Jedis源码解析
Posted 低调的洋仔
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Jedis源码解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
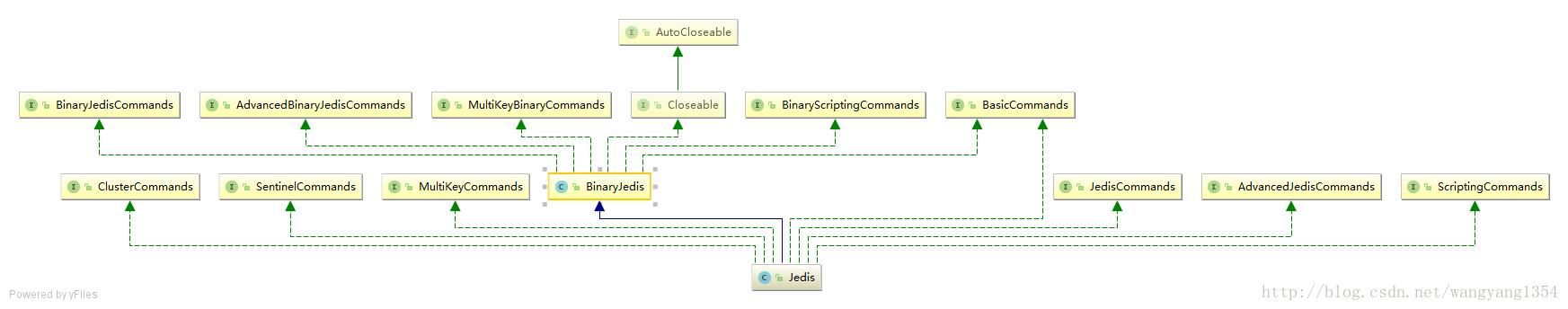
Jedis类
这个类主要是继承了BinaryJedis这个类。
这个类搞了一堆的实现接口,一开始看吐的感觉,但是这里我想了下,因为你的jedis要做到门面的效果来对外提供服务的,那么这个地方针对不同类型的命令啊都要进行支持,比如说查询单个的,查询多值的情况,为了统一,先划分开来,然后再统一这个继承体系。这样的情况下,如果后期要改变架构我可以只是改变下jedis的实现方式就可以了,接口不需要动。
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("", 2323);这个方法创建一个jedis的实例。
追踪进去就是:
public Jedis(String host, int port)
super(host, port);
调用了super的构造方法,也就是BinaryJedis这个构造方法。
public BinaryJedis(String host, int port)
this.client = new Client(host, port);
然后这个BinaryJedis这个类中聚合了Client作为内部的一个实例。
然后这个Client实例本质上是Connection的封装。
public Client(String host, int port)
super(host, port);
创建了一个Client的实例,调用了其父类的构造方法。
其父类又是一个BinaryClient的类,这个类的命名比较有意思的一件事情。
public class BinaryClient extends Connection
public BinaryClient(String host, int port)
super(host, port);
这个BinaryClient他又是继承了一个Connection的类。
public Connection(String host, int port)
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
然后将这个host和port封装进去了。
到这里之后整个的设置过程已经结束了,也就是创建了一个Jedis的实例。
首先是调用了jedis的父类BinaryJedis的构造方法,然后BinaryJedis的构造方法继续创建了一个Client的类的实例,这个实例是Connection的一个代理类,然后这个类调用了父类BinaryClient的构造方法,而BinaryClient又调用了其父类Connection的构造方法,添加了俩参数而已。
Set操作流程
public String set(String key, String value)
this.checkIsInMulti();
this.client.set(key, value);
return this.client.getStatusCodeReply();
首先检查是不是多个线程同时操作的,如果是的话就直接抛出异常了。
protected void checkIsInMulti()
if (this.client.isInMulti())
throw new JedisDataException("Cannot use Jedis when in Multi. Please use JedisTransaction instead.");
接下来是调用的set方法。
在Jedis中直接调用了父类中初始化的一个Client的实例方法。
public void set(String key, String value)
this.set(SafeEncoder.encode(key), SafeEncoder.encode(value));
调用了BinaryClient中的set方法,client又调用了自己的set方法。
public void set(byte[] key, byte[] value)
this.sendCommand(Command.SET, new byte[][]key, value);
这里面实际上就是封装了命令,然后key和value的数据了。
其中调用的这个sendCommand方法实际上是Connection中的方法。
protected Connection sendCommand(ProtocolCommand cmd, byte[]... args)
try
this.connect();
Protocol.sendCommand(this.outputStream, cmd, args);
++this.pipelinedCommands;
return this;
catch (JedisConnectionException var4)
this.broken = true;
throw var4;
这个地方现调用了connect方法建立连接,然后发送command,然后记录pipedlinedCommands。
public void connect()
if (!this.isConnected())
try
this.socket = new Socket();
this.socket.setReuseAddress(true);
this.socket.setKeepAlive(true);
this.socket.setTcpNoDelay(true);
this.socket.setSoLinger(true, 0);
this.socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress(this.host, this.port), this.connectionTimeout);
this.socket.setSoTimeout(this.soTimeout);
this.outputStream = new RedisOutputStream(this.socket.getOutputStream());
this.inputStream = new RedisInputStream(this.socket.getInputStream());
catch (IOException var2)
this.broken = true;
throw new JedisConnectionException(var2);
建立连接的过程其实就是Socket的过程。这个地方为什么不是NIO或者netty呢?是不是可以优化下了。可能NIO可以,但是Netty得双方都统一用这个才行的吧,但redis本身是c的,这个可能不太可行。NIO不太确定。
调用了Connection的sendCommand方法。
protected Connection sendCommand(ProtocolCommand cmd, byte[]... args)
try
this.connect();
Protocol.sendCommand(this.outputStream, cmd, args);
++this.pipelinedCommands;
return this;
catch (JedisConnectionException var4)
this.broken = true;
throw var4;
然后调用了Protocol的sendCommand方法来发送这个之类的信息。也就是说Connection只是维护一个连接而已,然后调用的是Protocol的sendCommand方法来发送请求。
public static void sendCommand(RedisOutputStream os, ProtocolCommand command, byte[]... args)
sendCommand(os, command.getRaw(), args);
private static void sendCommand(RedisOutputStream os, byte[] command, byte[]... args)
try
os.write((byte)42);
os.writeIntCrLf(args.length + 1);
os.write((byte)36);
os.writeIntCrLf(command.length);
os.write(command);
os.writeCrLf();
byte[][] arr$ = args;
int len$ = args.length;
for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$)
byte[] arg = arr$[i$];
os.write((byte)36);
os.writeIntCrLf(arg.length);
os.write(arg);
os.writeCrLf();
catch (IOException var7)
throw new JedisConnectionException(var7);
但是在Get方法里面是直接的调用了Connection的方法。
public String get(String key)
this.checkIsInMulti();
this.client.sendCommand(Command.GET, new String[]key);
return this.client.getBulkReply();
然后调用了一个sendCommand方法。
protected Connection sendCommand(ProtocolCommand cmd, String... args)
byte[][] bargs = new byte[args.length][];
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; ++i)
bargs[i] = SafeEncoder.encode(args[i]);
return this.sendCommand(cmd, bargs);
然后也调用了sendCommand方法,然后发送Get数据的请求。
protected Connection sendCommand(ProtocolCommand cmd, byte[]... args)
try
this.connect();
Protocol.sendCommand(this.outputStream, cmd, args);
++this.pipelinedCommands;
return this;
catch (JedisConnectionException var4)
this.broken = true;
throw var4;
下面是和set中的一样了。
getReply方法
public String get(String key)
this.checkIsInMulti();
this.client.sendCommand(Command.GET, new String[]key);
return this.client.getBulkReply();
最后调用一个getBulkReply方法返回最终的值。
public String set(String key, String value, String nxxx, String expx, long time)
this.checkIsInMulti();
this.client.set(key, value, nxxx, expx, time);
return this.client.getStatusCodeReply();
set这个返回的是getStatusCodeReply方法、
public String getStatusCodeReply()
this.flush();
--this.pipelinedCommands;
byte[] resp = (byte[])((byte[])this.readProtocolWithCheckingBroken());
return null == resp ? null : SafeEncoder.encode(resp);
然后调用了readProtocolWithCheckingBroken方法。
protected Object readProtocolWithCheckingBroken()
try
return Protocol.read(this.inputStream);
catch (JedisConnectionException var2)
this.broken = true;
throw var2;
调用了Protocol中的方法。
public static Object read(RedisInputStream is)
return process(is);
然后调用了process方法、
private static Object process(RedisInputStream is)
byte b = is.readByte();
if (b == 43)
return processStatusCodeReply(is);
else if (b == 36)
return processBulkReply(is);
else if (b == 42)
return processMultiBulkReply(is);
else if (b == 58)
return processInteger(is);
else if (b == 45)
processError(is);
return null;
else
throw new JedisConnectionException("Unknown reply: " + (char)b);
这里注意一点,很有意思的是上层用的时候分开了几个方法,但是底层实现的时候,实际上是用了同样的一个方法那就是上面这个方法process方法来处理的。
private static byte[] processStatusCodeReply(RedisInputStream is)
return is.readLineBytes();
调用了RedisInputStream的readLineBytes方法。
public byte[] readLineBytes()
this.ensureFill();
int pos = this.count;
byte[] buf = this.buf;
while(pos != this.limit)
if (buf[pos++] == 13)
if (pos == this.limit)
return this.readLineBytesSlowly();
if (buf[pos++] == 10)
int N = pos - this.count - 2;
byte[] line = new byte[N];
System.arraycopy(buf, this.count, line, 0, N);
this.count = pos;
return line;
return this.readLineBytesSlowly();
private byte[] readLineBytesSlowly()
ByteArrayOutputStream bout = null;
while(true)
while(true)
this.ensureFill();
byte b = this.buf[this.count++];
if (b == 13)
this.ensureFill();
byte c = this.buf[this.count++];
if (c == 10)
return bout == null ? new byte[0] : bout.toByteArray();
if (bout == null)
bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream(16);
bout.write(b);
bout.write(c);
else
if (bout == null)
bout = new ByteArrayOutputStream(16);
bout.write(b);
以上是关于Jedis源码解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章