Redis持久化--AOF
Posted harvyxu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Redis持久化--AOF相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
除了RDB持久化之外,Redis还提供了AOF(Append Only File)持久化功能。与RDB持久化通过保存数据库中键值对来保存数据库的状态不同,AOF持久化是通过保存Redis服务器所执行的写命令来记录数据库的状态。被写入AOF文件的所有命令都是以Redis的命令请求协议格式保存的,该格式是一种纯本文的格式,所以可以通过直接打开AOF文件,观察里面的类容。
1 AOF持久化的实现
AOF持久化功能的实现可以分为:命令追加(append),文件写入(write),文件同步(sync)三个步骤。
1.1 命令追加
AOF持久化需要将所有写命令记录在文件中来保存服务器状态,而文件写入操作效率比较低,如果每执行一条写命令都要写一次AOF文件无疑是低效的。为了提高效率,Redis提供了一个中间层 – AOF缓冲区,也就是说当Redis执行一条写命令后,先将该命令追加到AOF缓冲区中,在以后的某个时刻再将AOF缓冲区中的内容同步到文件中。当AOF持久化功能处于打开状态时,服务器在执行完一个写命令之后,会以协议格式将被执行的写命令追加到服务器状态的aof_buf缓冲区的末尾:
struct redisServer { ... sds aof_buf;/* AOF buffer, written before entering the event loop */ }
服务器执行完写命令,调用propagate进行命令追加。
//进行命令追加 void propagate(struct redisCommand *cmd, int dbid, robj **argv, int argc, int flags) { if (server.aof_state != AOF_OFF && flags & PROPAGATE_AOF) feedAppendOnlyFile(cmd,dbid,argv,argc); }
将命令追加到缓冲区中的操作由feedAppendOnlyFile函数实现,如果后台正在执行AOF文件后台重写操作,该命令还会被追加到AOF重写缓存中。
void feedAppendOnlyFile(struct redisCommand *cmd, int dictid, robj **argv, int argc) { sds buf = sdsempty(); robj *tmpargv[3]; /* The DB this command was targeting is not the same as the last command * we appended. To issue a SELECT command is needed. */ // 如果当前命令涉及的数据库与server.aof_selected_db指明的数据库不一致,需要加入SELECT命令显式设置 if (dictid != server.aof_selected_db) { char seldb[64]; snprintf(seldb,sizeof(seldb),"%d",dictid); buf = sdscatprintf(buf,"*2\\r\\n$6\\r\\nSELECT\\r\\n$%lu\\r\\n%s\\r\\n", (unsigned long)strlen(seldb),seldb); server.aof_selected_db = dictid; } // 处理EXPIRE, SETEX, EXPIREAT命令 if (cmd->proc == expireCommand || cmd->proc == pexpireCommand || cmd->proc == expireatCommand) { /* Translate EXPIRE/PEXPIRE/EXPIREAT into PEXPIREAT */ // 将EXPIRE/PEXPIRE/EXPIREAT命令都转换为PEXPIREAT命令 buf = catAppendOnlyExpireAtCommand(buf,cmd,argv[1],argv[2]); } // 处理SETEX、PSETEX命令 else if (cmd->proc == setexCommand || cmd->proc == psetexCommand) { /* Translate SETEX/PSETEX to SET and PEXPIREAT */ // 将SETEX/PSETEX命令转换为SET命令和PEXPIREAT命令 tmpargv[0] = createStringObject("SET",3); tmpargv[1] = argv[1]; tmpargv[2] = argv[3]; buf = catAppendOnlyGenericCommand(buf,3,tmpargv); decrRefCount(tmpargv[0]); buf = catAppendOnlyExpireAtCommand(buf,cmd,argv[1],argv[2]); } // 其它命令使用catAppendOnlyGenericCommand()函数处理 else { /* All the other commands don\'t need translation or need the * same translation already operated in the command vector * for the replication itself. */ // 所有其它命令并不需要转换操作或者已经完成转换,采用此函数将将写命令转化为命令协议格式的字符串 buf = catAppendOnlyGenericCommand(buf,argc,argv); } /* Append to the AOF buffer. This will be flushed on disk just before * of re-entering the event loop, so before the client will get a * positive reply about the operation performed. */ if (server.aof_state == REDIS_AOF_ON) server.aof_buf = sdscatlen(server.aof_buf,buf,sdslen(buf)); /* If a background append only file rewriting is in progress we want to * accumulate the differences between the child DB and the current one * in a buffer, so that when the child process will do its work we * can append the differences to the new append only file. */ // 如果后台正在执行AOF文件重写操作(即BGREWRITEAOF命令),为了记录当前正在重写的AOF文件和当前数据库的 // 差异信息,我们还需要将重构后的命令追加到AOF重写缓存中。 if (server.aof_child_pid != -1) aofRewriteBufferAppend((unsigned char*)buf,sdslen(buf)); sdsfree(buf); }
aof.c文件中的catAppendOnlyGenericCommand函数提供了根据传入命令和该命令的参数将其构造成满足AOF文件格式的字符串的功能。
sds catAppendOnlyGenericCommand(sds dst, int argc, robj **argv) { char buf[32]; int len, j; robj *o; // 构建格式为“*<count>\\r\\n"格式的字符串,<count>为命令参数个数 buf[0] = \'*\'; len = 1+ll2string(buf+1,sizeof(buf)-1,argc); buf[len++] = \'\\r\'; buf[len++] = \'\\n\'; dst = sdscatlen(dst,buf,len); // 重建命令,每个item的格式为“$<len>\\r\\n<content>\\r\\n”,其中<len>指明<content>的字符长度,<content>为参数内容 for (j = 0; j < argc; j++) { o = getDecodedObject(argv[j]); buf[0] = \'$\'; len = 1+ll2string(buf+1,sizeof(buf)-1,sdslen(o->ptr)); buf[len++] = \'\\r\'; buf[len++] = \'\\n\'; dst = sdscatlen(dst,buf,len); dst = sdscatlen(dst,o->ptr,sdslen(o->ptr)); dst = sdscatlen(dst,"\\r\\n",2); decrRefCount(o); } // 返回重建后的命令内容 return dst; }
1.2 文件写入(write)和同步(sync)
在上面的介绍中,我们调用feedAppendOnlyFile函数只是把命令追加到了AOF缓冲区server.aof_buf中,并没有写入到磁盘文件中。
在现代操作系统中,当用户将数据写入一个文件中时,为了提高效率,操作系统会先利用一个缓冲区来存放写入的内容,直到这个缓冲区满了或者超过指定的时间后才真正将缓冲区中的内容写入到磁盘文件中。为了强制让操作系统将缓冲区中的数据写入磁盘,一般可以通过fsync()函数来强制写入到磁盘中。而fsync()函数的调用频率就是我们这一小节要介绍的“同步策略”。
在处理文件事件时(写命令),命令被追加到aof_buf中;然后在处理时间事件时,serverCron函数会调用flushAppendOnlyFile函数进行文件的写入和同步。Redis可以通过配置redis.conf文件中的flush选项来指定AOF同步策略,主要支持以下三种同步策略:
-
AOF_FSYNC_NO
在该模式下,Redis服务器在每个事件循环都将AOF缓冲区server.aof_buf中的数据写入AOF文件中,但不执行同步fsync方法,由操作系统决定何时同步。该模式速度最快(无需执行同步操作)但也最不安全(如果机器崩溃将丢失上次同步后的所有数据)。
-
AOF_FSYNC_ALWAYS
在该模式下,Redis服务器在每个事件循环都将AOF缓冲区server.aof_buf中的数据写入AOF文件中,且执行一次AOF文件同步操作。该模式速度最慢(每个事件循环都要执行同步操作)但也最安全(如果机器崩溃只丢失当前事件循环中处理的新数据)。
-
AOF_FSYNC_EVERYSEC
在该模式下,Redis服务器在每个事件循环都将AOF缓冲区server.aof_buf中的数据写入AOF文件中,且每秒执行一次AOF文件同步操作。该模式效率和安全性(如果机器崩溃只丢失前一秒处理的新数据)比较适中,是Redis的默认同步策略。
void flushAppendOnlyFile(int force) { if (sdslen(server.aof_buf) == 0) return; if (server.aof_fsync == AOF_FSYNC_EVERYSEC) sync_in_progress = bioPendingJobsOfType(BIO_AOF_FSYNC) != 0; if (server.aof_fsync == AOF_FSYNC_EVERYSEC && !force) { if (sync_in_progress) { if (server.aof_flush_postponed_start == 0) { server.aof_flush_postponed_start = server.unixtime; return; } else if (server.unixtime - server.aof_flush_postponed_start < 2) { return; } server.aof_delayed_fsync++; } } //将aof_buf中的内容写入到aof文件 nwritten = write(server.aof_fd,server.aof_buf,sdslen(server.aof_buf)); server.aof_flush_postponed_start = 0; …… server.aof_current_size += nwritten; if ((sdslen(server.aof_buf)+sdsavail(server.aof_buf)) < 4000) { sdsclear(server.aof_buf); } else { sdsfree(server.aof_buf); server.aof_buf = sdsempty(); } /*Don\'t fsync if no-appendfsync-on-rewrite is set to yes and there are children doing I/O in the background. */
if (server.aof_no_fsync_on_rewrite && (server.aof_child_pid != -1 || server.rdb_child_pid != -1)) return; /* appendfsync为always */ if (server.aof_fsync == AOF_FSYNC_ALWAYS) {/ aof_fsync(server.aof_fd); //同步aof文件 server.aof_last_fsync = server.unixtime;//记录同步时间 } else if ((server.aof_fsync == AOF_FSYNC_EVERYSEC && server.unixtime > server.aof_last_fsync)) { /* appendfsync为EVERYSEC*/ if (!sync_in_progress) aof_background_fsync(server.aof_fd); server.aof_last_fsync = server.unixtime; } }
// 在另一个线程中,对给定的描述符 fd (指向 AOF 文件)执行一个后台 fsync() 操作。 void aof_background_fsync(int fd) { bioCreateBackgroundJob(BIO_AOF_FSYNC,(void*)(long)fd,NULL,NULL); }
2 AOF文件的载入与数据还原
数据还原就是将AOF文件中保存的命令解析并执行,这样就可以将数据库还原为原来的状态。因为在Redis中,命令必须由redisClient实例来执行,所以为了加载AOF文件需要创建一个伪Redis客户端。创建了伪Redis客户端后,执行数据还原的过程就是从AOF文件中读取命令并交给伪Redis客户端执行的过程。数据还原的功能由aof.c文件中的loadAppendOnlyFile函数完成。
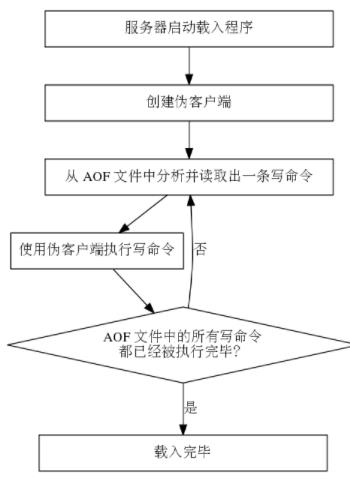
3 AOF重写
由于aof是通过不断追加写命令来记录数据库状态,所以服务器执行比较久之后,aof文件中的内容会越来越多,磁盘占有量越来越大,同时也是使通过过aof文件还原数据库的需要的时间也变得很久。所以就需要通过读取服务器当前的数据库状态来重写新的aof文件。新的AOF文件不会包含任何浪费空间的冗余命令,所以会比旧的AOF文件小很多。
由于AOF重写是会进行大量写入操作,势必为长时间阻塞主进程,因此redis把重写程序放到子进程执行。
这样做有两点好处:
1)子进程重写期间,主进程可以继续处理命令。
2)子进程带有主进程的数据副本,这样就可以避免与主进程竞争db->dict,这是线程实现不了的。
重写期间,主进程继续处理命令,对数据库状态进行修改,这样使得当前的数据库状态与重写的AOF文件所保存的数据库状态不一致。因此,redis设置了AOF重写缓冲区,在创建子进程后,主进程每执行一个写命令都会写到重写缓冲区。在子进程完成重写后,主进程会将AOF重写缓冲区的数据写入到重写的AOF文件,保证数据状态的一致。
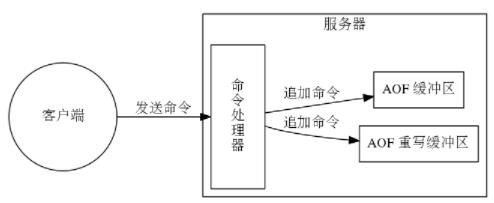
在子进程执行AOF重写期间,服务器进程需要执行以下三个操作:
(1)执行客户端发送过来的命令;
(2)将执行的命令追加到AOF缓冲区;
(3)将执行的命令追加到AOF重写缓冲期;
这样就可以保证:
- AOF缓冲区的类容会定期写入和同步到AOF文件,即对现有的AOF文件的工作会正常进行;
- 从创建子进程开始,服务器执行的所有写命令会被记录到AOF重写缓冲区里面。
当子进程执行完毕后,会向父进程发送一个信号。父进程收到信号后,将执行以下工作:
- 将AOF重写缓冲区的类容写入到新的AOF缓冲期中,这时新AOF缓冲区中数据库的状态和服务器的当前状态一致;
- 对新的AOF文件改名,源自地(automic)覆盖现有的AOF文件,完成新旧AOF文件的替换。整个AOF重写期间,只有信号处理函数执行时会对服务器进程造成阻塞。
3.1 redisServer结构体中与AOF相关的字段
struct redisServer{ // AOF 状态(开启/关闭/可写) int aof_state; /* REDIS_AOF_(ON|OFF|WAIT_REWRITE) */ // 所使用的 fsync 策略(每个写入/每秒/从不) int aof_fsync; /* Kind of fsync() policy */ char *aof_filename; /* Name of the AOF file */ int aof_no_fsync_on_rewrite; /* Don\'t fsync if a rewrite is in prog. */ int aof_rewrite_perc; /* Rewrite AOF if % growth is > M and... */ off_t aof_rewrite_min_size; /* the AOF file is at least N bytes. */ // 最后一次执行 BGREWRITEAOF 时, AOF 文件的大小 off_t aof_rewrite_base_size; /* AOF size on latest startup or rewrite. */ // AOF 文件的当前字节大小 off_t aof_current_size; /* AOF current size. */ int aof_rewrite_scheduled; /* Rewrite once BGSAVE terminates. */ // 负责进行 AOF 重写的子进程 ID pid_t aof_child_pid; /* PID if rewriting process */ // AOF 重写缓存链表,链接着多个缓存块 list *aof_rewrite_buf_blocks; /* Hold changes during an AOF rewrite. */ // AOF 缓冲区 sds aof_buf; /* AOF buffer, written before entering the event loop */ // AOF 文件的描述符 int aof_fd; /* File descriptor of currently selected AOF file */ // AOF 的当前目标数据库 int aof_selected_db; /* Currently selected DB in AOF */ // 推迟 write 操作的时间 time_t aof_flush_postponed_start; /* UNIX time of postponed AOF flush */ // 最后一直执行 fsync 的时间 time_t aof_last_fsync; /* UNIX time of last fsync() */ time_t aof_rewrite_time_last; /* Time used by last AOF rewrite run. */ // AOF 重写的开始时间 time_t aof_rewrite_time_start; /* Current AOF rewrite start time. */ // 最后一次执行 BGREWRITEAOF 的结果 int aof_lastbgrewrite_status; /* REDIS_OK or REDIS_ERR */ // 记录 AOF 的 write 操作被推迟了多少次 unsigned long aof_delayed_fsync; /* delayed AOF fsync() counter */ // 指示是否需要每写入一定量的数据,就主动执行一次 fsync() int aof_rewrite_incremental_fsync;/* fsync incrementally while rewriting? */ int aof_last_write_status; /* REDIS_OK or REDIS_ERR */ int aof_last_write_errno; /* Valid if aof_last_write_status is ERR */ /* RDB persistence */ }
3.2 重写AOF文件的命令
void bgrewriteaofCommand(client *c) { if (server.aof_child_pid != -1) { } else if (server.rdb_child_pid != -1) { server.aof_rewrite_scheduled = 1; } else if (rewriteAppendOnlyFileBackground() == C_OK) { } else { }
3.3 serverCron定时程序,触发AOF重写
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) { if (server.rdb_child_pid != -1 || server.aof_child_pid != -1 || ldbPendingChildren()) { …… } else { ……//检查是否触发AOF重写 if (server.rdb_child_pid == -1 &&server.aof_child_pid == -1 && server.aof_rewrite_perc &&server.aof_current_size > server.aof_rewrite_min_size) { long long base = server.aof_rewrite_base_size ?server.aof_rewrite_base_size : 1; long long growth = (server.aof_current_size*100/base) - 100; if (growth >= server.aof_rewrite_perc) { rewriteAppendOnlyFileBackground(); } } } }
后台重写的实现:
//后台重写AOF文件 int rewriteAppendOnlyFileBackground(void) { if (server.aof_child_pid != -1 || server.rdb_child_pid != -1) return C_ERR; if (aofCreatePipes() != C_OK) return C_ERR;//创建父进程与子进程的管道 openChildInfoPipe(); start = ustime(); if ((childpid = fork()) == 0) { char tmpfile[256]; snprintf(tmpfile,256,"temp-rewriteaof-bg-%d.aof", (int) getpid()); //在子进程中执行AOF重写 if (rewriteAppendOnlyFile(tmpfile) == C_OK) { …… } } else { /* Parent */ …… } return C_OK; /* unreached */ }
//重写AOF文件的程序 int rewriteAppendOnlyFile(char *filename) { snprintf(tmpfile,256,"temp-rewriteaof-%d.aof", (int) getpid()); server.aof_child_diff = sdsempty(); rioInitWithFile(&aof,fp); if (server.aof_rewrite_incremental_fsync) riosetAutoSync(&aof,AOF_AUTOSYNC_BYTES); //遍历数据库,进行重写操作 …… //写入、冲洗并同步到AOF文件 if (rewriteAppendOnlyFileRio(&aof) == C_ERR) goto werr; if (fflush(fp) == EOF) goto werr; if (fsync(fileno(fp)) == -1) goto werr; ... return C_OK; }//重写操作
子进程重写完成后,父进程进行处理
int serverCron(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, long long id, void *clientData) { if (server.rdb_child_pid != -1 || server.aof_child_pid != -1 || ldbPendingChildren()) { if ((pid = wait3(&statloc,WNOHANG,NULL)) != 0) { if(pid == server.aof_child_pid) { //子进程完成重写,父进程进行重写AOF文件的处理 backgroundRewriteDoneHandler(exitcode,bysignal); } } } }
void backgroundRewriteDoneHandler(int exitcode, int bysignal) { if (!bysignal && exitcode == 0) { snprintf(tmpfile,256,"temp-rewriteaof-bg-%d.aof", (int)server.aof_child_pid); newfd = open(tmpfile,O_WRONLY|O_APPEND); if (aofRewriteBufferWrite(newfd) == -1) { ……//将重写缓冲区的数据写入到重写AOF文件 } if (rename(tmpfile,server.aof_filename) == -1) { ……//覆盖旧的AOF文件 } …… } }
参考:
以上是关于Redis持久化--AOF的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章