MySQL之索引
Posted follow your heart.
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了MySQL之索引相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
索引是数据库中用来提高性能的最常用的工具,本次博客就来介绍一下索引,mysql版本5.7.19。
索引概述
所有MySQL列类型都可以被索引,对相关的列使用索引是可以提高SELECT操作性能的最佳途径。MyISAM和InnoDB存储引擎默认是BTREE索引。其实索引就像是一个字典的目录,你可以通过索引快速的定位到行的位置,索引会保存到额外的文件中。
索引的存储分类和作用
索引是在MySQL的存储引擎层中实现的,而不是在服务器层实现的,所以每种存储引擎的索引不一定完全相同,也不是所有的存储引擎都支持所有的索引类型。
MySQL目前支持以下4种索引:
B-tree索引:最常见的索引类型,大部分存储引擎都支持BTREE索引 HASH索引:只有MEMORY存储引擎支持,使用的场景比较简单 R-tree索引(空间索引):空间索引是MyISAM的一个特殊索引类型,主要用于地理空间数据类型,使用的较少 Full-text(全文索引):全文索引也是MyISAM的一个特殊索引类型,主要用于全文索引
三个常用引擎支持的索引:
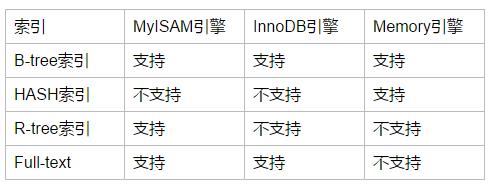
B-tree索引和HASH索引是比较常用的索引,HASH比较简单,也只有Memory和Heap引擎支持,Hash索引适合键-值的查询,且比B-Tree索引更快,但是hash索引不支持范围的查询,即如果Memory和heap引擎在where后面如果不使用“=”号的话,就不会使用Hash索引去查找,索引Memory和Heap只有在“=”的条件下才会使用Hash索引。
B-tree索引构造类似于二叉树,能根据键值提供一行或者一个行集的快速访问,通常只需要很少的读操作就可以找到正确的行。B-tree的B不代表一个二叉树,而是一个平衡树(balanced),结构如下:
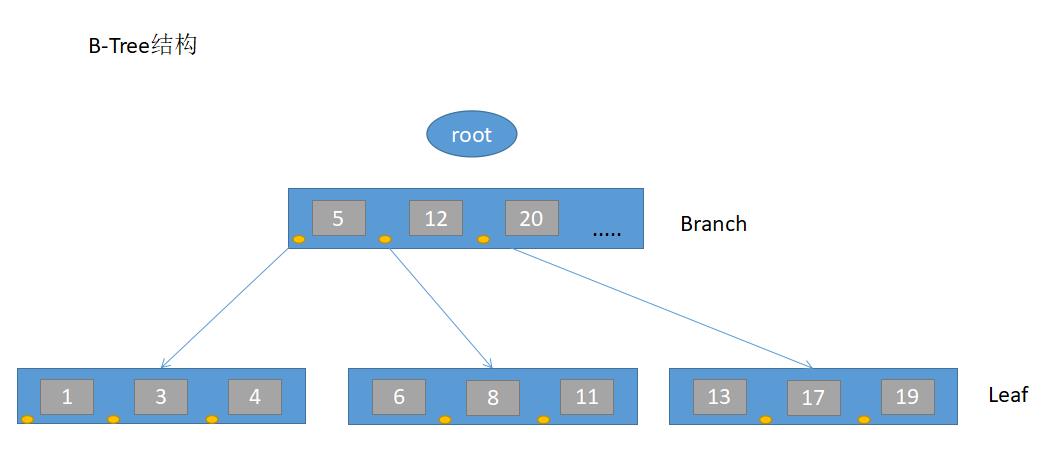
索引的存在可以加速查找,有的时候可以起到约束的作用。
索引的创建,删除和修改
创建索引
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table(column1,column2,...columnN); --创建普通的索引 CREATE UNIQUE INDEX index_name ON table(column1,column2,...columnN); --创建唯一索引 ALTER TABLE table ADD PRIMARY KEY(column); --增加主键索引
删除索引
DROP INDEX index_name ON table --删除普通的索引 ALTER TABLE tabel DROP INDEX index_name --删除索引 DROP UNIQUE INDEX index_name ON table --删除唯一索引 ALTER TABLE table DROP PRIMARY KEY; --删除主键索引 ALTER TABLE table MODIFY column INT,DROP PRIMARY KEY; --删除主键索引
修改
对于MySQL5.7及以上版本,可以使用RENAME:
ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME INDEX old_index_name TO new_index_name;
对于MySQL5.7以前的版本,只能先删除再增加了:
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP INDEX old_index_name; ALTER TABLE table_name ADD INDEX new_index_name(column_name);
举例:

mysql> create index name_index on t3(name); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> show index from t3 \\G; *************************** 1. row *************************** Table: t3 Non_unique: 1 Key_name: name_index Seq_in_index: 1 Column_name: name Collation: A Cardinality: 0 Sub_part: NULL Packed: NULL Null: YES Index_type: BTREE Comment: Index_comment: 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> mysql> mysql> alter table t3 rename index name_index to new_name_index; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> show index from t3 \\G; *************************** 1. row *************************** Table: t3 Non_unique: 1 Key_name: new_name_index Seq_in_index: 1 Column_name: name Collation: A Cardinality: 0 Sub_part: NULL Packed: NULL Null: YES Index_type: BTREE Comment: Index_comment: 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
通过EXPLAIN分析低效SQL的执行计划
现在有表如下:
mysql> show create table t1 \\G; *************************** 1. row *************************** Table: t1 Create Table: CREATE TABLE `t1` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` char(20) DEFAULT NULL, `email` char(100) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1000001 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select count(*) from t1; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 1000000 | +----------+ 1 row in set (1.25 sec)
id列为主键索引,都说索引可以加速查找,那么来测试一下他是否可以加速查找:
mysql> select * from t1 where id=8888; +------+----------+-----------------+ | id | name | email | +------+----------+-----------------+ | 8888 | test8888 | test8888@qq.com | +------+----------+-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from t1 where name=\'test8888\'; +------+----------+-----------------+ | id | name | email | +------+----------+-----------------+ | 8888 | test8888 | test8888@qq.com | +------+----------+-----------------+ 1 row in set (1.24 sec)
通过以上例子完全可以看出索引的存在可以加速行数据的查找。
这里可以通过explain命令来分析SQL的执行计划:
mysql> explain select * from t1 where id=8888; +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | const | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
各个字段的意思:

id:数字越大越先执行,当数字相同的时候,就从上往下执行,如果为null就表示是一个结果集,不需要使用它来进行查询 select_type:常见的如下 simple:简单表,即不使用表连接或者子查询,有连接查询时,外层的查询为simple,有且只有一个; primary:需要union操作或者含有子查询的select,位于最外层的单位查询的select_type即为primary,有且只有一个; union:UNiON中的第二个或者后面的查询语句; subquery:除了from字句中包含的子查询外,其他地方出现的子查询都可能是subquery; 除以上之外还有:dependent union,union result,dependent subquery,derived。 table:显示查询表名,如果使用的是别名,那么这里就是别名; type:表示MySQL在表中找到所需行的方式,或者叫访问类型,常见的如下: +-----+--------+-------+------+--------+---------------+-------+ | ALL | index | range | ref | eq_ref | const,system | NULL | +-----+--------+-------+------+--------+---------------+-------+ 从左至右,性能由最差到最好。 possible_keys:表示查询时可能使用的索引; key:表示实际使用的索引; partitions:显示SQL所需要访问的分区名字; key_len:使用到所以字段的长度; rows:预估扫描行的数量; ref:如果是使用的常数等值查询,这里会显示const; filtered:表示存储引擎返回的数据在server层过滤后,剩下多少满足查询的记录数量的比例,注意是百分比; extra:常见的如下: distinct:在select部分使用了distinc关键字; no tables used:不带from字句的查询; using filesort:排序时无法使用到索引时; using index:查询时不需要回表查询,直接通过索引就可以获取查询的数据; using temporary:表示使用了临时表存储中间结果; using where: 5.6之前:存储引擎只能根据限制条件扫描数据并返回,然后再回表进行过滤返回真正的查询的数据; 5.6之后:支持ICP特性,把条件限制都下推到存储引擎层来完成,这样就能降低不必要的IO访问。 filtered:
最左前缀匹配
创建索引如下:
mysql> create index index1 on t1(name,email,type); Query OK, 0 rows affected (17.45 sec) Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> desc t1; +-------+-----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | char(20) | YES | MUL | NULL | | | email | char(100) | YES | | NULL | | | type | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | dep | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+-----------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
那么最左前缀匹配是什么意思呢?
这里创建了一个名为index1的索引,包含三列,从左至右为:name,email,type,最左前缀匹配的意思就是,查询的时候条件必须包含name列才会使用索引去查找,否则就会全文去查询。
举例:

mysql> explain select * from t1 where name=\'test8888\' and email=\'test8888@qq.com\' and type=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ref | index1 | index1 | 367 | const,const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------------------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> mysql> explain select * from t1 where name=\'test8888\' and email=\'test8888@qq.com\'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ref | index1 | index1 | 362 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from t1 where name=\'test8888\' and type=1; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ref | index1 | index1 | 61 | const | 1 | 10.00 | Using index condition | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------+------+----------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from t1 where name=\'test8888\'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ref | index1 | index1 | 61 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from t1 where email=\'test8888@qq.com\' and type=1; --当不包含name的时候,就不会使用索引查找 +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 990448 | 1.00 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from t1 where email=\'test8888@qq.com\'; +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 990448 | 10.00 | Using where | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select * from t1 where email=\'test8888@qq.com\' and name=\'test8888\'; --name不必在条件语句的最左边 +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ref | index1 | index1 | 362 | const,const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+--------+---------+-------------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
组合索引:比如之前例子中create index index1 on t1(name,email,type),index1就是一个组合索引; 索引合并:索引合并,拿上一个例子来看,创建了一个索引包含了3个列,这个叫组合索引,如果我们针对每一个列创建一个索引,在使用查询语句的时候使用多个索引,即把多个单列索引合并使用,这就叫索引的合并。
那么它们的效率如何呢?
