTERM, shutting down here in a safe way, as it is * not ok doing so inside the signal handler. */ if (server.shutdown_asap) { if (prepareForShutdown(0) == REDIS_OK) exit(0); redisLog(REDIS_WARNING,"SIGTERM received but errors trying to shut down the server, check the logs for more information"); server.shutdown_asap = 0; }
6.管理客户端资源
serverCron函数会调用clientCron函数,client函数会对一定数量的客户端做以下检查:
如果客户端与服务器端连接已经超时,那么程序释放这个客户端;
如果客户端在上一次命令执行之后,输入缓冲区超过了一定长度,那么程序会释放客户端的缓冲区,并重新创建一块默认大小的输入缓冲区。
void clientsCron(void) { /* Make sure to process at least numclients/server.hz of clients * per call. Since this function is called server.hz times per second * we are sure that in the worst case we process all the clients in 1 * second. */ int numclients = listLength(server.clients); int iterations = numclients/server.hz; mstime_t now = mstime(); /* Process at least a few clients while we are at it, even if we need * to process less than CLIENTS_CRON_MIN_ITERATIONS to meet our contract * of processing each client once per second. */ if (iterations < CLIENTS_CRON_MIN_ITERATIONS) iterations = (numclients < CLIENTS_CRON_MIN_ITERATIONS) ? numclients : CLIENTS_CRON_MIN_ITERATIONS; while(listLength(server.clients) && iterations--) { redisClient *c; listNode *head; /* Rotate the list, take the current head, process. * This way if the client must be removed from the list it\'s the * first element and we don\'t incur into O(N) computation. */ listRotate(server.clients); head = listFirst(server.clients); c = listNodeValue(head); /* The following functions do different service checks on the client. * The protocol is that they return non-zero if the client was * terminated. */ if (clientsCronHandleTimeout(c,now)) continue; //释放超时连接 if (clientsCronResizeQueryBuffer(c)) continue; //resize缓冲区 } }
7.管理数据库资源
serverCron每次执行都会调用databasesCron函数,这个函数会对数据库中的一部分数据进行检查,释放过期键,对字典进行收缩操作;
void databasesCron(void) { /* Expire keys by random sampling. Not required for slaves * as master will synthesize DELs for us. */ if (server.active_expire_enabled && server.masterhost == NULL) activeExpireCycle(ACTIVE_EXPIRE_CYCLE_SLOW); /* Perform hash tables rehashing if needed, but only if there are no * other processes saving the DB on disk. Otherwise rehashing is bad * as will cause a lot of copy-on-write of memory pages. */ if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_child_pid == -1) { /* We use global counters so if we stop the computation at a given * DB we\'ll be able to start from the successive in the next * cron loop iteration. */ static unsigned int resize_db = 0; static unsigned int rehash_db = 0; int dbs_per_call = REDIS_DBCRON_DBS_PER_CALL; int j; /* Don\'t test more DBs than we have. */ if (dbs_per_call > server.dbnum) dbs_per_call = server.dbnum; /* Resize */ for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) { tryResizeHashTables(resize_db % server.dbnum); resize_db++; } /* Rehash */ if (server.activerehashing) { for (j = 0; j < dbs_per_call; j++) { int work_done = incrementallyRehash(rehash_db % server.dbnum); rehash_db++; if (work_done) { /* If the function did some work, stop here, we\'ll do * more at the next cron loop. */ break; } } } } }
8.执行被延时的bgrewriteaof
在执行bgsave命令期间,如果客户端发送bgrewriteaof命令,那么服务器会将bgrewriteaof命令延迟到bgsave命令后执行。
服务器的aof_rewrite_scheduled属性记录了是否为延时,如果值为1,代表bgrewriteaof被延时了。
int aof_rewrite_scheduled; /* Rewrite once BGSAVE terminates. */
/* Start a scheduled AOF rewrite if this was requested by the user while * a BGSAVE was in progress. */ if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_rewrite_scheduled) { rewriteAppendOnlyFileBackground(); }
9.检查持久化操作的运行状态
服务器用下面两个属性分别记录了bgsave和bgrewriteaof命令的子进程ID,这两个属性也可以查询这两个命令是否正在执行,如果id为-1,说明没有在执行;
pid_t rdb_child_pid; /* PID of RDB saving child */
pid_t aof_child_pid; /* PID if rewriting process */
每次serverCron函数执行,都会检查rdb_child_pid和aof_child_pid的值,如果有一个为-1,程序就会执行一次wait3函数,检查子进程是否有信号发送来服务器进程:
- 如果有,表示新的RBD文件已经生产完成或AOF文件已经重写完毕,服务器需要进行相应的后续操作,比如用新的RDB文件替换现有的RDB文件,或者用重写后的AOF文件替换现有的AOF文件;
- 如果没有,表示持久化操作没有完成,程序不做动作。
如果两个值均为-1,表示服务器没有在执行持久化操作,那么执行以下步骤:
- 检查bgrewriteaof是否延时了,如果有的话,执行新的bgrewriteaof操作;
- 检查服务器自动保存的条件是否满足,如果满足,并且服务器没有在执行其他持久化操作,那么服务器开始一次新的bgsave操作(条件1可能会引起一次持久化,所以在这个检查中,程序会再次确认服务器已经在执行持久化了。);
- 检查服务器自身设置的aof重新条件是否满足,如果条件满足,并且服务器没有在执行其他持久化操作,那么服务器开始一次新的bgrewriteaof操作。
下面图展示了这一过程:
/* Check if a background saving or AOF rewrite in progress terminated. */ if (server.rdb_child_pid != -1 || server.aof_child_pid != -1) { int statloc; pid_t pid; if ((pid = wait3(&statloc,WNOHANG,NULL)) != 0) { int exitcode = WEXITSTATUS(statloc); int bysignal = 0; if (WIFSIGNALED(statloc)) bysignal = WTERMSIG(statloc); if (pid == -1) { redisLog(LOG_WARNING,"wait3() returned an error: %s. " "rdb_child_pid = %d, aof_child_pid = %d", strerror(errno), (int) server.rdb_child_pid, (int) server.aof_child_pid); } else if (pid == server.rdb_child_pid) { backgroundSaveDoneHandler(exitcode,bysignal); } else if (pid == server.aof_child_pid) { backgroundRewriteDoneHandler(exitcode,bysignal); } else { redisLog(REDIS_WARNING, "Warning, detected child with unmatched pid: %ld", (long)pid); } updateDictResizePolicy(); } } else { /* If there is not a background saving/rewrite in progress check if * we have to save/rewrite now */ for (j = 0; j < server.saveparamslen; j++) { struct saveparam *sp = server.saveparams+j; /* Save if we reached the given amount of changes, * the given amount of seconds, and if the latest bgsave was * successful or if, in case of an error, at least * REDIS_BGSAVE_RETRY_DELAY seconds already elapsed. */ if (server.dirty >= sp->changes && server.unixtime-server.lastsave > sp->seconds &&以上是关于Redis 设计与实现(第十三章) -- 服务器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
