springboot请求参数绑定原理篇
Posted 香菜+
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了springboot请求参数绑定原理篇相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
上篇文章写了SpringBoot 参数接收只看这一篇文章就够了,只是写了使用方法,没有写为什么,原理是什么,这篇文章也是之前的预先的计划,稍微花点时间整理下,
知其然知其所以然,才算是能彻底掌握,但是说实在话,都是工具,会用是硬道理。有精力了再去搞原理。
1、原理
百度上看到一张图,还蛮好的,直接拿来用了,侵权删。
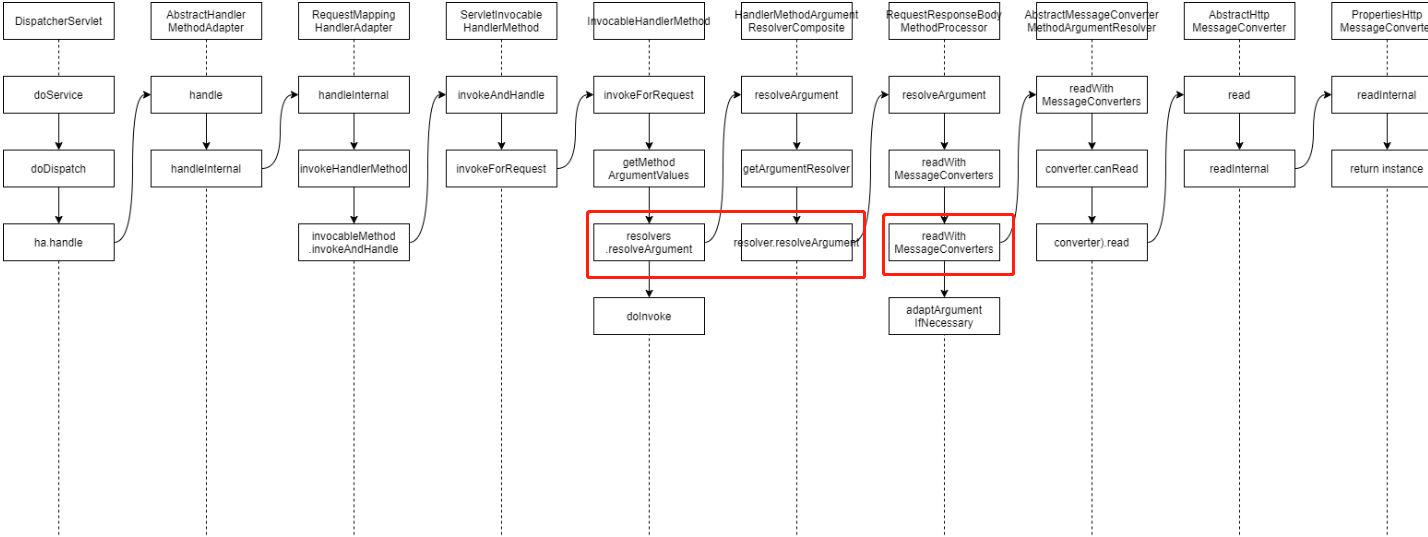
Spring容器管理的RequestMappingHandlerAdapter对象会自动帮我们分解参数并组装成所需要的对象。
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter完全按照名称匹配且只能组装在request的参数域中提供参数的对象。
上图我花了两个红色框,一个HttpMessageConverter 和 HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
这两个也是今天的重点。
2、HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
2.1 基础概念
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver 方法参数解析器,是Spring Web(SpringMVC)组件中的众多解析器之一,主要用来对Controller中方法的参数进行处理。
2.2 内置resolver
参数 | Resolver |
HttpServletRequest | ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver |
HttpServletResponse | ServletResponseMethodArgumentResolver |
@RequestParam | RequestParamMapMethodArgumentResolver |
@PathVariable | PathVariableMapMethodArgumentResolver |
@RequestHeader | RequestHeaderMapMethodArgumentResolver |
@RequestBody | RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor |
@ModelAttribute | ModelAttributeMethodProcessor |
@RequestPart | RequestPartMethodArgumentResolver |
@CookieValue | ServletCookieValueMethodArgumentResolver |
HttpEntity/RequestEntity | HttpEntityMethodProcessor |
2.3 接口说明
public interface HandlerMethodArgumentResolver/**
* 给定的方法参数parameter是否受此解析程序支持。
* @param parameter:要检查的方法参数
**/
booleansupportsParameter(MethodParameterparameter);
/**
* 将方法参数从给定请求解析为参数值。
* @param parameter: 请求参数
* @param mavContainer: 容器
* @param webRequest: 请求
* @param binderFactory: 用于创建一个WebDataBinder用于数据绑定、校验
**/
Object resolveArgument(MethodParameterparameter,@NullableModelAndViewContainermavContainer,
NativeWebRequestwebRequest,@NullableWebDataBinderFactorybinderFactory)throwsException;3、HttpMessageConverter
3.1 基础概念
负责将请求信息转换为一个对象(类型为 T)
3.2 内置Converter
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 负责读、写JSON格式数据(利用Jackson)
AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter 负责读、写Form表单数据
Jaxb2RootElementHttpMessageConverter 负责读、写XML格式数据(使用JAXB)
ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter 负责读、写二进制格式数据
StringHttpMessageConverter 负责读、写字符串格式数据
ResourceHttpMessageConverter 负责读、写资源文件数据
SourceHttpMessageConverter 负责读、写资源数据
3.3 接口说明
public interface HttpMessageConverter<T>
boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes();
default List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes(Class<?> clazz)
return !this.canRead(clazz, (MediaType)null) && !this.canWrite(clazz, (MediaType)null) ? Collections.emptyList() : this.getSupportedMediaTypes();
T read(Class<? extends T> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException;
void write(T t, @Nullable MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException;
getSupportedMediaTypes:获取支持的MediaType集合(如:text/html,text/plain,application/json)
canRead:判断是否能读,针对请求
read:将请求数据进行格式转换(canRead方法返回值为true时调用)
canWrite:判断是否能写,针对响应
write:将响应数据进行格式转换(canWrite方法返回值为true时调用)
4、自定义HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
自定义的过程基本上就是继承接口,然后加入到系统里
4.1、创建springboot项目
直接跟着指引,下一步就可以完成了,并没有太多的技术含量,这里也不再赘述
4.2、创建自定义HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
import com.example.webdemo.domain.po.Person;
import org.springframework.core.MethodParameter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.bind.support.WebDataBinderFactory;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.NativeWebRequest;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.HandlerMethodArgumentResolver;
import org.springframework.web.method.support.ModelAndViewContainer;
public class PersonArgumentResolver implements HandlerMethodArgumentResolver
@Override
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter)
return parameter.getParameterType().equals(Person.class);
@Override
public Object resolveArgument(MethodParameter parameter, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest, WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory) throws Exception
String s = webRequest.getParameter("person");
String[] split = s.split(":");
Person person = new Person();
person.setName(split[0]);
person.setAge(split[1]);
return person;
Person定义
@Data
public class Person
private String name;
private String age;
4.3、将自定义Resolver加入到系统中
@Configuration
public class MyWebmvcConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer
@Override
public void addArgumentResolvers(List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers)
resolvers.add(new PersonArgumentResolver());
4.4 测试接口
@RestController
@RequestMapping
public class TestController
@RequestMapping("/up")public Stringtest1(Personperson)
System.out.println(person);return"Hello";
测试脚本
curl --request GET \\
--url 'http://localhost:16002/up?person=chongxin: 1'记得在PersonArgumentResolver里面打个断点哦
5、自定义Converter
5.1、创建springboot项目
直接沿用上面的吧,稍微的删除下
5.2、自定义MessageConverter
public class SecondHttpMessageConverter extends AbstractHttpMessageConverter<Person>
public SecondHttpMessageConverter()
super(new MediaType("application", "x-xiangcai", Charset.forName("UTF-8")));
@Override
protected boolean supports(Class<?> clazz)
return Person.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz);
@Override
protected Person readInternal(Class<? extends Person> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException
String s = StreamUtils.copyToString(inputMessage.getBody(), Charset.defaultCharset());
String[] split = s.split(":");
Person person = new Person();
person.setName(split[0]);
person.setAge(split[1]);
return person;
@Override
protected void writeInternal(Person person, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage) throws IOException, HttpMessageNotWritableException
5.3 加入配置中
@Configuration
public class MyWebmvcConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer
@Override
public void extendMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>>converters)
SecondHttpMessageConvertersecondHttpMessageConverter=newSecondHttpMessageConverter();
converters.add(secondHttpMessageConverter);
5.4 测试代码
@RestController
public class TestController
@RequestMapping("/up")
public String test1(@RequestBody Person person)
System.out.println(person);
return "Hello";
注意看这里的代码和上面是不同的,不要使用上面的接口哦
测试脚本
curl --request POST \\
--url http://localhost:16002/up \\
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-xiangcai' \\
--header 'content-type: text/plain' \\
--data 'chongxin: 1'注意这里使用的是post,并且设置了Content-Type: application/x-xiangcai
5.5 注意点
处理过程会按集合顺序匹配合适的消息转换器,如果有合适的,就会使用该消息转换器处理(读、写),后续的消息转换器不再执行。
自定义的消息转换器要想生效,必须放到集合中相同类型的消息转换器前面,原因参考第二点。
WebMvcConfigurer.configureMessageConverters方法会覆盖默认消息转换器集合
WebMvcConfigurer.extendMessageConverters方法不会覆盖默认消息转换器集合
6、总结
6.1 converter和Resolver的区别:
Converter 主要是用来做数据body的计息,针对@RequestBody
Resolver 主要是用来做数据类型转换,主要是用来解析参数,针对基于键值对的
6.2 自定义套路
继承相应的接口,在Configuration加入列表中
6.3 调用顺序
从数据流图中可以看到先是使用resolver,然后调用converter
6.4 最后贴下debug的图
方便你找到断点,贯穿整个流程

赠人玫瑰,手留余香,感谢点赞
以上是关于springboot请求参数绑定原理篇的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章