-Controlling the Iterative Execution .3.1
Posted zhangrelay
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了-Controlling the Iterative Execution .3.1相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
2.3 ANALYZING THE BR2 BASICS PACKAGE 这一节内容有些多……
前一篇:
ROS2机器人编程简述humble-第二章-DEVELOPING THE FIRST NODE .2
里面只有节点,没有任何实际功能。
logger.cpp代码如下所示:
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
auto node = rclcpp::Node::make_shared("logger_node");
rclcpp::Rate loop_rate(500ms);
int counter = 0;
while (rclcpp::ok())
RCLCPP_INFO(node->get_logger(), "Hello %d", counter++);
rclcpp::spin_some(node);
loop_rate.sleep();
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
这是一段代码“实现在固定时间执行任务“
周期:rclcpp::Rate loop_rate(500ms);
消息:RCLCPP_INFO(node->get_logger(), "Hello %d", counter++);
ROS消息通常具备时间戳!
rclcpp::spin_some(node);
参考官方文档如下:
rclcpp::spin
Create a default single-threaded executor and spin the specified node.
创建默认的单线程执行器并跳转指定的节点。
rclcpp::spin_some
Create a default single-threaded executor and execute any immediately available work.
创建默认的单线程执行器并执行任何立即可用的工作。
rclcpp::spin_until_future_complete
rcl_interfaces/msg/Log.msg
# Debug is for pedantic information, which is useful when debugging issues.
byte DEBUG=10
# Info is the standard informational level and is used to report expected
# information.
byte INFO=20
# Warning is for information that may potentially cause issues or possibly unexpected
# behavior.
byte WARN=30
# Error is for information that this node cannot resolve.
byte ERROR=40
# Information about a impending node shutdown.
byte FATAL=50
#
# Fields
#
# Timestamp when this message was generated by the node.
builtin_interfaces/Time stamp
# Corresponding log level, see above definitions.
uint8 level
# The name representing the logger this message came from.
string name
# The full log message.
string msg
# The file the message came from.
string file
# The function the message came from.
string function
# The line in the file the message came from.
uint32 line
重要图示:


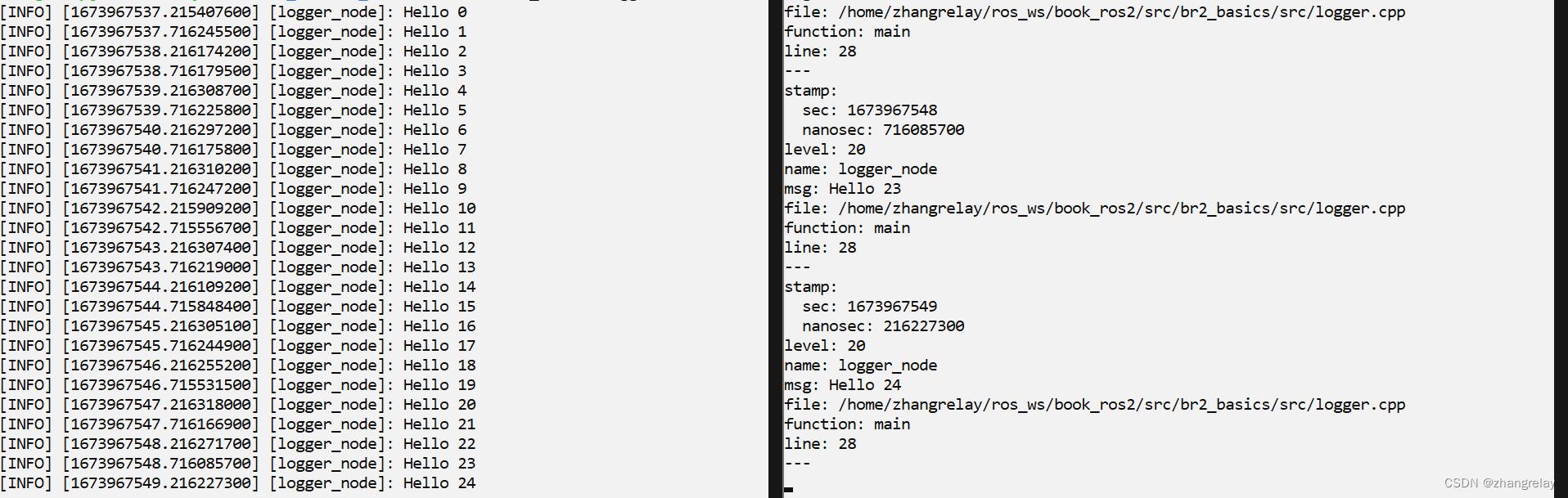
ros2 run br2_basics logger
ros2 topic echo /rosout
ros2 interface show rcl_interfaces/msg/Log
另一种实现方法:
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
class LoggerNode : public rclcpp::Node
public:
LoggerNode()
: Node("logger_node")
counter_ = 0;
timer_ = create_wall_timer(
500ms, std::bind(&LoggerNode::timer_callback, this));
void timer_callback()
RCLCPP_INFO(get_logger(), "Hello %d", counter_++);
private:
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
int counter_;
;
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
auto node = std::make_shared<LoggerNode>();
rclcpp::spin(node);
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
计时器控制控制回路。该计时器以所需频率产生事件。当发生此事件时,它调用处理它的回调。优点是节点在内部调整执行频率,而不将此决定委托给外部代码。安排节点以了解它们的运行频率。
timer_ = create_wall_timer(
500ms, std::bind(&LoggerNode::timer_callback, this));
rclcpp: ROS Client Library for C++
rclcpp provides the canonical C++ API for interacting with ROS. It consists of these main components:
Node
rclcpp::Node
rclcpp/node.hpp
Publisher
rclcpp::Node::create_publisher()
rclcpp::Publisher
rclcpp::Publisher::publish()
rclcpp/publisher.hpp
Subscription
rclcpp::Node::create_subscription()
rclcpp::Subscription
rclcpp/subscription.hpp
Service Client
rclcpp::Node::create_client()
rclcpp::Client
rclcpp/client.hpp
Service Server
rclcpp::Node::create_service()
rclcpp::Service
rclcpp/service.hpp
Timer
rclcpp::Node::create_wall_timer()
rclcpp::WallTimer
rclcpp::TimerBase
rclcpp/timer.hpp
Parameters:
rclcpp::Node::set_parameters()
rclcpp::Node::get_parameters()
rclcpp::Node::get_parameter()
rclcpp::Node::describe_parameters()
rclcpp::Node::list_parameters()
rclcpp::Node::add_on_set_parameters_callback()
rclcpp::Node::remove_on_set_parameters_callback()
rclcpp::Parameter
rclcpp::ParameterValue
rclcpp::AsyncParametersClient
rclcpp::SyncParametersClient
rclcpp/parameter.hpp
rclcpp/parameter_value.hpp
rclcpp/parameter_client.hpp
rclcpp/parameter_service.hpp
Rate:
rclcpp::Rate
rclcpp::WallRate
rclcpp/rate.hpp
There are also some components which help control the execution of callbacks:
Executors (responsible for execution of callbacks through a blocking spin):
rclcpp::spin()
rclcpp::spin_some()
rclcpp::spin_until_future_complete()
rclcpp::executors::SingleThreadedExecutor
rclcpp::executors::SingleThreadedExecutor::add_node()
rclcpp::executors::SingleThreadedExecutor::spin()
rclcpp::executors::MultiThreadedExecutor
rclcpp::executors::MultiThreadedExecutor::add_node()
rclcpp::executors::MultiThreadedExecutor::spin()
rclcpp/executor.hpp
rclcpp/executors.hpp
rclcpp/executors/single_threaded_executor.hpp
rclcpp/executors/multi_threaded_executor.hpp
CallbackGroups (mechanism for enforcing concurrency rules for callbacks):
rclcpp::Node::create_callback_group()
rclcpp::CallbackGroup
rclcpp/callback_group.hpp
Additionally, there are some methods for introspecting the ROS graph:
Graph Events (a waitable event object that wakes up when the graph changes):
rclcpp::Node::get_graph_event()
rclcpp::Node::wait_for_graph_change()
rclcpp::Event
List topic names and types:
rclcpp::Node::get_topic_names_and_types()
Get the number of publishers or subscribers on a topic:
rclcpp::Node::count_publishers()
rclcpp::Node::count_subscribers()
And components related to logging:
Logging macros:
Some examples (not exhaustive):
RCLCPP_DEBUG()
RCLCPP_INFO()
RCLCPP_WARN_ONCE()
RCLCPP_ERROR_SKIPFIRST()
rclcpp/logging.hpp
Logger:
rclcpp::Logger
rclcpp/logger.hpp
rclcpp::Node::get_logger()
Finally, there are many internal API's and utilities:
Exceptions:
rclcpp/exceptions.hpp
Allocator related items:
rclcpp/allocator/allocator_common.hpp
rclcpp/allocator/allocator_deleter.hpp
Memory management tools:
rclcpp/memory_strategies.hpp
rclcpp/memory_strategy.hpp
rclcpp/message_memory_strategy.hpp
rclcpp/strategies/allocator_memory_strategy.hpp
rclcpp/strategies/message_pool_memory_strategy.hpp
Context object which is shared amongst multiple Nodes:
rclcpp::Context
rclcpp/context.hpp
rclcpp/contexts/default_context.hpp
Various utilities:
rclcpp/duration.hpp
rclcpp/function_traits.hpp
rclcpp/macros.hpp
rclcpp/scope_exit.hpp
rclcpp/time.hpp
rclcpp/utilities.hpp
rclcpp/visibility_control.hpp
以上是关于-Controlling the Iterative Execution .3.1的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
The goddess, the bird, the bell, the temptation of the house
Read the ads,Match the titles with the
simplify the design of the hardware forming the interface between the processor and thememory system
Word2010 Error:The name in the end tag of the element must match the element type in the start tag.
Word2010 Error:The name in the end tag of the element must match the element type in the start tag.