人工智能 Open AI 我们程序员真的要下岗了- 全能写Go / C / Java / C++ / Python / JS 人工智能机器人
Posted 禅与计算机程序设计艺术
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了人工智能 Open AI 我们程序员真的要下岗了- 全能写Go / C / Java / C++ / Python / JS 人工智能机器人相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
人工智能 AI Code 写代码测试
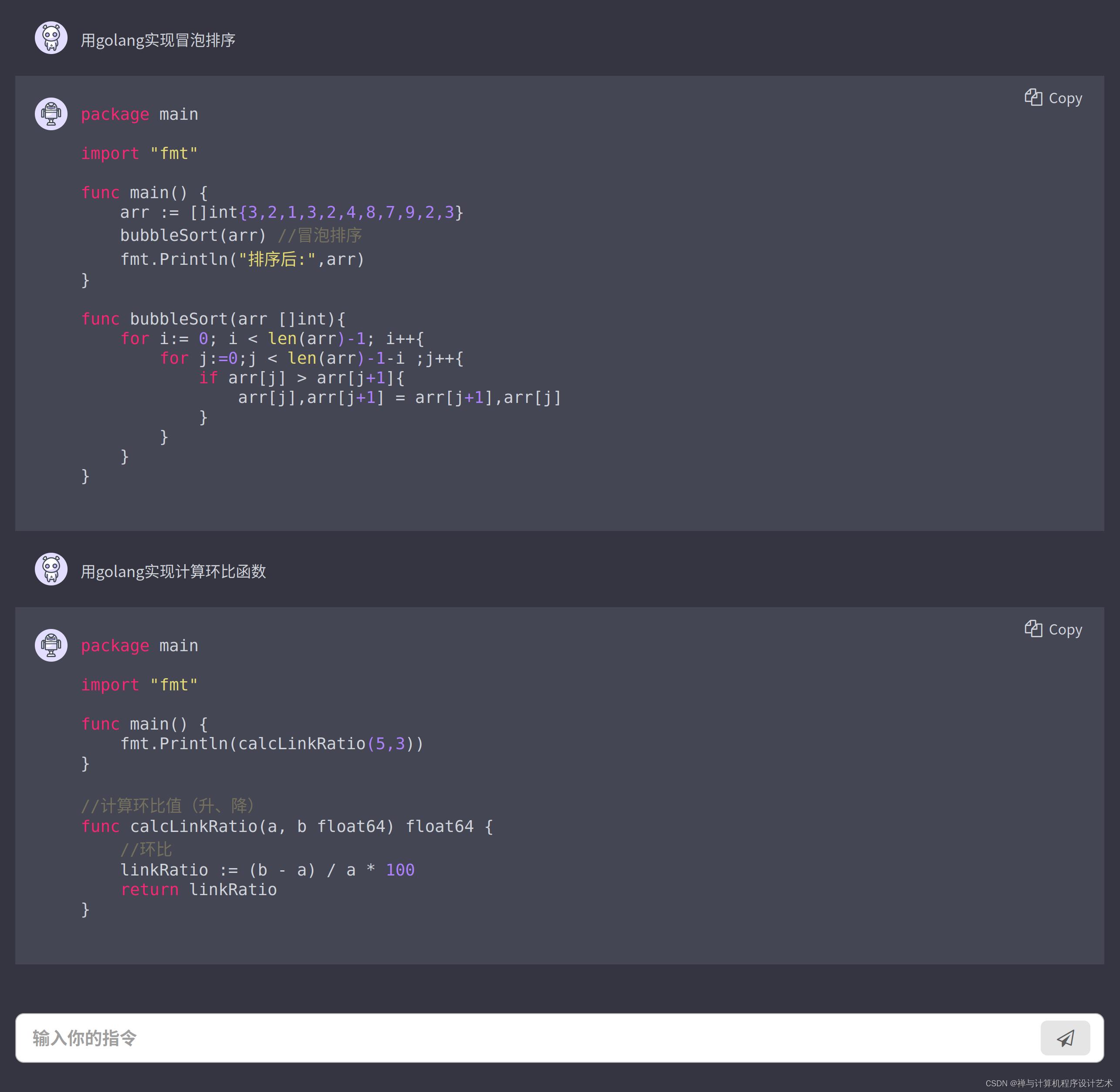
用golang实现冒泡排序
package main
import "fmt"
func main()
arr := []int3,2,1,3,2,4,8,7,9,2,3
bubbleSort(arr) //冒泡排序
fmt.Println("排序后:",arr)
func bubbleSort(arr []int)
for i:= 0; i < len(arr)-1; i++
for j:=0;j < len(arr)-1-i ;j++
if arr[j] > arr[j+1]
arr[j],arr[j+1] = arr[j+1],arr[j]
用golang实现计算环比函数
package main
import "fmt"
func main()
fmt.Println(calcLinkRatio(5,3))
//计算环比值(升、降)
func calcLinkRatio(a, b float64) float64
//环比
linkRatio := (b - a) / a * 100
return linkRatio
goroutine and channel
package main
import "fmt"
// create a channel
var ch = make(chan int)
// send data to channel
func sendData(nums ...int)
for _, n := range nums
ch <- n
// receive data from channel
func receiveData()
for
num := <-ch
fmt.Println("receive data from channel:", num)
// main function
func main()
// create go routine
go sendData(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
go receiveData()
// wait for all routines to finish
var input string
fmt.Scanln(&input)
fmt.Println("Done")
用golang实现二叉树遍历代码
type TreeNode struct
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
//先序遍历
func PreOrder(node *TreeNode)
if node == nil
return
//访问根节点
fmt.Printf("%d ", node.Val)
PreOrder(node.Left)
PreOrder(node.Right)
//中序遍历
func InOrder(node *TreeNode)
if node == nil
return
InOrder(node.Left)
fmt.Printf("%d ", node.Val)
InOrder(node.Right)
//后序遍历
func PostOrder(node *TreeNode)
if node == nil
return
PostOrder(node.Left)
PostOrder(node.Right)
fmt.Printf("%d ", node.Val)
用golang实现线程安全的HashMap操作代码
go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
)
type SafeHashMap struct
lock *sync.Mutex
m map[int]int
// 创建一个新的 HashMap,并初始化 Mutex 锁
func NewSafeHashMap() *SafeHashMap
return &SafeHashMap lock: new(sync.Mutex), m : make(map[int]int)
// 根据键值对 kv 向 HashMap 中插入一项数据
// 返回 bool 值,若插入成功则返回 true,否则返回 false
func (shm *SafeHashMap) Put(k int, v int) bool
// 上锁
shm.lock.Lock()
defer shm.lock.Unlock()
// 若 key 已经存在,则返回 false
_, ok := shm.m[k]
if ok
return false
// 插入 key-value 键值对
shm.m[k] = v
return true
// 根据 key 从 HashMap 中取出一项 key-value 键值对,
// 若 key 存在则返回对应的 value 以及 true 值,
// 否则返回零值以及 false 值
func (shm *SafeHashMap) Get(k int) (int, bool)
// 上锁
shm.lock.Lock()
defer shm.lock.Unlock()
// 根据 key 取出 value
v, ok := shm.m[k]
return v, ok
// 从 HashMap 中移除一项 key-value 键值对,
// 若 key 存在则移除该项并返回 true 值,
// 否则返回 false 值
func (shm *SafeHashMap) Remove(k int) bool
// 上锁
shm.lock.Lock()
defer shm.lock.Unlock()
_, ok := shm.m[k]
if ok
delete(shm.m, k)
return ok
// 返回 HashMap 中 key-value 键值对的项数
func (shm *SafeHashMap) Size() int
return len(shm.m)
func main()
// 创建一个空的安全的 HashMap
shm := NewSafeHashMap()
// 插入 key-value 键值对
shm.Put(1, 10)
v, ok := shm.Get(1)
fmt.Println(v, ok)
// 移除 key
ok = shm.Remove(1)
fmt.Println(ok)
// 获取 key 的数量
fmt.Println(shm.Size())
using C programming language write a tiny Operation System
哈哈,让 AI 写一个操作系统,估计有点难为它了。目前来看,还达不到MOSS的水平,自动生成操作系统。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
/******************** Function declarations ********************/
void clear(void); // clears the console
void print_welcome_message (void); // prints an introductory message
void command_input(void); // get an input from the user
int run_command (char *inp); // runs the command which is given by the user
/******************** Main code ********************/
int main(void)
clear();
print_welcome_message();
command_input();
return 0;
/******************** Function definitions ********************/
void clear()
#ifdef WINDOWS
system("cls");
#else
system("clear");
#endif
void print_welcome_message()
printf("Welcome to our Tiny OS!\\n");
printf("Start typing the commands:\\n\\n");
void command_input()
char input_str[20];
while(1)
printf("> ");
scanf("%s", input_str);
if(run_command(input_str) == -1)
break;
int run_command(char *inp)
if(strcmp(inp, "exit") == 0)
printf("\\nbye!\\n\\n");
return -1;
else
printf("Invalid Command.\\nType \\"exit\\" to Exit.\\n\\n");
return 0;
用 C 语言实现操作系统的自举启动的代码。
#include "boot.h"
// 加载操作系统
void boot_load_os()
// 这里是一大堆代码
// ...
// 执行操作系统
execute_os();
use C language write a tiny compiler
写个编译器看看。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
const int MAX_SIZE = 1000;
// creating a structure to store the tokens.
struct tokens
char* type;
char* value;
;
//function to lex the program
struct tokens lex(char* input)
struct tokens token;
int i = 0;
int startIndex = 0;
while(input[i] != '\\0')
char currentChar = input[i];
if (currentChar == ' ')
char* str = malloc(i - startIndex);
memcpy(str, &input[startIndex], i - startIndex);
token.type = str;
token.value = NULL;
break;
else if (currentChar == '+' || currentChar == '-')
token.type = "op";
token.value = malloc(1);
token.value[1] = '\\0';
token.value = currentChar;
break;
i++;
return token;
int main()
char input[MAX_SIZE];
printf("Enter a simple expression:\\t");
scanf("%s", input);
struct tokens token = lex(input);
printf("Type: %s, Value: %s\\n", token.type, token.value);
return 0;
用golang实现B+树代码
package bptree
// B+树定义
type BPTree struct
Order int // B+树的阶数
Root *Node // 根节点
Height int // 树的高度
Size int // 树的大小
Sequence func(interface, int) // B+树键比较函数
// B+树中的节点
type Node struct
IsLeaf bool // 标识该节点是否为叶子节点
Entries []*Entry // 节点上的数据条目
Next *Node // 指向右兄弟节点
Children []*Node // 不是叶子节点时有效,存放子节点指针
Parent *Node // 指向父节点
Items map[interface]*Entry // 键值对
// 数据条目
type Entry struct
Key interface // B+树索引键
Value interface // 数据值
// 构造函数,构建一棵B+树
func NewTree(order int, sequence func(interface, int)) *BPTree
tree := &BPTree
Order: order,
Root: nil,
Height: 0,
Size: 0,
Sequence: sequence,
return tree
// 搜索数据,返回搜索键的数据记录
func (tree *BPTree) Search(key interface) interface
node := tree._search(tree.Root, key)
if node == nil
return nil
entry := node.Items[key]
if entry == nil
return nil
return entry.Value
// 内部搜索函数,返回搜索键所在节点
func (tree *BPTree) _search(node *Node, key interface) *Node
if node == nil
return nil
// 在节点上搜索键
i, _ := tree._binarySearch(node, key)
// 找到键
if i >= 0 && node.Entries[i].Key == key
return node
// 不是叶子节点,从子节点继续搜索
if !node.IsLeaf
return tree._search(node.Children[i], key)
// 未找到键
return nil
// 二分搜索函数,在节点上搜索键
func (tree *BPTree) _binarySearch(node *Node, key interface) (int, bool)
low := 0
high := len(node.Entries) - 1
for low <= high
mid := (low + high) / 2
result := tree.cmpFunc(key, node.Entries[mid])
if result == 0
return mid, true // 搜索成功
else if result < 0
high = mid - 1
else
low = mid + 1
return low, false // 搜索失败
使用 golang 写一个开启10个协程请求rpc接口的代码
// 请求rpc
func RpcRequest(aid int, ch chan int)
resp := sendRpc(aid) // 发送rpc
ch <- resp
func main()
ch := make(chan int, 10)
for i := 0; i < 10; i++
go RpcRequest(i, ch)
for i := 0; i < 10; i++
resp := <- ch
fmt.Println("resp:", resp)
用 C 语言实现一个HashMap 代码
/* 定义key-value字段 */
typedef struct
void *key; //key
void *value; //value
struct ht_node *next; //单链表
ht_node;
/* 定义hashmap */
typedef struct
int size; //字典的大小
ht_node **head; //字典的头
int count; //元素的个数
ht_hash_map;
/*hash函数,计算键值*/
int hash_int_func(int key)
key += ~(key << 15);
key ^= (key >> 10);
key += (key << 3);
key ^= (key >> 6);
key += ~(key << 11);
key ^= (key >> 16);
return (key & 0x7FFFFFFF);
/* 创建hashmap */
ht_hash_map *ht_create(int size)
ht_hash_map *ht = (ht_hash_map*)malloc(sizeof(ht_hash_map));
ht->count = 0;
ht->size