Vue3 和Vue2的组件通信方式,建议收藏
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Vue3 和Vue2的组件通信方式,建议收藏相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A先来看看Vue3的几种组件通信方式:
下面分别介绍这几种方式的写法:
1、props
2、$emit
3、expose / ref
4、attrs
5、v-model
6. provide / inject
接下来是Vue2.x 组件通信使用方法:
1、 props
2、.sync
3、v-model
4、ref
5、$emit / v-on
6、children/parent
7、EventBus
8、Vuex (这个就不举例子了........懂的都懂!)
创作不易,你的关注就是我前进的动力![奋斗][奋斗]
Vue组件间的通信方式(多种场景,通俗易懂,建议收藏)
以下是我在开发中用到过的vue组件之间的通信方式,不同的场景使用不同的方式,基本满足所有开发场景中的通信需求,从最简单的事例着手,讲述如何使用,话不多说直接开始,满满的干货,建议看完。
1、Props
父 >>> 子 (Props)
一个组件里面引入另外一个组件,此时构成了一种“父子关系”,当前组件为“父”,引入的组件为“子”,如当前组件(父),在父组件中通过 “:message” 向子组件通信。
<template>
<div class="parent-box">
<div>
<div>我是父页面</div>
<div>{{message}}</div>
</div>
<children :message="toChildrenMsg"></children>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Children from './Children.vue' //当前页引入子组件
export default {
name:"Parent",
components:{
Children
},
data(){
return {
message:'我是父页面的内容',
toChildrenMsg:'从父页面传过到子页面的内容'
}
}
}
</script>在子组件通过props进行接收,注意子组件props里面接收的对象名称必须与父组件中在子组件绑定的名称一致,当前例子为“message”,可以在组件return中this.的方式使用props里面的值。
<template>
<div class="children-box">
<div>
<div>我是子页面</div>
<div>{{message}}</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:"Children",
props:{
message:{
type:String, //类型判断
default:'' //默认值
}
}
}
</script>子组件接收到父组件传过来的内容,实现效果如下图所示:

子 >>> 父 ($emit)
在子组件中通过this.$emit()方法向父组件通信,如下,点击触发事件,执行this.$emit('fromChildMethod'),触发父组件的fromChildMethod方法。
<template>
<div class="children-box">
<div>
<div>我是子页面</div>
<div>{{message}}</div>
<div><span @click="toParentMethod">点击触发父页面事件</span></div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:"Children",
props:{
message:{
type:String,
default:''
}
},
methods:{
toParentMethod(){
this.$emit('fromChildMethod')
}
}
}
</script>在父组件的子组件上绑定fromChildMethod方法,对该方法进行监听,当该方法触发时,执行父组件中相应的方法fromChild。
<template>
<div class="parent-box">
<div>
<div>我是父页面</div>
<div style="font-size:12px;">{{message}}</div>
<div style="font-size:12px;color:red">{{fromChildMsg}}</div>
</div>
<children :message="toChildrenMsg" @fromChildMethod="fromChild"></children>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Children from './Children.vue'
export default {
name:"Parent",
components:{
Children
},
data(){
return {
message:'我是父页面的内容',
toChildrenMsg:'从父页面传过到子页面的内容',
fromChildMsg:''
}
},
methods:{
fromChild(){
this.fromChildMsg = '子页面触发的方法' //监听到子组件触发的方法,显示该内容
}
}
}
</script>当点击子组件的对应的span,触发方法,向父组件进行通知。


小结:父传子,props;子传父,this.$emit();触发、监听名称须一致。
2、Bus事件总线
真实的场景中,组件不仅仅是“父子”关系,还有“兄弟”关系跟跨层级组件等等。这时候props跟$emit可能就不太适用了,这时候它出现了,那就是Bus(事件总线),父子组件同样适用。
Bus之触发$emit、监听$on、关闭$off,主要用到的就是$emit跟$on。
先在项目中新建一个文件夹bus,里面有个index.js文件,创建一个新的Vue实例,然后导出模块。
接下来import这个新的Vue实例,也就是bus,常用的两种导入方式,一种是全局导入,另外一种是局部导入(需每个组件都导入一次)。以下为全局导入,在main.js里面将该bus作为当前Vue实例的原型方法,能直接在各组件里面通过this.bus的方式调用。
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import bus from './bus/index'
Vue.prototype.bus = bus
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})下面展示实现bus通信过程,场景为父子,同样的,兄弟、跨层级用法与其类似:
Parent组件中向Children组件通信,通过this.bus.$emit()触发
<template>
<div class="parent-box">
<div>
<div>我是父页面</div>
<div @click="toChildBus"><span>向子组件通信</span></div>
</div>
<children></children>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Children from './Children.vue'
export default {
name:"Parent",
components:{
Children
},
methods:{
toChildBus(){
let val = '父组件向子组件通信'
this.bus.$emit('toChild',val) //val为传过去的值,非必传
}
}
}
</script>Children组件监听Parent组件触发的事件(在mounted阶段进行绑定监听),注意事件名称要一致,通过this.bus.$on()监听,当总线中监听到触发该方法,拿到传过来的值(也可以在里面执行自定义方法)。
<template>
<div class="children-box">
<div>
<div>我是子页面</div>
<div style="font-size:12px;color:blue;">{{fromParentMsg}}</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:"Children",
data(){
return {
fromParentMsg:''
}
},
mounted(){
this.bus.$off('toChild')
this.bus.$on('toChild',val=>{
this.fromParentMsg = val //此处为复制操作,也可在里面执行相应的方法
})
}
}
</script>效果图:


总结:父子,兄弟,跨级(祖孙等)通信写法相同,就不一一举例了,都是通过this.bus.$emit()触发,通过this.bus.$on()监听,执行相应的操作,切记:触发、监听名称必须相同!
3、Vuex状态管理库
Vuex相当于一个仓库,你可以往仓库里面放一些东西,保持存进去的时的状态,可以修改,也可以在需要的时候取出,是一个全局状态。本次只讲如何使用vuex进行通信,不深究其原理。
安装vuex
npm install vuex --save这里我新建一个文件夹,名称为store,里面有一个index.js文件,创建一个Vuex.Store实例,然后导出这个实例,从图中可以明确看出store的大致结构及其要素,具体不展开讲,关于vuex的相关文章数不胜数,可以自行去了解,这里主要讲大致用法。
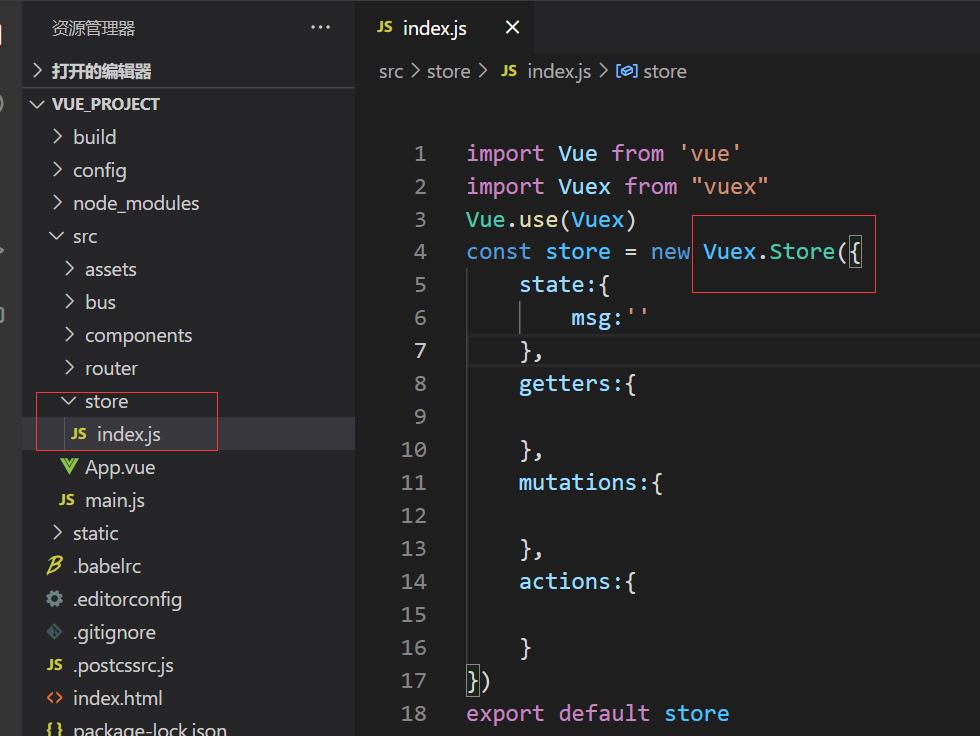
在mian.js全局引入,之后就可以直接使用了。
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import bus from './bus/index'
import store from './store/index'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.prototype.bus = bus
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})方式一,this.$store.state.xxx,直接对state进行操作,在一个组件mounted阶段将值存如store中,当然也可在你想在的方法中进行操作。
<template>
<div class="parent-box">
<div>
<div>我是父页面</div>
</div>
<children></children>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Children from './Children.vue'
export default {
name:"Parent",
components:{
Children
},
data(){
return {
fromChildMsg:''
}
}
mounted(){
this.$store.state.msg = '父组件存入' //在此处通过方式一存起来
}
}
</script>其他组件从store中取出,当然同样也可以进行修改。
<template>
<div class="children-box">
<div>
<div>我是子页面</div>
<div @click="fromStore"><span>从store里面取</span></div>
<div>{{fromStoreMsg}}</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:"Children",
data(){
return {
fromStoreMsg:''
}
},
methods:{
fromStore(){
this.fromStoreMsg = this.$store.state.msg
}
}
}
</script>效果图:


方式二,通过this.$store.getters.xxx、mapGetters进行取出。
// store/index.js
getters:{
getMsg:state=>{
return state.msg
}
},
//组件中取
this.$store.getters.getMsg
//也可以用mapGetters的方式
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapGetters(['getMsg'])
},对store存入数据该可以用mutations、actions(可异步)进行存入,具体就不展开了,有兴趣可以自己去深究。
4、Router
可以通过动态路由、路由跳转方式进行传值,如this.$router.push({path:'xxx',query:{value:'xxx'}}),在跳转的时候顺便传值,通过this.$route.params.value和this.$route.query.value获取到传过来的参数。该方式有局限性,只能在相互跳转的组件通信取值,且直接在跳转之后的页面进行刷新取不到值,视情况而用。
5、缓存
sessionStorage、localStorage、cookie
多个组件之间的通信除了可以用bus、store之外,还比较一种常用的方式--缓存,在同一个窗口不关闭的情况下,该窗口下的其他组件都可以取到缓存中已经存好的值,利用sessionStorage.setItem(key,value)、localStorage.setItem(key,value)等将值存起来,其他组件可以通过sessionStorage.getItem(key)、localStorage.getItem(key)等方式拿到,多个页面共享缓存数据,刷新页面数据不会销毁,可以用sessionStorage.removeItem(key)、localStorage.removeItem(key)的方式将缓存移除,可用场景还是比较多的。
总结:大致介绍vue组件中几种常用的通信、传值方式,考虑不同的场景使用不同的方式,提高开发效率,减少bug的产生。
ps:该文原创,若有错误不足之处还请不吝赐教;若觉得对您有些许帮助,一键三连可好?
以上是关于Vue3 和Vue2的组件通信方式,建议收藏的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章