大数据中的数据类型
Posted 曹军
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了大数据中的数据类型相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一:概述
1.数据类型
<key,value>频繁的在磁盘中进行读写,所以需要重新定义数据类型。
数据类型都实现Writable接口,以便使用这些类型对数据进行序列化,方便网络传输和文件存储。
2.基本数据类型
BooleanWritable
ByteWritable
DoubleWritable
FloatWritable
IntWritable
LongWritable
Text
NullWritable
3.数据类型中要实现的两种接口
1).Writable
value必须实现。
write()把每个对象序列化到输出流
readFileds()是把输入流字节反序列化
2).WritableComparable
这个是一个新接口,将Writable与Comparable接口封装在一起形成的新接口。
key必须实现。
实现了两个接口。
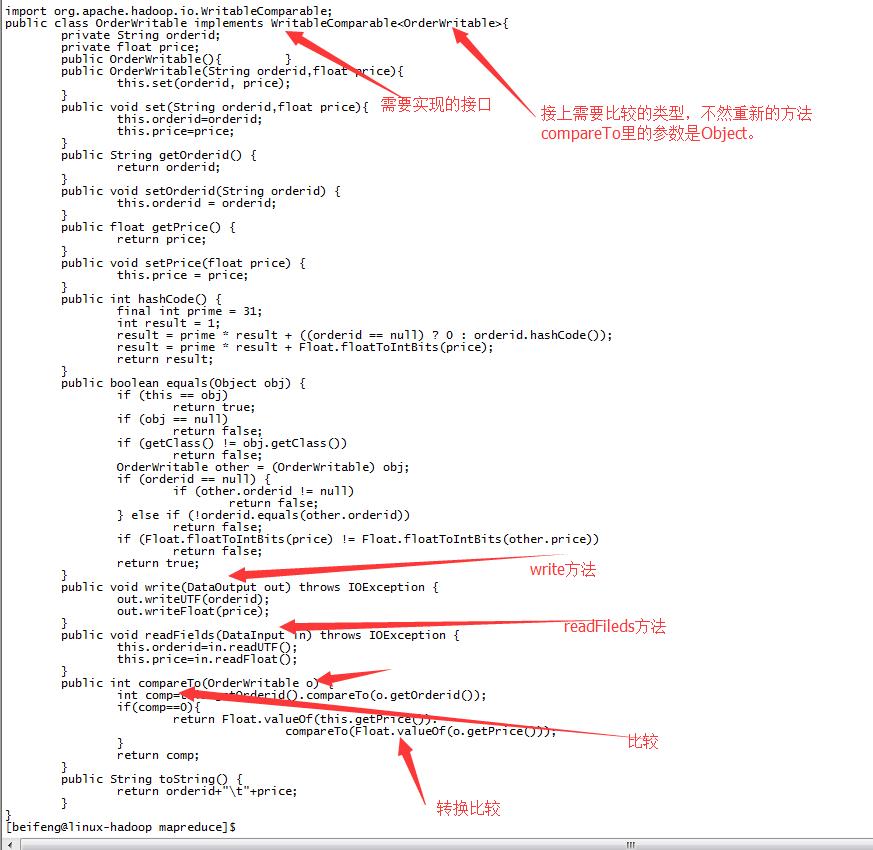
二:自定义数据类型
1.要求
User,Order类。
必须实现toString(),hashCode(),equals()。
2.实现实例UserWritable

3.实现实例OrderWritable
三:完整代码
1.UserWritable
1 package com.senior.type; 2 3 import java.io.DataInput; 4 import java.io.DataOutput; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable; 8 9 public class UserWritable implements Writable{ 10 11 private int id; 12 private String name; 13 public UserWritable(){} 14 public UserWritable(int id,String name){ 15 this.id=id; 16 this.name=name; 17 } 18 public int getId() { 19 return id; 20 } 21 public void setId(int id) { 22 this.id = id; 23 } 24 public String getName() { 25 return name; 26 } 27 public void setName(String name) { 28 this.name = name; 29 } 30 //write 31 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 32 out.writeInt(id); 33 out.writeUTF(name); 34 } 35 //readFields 36 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 37 this.id=in.readInt(); 38 this.name=in.readUTF(); 39 } 40 //toString 41 @Override 42 public String toString() { 43 return "UserWritable [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + "]"; 44 } 45 //hashCode 46 @Override 47 public int hashCode() { 48 final int prime = 31; 49 int result = 1; 50 result = prime * result + id; 51 result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); 52 return result; 53 } 54 //equals 55 @Override 56 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 57 if (this == obj) 58 return true; 59 if (obj == null) 60 return false; 61 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 62 return false; 63 UserWritable other = (UserWritable) obj; 64 if (id != other.id) 65 return false; 66 if (name == null) { 67 if (other.name != null) 68 return false; 69 } else if (!name.equals(other.name)) 70 return false; 71 return true; 72 } 73 74 }
2.OrderWritable
1 package com.senior.type; 2 3 import java.io.DataInput; 4 import java.io.DataOutput; 5 import java.io.IOException; 6 7 import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; 8 9 public class OrderWritable implements WritableComparable<OrderWritable>{ 10 private String orderId; 11 private float price; 12 public OrderWritable(){} 13 public OrderWritable(String orderId,float price){ 14 this.orderId=orderId; 15 this.price=price; 16 } 17 public String getOrderId() { 18 return orderId; 19 } 20 public void setOrderId(String orderId) { 21 this.orderId = orderId; 22 } 23 public float getPrice() { 24 return price; 25 } 26 public void setPrice(float price) { 27 this.price = price; 28 } 29 30 //write 31 public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { 32 out.writeUTF(orderId); 33 out.writeFloat(price); 34 } 35 //readFields 36 public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { 37 in.readUTF(); 38 in.readFloat(); 39 } 40 41 //compareTo 42 public int compareTo(OrderWritable o) { 43 int comp=this.getOrderId().compareTo(o.getOrderId()); 44 if(comp==0){ 45 return Float.valueOf(this.getPrice()).compareTo(Float.valueOf(o.getPrice())); 46 } 47 return comp; 48 } 49 50 //toString 51 @Override 52 public String toString() { 53 return "OrderWritable [orderId=" + orderId + ", price=" + price + "]"; 54 } 55 //hashCode 56 @Override 57 public int hashCode() { 58 final int prime = 31; 59 int result = 1; 60 result = prime * result + ((orderId == null) ? 0 : orderId.hashCode()); 61 result = prime * result + Float.floatToIntBits(price); 62 return result; 63 } 64 //equals 65 @Override 66 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 67 if (this == obj) 68 return true; 69 if (obj == null) 70 return false; 71 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 72 return false; 73 OrderWritable other = (OrderWritable) obj; 74 if (orderId == null) { 75 if (other.orderId != null) 76 return false; 77 } else if (!orderId.equals(other.orderId)) 78 return false; 79 if (Float.floatToIntBits(price) != Float.floatToIntBits(other.price)) 80 return false; 81 return true; 82 } 83 84 // 85 86 87 88 89 90 }
以上是关于大数据中的数据类型的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Android 上的 Kotlin:如何在片段中使用数据库中的 LiveData?
如何从 Firebase 获取数据到 Recyclerview 中的片段?