android 皮肤包换肤之Resources加载
Posted 史大拿
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了android 皮肤包换肤之Resources加载相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
android 换肤之资源(Resources)加载(一)
本系列计划3篇:
- Android 换肤之资源(Resources)加载(一) — 本篇
- setContentView() / LayoutInflater源码分析(二)
- 换肤框架搭建(三)
看完本篇你可以学会什么?
-
Resources在什么时候被解析并加载的
- Application#Resources
- Activity#Resources
-
drawable 如何加载出来的
-
创建自己的Resources加载自己的资源
-
制作皮肤包"皮肤包"
-
加载“皮肤包”中的资源
tips:源码基于android-30
阅读源码后本篇实现的效果:

效果很简单,2个按钮
- 换肤
- 还原
效果很简单,重点是换肤的时候是加载“皮肤包”中的资源
Resources在什么时候被解析并加载的
Application#Resources
众所周知,java程序都是由main方法开始的,所以我们就从ActivityThread#main()方法开始阅读源码
在ActivityThread#main()方法中,我们经常会说到一些关于Looper,handler的逻辑代码,本篇不展开说Looper
#ActivityThread.java
public static void main(String[] args)
....
// looper
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// szj 创建 activityThread
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false, startSeq);
.....
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
本篇重点不是Looper, 来看看 thread.attach(false, startSeq); 方法
#ActivityThread.java
private void attach(boolean system, long startSeq)
if (!system)
...
else
try
// 很关键的一个类,用来分发activity生命周期
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
mInstrumentation.basicInit(this);
// szj 创建Application Context
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(
this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo);
// szj 反射创建 application
mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null);
// 执行application的onCreate() 方法
mInitialApplication.onCreate();
catch (Exception e)
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e);
- 通过ContextImpl.createAppContext() 创建Context
- 通过反射创建application
- 创建好application后会调用 Application#onCreate()方法
接着执行ContextImpl.createAppContext()

最终会走到LoadedApk#getResources() 上
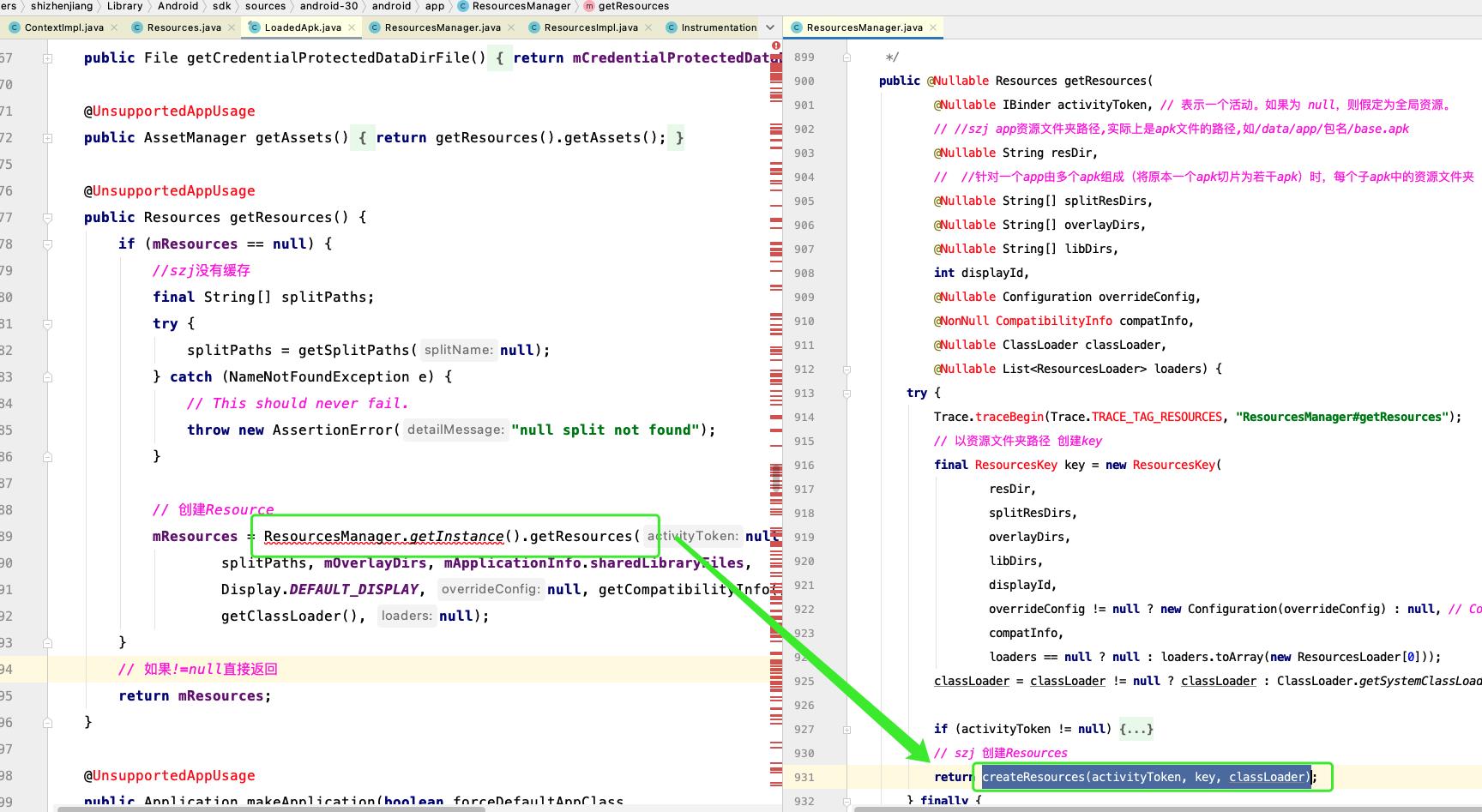
然后会从LoadedApk#getResources() 执行到 ResourcesManager#getResources()
最终在ResourcesManager中创建Resources
这段源码我们知道:
-
在程序运行到main方法的时候,我们会在
ActivtyThread.#attach()中创建Context,创建Application,并且执行Application#onCreate() -
然后会执行到
LoadedApk.getResources()去解析获取Resources()- LoadedApk.java 从类名我们就知道这个类是用来对apk信息解析的
-
最终解析Resources的任务交给了
ResourcesManager#createResources()
好了,读到这里就可以了,来看看Activity#Resources是如何解析并加载的
Activity#Resources
源码分析从 ActivityThread#performLaunchActivity()开始
为什么要从这里开始? 写完换肤之后开始framework系列,到时候具体聊~
#ActivityThread.java
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent)
.... 省略部分代码
// szj 创建 activity 的上下文
ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r);
Activity activity = null;
try
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
// 通过反射创建 activity 的实例
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
catch (Exception e)
.....
try
if (activity != null)
// szj 创建 PhoneWindow,设置windowManager等操作
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.configCallback,
r.assistToken);
activity.mCalled = false;
// szj 分发 onCreate() 事件
if (r.isPersistable())
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
else
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
// 判断是否调用super.onCreate() 方法
if (!activity.mCalled)
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
...
catch (Exception e)
...
return activity;
在performLaunchActivity()这段代码中有几个重点:
- createBaseContextForActivity() 创建ContextImpl
- mInstrumentation.newActivity(,); 通过反射创建Activity实例
- 然后会调用Activity#attach() 方法绑定window等操作
- 绑定了window之后会立即调用Activity#onCreate()进行页面初始化
本篇重点是Context,其他的先不关注,先来看看createBaseContextForActivity() 代码
# ContextImpl.java
@UnsupportedAppUsage
static ContextImpl createActivityContext(ActivityThread mainThread,
LoadedApk packageInfo, ActivityInfo activityInfo, IBinder activityToken, int displayId,
Configuration overrideConfiguration)
....
/// szj创建Context
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread, packageInfo, null,
activityInfo.splitName, activityToken, null, 0, classLoader, null);
...
final ResourcesManager resourcesManager = ResourcesManager.getInstance();
/// szj 通过ResourcesManager创建Resources
context.setResources(resourcesManager.createBaseTokenResources(activityToken,
packageInfo.getResDir(),
....));
return context;
最终会调用到 ResourcesManager.getInstance().createBaseTokenResources() 方法

最终
- activity创建Resurces
- application创建Resurces
都是调用到ResourcesManager#createResources()来创建Resources
这里还用到了一个类:ResourcesKey 这个类主要作用就是来存储数据,以及做一些校验等
ResourcesManager#createResources()源码分析
#ResourcesManager.java
private @Nullable Resources createResources(@Nullable IBinder activityToken,
@NonNull ResourcesKey key, @NonNull ClassLoader classLoader)
synchronized (this)
//szj 从缓存中找 ResourcesImpl 如果不存在就创建
代码1: ResourcesImpl resourcesImpl = findOrCreateResourcesImplForKeyLocked(key);
if (resourcesImpl == null)
return null;
if (activityToken != null)
// 创建Resources
return createResourcesForActivityLocked(activityToken, classLoader,
resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo);
else
// 直接创建Resources对象
return createResourcesLocked(classLoader, resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo);
先来看findOrCreateResourcesImplForKeyLocked(key);
#ResourcesManager.java
private @Nullable ResourcesImpl findOrCreateResourcesImplForKeyLocked(
@NonNull ResourcesKey key)
// szj查找与ResourcesImpl匹配的缓存资源
ResourcesImpl impl = findResourcesImplForKeyLocked(key);
if (impl == null)
// szj 创建ResourcesImpl
impl = createResourcesImpl(key);
if (impl != null)
// 加入到缓存中
mResourceImpls.put(key, new WeakReference<>(impl));
return impl;
这段代码很简单,做了一些缓存,通过createResourcesImpl() 创建了ResourcesImpl
#ResourcesManager.java
private @Nullable ResourcesImpl createResourcesImpl(@NonNull ResourcesKey key)
final DisplayAdjustments daj = new DisplayAdjustments(key.mOverrideConfiguration);
daj.setCompatibilityInfo(key.mCompatInfo);
// szj创建 AssetManager
final AssetManager assets = createAssetManager(key);
if (assets == null)
return null;
final DisplayMetrics dm = getDisplayMetrics(key.mDisplayId, daj);
final Configuration config = generateConfig(key, dm);
// 根据assetManager 创建一个ResourceImpl
// 其实找资源是 Resources -> ResourcesImpl -> AssetManager
final ResourcesImpl impl = new ResourcesImpl(assets, dm, config, daj);
...
return impl;
关键点又来了:
创建ResourcesImpl需要4个参数:
-
参数一: AssetManager 具体资源管理
(重要) -
参数二: DisplayMetrics 屏幕的一些封装
- 通过getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density 获取过屏幕的密度
- 通过getResources().getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels 获取过屏幕的宽度等
-
参数三: Configuration 一些配置信息[对本篇来说不重要]
-
参数四: DisplayAdjustments 资源的兼容性等 [对本篇来说不重要]
createAssetManager方法:
#ResourcesManager.java
protected @Nullable AssetManager createAssetManager(@NonNull final ResourcesKey key)
// szj 创建AssetManager对象
final AssetManager.Builder builder = new AssetManager.Builder();
// key.mResDir 就是apk在手机内存中的的完整路径
if (key.mResDir != null)
try
builder.addApkAssets(loadApkAssets(key.mResDir, false, false));
catch (IOException e)
return null;
....
if (key.mLibDirs != null)
/// 循环lib中的资源
for (final String libDir : key.mLibDirs)
// .apk
/// 只有.apk文件中才有资源,所以只要有资源的地方
if (libDir.endsWith(".apk"))
try
builder.addApkAssets(loadApkAssets(libDir, true /*sharedLib*/,
false /*overlay*/));
catch (IOException e)
...
return builder.build();
这段代码通过Builder设计模式,将多个资源文件下的资源都保存起来
多个资源指的是一个项目中的多个lib
来看看单个资源是如何加载的的(loadApkAssets):
#ResourcesManager.java
// path 表示当前apk在手机中的的完整路径
private @NonNull ApkAssets loadApkAssets(String path, boolean sharedLib, boolean overlay)
throws IOException
....
// We must load this from disk.
/// 从磁盘加载apk资源
if (overlay)
apkAssets = ApkAssets.loadOverlayFromPath(overlayPathToIdmapPath(path), 0 /*flags*/);
else
apkAssets = ApkAssets.loadFromPath(path, sharedLib ? ApkAssets.PROPERTY_DYNAMIC : 0);
....
return apkAssets;
最终通过静态方法创建ApkAssets:
# ApkAssets.java
public static @NonNull ApkAssets loadOverlayFromPath(@NonNull String idmapPath,
@PropertyFlags int flags) throws IOException
return new ApkAssets(FORMAT_IDMAP, idmapPath, flags, null /* assets */);
public static @NonNull ApkAssets loadFromPath(@NonNull String path, @PropertyFlags int flags)
throws IOException
return new ApkAssets(FORMAT_APK, path, flags, null /* assets */);
创建ApkAssets的时候就是通过
- 一个变量来标记当前是什么文件
- 并且保存文件路径
这个变量一共有4种类型:

- FORMAT_APK 标记为apk文件
- FORMAT_IDMAP 标记为idmap文件
- FORMAT_ARSC 标记为 resources.arsc文件
- FORMAT_DIR 标记为是一个目录
默认都是标记为apk文件,因为默认加载的就是.apk文件
这里着重提一下 resources.arsc 文件

这个文件是打包的时候自动生成的,会存放一些资源下的信息,例如图中的id等等,全部资源都可以在这里面找到!
OK,回到主题,这里就不扯了
当解析了apk之后,就会调用 AssetManager.Builder#build()方法
#ResourcesManager.java
protected @Nullable AssetManager createAssetManager(@NonNull final ResourcesKey key)
final AssetManager.Builder builder = new AssetManager.Builder();
if (key.mResDir != null)
try
/// 上面代码将apk路径都解析好了
builder.addApkAssets(loadApkAssets(key.mResDir, false, false));
catch (IOException e)
return null;
...
// 现在执行build()
return builder.build();
#AssetManager.Builder.java
public AssetManager build()
....
final ApkAssets[] apkAssets = new ApkAssets[totalApkAssetCount];
....
final AssetManager assetManager = new AssetManager(false /*sentinel*/);
// 最终交给 nativeSetApkAssets() 来管理
AssetManager.nativeSetApkAssets(assetManager.mObject, apkAssets,
false /*invalidateCaches*/);
assetManager.mLoaders = mLoaders.isEmpty() ? null
: mLoaders.toArray(new ResourcesLoader[0]);
return assetManager;
最终通过AssetManager.Builder 来创建了AssetManager
并且由ApkAssets保存了apk的一些信息,例如路径,文件类型等
最终创建好AssetManager交给ResourcesImpl来管理
#ResourcesManager.java
private @Nullable ResourcesImpl createResourcesImpl(@NonNull ResourcesKey key)
final DisplayAdjustments daj = new DisplayAdjustments(key.mOverrideConfiguration);
daj.setCompatibilityInfo(key.mCompatInfo);
/// 刚才通过AssetManager.Builder() 来创建的AssetManager
final AssetManager assets = createAssetManager(key);
if (assets == null)
return null;
// 交给ResourcesImpl 来管理
final ResourcesImpl impl = new ResourcesImpl(assets, dm, config, daj);
return impl;
在退回到最外层:
#ResourcesManager.java
private @Nullable Resources createResources(@Nullable IBinder activityToken,
@NonNull ResourcesKey key, @NonNull ClassLoader classLoader)
synchronized (this)
/// 刚才走的这创建的ResourcesImpl
ResourcesImpl resourcesImpl = findOrCreateResourcesImplForKeyLocked(key);
if (resourcesImpl == null)
return null;
if (activityToken != null)
// 创建Resources
return createResourcesForActivityLocked(activityToken, classLoader,
resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo);
else
// 直接创建Resources对象
return createResourcesLocked(classLoader, resourcesImpl, key.mCompatInfo);
通过findOrCreateResourcesImplForKeyLocked() 中找或者创建 ResourcesImpl
最终将ResourcesImpl交给Resources来管理

走到这里Resources就创建好了
这里有很多角色来捋一下:
- ResourcesManager 用来创建Resources
- ResourcesImpl 用来创建AssetManager,Resources的具体实现,用来具体读取资源
- AssetManager 管理apk,解析app/多个lib 下的资源
- ApkAssets 用来记录apk信息
- Resources 用来管理ResourcesImpl
drawable 如何加载出来的
相信大家在开发中经常写这种代码,这一小节来看看他是如何加载出来的

#Context.java
public final Drawable getDrawable(@DrawableRes int id)
return getResources().getDrawable(id, getTheme());
#Resources.java
public Drawable getDrawable(@DrawableRes int id, @Nullable Theme theme)
throws NotFoundException
return getDrawableForDensity(id, 0, theme);
<以上是关于android 皮肤包换肤之Resources加载的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章