K8s使用Ceph纠删码池做持久化卷
Posted 薛定谔de猪
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了K8s使用Ceph纠删码池做持久化卷相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
K8s使用Ceph纠删码池做持久化卷
Kubernetes版本:v1.20.4
Ceph版本:v14.2.20(nautilus)
Linux版本:x86_64-Centos7.6
KubeSphere 版本 : v3.1.0
provisioner:rbd.csi.ceph.com
Ceph侧准备
Ceph纠删码相关
Ceph pool有两种保护数据冗余机制,即纠删码(erasure code,简称ec)和复制集(replicated,简称rc)
Ceph pool要保证部分osd损坏时数据不丢失(一般情况下一个disk设置为一个osd);默认情况下创建pool时rule类型选择replicated,即object在多个disk中拷贝保存;pool的另一种rule类型是erasure,这种pool可以节省空间;
纠删码原理
比如 K=3 M=2 K+M=5
这个意思是:
K原始数据盘个数或恢复数据需要的磁盘个数
M校验盘个数或允许出故障的盘个数
使用编码算法,通过K个原始数据生成K+M个新数据
通过任何K个新数据都能还原出原始的K个数据
即允许M个数据盘出故障,数据仍然不会丢失;
参考文档: 浅谈Ceph纠删码_niuanxins的专栏-CSDN博客_ceph 纠删码
我们需要使用rbd作为k8s后端存储,但默认情况下,纠删存储池只能比较好的支持rgw。从L版本开始,纠删存储池支持开启allow_ec_overwrites属性,从而使得纠删存储池可以作为rbd或者cephfs的数据池。支持rbd需要有如下几个条件:
-
版本大于等于L
ceph --version -
开启allow_ec_overwrites
ceph osd pool set ec_pool allow_ec_overwrites true
bluestore存储引擎
方法ceph daemon osd.0 config show | grep osd_objectstore

-
纠删存储池不支持omap,需要一个副本存储池存储块设备的元数据等信息。该副本存储池可以初始化为rbd应用,
在rc池创建image,指定–data-pool为ec池
创建纠删码规则
参考文档: ceph 之 纠删码操作
- 首先,需要创建 erasure-code-profile ,当然,也可以使用默认的 erasure-code-profile ,列出现有的 erasure-code-profile
ceph osd erasure-code-profile ls

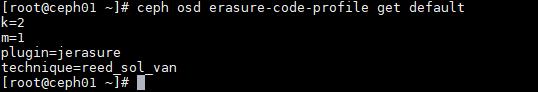
- 查看指定erasure-code-profile 的详细内容:
ceph osd erasure-code-profile get default
- 注:删除纠删码配置信息命令
ceph osd erasure-code-profile rm <profile>
- (可选)自定义erasure-code-profile , 创建一个只用hdd的 erasure-code-profile,我这里没有创建,这里说下方法:
-ceph osd erasure-code-profile set hdd-3-2 k=3 m=2 crush-device-class=hdd
可用的选项有:
- crush-root: the name of the CRUSH node to place data under [default: default].
- crush-failure-domain(故障域): the CRUSH type to separate erasure-coded shards across [default: host].
- crush-device-class(设备分类): the device class to place data on [default: none, meaning all devices are used].
- k and m (and, for the lrc plugin, l): these determine the number of erasure code shards, affecting the resulting CRUSH rule.
- 根据erasure-code-profile 创建crush rule,注:我这里并没有采用上一步创建的hdd-3-2的erasure-code-profile,直接使用了默认default erasure-code-profile:
ceph osd crush rule create-erasure default default
- 查看crush rule:
ceph osd crush rule dump default

创建纠删码池
创建一个使用纠删码规则default的pool
ceph osd pool create ec 128 128 default default
语法: osd pool create <int[0-]> <int[0-]> replicated|erasure [<erasure_code_profile>]
尽管crush rule 也是根据erasure_code_profile来创建的,但是这里创建纠删码pool的时候,还是需要明确指定erasure_code_profile的
注:pg数量系统不能自动识别,必须根据系统环境计算后指定,计算方法网上较多,自行百度谷歌
由于纠删码池不支持存储omap类型数据,但rbd image的元数据是基于rados的omap实现,所以纠删码池无法创建rbd image,必须创建一个复制集池存放image元数据


如上图报错所示,纠删码池不支持创建image镜像
- 调优
ceph osd pool set ec 1
目前,这个fast_read 之针对纠删码池有效的
- 开启allow_ec_overwrites
ceph osd pool set ec allow_ec_overwrites true
创建复制集池
- 创建一个replication pool来存放image元数据
ceph osd pool create rc 128
- 检查ceph健康状态
ceph health detail

可以看到有告警,这是因为未设置池子应用类型所致,我们可以将他们均设置为rbd
ceph osd pool application enable ec rbd
ceph osd pool application enable rc rbd
ceph health detail

可以看到已经HEALTH OK了
创建用户并授权
- 创建用户并授权
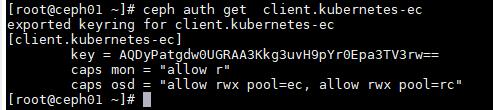
ceph auth get-or-create client.kubernetes-ec mon 'allow r' osd 'allow rwx pool=ec, allow rwx pool=rc' -o /etc/ceph/ceph.client.kubernetes-ec.keyring - 查看用户key和权限
ceph auth get client.kubernetes-ec
K8s消费ec池
前置条件:已经安装ceph-rbd-csi,安装步骤请见我的第一篇文档 KubeSphere使用rbd-csi创建快照
- 创建secret
- 查看前面在ceph节点创建的用户的信息
ceph auth get client.kubernetes-ec
[root@ceph01 ~]# ceph auth get client.kubernetes-ec
exported keyring for client.kubernetes-ec
[client.kubernetes-ec]
key = AQDyPatgdw0UGRAA3Kkg3uvH9pYr0Epa3TV3rw==
caps mon = "allow r"
caps osd = "allow rwx pool=ec, allow rwx pool=rc"
- 创建或修改 vim secret.yaml
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: csi-rbd-ec-secret
namespace: kube-system
stringData:
# Key values correspond to a user name and its key, as defined in the
# ceph cluster. User ID should have required access to the 'pool'
# specified in the storage class
userID: kubernetes-ec # ceph用户
userKey: AQDyPatgdw0UGRAA3Kkg3uvH9pYr0Epa3TV3rw== # 上一步中的key
# Encryption passphrase
# encryptionPassphrase: test_passphrase
- 创建secret
kubectl apply -f secret.yaml
- 创建存储类storageclass
- 创建或修改 vim storageclass.yaml
---
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: csi-rbd-ec-sc
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
storageclass.kubesphere.io/support-snapshot: 'true' # 必须置位true,否则 Kubesphere不支持创建快照
storageclass.kubesphere.io/supported-access-modes: '["ReadWriteOnce"]'
provisioner: rbd.csi.ceph.com
# If topology based provisioning is desired, delayed provisioning of
# PV is required and is enabled using the following attribute
# For further information read TODO<doc>
# volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
parameters:
# (required) String representing a Ceph cluster to provision storage from.
# Should be unique across all Ceph clusters in use for provisioning,
# cannot be greater than 36 bytes in length, and should remain immutable for
# the lifetime of the StorageClass in use.
# Ensure to create an entry in the configmap named ceph-csi-config, based on
# csi-config-map-sample.yaml, to accompany the string chosen to
# represent the Ceph cluster in clusterID below
clusterID: b93a2e42-43e1-4975-bc7d-5998ca61a7c4 # ceph集群id 上文中的fsid
# (optional) If you want to use erasure coded pool with RBD, you need to
# create two pools. one erasure coded and one replicated.
# You need to specify the replicated pool here in the `pool` parameter, it is
# used for the metadata of the images.
# The erasure coded pool must be set as the `dataPool` parameter below.
dataPool: ec # 纠删码存储池
# (required) Ceph pool into which the RBD image shall be created
# eg: pool: rbdpool
pool: rc # 复制集存储池
# Set thickProvision to true if you want RBD images to be fully allocated on
# creation (thin provisioning is the default).
thickProvision: "false"
# (required) RBD image features, CSI creates image with image-format 2
# CSI RBD currently supports `layering`, `journaling`, `exclusive-lock`
# features. If `journaling` is enabled, must enable `exclusive-lock` too.
# imageFeatures: layering,journaling,exclusive-lock
imageFeatures: layering
# (optional) mapOptions is a comma-separated list of map options.
# For krbd options refer
# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd/#kernel-rbd-krbd-options
# For nbd options refer
# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd-nbd/#options
# mapOptions: lock_on_read,queue_depth=1024
# (optional) unmapOptions is a comma-separated list of unmap options.
# For krbd options refer
# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd/#kernel-rbd-krbd-options
# For nbd options refer
# https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd-nbd/#options
# unmapOptions: force
# The secrets have to contain Ceph credentials with required access
# to the 'pool'.
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: csi-rbd-ec-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: kube-system
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: csi-rbd-ec-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: kube-system
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: csi-rbd-ec-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: kube-system
# (optional) Specify the filesystem type of the volume. If not specified,
# csi-provisioner will set default as `ext4`.
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4
# (optional) uncomment the following to use rbd-nbd as mounter
# on supported nodes
# mounter: rbd-nbd
# (optional) Prefix to use for naming RBD images.
# If omitted, defaults to "csi-vol-".
# volumeNamePrefix: "foo-bar-"
# (optional) Instruct the plugin it has to encrypt the volume
# By default it is disabled. Valid values are "true" or "false".
# A string is expected here, i.e. "true", not true.
# encrypted: "true"
# (optional) Use external key management system for encryption passphrases by
# specifying a unique ID matching KMS ConfigMap. The ID is only used for
# correlation to configmap entry.
# encryptionKMSID: <kms-config-id>
# Add topology constrained pools configuration, if topology based pools
# are setup, and topology constrained provisioning is required.
# For further information read TODO<doc>
# topologyConstrainedPools: |
# ["poolName":"pool0",
# "dataPool":"ec-pool0" # optional, erasure-coded pool for data
# "domainSegments":[
# "domainLabel":"region","value":"east",
# "domainLabel":"zone","value":"zone1"],
# "poolName":"pool1",
# "dataPool":"ec-pool1" # optional, erasure-coded pool for data
# "domainSegments":[
# "domainLabel":"region","value":"east",
# "domainLabel":"zone","value":"zone2"],
# "poolName":"pool2",
# "dataPool":"ec-pool2" # optional, erasure-coded pool for data
# "domainSegments":[
# "domainLabel":"region","value":"west",
# "domainLabel":"zone","value":"zone1"]
# ]
reclaimPolicy: Delete
allowVolumeExpansion: true
mountOptions:
- discard
- 创建 storageclass
kubectl apply -f storageclass.yaml
- 创建酷照类snapshotclass
- 在K8s节点(192.168.10.182)创建或修改 vim snapshotclass.yaml
---
# Snapshot API version compatibility matrix:
# v1betav1:
# v1.17 =< k8s < v1.20
# 2.x =< snapshot-controller < v4.x
# v1:
# k8s >= v1.20
# snapshot-controller >= v4.x
# We recommend to use sidecar, controller, crds of same version
apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: VolumeSnapshotClass
metadata:
name: csi-rbd-ec-sc # 注意:必须和存储类同名,否则Kubesphere无法创建存储卷对应快照
driver: rbd.csi.ceph.com
parameters:
# String representing a Ceph cluster to provision storage from.
# Should be unique across all Ceph clusters in use for provisioning,
# cannot be greater than 36 bytes in length, and should remain immutable for
# the lifetime of the StorageClass in use.
# Ensure to create an entry in the configmap named ceph-csi-config, based on
# csi-config-map-sample.yaml, to accompany the string chosen to
# represent the Ceph cluster in clusterID below
clusterID: b93a2e42-43e1-4975-bc7d-5998ca61a7c4 # ceph集群id,上文的fsid
# Prefix to use for naming RBD snapshots.
# If omitted, defaults to "csi-snap-".
# snapshotNamePrefix: "foo-bar-"
csi.storage.k8s.io/snapshotter-secret-name: csi-rbd-ec-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/snapshotter-secret-namespace: kube-system
deletionPolicy: Delete
- 创建snapshotclass
kubectl apply -f snapshotclass.yaml
验证
- 使用csi-rbd-ec-sc存储类创建一个pvc,可在后台通过kubectl创建,也可Kubesphere界面操作,这里不再演示 参考 我的第一篇文档 KubeSphere使用rbd-csi创建快照
- 将pvc挂载到pod中
- 写入5GB数据
dd if=/dev/zero of=test-file1 bs=10M count=500 - 观察结果
- 到pod所在宿主机观察map结果
rbd showmapped | grep -E rc\\|ec

显然挂载的复制集池子
- 查看池子占用情况
ceph df |grep -E rc\\|ec

的确是纠删码池子写入了5GiB数据,而占用了7.6GiB存储空间,符合纠删码K,M定义
- 查看image情况
rbd ls ec

无image
rbd ls rc

有一个image
这印证了前文所说的复制集存储image元数据,纠删码池存储用户数据。
- 查看image信息
rbd info rc/172-vo-d3fc8d23-bc54-11eb-bb49-22f8864ed6ad
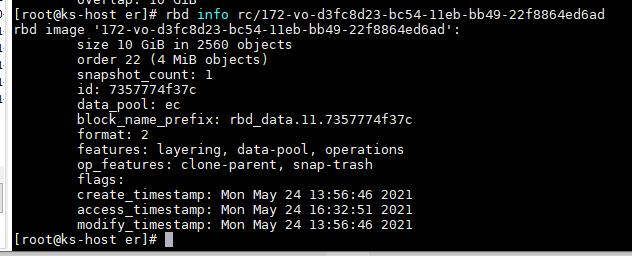
其中指定了data_pool
这和手动创建image指定–data-pool效果是一致的
rbd create --size 10G --data-pool ec rc/<image_name>
- 查看池子里的对象
rados -p rc ls

可以看到,复制集池子里只有少量的对象,而纠删码池子有海量的对象(命令是:rados -p ec ls,数据量很大,这里不做展示,请自行查看),符合预期
重点说下rbd_header.7357774f37c这个对象,这个对象存放了rbd image的的一些重要参数,如大小,特性order等等。
rados -p rc listomapvals rbd_header.7357774f37c

资料显示,纠删码池不支持存放如上图所示的omap数据,所以无法在纠删码池上无法直接创建image,具体原因,需要对ceph进行深入研究。
(可选)缓存方式
如果你不想改变原有形式在复制集pool上创建image,例如opendtack nova cinder glance 原生不支持指定 datapool,又不想二次开发,可尝试这种方式,原理是给纠删码池创建一个复制集缓存池,让复制集池覆盖在纠删码池上,将所有的请求都引流到缓存池上,来实现类似在纠删码池上创建image的效果。
参考文档:
ceph 之 纠删码操作
管理ceph缓存池
- 创建一个缓存池,也可直接用原有的rc池做缓存池
ceph osd create pool cache 128
2. 设置缓存层
- 将上面创建的cache池绑定至存储池的前端,ec即为我们的后端存储池
ceph osd tier add ec cache
- 设置缓存模式为writeback
ceph osd tier cache-mode cache writeback
注:本场景貌似只能设置成 writeback模式,readony会导致创建image失败,需要深入研究
附:几种缓存配置模式 (参考文档: ceph cache teir配置模式以及参数说明)
writeback mode: 当配置为writeback模式时,ceph客户端将数据写入到缓存层并且从缓存层得到已经写入的确认信息。在缓存层中的数据会及时迁移到存储层并且刷新缓存层。当读取数据时,如果数据在缓存层,那么直接在缓存层操作数据,如果缓存没有所需数据,则从存储层将数据读取到缓存层,然后发送给客户端。
readproxy mode : 当配置为此模式时,如果数据在缓存层,则直接操作缓存中的数据,如果不在缓存层,则去存储层操作。假如突然禁用了缓存模式,这种模式则很有用,因为可以直接可以请求存储层。而且在这种模式下,就算缓存耗尽,ceph集群也会从存储层继续提供读写,这样只是IO性能下降了,但是IO还可以继续响应。
readonly mode: 当配置为readonly模式时,Ceph客户端在写数据的时候,直接将数据写入到后端存储层。当读取数据时,Ceph会将请求的对象从存储层复制到缓存层。当在存储层中更新对象时,Ceph不会将这些更新同步到缓存层中相应的对象,所以这个模式在生产环境不推荐使用。
none: 禁用缓存模式。
- 将所有客户端请求从标准池引导至缓存池
ceph osd tier set-overlay ec cache
其实,不仅纠删码池可以做cache tier,replication 池子也能做cache tier,例如,我们可能有一批ssd盘,我们就可以在ssd上创建pool来充当sas盘的cache tier以提高性能;结合纠删码、replication、sas、ssd,我们可以做出多种不同性能的存储用以应对不同的场景。
- 如果 ceph 提示: 1 cache pools are missing hit_sets , 还要设置 hit_set_count 和 hit_set_type
ceph osd pool set cache hit_set_count 1
ceph osd pool set cache hit_set_type bloom
- 设置当缓存池中的数据达到多少个对象时,缓存分层代理就开始从缓存池刷新对象至后端存储池并驱逐:
ceph osd pool set cache target_max_objects 1000
这里为了观察效果,故设置为1000个,实际环境中这个值太小了
还可以设置其他参数,例如
当缓存池中的数据量达到多少字节时开始刷盘并驱逐
ceph osd pool set cache target_max_bytes 10000000000
当脏对象占比达到10%时开始刷盘
ceph osd pool set cache cache_target_dirty_ratio 0.1
当脏对象占比达到60%时开始高速刷盘
cache_target_dirty_high_ratio: 0.6
当缓存池的使用量达到其总量的一定百分比时,缓存分层代理将驱逐对象以维护可用容量(达到该限制时,就认为缓存池满了),此时会将未修改的(干净的)对象刷盘
ceph osd pool set cache cache_target_full_ratio 0.8
定义缓存层将对象刷至存储层或者驱逐的时间:
ceph osd pool set cache cache_min_flush_age 600
ceph osd pool set cache cache_min_evict_age 600
也可将缓存池类型设置为rbd
ceph osd pool application enable cache rbd
- 测试
可直接在纠删码池直接创建image
rbd create --size 1GiB ec/test.image
是可以成功的,并且cache也有同名的image
rbd ls cache
rbd info cache/test.image
4. 删除缓存池
- 将缓存模式更改为转发,以便新的和修改的对象刷新至后端存储池:
ceph osd tier cache-mode cache forward
- 手动刷新
rados -p cache cache-flush-evict-all
- 查看缓存池以确保所有的对象都被刷新
rados -p cache ls
其实是无法将对象全部刷进ec池的,因为ec池无法存储omap元数控
只好删除image
- 删除iamge
rbd rm cahce/test.image
- 删除覆盖层,以使客户端不再将流量引导至缓存
ceph osd tier remove-overlay ec
- 解除存储池与缓存池的绑定
ceph osd tier remove ec cache
- 删除缓存池
ceph osd pool delete cache cache --yes-i-really-really-mean-it
注:ceph防止误删,所以命令比较长
以上是关于K8s使用Ceph纠删码池做持久化卷的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章