mysql图形化工具使用及常用操作
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mysql图形化工具使用及常用操作相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
mysql图形化工具使用
(以Navicat for Mysql软件为例)
使用Navicat连接我们的数据库:
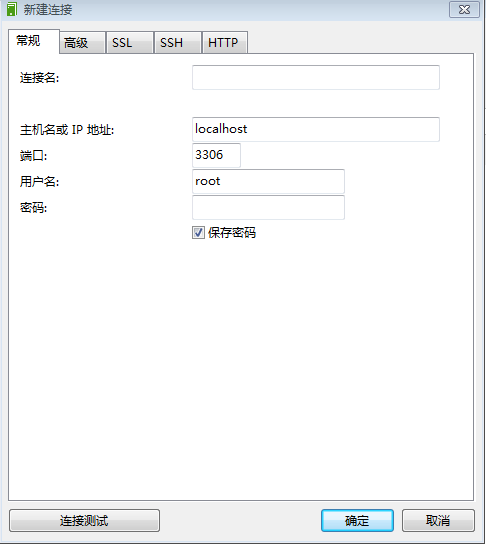
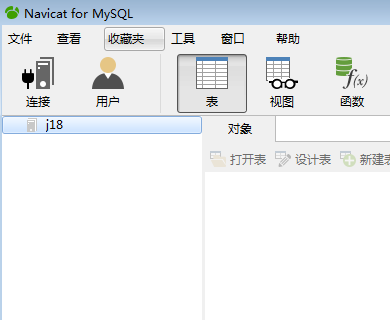
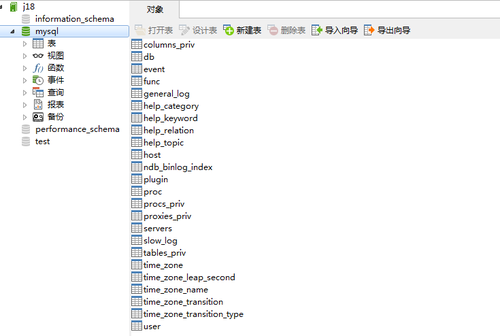
点击连接 主机名或IP地址:就是数据库安装电脑的电脑名或IP地址 localhost、127.0.0.1 端口:就是MySQL安装时候的默认端口 3306 用户名:MySql安装的默认用户名 root 密码:MySQL安装时你指定的密码: root 连接名:只是一个名字而已,作用是让我们知道是什么业务的数据库 完成以上几个信息的配置,点击确定: 点击J18这个数据库连接 展示 全部的数据库; 几个数据库都是可以点击的,点击之后进入对应的数据库; 暂时我们只 注意 表、查询、备份 点击表之后,把该数据库下面的所有表全部展示出来: 点击查询: 新建查询 该操作面板就可以 写 insert delete update create select 等等语句; 点击备份: 该页面主要是对数据库的备份、恢复操作。 |
数据操作语句
新增
Insert into 表名(列名1, 列名2, 列名3...)values(列名1值,列名2值, 列名3值.) 两种新增数据的方式 Insert into stu(sid,sname,sage)values(1,’李林’,22); Insert into stu values(1,’李林’,22); |
删除
Delete from 表名 Delete from stu; |
修改
Update 表名 set 列名1=修改的值,列名2=修改的值; update stu SET sage=23,sname=‘李琳‘; 修改某一行某一列的值: update users set age=18 where name=‘李琳‘; 修改李琳那一行的年龄那一列的值为18 |
数据查询语句
SELECT查询内容
FROM 表名
WHERE条件
GROUP BY
HAVING
ORDER BY
LIMIT
查询全部数据 Select * from 表名; Select * from stu; 根据条件查询指定的数据 Select * from 表名 where 列名1=值 and 列名2=值.... Select * from stu where sid=9 and ssex=‘女‘; 查询数据,返回指定的列 Select 列名1,列名2 from stu; Select sid,sname from stu; 给指定返回列取别名(小名) 两种方式: Select 列名 别名,列名2 别名2... from 表名; Select 列名 as 别名,列名2 as 别名2... from 表名; Select sid 学号,sname 姓名,ssex 性别 from stu; Select sid as 学号,sname as 姓名,ssex as 性别 from stu; 在条件中使用比较运算符 SELECT * FROM 表名 where 字段 > < >= <= !=或<> select * from j18 where xsnianling !=18 多条件的查询: AND OR NOT select * from j18 where xsnianling <=21 and xsxingbie=‘女‘ select * from j18 where xsnianling <21 or xsxingbie=‘女‘ select * from j18 where xsnianling not in(18,21,25) 对空值的查询:is null 对应列是否null查询 select * from j18 where xsxueli is not null select * from j18 where xsxueli is null BETWEEN A AND B 在A和B之间,包含AB的值 select * from j18 where xsnianling BETWEEN 18 and 21 IN select * from j18 where xsnianling in(18,21,25) 模糊查询 LIKE %:指代不明确值的位置或长度 _:指代明确值的位置或已知字符串长度 select * from j18 where xsxingming like ‘_灵%‘ 查询中使用算术表达式:+ - * / select xsxuehao+xsnianling from j18 where xsxingming like ‘_灵%‘ 处理重复值:DISTINCT 排除重复展示,只展示一次 select DISTINCT xsxingbie from j18;
查询返回限定行数:LIMIT Limit 10 取查询数据的前10位 Limit 10,10 从查询数据的第10位开始,向后取10位数据展示,不满足10位也不会报错
通过查询复制表 create table stu1 select * from stu;
--只复制结构 create table stu2 select * from stu where 1=2;
分组 group by select ssex,COUNT(*) from stu GROUP BY ssex 分组使用的时候,,group by 字段,一定要在 select 后面出现,如果使用了group by select 后面就不要出现 *
排序 order by 字段名 :字段名就是我们需要排序的字段 order by xsnianling 升序 默认 order by xsnianling desc 降序 |
常用函数
得到需要查询字符的ASCII码 SELECT ASCII(‘中‘); SELECT CHAR(97); 根据字符集查询得到字符串的长度 SELECT CHAR_LENGTH("中国"); SELECT CHAR_LENGTH(sname) FROM student; --utf8编码下,一个中文字占3个字符长度 SELECT LENGTH("中"); --拼接字符串 SELECT CONCAT(‘My‘, ‘S‘, ‘QL‘); SELECT CONCAT(sname,sage) FROM student; SELECT sname,sage FROM student; --大写转小写 SELECT LOWER("ABC"); --小写转大写 SELECT UPPER("abc"); --查询学生表中所有学生姓名的最后一个字 SELECT RIGHT(sname,1) FROM student; --查询学生表中所有学生姓什么 SELECT LEFT(sname,1) from student; SELECT FLOOR(4.9); ---------------------------- --查询得到本地时间 SELECT NOW(); CREATE TABLE teset( tid int PRIMARY KEY auto_increment, ttime datetime ); SELECT * FROM teset; INSERT INTO teset(ttime) values (NOW()); SELECT CURDATE(),CURTIME(); SELECT CURTIME(); 聚合函数: COUNT 统计数量:select count(xsnianling) from j18 SUM 求和:select sum(xsnianling) from j18 MAX 求最大值:select max(xsnianling) from j18 MIN 求最小值:select min(xsnianling) from j18 AVG 平均数:select avg(xsnianling) from j18 |
补充
Truncate table 表名 直接删除表中全部数据,与delete不同的是,此方法无法使用where选择,只能全部删除。 truncate table users; |
以上是关于mysql图形化工具使用及常用操作的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章