Android 实现定时任务的五种方式
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android 实现定时任务的五种方式相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 1、普通线程sleep的方式,可用于一般的轮询Pollingnew Thread(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
while (true)
//todo
try
Thread.sleep(iDelay);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
).start();
优点:非常简单的实现,逻辑清晰明了,也是最常见的写法
缺点:在sleep结束后,并不能保证竞争到cpu资源,这也就导致了下次执行时间必定>=iDelay,存在时间精度问题
2、Timer定时器
//Timer + TimerTask结合的方法
private final Timer timer = new Timer();
private TimerTask timerTask = new TimerTask()
@Override
public void run()
//todo
;
启动定时器方法:
timer.schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period)
立即执行
timer.schedule(timerTask, 0, 1000); //立刻执行,间隔1秒循环执行
延时执行
timer.schedule(timerTask, 2000, 1000); //等待2秒后再执行,间隔1秒循环执行
关闭定时器方法:timer.cancel();
优点:纯正的定时任务,纯java SDK,单独线程执行,比较安全,而且还可以在运行过程中取消执行
缺点:基于单线程执行,多个任务之间会相互影响,多个任务的执行是串行的,性能较低,而且timer也无法保证时间精确度,是因为手机休眠的时候,无法唤醒cpu,不适合后台任务的定时
3、ScheduledExecutorService
private Runnable runnable2 = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
//todo
;
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(runnable2, 0, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
关于scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit) 方法说明:
command:需要执行的线程
initialDelay:第一次执行需要延时的时间,如若立即执行,则initialDelay = 0
period:固定频率,周期性执行的时间
unit:时间单位,常用的有MILLISECONDS、SECONDS和MINUTES等,需要注意的是,这个单位会影响initialDelay和period,如果unit = MILLISECONDS,则initialDelay和period传入的是毫秒,如果unit = SECONDS,则initialDelay和period传入的是秒
补充一下: 还有一个方法跟上面的很相似:scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit),这个也是带延迟时间的调度,并且也是循环执行,唯一的不同就是固定延迟时间循环执行,上面的是固定频率的循环执行。那这两者的区别?
举例子:
使用scheduleAtFixedRate,任务初始延迟3秒,任务执行3秒,任务执行间隔为5秒:
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
Log.e(TAG, "schedule just start! time =" + simpleDateFormat.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
SystemClock.sleep(3000L);
Log.e(TAG, "runnable just do it! time =" + simpleDateFormat.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
, 3, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
执行结果截图:
使用scheduleWithFixedDelay,任务初始延迟3秒,任务执行3秒,任务执行延迟为5秒:
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
Log.e(TAG, "schedule just start! time =" + simpleDateFormat.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
SystemClock.sleep(3000L);
Log.e(TAG, "runnable just do it! time =" + simpleDateFormat.format(System.currentTimeMillis()));
, 3, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
执行结果截图:
从这两者的运行结果就可以看到区别了:scheduleAtFixedRate是相对于任务执行的开始时间,而scheduleWithFixedDelay是相对于任务执行的结束时间。
优点:ScheduledExecutorService是一个线程池,其内部使用的延迟队列,本身就是基于等待/唤醒机制实现的,所以CPU并不会一直繁忙。解决了Timer&TimerTask存在的问题,多任务处理时效率高
缺点:取消时需要打断线程池的运行,而且和外界的通信不太好处理
4、使用Handler中的postDelayed方法
private Handler mHandler = new Handler();
private Runnable runnable = new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
//todo
mHandler.postDelayed(this, iDelay);
;
mHandler.post(runnable); //立即执行
mHandler.postDelayed(runnable, iDelay); //延时执行
mHandler.removeCallbacks(runnable); //取消执行
优点:比较简单的android实现,适用UI线程
缺点:没想到,手动捂脸。。。。我估计是使用不当会造成内存泄露吧
5、Service + AlarmManger + BroadcastReceiver
定时任务的五种创建方式,你都会么?

作者:兮家小二
blog.csdn.net/qq_41463655/article/details/100839629
Quartz表达式生成地址:http://cron.qqe2.com/
支持生成定时任务表达式和反解析,使用Quartz表达式的定时任务如下
xxl-job
springboot 的 @Scheduled
Quartz 框架
一、job 定时任务的五种创建方式
1、使用线程创建 job 定时任务
/**
* TODO 使用线程创建 job 定时任务
* @author 王松
*/
public class JobThread {
public static class Demo01 {
static long count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
count++;
System.out.println(count);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
};
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.start();
}
}
}
2、使用 TimerTask 创建job定时任务
/**
* TODO 使用 TimerTask 创建job定时任务
* @author 王松
*/
public class JobTimerTask {
static long count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
TimerTask timerTask = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
count++;
System.out.println(count);
}
};
//创建timer对象设置间隔时间
Timer timer = new Timer();
// 间隔天数
long delay = 0;
// 间隔毫秒数
long period = 1000;
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(timerTask, delay, period);
}
}
3、使用线程池创建 job定时任务
/**
* TODO 使用线程池创建 job定时任务
* @author 王松
*/
public class JobScheduledExecutorService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// task to run goes here
System.out.println("Hello !!");
}
};
ScheduledExecutorService service = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
// 第二个参数为首次执行的延时时间,第三个参数为定时执行的间隔时间
service.scheduleAtFixedRate(runnable, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}
4.Quartz 框架
1.引入maven依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- quartz -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.quartz-scheduler</groupId>
<artifactId>quartz</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.quartz-scheduler</groupId>
<artifactId>quartz-jobs</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.任务调度类
public class MyJob implements Job {
@Override
public void execute(JobExecutionContext context) throws JobExecutionException {
System.out.println("quartz MyJob date:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
3.启动类
public class JobQuartz {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SchedulerException {
//1.创建Scheduler的工厂
SchedulerFactory sf = new StdSchedulerFactory();
//2.从工厂中获取调度器实例
Scheduler scheduler = sf.getScheduler();
//3.创建JobDetail,
JobDetail jb = JobBuilder.newJob(MyJob.class)
//job的描述
.withDescription("this is a ram job")
//job 的name和group
.withIdentity("ramJob", "ramGroup")
.build();
//任务运行的时间,SimpleSchedle类型触发器有效,3秒后启动任务
long time= System.currentTimeMillis() + 3*1000L;
Date statTime = new Date(time);
//4.创建Trigger
//使用SimpleScheduleBuilder或者CronScheduleBuilder
Trigger t = TriggerBuilder.newTrigger()
.withDescription("")
.withIdentity("ramTrigger", "ramTriggerGroup")
//.withSchedule(SimpleScheduleBuilder.simpleSchedule())
//默认当前时间启动
.startAt(statTime)
//两秒执行一次,Quartz表达式,支持各种牛逼表达式
.withSchedule(CronScheduleBuilder.cronSchedule("0/2 * * * * ?"))
.build();
//5.注册任务和定时器
scheduler.scheduleJob(jb, t);
//6.启动 调度器
scheduler.start();
}
5. springboot 的 @Scheduled 注解
@Component
@Configuration //1.主要用于标记配置类,兼备Component的效果。
@EnableScheduling // 2.开启定时任务
public class SaticScheduleTask {
@Scheduled(cron = "0/5 * * * * ?") //3.添加定时任务
//@Scheduled(fixedRate=5000) //或直接指定时间间隔,例如:5秒
private void configureTasks() {
System.err.println("执行静态定时任务时间: " + LocalDateTime.now());
}
}
二、xxl-job 任务调度后台 Admin
xxl-job 有什么用?
分布式集群的情况下,保证定时任务不被重复执行。
执行原理同Nginx 类型,所有定时任务通过任务调度平台分发,也可配置负载均衡等等
首先让我们能够使用起来,搭建一个自己的任务
第一步: github下载源码导入
下载地址:https://github.com/xuxueli/xxl-job/
当前版本目录结构 2.1.1
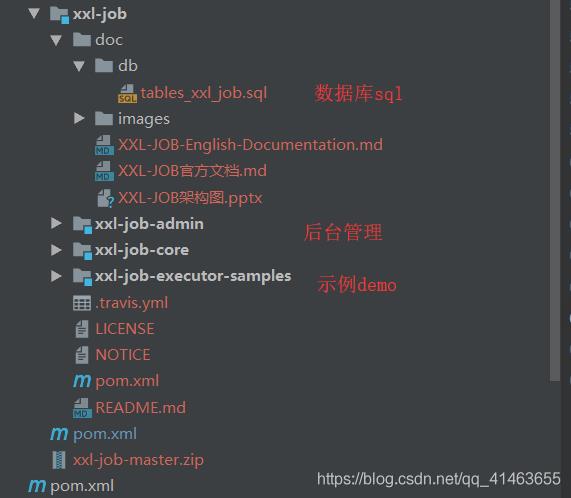
第二步: 执行sql
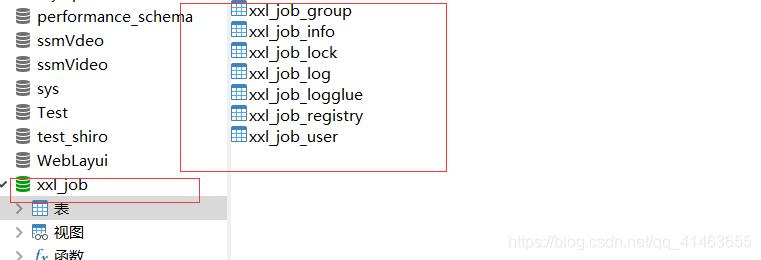
文件地址:xxl-job/doc/db/tables_xxl_job.sql
当前2.1.1版本sql
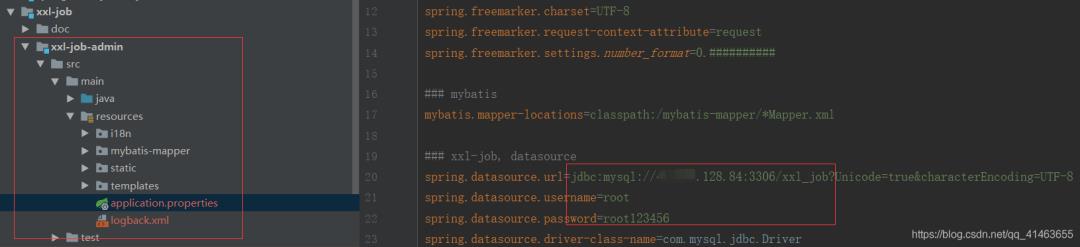
第三步: 修改xxl-job-admin项目配置
配置文件:application.properties
修改数据库连接
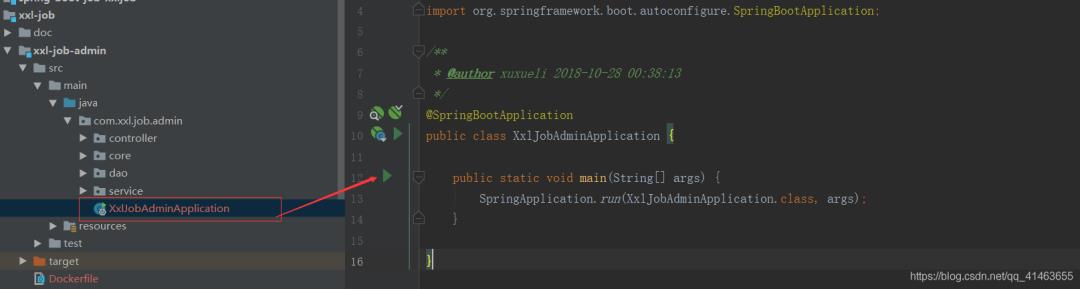
第四步: 启动admin项目
springboot 方式启动项目,
访问 http://localhost:8080/xxl-job-admin/
账号密码:admin / 123456
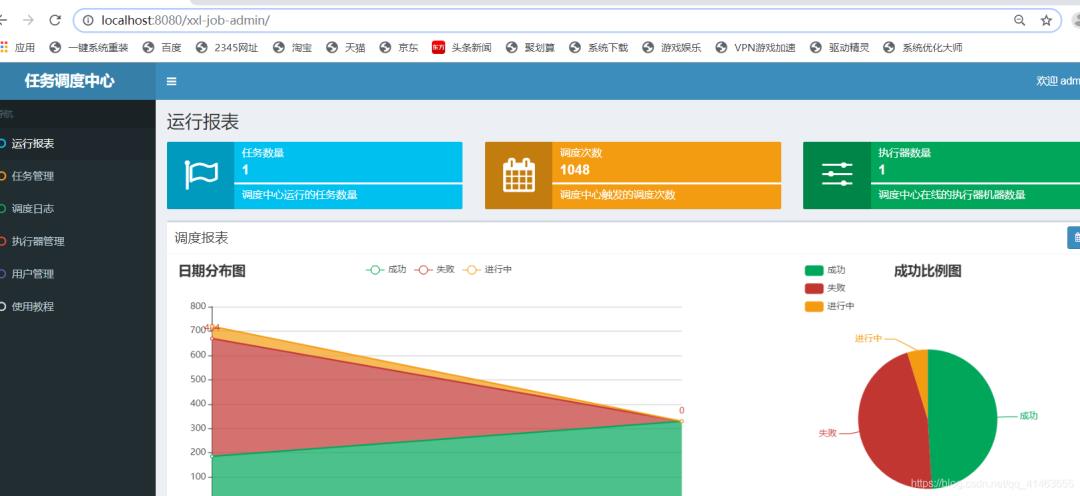
任务调度中心就搭建好了
接下来需要创建一个服务器连接任务调度中心
三、自创建boot项目的任务xxl-job 示例demo
创建一个 boot 项目
我的目录结构
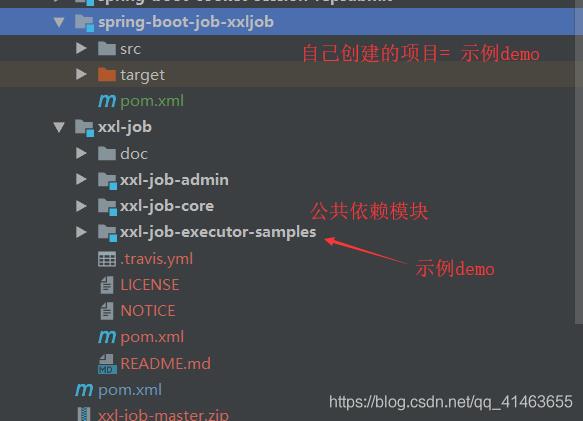
pom.xml
web核心及 xxl-job-core
<!-- spring-boot-starter-web (spring-webmvc + tomcat) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- xxl-job-core 版本号根据自己下载的版本修改 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.xuxueli</groupId>
<artifactId>xxl-job-core</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
logback.xml
日志配置直接拷贝
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration debug="false" scan="true" scanPeriod="1 seconds">
<contextName>logback</contextName>
<property name="log.path" value="/data/applogs/xxl-job/xxl-job-executor-sample-springboot.log"/>
<appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} %contextName [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<appender name="file" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${log.path}</file>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>${log.path}.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.zip</fileNamePattern>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<pattern>%date %level [%thread] %logger{36} [%file : %line] %msg%n
</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="console"/>
<appender-ref ref="file"/>
</root>
</configuration>
application.properties 加入配置
需修改或自定义
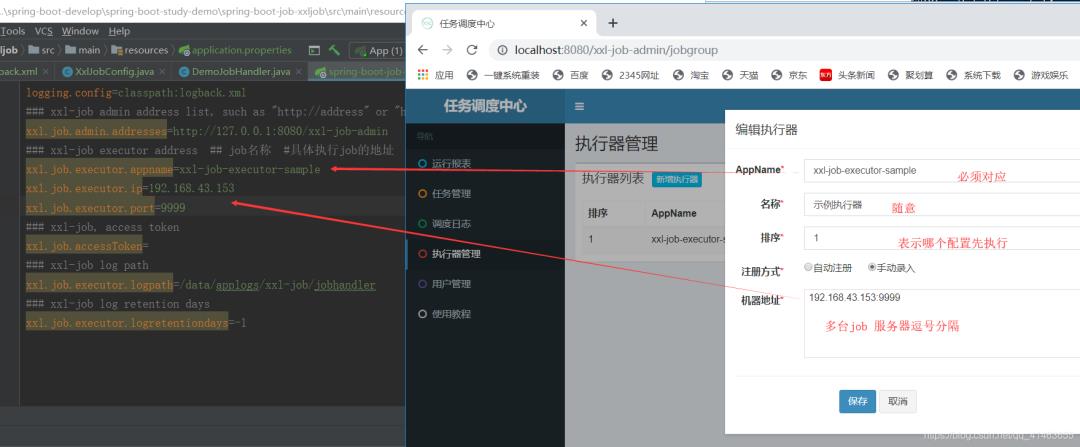
xxl-job admin 地址
xxl.job.executor.appname 自定义名称,后台配置必须对应
xxl.job.executor.ip 当前电脑Ip,或部署项目的电脑Ip
xxl.job.executor.port 端口
# 端口号
server.port=8081
# 日志
logging.config=classpath:logback.xml
### xxl-job admin 地址,多个逗号分隔"
xxl.job.admin.addresses=http://127.0.0.1:8080/xxl-job-admin
### xxl-job名称 || socket ip 当前项目部署的ip地址/本机ip || socket 端口号
xxl.job.executor.appname=xxl-job-executor-sample
xxl.job.executor.ip=192.168.43.153
xxl.job.executor.port=9999
### xxl-job, access token
xxl.job.accessToken=
### xxl-job log path
xxl.job.executor.logpath=/data/applogs/xxl-job/jobhandler
### xxl-job log retention days
xxl.job.executor.logretentiondays=-1
添加boot配置类 XxlJobConfig
package xxljob.config;
import com.xxl.job.core.executor.impl.XxlJobSpringExecutor;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* xxl-job xxljob.config
*/
@SuppressWarnings("ALL")
@Configuration
public class XxlJobConfig {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(XxlJobConfig.class);
@Value("${xxl.job.admin.addresses}")
private String adminAddresses;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.appname}")
private String appName;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.ip}")
private String ip;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.port}")
private int port;
@Value("${xxl.job.accessToken}")
private String accessToken;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.logpath}")
private String logPath;
@Value("${xxl.job.executor.logretentiondays}")
private int logRetentionDays;
@Bean(initMethod = "start", destroyMethod = "destroy")
public XxlJobSpringExecutor xxlJobExecutor() {
logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-job xxljob.config init.");
XxlJobSpringExecutor xxlJobSpringExecutor = new XxlJobSpringExecutor();
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAdminAddresses(adminAddresses);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAppName(appName);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setIp(ip);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setPort(port);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setAccessToken(accessToken);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setLogPath(logPath);
xxlJobSpringExecutor.setLogRetentionDays(logRetentionDays);
System.err.println(ip+":"+port);
return xxlJobSpringExecutor;
}
/**
* 针对多网卡、容器内部署等情况,可借助 "spring-cloud-commons" 提供的 "InetUtils" 组件灵活定制注册IP;
*
* 1、引入依赖:
* <dependency>
* <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
* <artifactId>spring-cloud-commons</artifactId>
* <version>${version}</version>
* </dependency>
*
* 2、配置文件,或者容器启动变量
* spring.cloud.inetutils.preferred-networks: 'xxx.xxx.xxx.'
*
* 3、获取IP
* String ip_ = inetUtils.findFirstNonLoopbackHostInfo().getIpAddress();
*/
}
任务job
@JobHandler(value="demoJobHandler")
@Component
public class DemoJobHandler extends IJobHandler {
static int count;
@Override
public ReturnT<String> execute(String param) throws Exception {
System.out.println("执行job任务"+count++);
return SUCCESS;
}
}
admin 后台配置
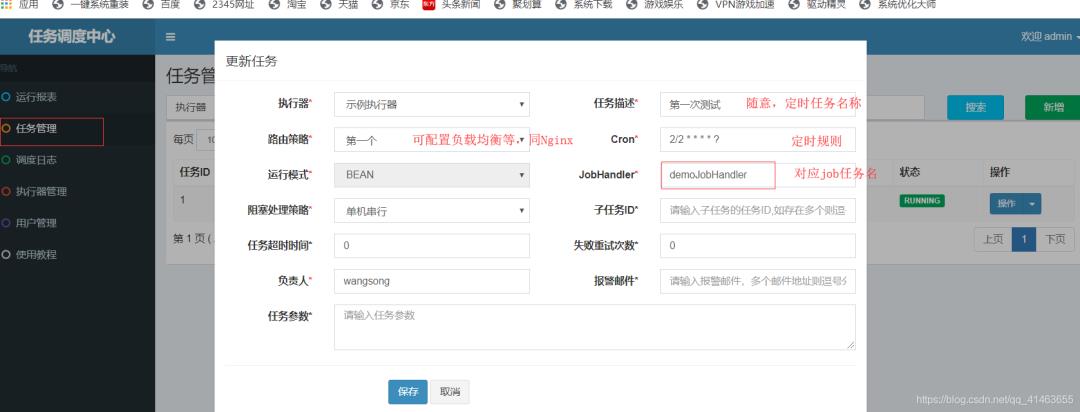
执行管理器下
任务管理下编辑任务
定时规则生成:http://cron.qqe2.com/
job任务名:@JobHandler注解值 >> 如:@JobHandler(value=“demoJobHandler”)
启动
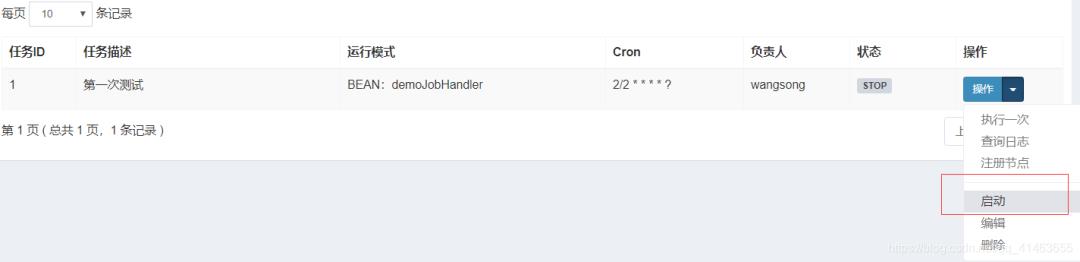
这样就配置完成了
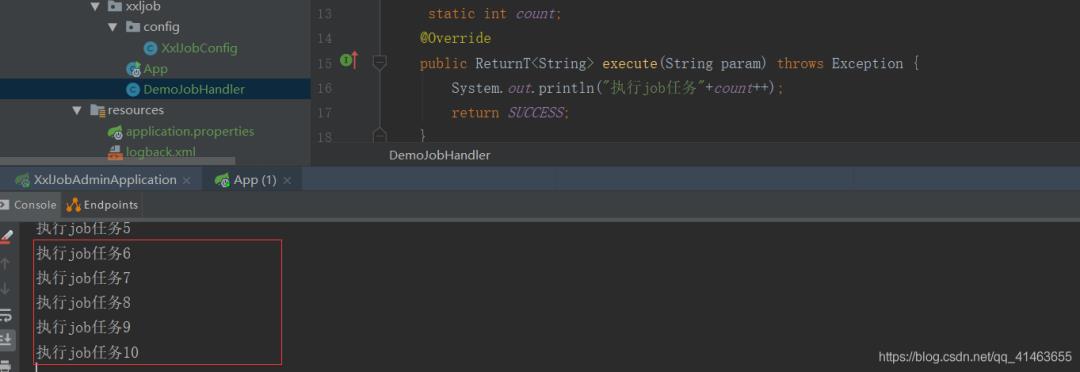
完成
应用项目:https://gitee.com/wslxm/spring-boot-plus2
推荐好文
>>【练手项目】基于SpringBoot的ERP系统,自带进销存+财务+生产功能>>分享一套基于SpringBoot和Vue的企业级中后台开源项目,代码很规范!
>>能挣钱的,开源 SpringBoot 商城系统,功能超全,超漂亮!
以上是关于Android 实现定时任务的五种方式的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章