Nginx学习整理
Posted zch981964
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Nginx学习整理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
nginx学习
- 第一章 Nginx概述
- 第二章 Nginx单实例安装
- 第三章 Nginx正向代理、反向代理
- 第四章 Nginx负载均衡
- 第五章 Nginx动静分离
- 第六章 Nginx高可用集群
- 第七章 Nginx配置详解
- 第八章 Nginx原理分析
第一章 Nginx概述
1.1、Nginx概述
Nginx (“engine x”) 是一个高性能的 HTTP 和反向代理服务器,特点是占有内存少,并发能力强,事实上 Nginx 的并发能力确实在同类型的网页服务器中表现较好,中国大陆使用 Nginx 网站用户有:百度、京东、新浪、网易、腾讯、淘宝等。
1.2、Nginx官网
官网地址:点击打开
1.3、Nginx用处
- Nginx 可以作为静态页面的 web 服务器,同时还支持 CGI 协议的动态语言,比如 perl、php 等。但是不支持 Java。Java 程序只能通过与 tomcat 配合完成。
- Nginx 专为性能优化而开发,性能是其最重要的考量,实现上非常注重效率,能经受高负载的考验,有报告表明能支持高达 50000 个并发连接数。
第二章 Nginx单实例安装
2.1、环境说明
- 模拟工具:VMware-workstation-full-15.5.6-16341506.exe
- 操作系统:CentOS-6.10-x86_64-bin-DVD1.iso、纯净安装、桌面版
- 内存大小:2GB
- 连接工具:SecureCRT
2.2、安装依赖
[root@caochenlei ~]# yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ make libtool wget pcre pcre-devel zlib zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel
2.3、Nginx下载
[root@caochenlei ~]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
2.4、Nginx解压
[root@caochenlei ~]# tar -zxvf nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
2.5、Nginx安装
[root@caochenlei ~]# cd nginx-1.18.0
[root@caochenlei nginx-1.18.0]# ./configure
[root@caochenlei nginx-1.18.0]# make && make install
注意:安装完成后的路径为:/usr/local/nginx
2.6、Nginx命令
- 普通启动服务:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 配置文件启动:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- 暴力停止服务:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
- 优雅停止服务:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit
- 检查配置文件:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
- 重新加载配置:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
- 查看相关进程:ps -ef | grep nginx
2.7、开放防火墙
[root@caochenlei ~]# /sbin/iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
[root@caochenlei ~]# /etc/rc.d/init.d/iptables save
iptables:将防火墙规则保存到 /etc/sysconfig/iptables:[确定]
2.8、启动后效果

nginx默认端口为80,直接用本机ip地址即可访问。
第三章 Nginx正向代理、反向代理
3.1、概述
-
正向代理
Nginx 不仅可以做反向代理,实现负载均衡。还能用作正向代理来进行上网等功能。 正向代理:如果把局域网外的 Internet 想象成一个巨大的资源库,则局域网中的客户端要访 问 Internet,则需要通过代理服务器来访问,这种代理服务就称为正向代理。简单一点:通过代理服务器来访问服务器的过程 就叫 正向代理。
需要在客户端配置代理服务器进行指定网站访问 -
反向代理
反向代理,其实客户端对代理是无感知的,因为客户端不需要任何配置就可以访问。
我们只 需要将请求发送到反向代理服务器,由反向代理服务器去选择目标服务器获取数据后,在返 回给客户端,此时反向代理服务器和目标服务器对外就是一个服务器,暴露的是代理服务器 地址,隐藏了真实服务器 IP 地址。
3.2、反向代理配置实例1
3.2.1、实现效果
打开浏览器,在浏览器地址栏输入地址:http://www.123.com,跳转到 Liunx 系统 Tomcat 主页面中。

3.2.2、实现思路

3.2.3、实现步骤
步骤一:修改Windows中的hosts域名映射
复制“ C:\\Windows\\System32\\drivers\\etc\\hosts ”到桌面,右键记事本打开,在里边加上以下代码保存,然后再复制回去,不要直接修改,会不让保存!
#虚拟机域名 映射的网址
192.168.206.128 www.123.com
步骤二:修改Nginx中的配置文件并启动
[root@caochenlei ~]# vi /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.206.128;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location /
proxy_pass http:127.0.0.1:8080;
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
步骤三:下载Tomcat、解压Tomcat、安装Tomcat、启动Tomcat
注意:Tomcat启动需要JDK,在这里我没有安装,使用系统自带的OpenJDK Runtime Environment (rhel-2.6.14.10.el6-x86_64 u181-b00)
下载:
[root@caochenlei ~]# wget https://mirror.bit.edu.cn/apache/tomcat/tomcat-7/v7.0.105/bin/apache-tomcat-7.0.105.tar.gz
解压:
[root@caochenlei ~]# tar -zxvf apache-tomcat-7.0.105.tar.gz
安装:
[root@caochenlei ~]# mv apache-tomcat-7.0.105 /usr/local/tomcat
启动:
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh
添加到防火墙:
[root@caochenlei ~]# /sbin/iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
[root@caochenlei ~]# /etc/rc.d/init.d/iptables save
如果关闭请用:
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh
3.2.4、关闭服务
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh
3.3、反向代理配置实例2
3.3.1、实现效果
使用 nginx 反向代理,根据访问的路径跳转到不同端口的服务中。

3.3.2、实现思路
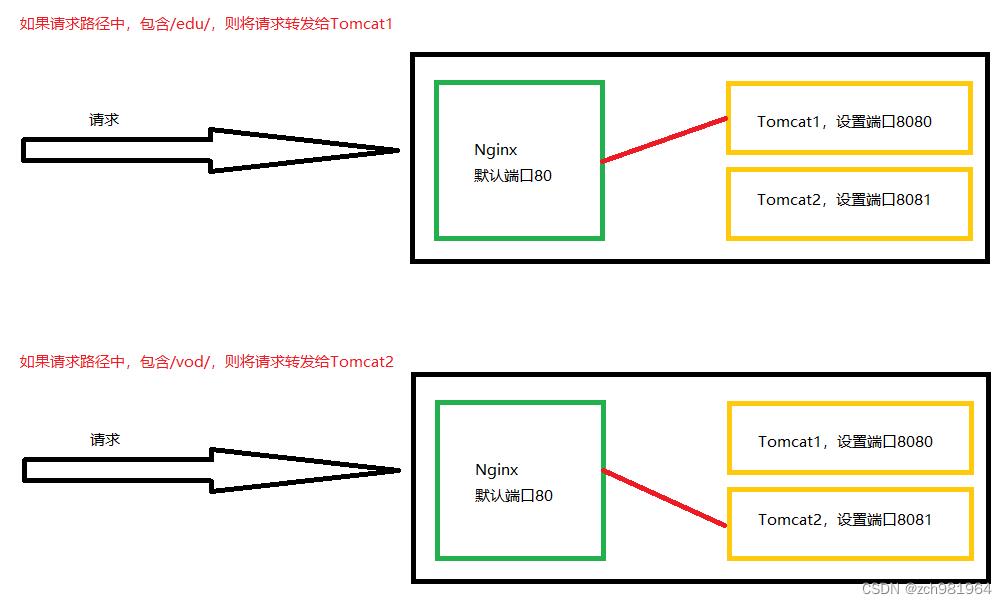
3.3.3、实现步骤
步骤一:修改Nginx的配置文件,然后启动
[root@caochenlei ~]# vi /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.206.128;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location ~ /edu/
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
location ~ /vod/
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8081;
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
步骤二:拷贝两个Tomcat,将其中一个的端口信息修改为8081,开启防火墙,然后分别启动这两台Tomcat
解压:
[root@caochenlei ~]# tar -zxvf apache-tomcat-7.0.105.tar.gz
[root@caochenlei ~]# mv apache-tomcat-7.0.105 /usr/local/tomcat1
[root@caochenlei ~]# tar -zxvf apache-tomcat-7.0.105.tar.gz
[root@caochenlei ~]# mv apache-tomcat-7.0.105 /usr/local/tomcat2
删除:
[root@caochenlei ~]# rm -f /usr/local/tomcat2/conf/server.xml
添加:
[root@caochenlei ~]# vi /usr/local/tomcat2/conf/server.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
<!-- Note: A "Server" is not itself a "Container", so you may not
define subcomponents such as "Valves" at this level.
Documentation at /docs/config/server.html
-->
<Server port="8006" shutdown="SHUTDOWN">
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.startup.VersionLoggerListener" />
<!-- Security listener. Documentation at /docs/config/listeners.html
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.security.SecurityListener" />
-->
<!--APR library loader. Documentation at /docs/apr.html -->
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener" SSLEngine="on" />
<!--Initialize Jasper prior to webapps are loaded. Documentation at /docs/jasper-howto.html -->
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JasperListener" />
<!-- Prevent memory leaks due to use of particular java/javax APIs-->
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener" />
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.ThreadLocalLeakPreventionListener" />
<!-- Global JNDI resources
Documentation at /docs/jndi-resources-howto.html
-->
<GlobalNamingResources>
<!-- Editable user database that can also be used by
UserDatabaseRealm to authenticate users
-->
<Resource name="UserDatabase" auth="Container"
type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase"
description="User database that can be updated and saved"
factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory"
pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml" />
</GlobalNamingResources>
<!-- A "Service" is a collection of one or more "Connectors" that share
a single "Container" Note: A "Service" is not itself a "Container",
so you may not define subcomponents such as "Valves" at this level.
Documentation at /docs/config/service.html
-->
<Service name="Catalina">
<!--The connectors can use a shared executor, you can define one or more named thread pools-->
<!--
<Executor name="tomcatThreadPool" namePrefix="catalina-exec-"
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="4"/>
-->
<!-- A "Connector" represents an endpoint by which requests are received
and responses are returned. Documentation at :
Java HTTP Connector: /docs/config/http.html (blocking & non-blocking)
Java AJP Connector: /docs/config/ajp.html
APR (HTTP/AJP) Connector: /docs/apr.html
Define a non-SSL HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8080
-->
<Connector port="8081" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8444" />
<!-- A "Connector" using the shared thread pool-->
<!--
<Connector executor="tomcatThreadPool"
port="8081" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8444" />
-->
<!-- Define an SSL HTTP/1.1 Connector on port 8443
This connector uses the BIO implementation that requires the JSSE
style configuration. When using the APR/native implementation, the
OpenSSL style configuration is required as described in the APR/native
documentation -->
<!--
<Connector port="8444" protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Protocol"
maxThreads="150" SSLEnabled="true" scheme="https" secure="true"
clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS" />
-->
<!-- Define an AJP 1.3 Connector on port 8009 -->
<!--
<Connector protocol="AJP/1.3"
address="::1"
port="8010"
redirectPort="8444" />
-->
<!-- An Engine represents the entry point (within Catalina) that processes
every request. The Engine implementation for Tomcat stand alone
analyzes the HTTP headers included with the request, and passes them
on to the appropriate Host (virtual host).
Documentation at /docs/config/engine.html -->
<!-- You should set jvmRoute to support load-balancing via AJP ie :
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost" jvmRoute="jvm1">
-->
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost">
<!--For clustering, please take a look at documentation at:
/docs/cluster-howto.html (simple how to)
/docs/config/cluster.html (reference documentation) -->
<!--
<Cluster className="org.apache.catalina.ha.tcp.SimpleTcpCluster"/>
-->
<!-- Use the LockOutRealm to prevent attempts to guess user passwords
via a brute-force attack -->
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm">
<!-- This Realm uses the UserDatabase configured in the global JNDI
resources under the key "UserDatabase". Any edits
that are performed against this UserDatabase are immediately
available for use by the Realm. -->
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm"
resourceName="UserDatabase"/>
</Realm>
<Host name="localhost" appBase="webapps"
unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">
<!-- SingleSignOn valve, share authentication between web applications
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html -->
<!--
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.authenticator.SingleSignOn" />
-->
<!-- Access log processes all example.
Documentation at: /docs/config/valve.html
Note: The pattern used is equivalent to using pattern="common" -->
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"
prefix="localhost_access_log." suffix=".txt"
pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" />
</Host>
</Engine>
</Service>
</Server>
开启Tomcat2的防火墙:
[root@caochenlei ~]# /sbin/iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 8081 -j ACCEPT
[root@caochenlei ~]# /etc/rc.d/init.d/iptables save
在每一个Tomcat的webapps中创建一个文件夹和一个a.html文件:
[root@caochenlei ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/tomcat1/webapps/edu
[root@caochenlei ~]# echo "<h1>This is 8080 Port</h1>" > /usr/local/tomcat1/webapps/edu/a.html
[root@caochenlei ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/tomcat2/webapps/vod
[root@caochenlei ~]# echo "<h1>This is 8081 Port</h1>" > /usr/local/tomcat2/webapps/vod/a.html
启动:
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat1/bin/startup.sh
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat2/bin/startup.sh
步骤三:打开本机浏览器进行测试
在浏览器输入 http://192.168.206.128/edu/a.html

在浏览器输入 http://192.168.206.128/vod/a.html

3.3.4、关闭服务
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat1/bin/shutdown.sh
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat2/bin/shutdown.sh
3.4、location指令说明
描述:该指令用于匹配URL
语法
- = :用于不含正则表达式的 uri 前,要求请求字符串与 uri 严格匹配,如果匹配 成功,就停止继续向下搜索并立即处理该请求。
- ~:用于表示 uri 包含正则表达式,并且区分大小写。
- ~*:用于表示 uri 包含正则表达式,并且不区分大小写。
- ^~:用于不含正则表达式的 uri 前,要求 Nginx 服务器找到标识 uri 和请求字 符串匹配度最高的 location 后,立即使用此 location 处理请求,而不再使用 location 块中的正则 uri 和请求字符串做匹配。
注意:如果 uri 包含正则表达式,则必须要有 ~ 或者 ~* 标识。
第四章 Nginx负载均衡
4.1、概述
客户端发送多个请求到服务器,服务器处理请求,有一些可能要与数据库进行交互,服务器处理完毕后,再将结果返回给客户端。
这种架构模式对于早期的系统相对单一,并发请求相对较少的情况下是比较适合的,成本也低。但是随着信息数量的不断增长,访问量和数据量的飞速增长,以及系统业务的复杂度增加,这种架构会造成服务器相应客户端的请求日益缓慢,并发量特别大的时候,还容易造成服务器直接崩溃。很明显这是由于服务器性能的瓶颈造成的问题,那么如何解决这种情况呢?
我们首先想到的可能是升级服务器的配置,比如提高 CPU 执行频率,加大内存等提高机器的物理性能来解决此问题,但是我们知道摩尔定律的日益失效,硬件的性能提升已经不能满足日益提升的需求了。最明显的一个例子,天猫双十一当天,某个热销商品的瞬时访问量是极其庞大的,那么类似上面的系统架构,将机器都增加到现有的顶级物理配置,都是不能够满足需求的。那么怎么办呢?
上面的分析我们去掉了增加服务器物理配置来解决问题的办法,也就是说纵向解决问题的办法行不通了,那么横向增加服务器的数量呢?这时候集群的概念产生了,单个服务器解决不了,我们增加服务器的数量,然后将请求分发到各个服务器上,将原先请求集中到单个服务器上的情况改为将请求分发到多个服务器上,将负载分发到不同的服务器,也就是我们所说的负载均衡。

4.2、实现效果
浏览器地址栏输入地址 http://192.168.206.128/edu/a.html,负载均衡效果,将请求平均到 8080 和 8081 端口中。

4.3、实现思路

4.4、实现步骤
第一步:修改Nginx的配置文件
[root@caochenlei ~]# vi /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
upstream myserver
server 192.168.206.128:8080;
server 192.168.206.128:8081;
server
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.206.128;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location /
proxy_pass http://myserver;
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
步骤二:在Tomcat2的webapps文件夹中,创建一个edu文件夹,在里边创建a.html
创建:
[root@caochenlei ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/tomcat2/webapps/edu
[root@caochenlei ~]# echo "<h1>This is 8081 Port</h1>" > /usr/local/tomcat2/webapps/edu/a.html
启动:
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat1/bin/startup.sh
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat2/bin/startup.sh
步骤三:测试效果
打开IE浏览器输入:http://192.168.206.128/edu/a.html
 打开IE浏览器输入: http://192.168.206.128/edu/a.html
打开IE浏览器输入: http://192.168.206.128/edu/a.html

4.5、关闭服务
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat1/bin/shutdown.sh
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat2/bin/shutdown.sh
4.6、分配策略
- 轮询(默认):
每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器 down 掉,能自动剔除。

- weight:
weight 代表权重,默认为1,权重越高被分配的客户端越多,weight 和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况。 例如:

- ip_hash:
每个请求按访问 ip 的 hash 结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,可以解决 session 的问题。 例如:

- fair(第三方):
按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。例如:

第五章 Nginx动静分离
5.1、概述
Nginx 动静分离简单来说就是把动态跟静态请求分开,不能理解成只是单纯的把动态页面和静态页面物理分离。严格意义上说应该是动态请求跟静态请求分开,可以理解成使用 Nginx 处理静态页面,Tomcat 处理动态页面。动静分离从目前实现角度来讲大致分为两种,一种是纯粹把静态文件独立成单独的域名,放在独立的服务器上,也是目前主流推崇的方案;另外一种方法就是动态跟静态文件混合在一起发布,通过 Nginx 来分开。
5.2、实现效果
如果不设置动静分离,默认会通过Nginx的反向代理去找Tomcat对应的资源,现在我们在根目录下创建一个/data/www/文件夹,里边放上静态资源,比如一个html页面,在8080的那台Tomcat的webapps下也创建一个www目录,同样是放一个静态资源,当输入这个静态资源的请求时,访问到的是/data/www中的数据

5.3、实现思路

5.4、实现步骤
第一步:创建静态资源文件,为了对比,tomcat中也放一个
[root@caochenlei ~]# mkdir -p /data/www/
[root@caochenlei ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/www
[root@caochenlei ~]# echo "<h1>/data/www/a.html</h1>" > /data/www/a.html
[root@caochenlei ~]# echo "<h1>/usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/www/a.html</h1>" > /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT/www/a.html
- 第二步:修改Nginx的配置文件
[root@caochenlei ~]# vi /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.206.128;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location /www/
root /data/;
index index.html index.htm;
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
- 步骤三:启动Tomcat
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh
第四步:启动浏览器进行测试
打开浏览器输入: http://192.168.206.128/www/a.html

5.5、关闭服务
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh
第六章 Nginx高可用集群
6.1、概述
前边我们学习了反向代理、负载均衡、动静分离,但试想一下,如果Nginx挂掉了,那么服务肯定就没有了,有没有一种解决方案,可以保证Nginx挂掉了,服务也可以照常使用,答案肯定是有的,这就是我们接下来要学习的高可用集群,采用的是一主一备的模式,当主节点Nginx挂掉,备份服务器Nginx立刻跟上,这样就保证了服务的高可用性。
6.2、实现效果
当主节点Nginx挂掉以后,服务依然可以正常使用。
6.3、实现思路

6.4、实现步骤
第一步:修改主节点上的Nginx的配置文件
[root@caochenlei ~]# vi /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
upstream myserver
server 192.168.206.128:8080;
server 192.168.206.128:8081;
server
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.206.128;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location /
proxy_pass http://myserver;
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
第二步:启动主节点上的两台Tomcat
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat1/bin/startup.sh
[root@caochenlei ~]# /usr/local/tomcat2/bin/startup.sh
第三步:安装主节点上的keepalived
安装keepalived:
[root@caochenlei ~]# yum install -y keepalived
删除keepalived的配置文件:
[root@caochenlei ~]# rm -f /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
新增keepalived的配置文件:
[root@caochenlei ~]# vi /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
注意:一定要注意router_id、state、interface的值,我就在这里踩坑了
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs
notification_email
acassen@firewall.loc
failover@firewall.loc
sysadmin@firewall.loc
notification_email_from Alexandre.Cassen@firewall.loc
#邮件服务器通知地址(暂不配置,默认即可)
smtp_server 192.168.200.1
#邮件服务器超时时间(暂不配置,默认即可)
smtp_connect_timeout 30
#当前虚拟机的IP地址
router_id 192.168.206.128
vrrp_script Monitor_Nginx
script "/etc/keepalived/nginx_check.sh" #检测脚本执行的路径
interval 2 #检测脚本执行的间隔
weight 2 #检测脚本执行的权重
vrrp_instance VI_1
state MASTER #标识这个机器是MASTER还是BACKUP
interface eth0 #当前机器的网卡名称
virtual_router_id 51 #虚拟路由的编号,主备必须一致
priority 100 #主、备机取不同的优先级,主机值较大,备份机值较小
advert_int 1 #(VRRP Multicast广播周期秒数)
authentication
auth_type PASS #(VRRP认证方式)
auth_pass 1111 #(密码)
track_script
Monitor_Nginx #(调用nginx进程检测脚本)
virtual_ipaddress
192.168.206.50 #虚拟IP地址
新增keepalived的检测脚本:
[root@caochenlei ~]# vi /etc/keepalived/nginx_check.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ "$(ps -ef | grep "nginx: master process" | grep -v grep )" == "" ]
then
killall keepalived
fi
启动keepalived服务:
[root@caochenlei ~]# service keepalived start
第五步:测试两个Nginx是否能正确的将请求分发到不同的Tomcat(负载均衡)
打开IE浏览器输入:http://192.168.206.128/edu/a.html

按住F5多刷新两遍,看看会不会,将请求转发到Tomcat2中去
 打开IE浏览器输入:http://192.168.206.129/edu/a.html
打开IE浏览器输入:http://192.168.206.129/edu/a.html

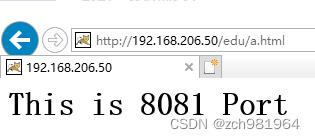
打开IE浏览器输入:http://192.168.206.50/edu/a.html,测试虚拟IP能不能实现负载均衡

按住F5多刷新两遍,看看会不会,将请求转发到Tomcat2中去
 经过测试,我们发现一主一从、虚拟IP都能正常的进行负载均衡,接下来我们测试主节点挂掉,从节点会不会自动顶上,打开主节点机器,查看相关进程,杀死Nginx,然后打开浏览器,输入配置的虚拟IP地址:http://192.168.206.50/edu/a.html,发现负载均衡的效果还在,说明配置成功了
经过测试,我们发现一主一从、虚拟IP都能正常的进行负载均衡,接下来我们测试主节点挂掉,从节点会不会自动顶上,打开主节点机器,查看相关进程,杀死Nginx,然后打开浏览器,输入配置的虚拟IP地址:http://192.168.206.50/edu/a.html,发现负载均衡的效果还在,说明配置成功了

6.5、关闭服务
主机节点
[root@caochenlei ~]# service keepalived stop以上是关于Nginx学习整理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章