Android ANR详解
Posted 一叶飘舟
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android ANR详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、什么是ANR?
ANR(Application Not responding),是指应用程序未响应,android系统对于一些事件需要在一定的时间范围内完成,如果超过预定时间能未能得到有效响应或者响应时间过长,都会造成ANR。一般地,这时往往会弹出一个提示框,告知用户当前xxx未响应,用户可选择继续等待或者Force Close。
哪些场景会造成ANR呢?
Service Timeout:前台服务在20s内未执行完成;
BroadcastQueue Timeout:前台广播在10s内未执行完成
ContentProvider Timeout:内容提供者在publish过超时10s;
InputDispatching Timeout:输入事件分发超时5s,包括按键和触摸事件。
二、ANR原理
发生ANR时会调用AppNotRespondingDialog.show()方法弹出对话框提示用户,该对话框的依次调用关系:
AppErrors.appNotResponding(); //ANR对话框的唯一入口
AMS.UiHandler.sendMessage(ActivityManagerService.SHOW_NOT_RESPONDING_UI_MSG);
AppErrors.handleShowAnrUi();
AppNotRespondingDialog.show();根据造成ANR的场景,产生ANR的来源可以总结为两大类:组件类ANR和Input ANR。
(一)Service超时机制
对于Service、Broadcast、Provider组件类的ANR而言,如果把发生ANR比作是引爆炸弹,那么整个流程包含三部分组成:
埋炸弹:中控系统(system_server进程)启动倒计时,在规定时间内如果目标(应用进程)没有干完所有的活,则中控系统会定向炸毁(杀进程)目标。
拆炸弹:在规定的时间内干完工地的所有活,并及时向中控系统报告完成,请求解除定时炸弹,则幸免于难。
引爆炸弹:中控系统立即封装现场,抓取快照,搜集目标执行慢的罪证(traces),便于后续调试分析,最后是炸毁目标。
bumpServiceExecutingLocked;
scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked; //监听Service运行时间
AMS.post(SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG); //记录executeingService并发送超时消息
ActiveServices.serviceTimeout; //判断是否超时
AppErrors.appNotResponding;bumpServiceExecutingLocked 在很多地方被调用:
requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord, IntentBindRecord, boolean, boolean)
realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord, ProcessRecord, boolean)
sendServiceArgsLocked(ServiceRecord, boolean, boolean)
bringDownServiceLocked(ServiceRecord)
removeConnectionLocked(ConnectionRecord, ProcessRecord, ActivityRecord)每个调用的地方都对应着Service的一个生命周期,也就是说Service的每个生命周期开始时都会调用到scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked用于监听Service运行的时间。
(二)输入事件超时机制
Input类型的ANR在日常开发中更为常见且更复杂,比如用户或者测试反馈,点击屏幕中的UI元素导致卡死。
与组件类ANR不同的是,Input类型的超时机制并非时间到了一定就会爆炸,而是处理后续上报事件的过程才会去检测是否该爆炸,所以更像是扫雷过程。
什么叫做扫雷呢,对于输入系统而言,即使某次事件执行时间超过预期的时长,只要用户后续没有再生成输入事件,那么也不需要ANR。而只有当新一轮的输入事件到来,此时正在分发事件的窗口(即App应用本身)迟迟无法释放资源给新的事件去分发,这时InputDispatcher才会根据超时时间,动态的判断是否需要向对应的窗口提示ANR信息。
InputDispatcher的源码实现中,整体的事件分发流程共使用到3个事件队列:
inBoundQueue:用于记录InputReader发送过来的输入事件;
outBoundQueue:用于记录即将分发给目标应用窗口的输入事件;
waitQueue:用于记录已分发给目标应用,且应用尚未处理完成的输入事件。
1. 第一轮事件分发
首先InputReader线程 通过EventHub监听到底层的输入事件上报,并将其放入了inBoundQueue中,同时唤醒了InputDispatcher线程。
然后InputDispatcher开始了第一轮的事件分发,此时并没有正在处理的事件,因此InputDispatcher从inBoundQueue队列头部取出事件,并重置ANR的计时,并检查窗口是否就绪,此时窗口准备就绪,将该事件转移到了outBoundQueue队列中,因为应用管道对端连接正常,因此事件从outBoundQueue取出,然后放入了waitQueue队列,因为Socket双向通信已经建立,接下来就是 应用进程 接收到新的事件,然后对其进行分发。
如果应用进程事件分发正常,那么会通过Socket向system_server通知完成,则对应的事件最终会从waitQueue队列中移除。
2. 第二轮事件分发
如果第一轮事件分发尚未接收到回调通知,第二轮事件分发抵达又是如何处理的呢?
第二轮事件到达InputDispatcher时,此时InputDispatcher发现有事件正在处理,因此不会从inBoundQueue取出新的事件,而是直接检查窗口是否就绪,若未就绪,则进入ANR检测状态。
至此,输入系统检测到了ANR的发生,并向上层抛出了本次ANR的相关信息。
这里我们来总结一下,有哪些路径会引发ANR?

从埋下定时炸弹到拆炸弹之间的任何一个或多个路径执行慢都会导致ANR(以service为例),可以是service的生命周期的回调方法(比如onStartCommand)执行慢,可以是主线程的消息队列存在其他耗时消息让service回调方法迟迟得不到执行,可以是SP操作执行慢,可以是system_server进程的binder线程繁忙而导致没有及时收到拆炸弹的指令。
三、ANR调试
对于service、broadcast、provider、input发生ANR后,中控系统会马上去抓取现场的信息,用于调试分析。收集的信息包括如下:
将am_anr信息输出到EventLog,也就是说ANR触发的时间点最接近的就是EventLog中输出的am_anr信息
收集以下重要进程的各个线程调用栈trace信息,保存在 data/anr/traces.txt文件
当前发生ANR的进程,system_server进程以及所有persistent进程
audioserver, cameraserver, mediaserver, surfaceflinger等重要的native进程
CPU使用率排名前5的进程
将发生ANR的reason以及CPU使用情况信息输出到main log
将traces文件和CPU使用情况信息保存到dropbox,即data/system/dropbox目录
对用户可感知的进程则弹出ANR对话框告知用户,对用户不可感知的进程发生ANR则直接杀掉
Demo:
mBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
try
Thread.sleep(100000);
catch (InterruptedException e)
e.printStackTrace();
);
mBtn2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
mBtn2.setText("hah");
log文件:
2020-12-03 17:05:51.802 3105-3180/system_process E/ActivityManager: ANR in com.example.produceanr (com.example.produceanr/.MainActivity)
PID: 27806
Reason: Input dispatching timed out
//ANR 发生所处的 activity,进程ID,以及ANR原因
(com.example.produceanr/com.example.produceanr.MainActivity, Waiting to send non-key event because the touched window has not finished processing certain input events that were delivered to it over 500.0ms ago. Wait queue length: 2. Wait queue head age: 8559.5ms.)
Parent: com.example.produceanr/.MainActivity
Load: 6.09 / 5.99 / 5.74
CPU usage from 0ms to 6042ms later (2020-12-03 17:05:45.718 to 2020-12-03 17:05:51.760):
16% 3105/system_server: 7.9% user + 8.1% kernel / faults: 6549 minor
0.3% 2779/media.codec: 0.2% user + 0% kernel / faults: 35716 minor
10% 763/surfaceflinger: 8.2% user + 2.6% kernel / faults: 419 minor
...
0.1% 27263/kworker/4:2: 0% user + 0.1% kernel
0.1% 27743/kworker/0:0: 0% user + 0.1% kernel
15% TOTAL: 10% user + 5.4% kernel + 0.1% iowait + 0.2% irq + 0% softirq
//ANR前后cpu的使用情况
//如果CPU使用量接近100%,说明当前设备很忙,有可能是CPU饥饿导致ANR
//如果CPU使用量很少,说明主线程被block了
//如果IOwait很高,说明主线程在进行I/O操作trace文件:
log 文件只是告诉你 ANR 发生时间,但是并具体详细的信息,这时候就得查看 trace 文件(App 的进程发生 ANR 时,系统让活跃的 Top 进程都进行了一下 dump,进程中的各种Thread 就都 dump 到这个 trace 文件里了,所以 trace 文件中包含了每一条线程的运行时状态)。
拉取trace文件:
adb pull data/anr/anr_2020-12-03-17-30-41-366anr_2020-12-03-17-30-41-366.txt:
----- pid 28207 at 2020-12-03 17:30:41 -----
Cmd line: com.example.produceanr
//进程号、ANR发生时间和进程名称
DALVIK THREADS (14):
"main" prio=5 tid=1 Sleeping
//线程名、线程优先级、线程号、线程当前状态
| group="main" sCount=1 dsCount=0 flags=1 obj=0x76e543c8 self=0x6ffcf70000
| sysTid=28207 nice=-10 cgrp=default sched=0/0 handle=0x6ffe4d7ed0
| state=S schedstat=( 1106323008 54303290 408 ) utm=97 stm=13 core=4 HZ=100
| stack=0x7fcbd76000-0x7fcbd78000 stackSize=8192KB
| held mutexes=
at java.lang.Thread.sleep(Native method)
- sleeping on <0x0a2aeaaf> (a java.lang.Object)
at java.lang.Thread.sleep(Thread.java:440)
- locked <0x0a2aeaaf> (a java.lang.Object)
at java.lang.Thread.sleep(Thread.java:356)
at com.example.produceanr.MainActivity$1.onClick(MainActivity.java:23)
四、避免ANR
绝对不要在主线程上进行复杂耗时的操作,比如说发送接收网络数据、进行大量计算、操作数据库、读写文件等,统统采用异步操作
Service中的耗时操作最好也是采用异步任务
在设计及代码编写阶段避免出现出现死锁、死循环等不恰当情况
一些避免、检测ANR的工具
StrictMode:用来检测代码中是否存在违规操作的工具类(检测主线程是否存在耗时操作)
BlockCanary:用来监控应用主线程的卡顿
参考:Android性能调优——严苛模式StrictMode
BlockCanary源码解析
在讲解BlockCanary源码之前,我们还是需要将一些前置的知识点。本文不讲Handler的原理了,不太懂的同学自己去百度看一下吧。
什么是卡顿
在讲解卡顿问题之前,我们需要讲一下帧率这个概念。帧率是以帧称为单位的位图图像连续出现在显示器上的频率。我将一个例子,电影播放。电影其实就是很多张照片(帧)的一个集合,那为什么看起来是一个连续的过程呢?因为电影每一秒出现过的图片不止一张。实际上电影一般一秒出现的图片张数会在20-30张。假设电影一秒出现了24张图片,那么这个电影的帧率就是24。帧率就是一秒中,出现了多少帧。
知道了什么是帧率,那么问题来了,为什么会出现卡顿呢?卡顿在我们的视觉上面的表现就是原本是流畅的动画画面,现在变的不流畅了。我们上面讲过,动画其实是由很多图片构成。如果在一个24帧的电影中,突然有一秒钟,在这一秒钟出现了掉帧。也就是原本0…23的图片变成了 0…10…12…23.中间的某一帧没有渲染出来,那么这个在我们视觉上就会出现不流畅的现象。也就是卡顿的现象。上面就是电影上出现卡顿的现象。那么在我们android系统上呢?
Android渲染机制
在高刷手机没有出现之前,我们手机屏幕的帧率是60。就是意味着1秒钟会有60个画面出现。那么也就是16ms就要有一个画面渲染。Android系统每隔16ms发出VSYNC信号,触发对UI进行渲染, 如果每次渲染都成功,这样就能够达到流畅的画面所需要的60帧,为了能够实现60fps,这意味着程序的大多数操作都必须在16ms内完成。如果超过了16ms那么可能就出现丢帧的情况。如果掉帧的频率很高,也就是导致卡顿的情况。
BlockCanary源码解析
那么在android中,BlockCanary是怎么帮助我们去做卡顿检测的呢。今天我们就来讲解一下BlockCanary检测卡顿的原理。
一般我们都通过以下的代码方式去开启我们的卡顿检测。
public class DemoApplication extends Application
@Override
public void onCreate()
// ...
// Do it on main process
BlockCanary.install(this, new AppBlockCanaryContext()).start();
这段代码主要有两部分,一部分是install,一部分是start。我们先看install部分
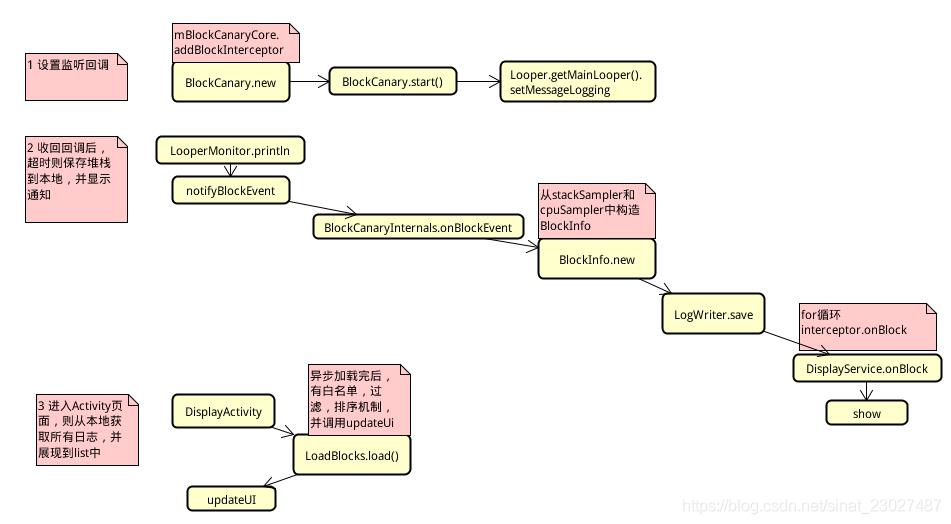
install阶段
BlockCanary#install()
public static BlockCanary install(Context context, BlockCanaryContext blockCanaryContext)
//BlockCanaryContext.init会将保存应用的applicationContext和用户设置的配置参数
BlockCanaryContext.init(context, blockCanaryContext);
//etEnabled将根据用户的通知栏消息配置开启
setEnabled(context, DisplayActivity.class, BlockCanaryContext.get().displayNotification());
return get();
BlockCanary#get()
//使用单例创建了一个BlockCanary对象
public static BlockCanary get()
if (sInstance == null)
synchronized (BlockCanary.class)
if (sInstance == null)
sInstance = new BlockCanary();
return sInstance;
BlockCanary()
private BlockCanary()
//初始化blockCanaryInternals调度类
BlockCanaryInternals.setContext(BlockCanaryContext.get());
mBlockCanaryCore = BlockCanaryInternals.getInstance();
//为BlockCanaryInternals添加拦截器(责任链)BlockCanaryContext对BlockInterceptor是空实现
mBlockCanaryCore.addBlockInterceptor(BlockCanaryContext.get());
if (!BlockCanaryContext.get().displayNotification())
return;
//DisplayService只在开启通知栏消息的时候添加,当卡顿发生时将通过DisplayService发起通知栏消息
mBlockCanaryCore.addBlockInterceptor(new DisplayService());
BlockCanaryInternals.getInstance()
static BlockCanaryInternals getInstance()
if (sInstance == null)
synchronized (BlockCanaryInternals.class)
if (sInstance == null)
sInstance = new BlockCanaryInternals();
return sInstance;
BlockCanaryInternals
public BlockCanaryInternals()
//初始化栈采集器
stackSampler = new StackSampler(
Looper.getMainLooper().getThread(),
sContext.provideDumpInterval());
//初始化cpu采集器
cpuSampler = new CpuSampler(sContext.provideDumpInterval());
//初始化LooperMonitor,并实现了onBlockEvent的回调,该回调会在触发阈值后被调用,这里面比较重要
setMonitor(new LooperMonitor(new LooperMonitor.BlockListener()
@Override
public void onBlockEvent(long realTimeStart, long realTimeEnd,
long threadTimeStart, long threadTimeEnd)
ArrayList<String> threadStackEntries = stackSampler
.getThreadStackEntries(realTimeStart, realTimeEnd);
if (!threadStackEntries.isEmpty())
BlockInfo blockInfo = BlockInfo.newInstance()
.setMainThreadTimeCost(realTimeStart, realTimeEnd, threadTimeStart, threadTimeEnd)
.setCpuBusyFlag(cpuSampler.isCpuBusy(realTimeStart, realTimeEnd))
.setRecentCpuRate(cpuSampler.getCpuRateInfo())
.setThreadStackEntries(threadStackEntries)
.flushString();
LogWriter.save(blockInfo.toString());
if (mInterceptorChain.size() != 0)
for (BlockInterceptor interceptor : mInterceptorChain)
interceptor.onBlock(getContext().provideContext(), blockInfo);
, getContext().provideBlockThreshold(), getContext().stopWhenDebugging()));
LogWriter.cleanObsolete();
当install进行初始化完成后,接着会调用start()方法,实现如下:
start阶段
BlockCanary#start()
//BlockCanary#start()
public void start()
if (!mMonitorStarted)
mMonitorStarted = true;
//把mBlockCanaryCore中的monitor设置MainLooper中进行监听
Looper.getMainLooper().setMessageLogging(mBlockCanaryCore.monitor);
这里面的实现也比较简单,就是获取到主线程Looper然后将上一步创建的LooperMonitor设置到主线程Looper里面的MessageLogging。
到这里然后呢?卧槽,没了一开始看这里的源码的时候我也是很懵逼的。然后我就去github上看了,然后呢,我看到了这么一张图。
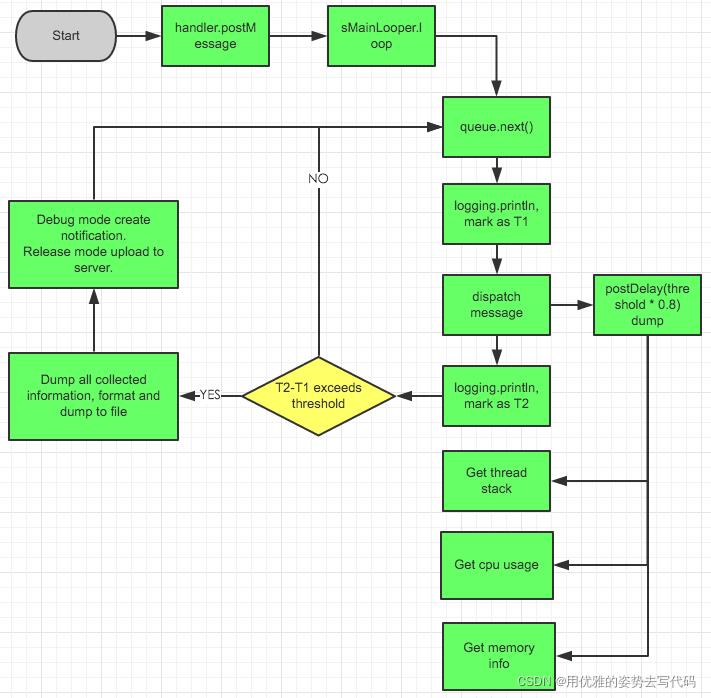
通过这张图,我可以知道,真正开始检测的不是start(),而是Looper里面loop()函数
Looper#loop
public static void loop()
final Looper me = myLooper();
if (me == null)
throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");
if (me.mInLoop)
Slog.w(TAG, "Loop again would have the queued messages be executed"
+ " before this one completed.");
me.mInLoop = true;
final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;
// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,
// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.
Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
// Allow overriding a threshold with a system prop. e.g.
// adb shell 'setprop log.looper.1000.main.slow 1 && stop && start'
final int thresholdOverride =
SystemProperties.getInt("log.looper."
+ Process.myUid() + "."
+ Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ".slow", 0);
boolean slowDeliveryDetected = false;
for (;;)
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
if (msg == null)
// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.
return;
// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger
final Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null)
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
// Make sure the observer won't change while processing a transaction.
final Observer observer = sObserver;
final long traceTag = me.mTraceTag;
long slowDispatchThresholdMs = me.mSlowDispatchThresholdMs;
long slowDeliveryThresholdMs = me.mSlowDeliveryThresholdMs;
if (thresholdOverride > 0)
slowDispatchThresholdMs = thresholdOverride;
slowDeliveryThresholdMs = thresholdOverride;
final boolean logSlowDelivery = (slowDeliveryThresholdMs > 0) && (msg.when > 0);
final boolean logSlowDispatch = (slowDispatchThresholdMs > 0);
final boolean needStartTime = logSlowDelivery || logSlowDispatch;
final boolean needEndTime = logSlowDispatch;
if (traceTag != 0 && Trace.isTagEnabled(traceTag))
Trace.traceBegin(traceTag, msg.target.getTraceName(msg));
final long dispatchStart = needStartTime ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : 0;
final long dispatchEnd;
Object token = null;
if (observer != null)
token = observer.messageDispatchStarting();
long origWorkSource = ThreadLocalWorkSource.setUid(msg.workSourceUid);
try
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
if (observer != null)
observer.messageDispatched(token, msg);
dispatchEnd = needEndTime ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : 0;
catch (Exception exception)
if (observer != null)
observer.dispatchingThrewException(token, msg, exception);
throw exception;
finally
ThreadLocalWorkSource.restore(origWorkSource);
if (traceTag != 0)
Trace.traceEnd(traceTag);
if (logSlowDelivery)
if (slowDeliveryDetected)
if ((dispatchStart - msg.when) <= 10)
Slog.w(TAG, "Drained");
slowDeliveryDetected = false;
else
if (showSlowLog(slowDeliveryThresholdMs, msg.when, dispatchStart, "delivery",
msg))
// Once we write a slow delivery log, suppress until the queue drains.
slowDeliveryDetected = true;
if (logSlowDispatch)
showSlowLog(slowDispatchThresholdMs, dispatchStart, dispatchEnd, "dispatch", msg);
if (logging != null)
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the
// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.
final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
if (ident != newIdent)
Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x"
+ Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to "
+ msg.target.getClass().getName() + " "
+ msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what);
msg.recycleUnchecked();
loop()里面的代码很长,我们讲解blockCanary的时候不需要过分关注其他部分,还记得我们start做的事情吗,我们去设置了setMessageLogging。所以先看看setMessageLogging方法
Looper#setMessageLogging
public void setMessageLogging(@Nullable Printer printer)
mLogging = printer;
其实就是将创建的LooperMonitor赋值给mLogging,那么我们只需要关注mLogging在loop()中的代码就好了。我们发现就是调用了两次println。一个是在msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg)之前,一个是在msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg)之后。也就是说这两次调用,一次是处理信号之前,一个是处理信号之后。那么通过实现LooperMonitor里面的println方法,我们就可以得出一些时间差。所以,接下来我们要看的是LooperMonitor里面的println方法
MainLooper#println()
//MainLooper#println()
@Override
public void println(String x)
//如果再debug模式,不执行监听
if (mStopWhenDebugging && Debug.isDebuggerConnected())
return;
if (!mPrintingStarted) //dispatchMesage前执行的println
//记录开始时间
mStartTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
mStartThreadTimestamp = SystemClock.currentThreadTimeMillis();
mPrintingStarted = true;
//开始采集栈及cpu信息
startDump();
else //dispatchMesage后执行的println
//获取结束时间
final long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
mPrintingStarted = false;
//判断耗时是否超过阈值
if (isBlock(endTime))
notifyBlockEvent(endTime);
stopDump();
//判断是否超过阈值
private boolean isBlock(long endTime)
return endTime - mStartTimestamp > mBlockThresholdMillis;//这个阈值是我们自己设置的
//如果超过阈值,回调卡顿的监听,说明卡顿了
private void notifyBlockEvent(final long endTime)
final long startTime = mStartTimestamp;
final long startThreadTime = mStartThreadTimestamp;
final long endThreadTime = SystemClock.currentThreadTimeMillis();
HandlerThreadFactory.getWriteLogThreadHandler().post(new Runnable()
@Override
public void run()
mBlockListener.onBlockEvent(startTime, endTime, startThreadTime, endThreadTime);
);
其实这里卡顿检测的源码也还是比较简单的,它的原理就是通过重新实现looper里面的logging,然后通过println函数去判断有没有出现卡顿。BlockCanary的流程图在上面也出现了。希望对大家,对于卡顿的理解有一定的帮助。
ANRWatchDog、BlockCanary、Matrix的TraceCanary对比
ANRWatchDog
原理
主线程一直会处理消息循环,如果发给主线程的消息,在5秒后还未得到执行,则认为是卡顿
流程描述
起来一个子进程,子进程是一个for循环,会永远执行。 向主进程的handler发送一个message; 然后sleep 5秒(也可以设置)。
如果这中间,主进程被卡主了,意味着,上面那个message没有被执行, 则获取当前的堆栈,并回调给上层。
如果执行了,意味着,没有被卡主的,for循环,继续正常发送message
结论
可能是发送了太多消息导致的; 也可能获取的堆栈并非较卡的地方,非常不精准
BlockCanary
原理
主线程looper的loop方法在寻找msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg)时的前后会分别打印一段log,记录两次log的时间差,这样就可以大致认为是主线程处理msg的时间,如果时间过长则认为卡顿
流程描述
给主进程的Looper设置打印监听,在其dispatch时前后会收到通知,进而判断前后时间是否超过1秒。 如果超过了1秒,则有一个子进程去获取堆栈并保存并通知。
如果方法没有超过1秒,则只有一个回调,不会去获取堆栈。
其他:
精准性比ANRWatchDog高,一样对性能无影响; 但是依然可能获取堆栈的时候准确性差
核心是Looper.getMainLooper.setMessageLoging,他在dispatch的前后都有打印,关键在于抓这两次打印.
cpu信息在于读取 /proc/stat 这个文件
获取堆栈在于 thread.getStackTrace这个类
流程图
微信Matrix的TraceCanary
原理
Choreographer,Choreographer就是一个消息处理器,根据vsync 信号 来计算frame,在doFrame方法里可以收到当前帧绘制完后的当前时间. 正常绘制两次doFrame的时间差应该是1000/60=16.6666毫秒(每秒60帧),但是遇到卡顿或过度重绘等会导致时间拉长
ASM
ASM 是一个 Java 字节码操控框架。它能被用来动态生成类或者增强既有类的功能。ASM 可以直接产生二进制 class 文件,也可以在类被加载入 Java 虚拟机之前动态改变类行为
Java class 被存储在严格格式定义的 .class 文件里,这些类文件拥有足够的元数据来解析类中的所有元素:类名称、方法、属性以及 Java 字节码(指令)。ASM 从类文件中读入信息后,能够改变类行为,分析类信息,甚至能够根据用户要求生成新类。
对于自己代码,比动态代理优势明显
流程描述
首先打包时,利用gradle脚本,会将设有方法在调用前调用后,都调用一个静态方法。此时将得到一个方法id和每一个方法对应的序列。 在执行方法的时候,会将每个方法的执行id、执行时间、深度、次数等都存到buffer中
执行时Choreographer不停循环发送消息,接收回调,按理每次16.66毫秒每次接受到回调
如果两帧之间超过1秒,handleBuffer去从buffer中去获取卡顿的堆栈序列
上传序列到后台,由后台根据执行顺序id,给出卡顿堆栈
流程图

以上是关于Android ANR详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章