日常系列LeetCode《15·链表2》
Posted 常某某的好奇心
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了日常系列LeetCode《15·链表2》相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
数据规模->时间复杂度
<=10^4 😮(n^2)
<=10^7:o(nlogn)
<=10^8:o(n)
10^8<=:o(logn),o(1)
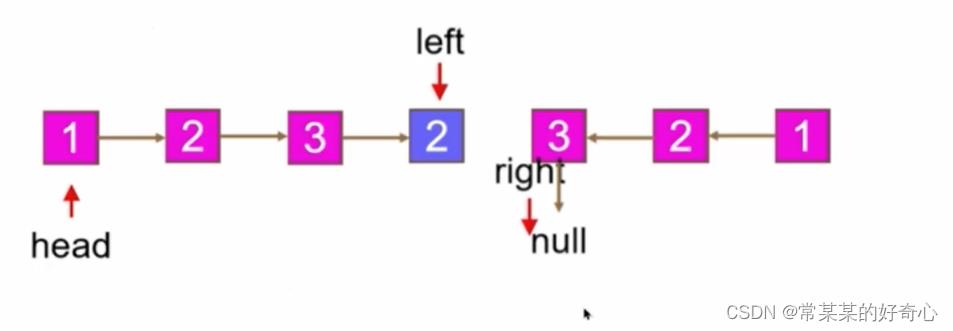
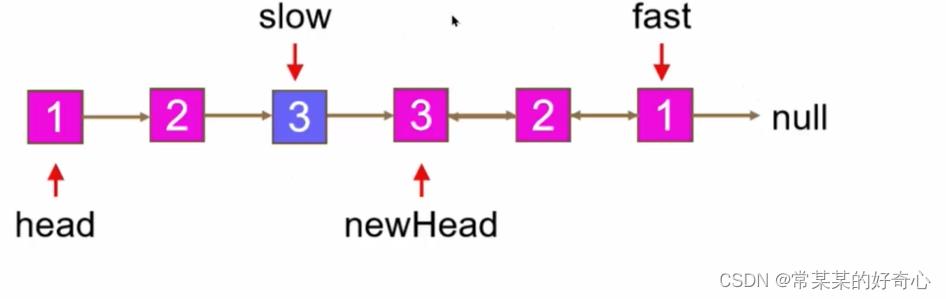
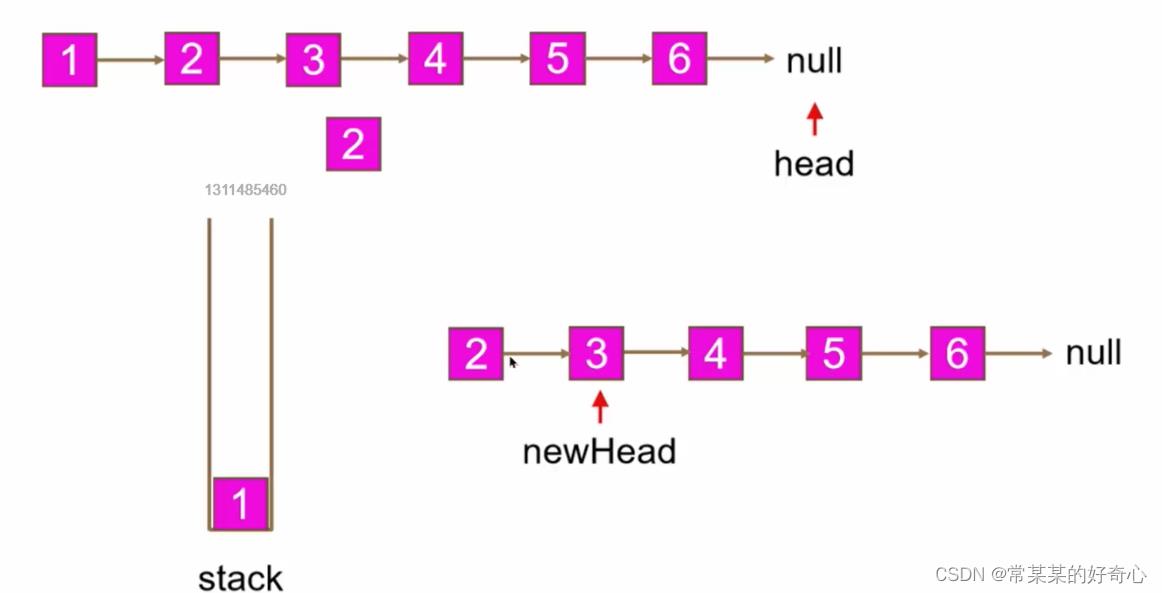
lc 234【剑指 027 】【top100】:回文链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-linked-list/
提示:
链表中节点数目在范围[1, 10^5] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 9
进阶:
你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
if not head or not head.next:return True
#
slow=head
fast=head.next
while fast and fast.next:
slow=slow.next
fast=fast.next.next
newhead=slow.next
slow.next=None
#
left=head
right=self.reverseList(newhead)
while right:
if left.val!=right.val:return False
left,right=left.next,right.next
return True
def reverseList(self,node):
prev=None
curr=node
while curr:
nextN=curr.next
curr.next=prev
prev=curr
curr=nextN
return prev
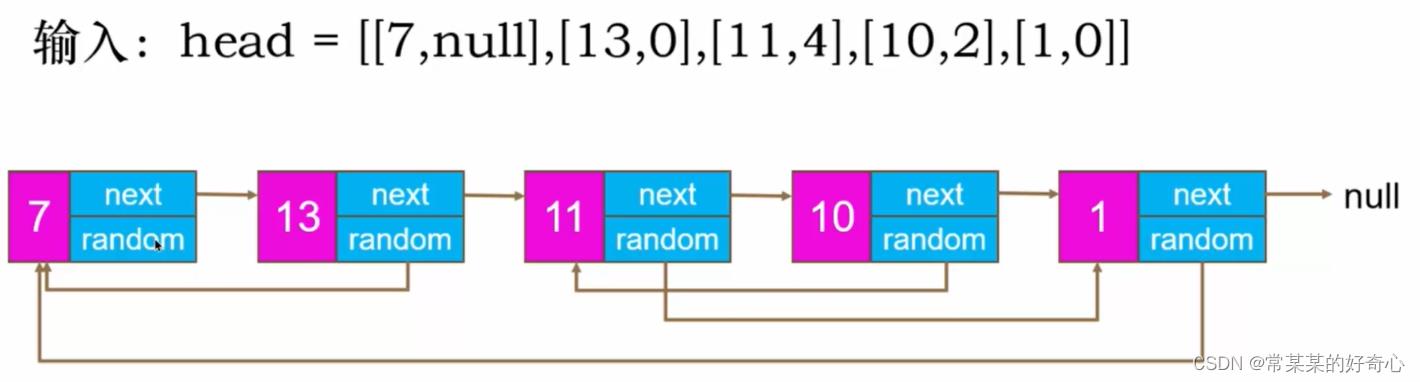
lc 138【剑指 35】 :复制带随机指针的链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/fu-za-lian-biao-de-fu-zhi-lcof/
提示:
-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000
Node.random 为空(null)或指向链表中的节点。
节点数目不超过 1000 。
#方案一:递归
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.Map=
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
#
if not head:return head
#
newnode=Node(head.val)
self.Map[head]=newnode #key-key-key:random的映射
newnode.next=self.copyRandomList(head.next)
if head.random:
newnode.random=self.Map[head.random]
return newnode
#方案二:迭代
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.Map=
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
#
if not head:return head
#
newnode=Node(head.val)
self.Map[head]=newnode #key-key-key:random的映射
newhead=newnode
#
while head:
newnode.next=self.get_cloned_node(head.next)
newnode.random=self.get_cloned_node(head.random)
newnode=newnode.next
head=head.next
return newhead
def get_cloned_node(self,node):
if not node:return None
if node not in self.Map:self.Map[node]=Node(node.val) #key-key-key
return self.Map[node]
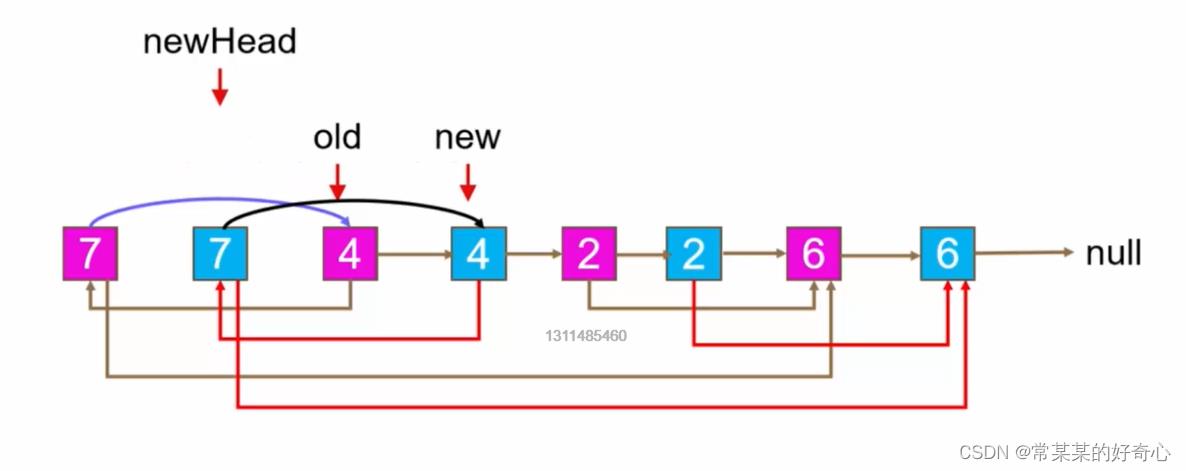
#方案三:新旧节点交替,代替Map
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):
self.val = int(x)
self.next = next
self.random = random
"""
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.Map=
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':
#
if not head:return head
#建立新旧节点交替
curr=head
while curr:
newnode=Node(curr.val)
newnode.next=curr.next
curr.next=newnode
curr=newnode.next
#设置random
curr=head
while curr:
curr.next.random=curr.random.next if curr.random else None
curr=curr.next.next
#分割
old=head
new=head.next
newhead=head.next
while new:
old.next=old.next.next
new.next=new.next.next if new.next else None
old=old.next
new=new.next
return newhead
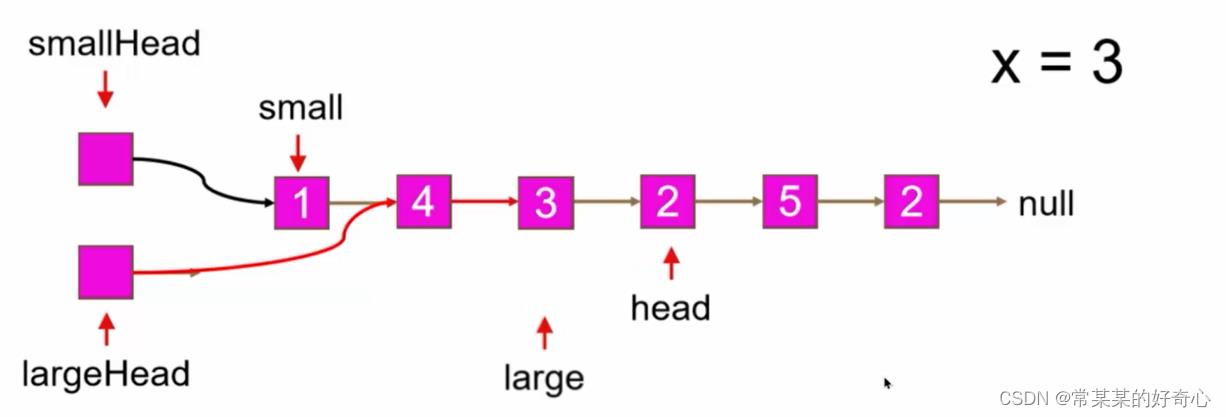
lc 86 :分隔链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/partition-list/
提示:
链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 200] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
-200 <= x <= 200
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def partition(self, head: Optional[ListNode], x: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head or not head.next:return head
#
smallhead=ListNode(-1)
small=smallhead
largehead=ListNode(-1)
large=largehead
#
while head:
if head.val<x:
small.next=head
small=small.next
else:
large.next=head
large=large.next
head=head.next
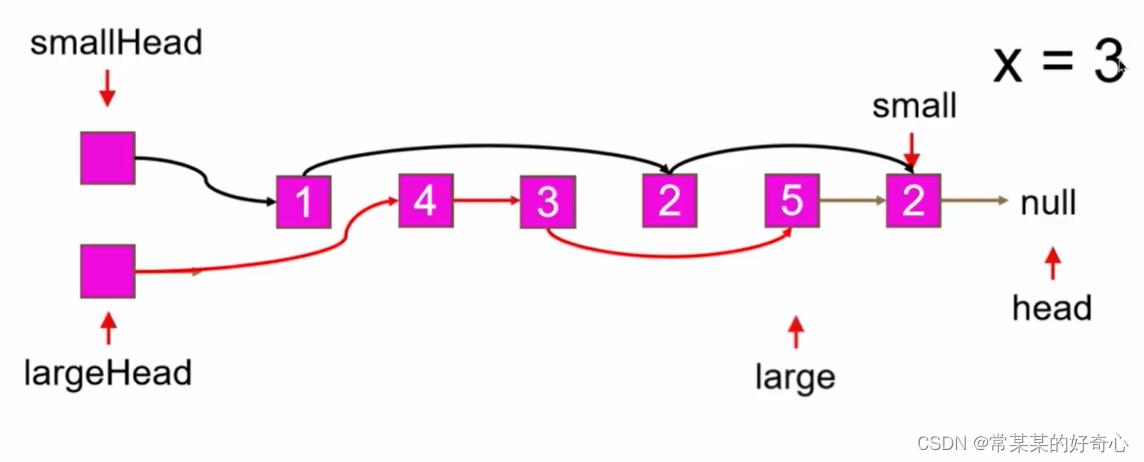
#
large.next=None
small.next=largehead.next
return smallhead.next
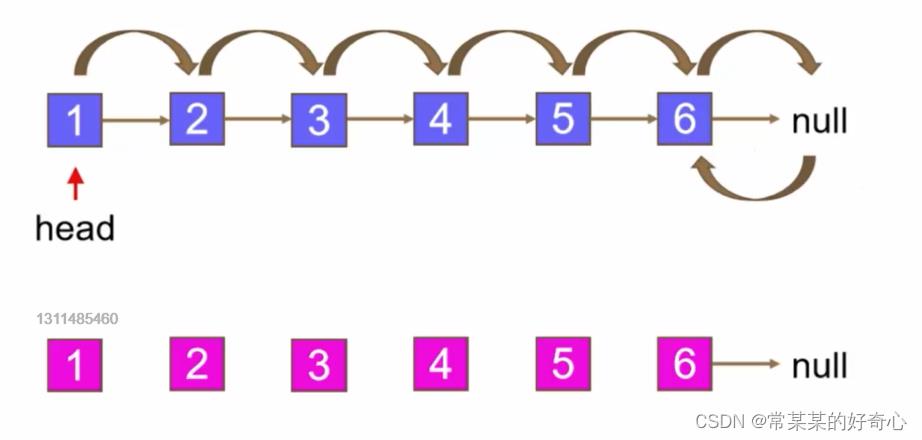
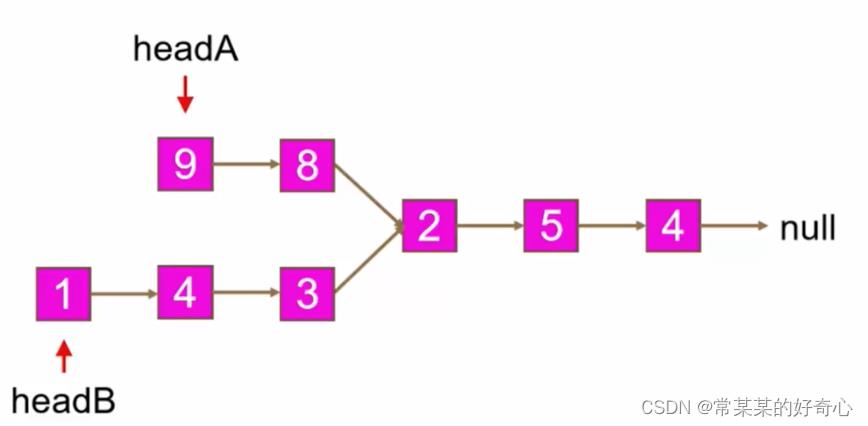
lc 160【剑指 023】【top100】:相交链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
提示:
listA 中节点数目为 m
listB 中节点数目为 n
1 <= m, n <= 3 * 10^4
1 <= Node.val <= 10^5
0 <= skipA <= m
0 <= skipB <= n
如果 listA 和 listB 没有交点,intersectVal 为 0
如果 listA 和 listB 有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]
进阶:
你能否设计一个时间复杂度 O(m + n) 、仅用 O(1) 内存的解决方案?
#方案一:hash
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> Optional[ListNode]:
common=set()
while headA:
common.add(headA)
headA=headA.next
while headB:
if headB in common:return headB
headB=headB.next
return None
#方案二:双指针(相交时步数一致)
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
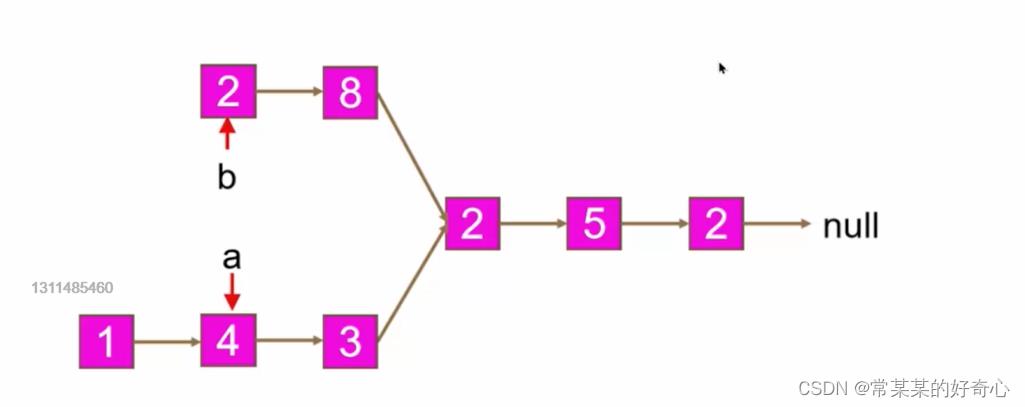
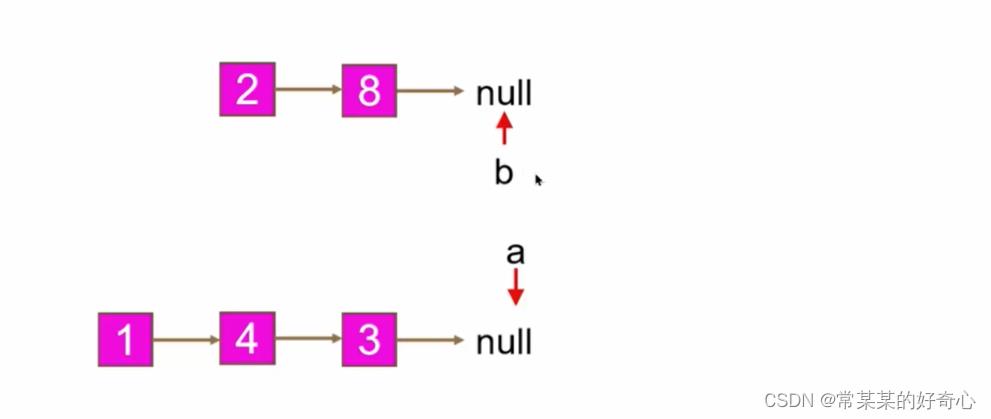
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not headA or not headB:return None
a=headA
b=headB
while a!=b:
a=a.next if a else headB
b=b.next if b else headA
return a
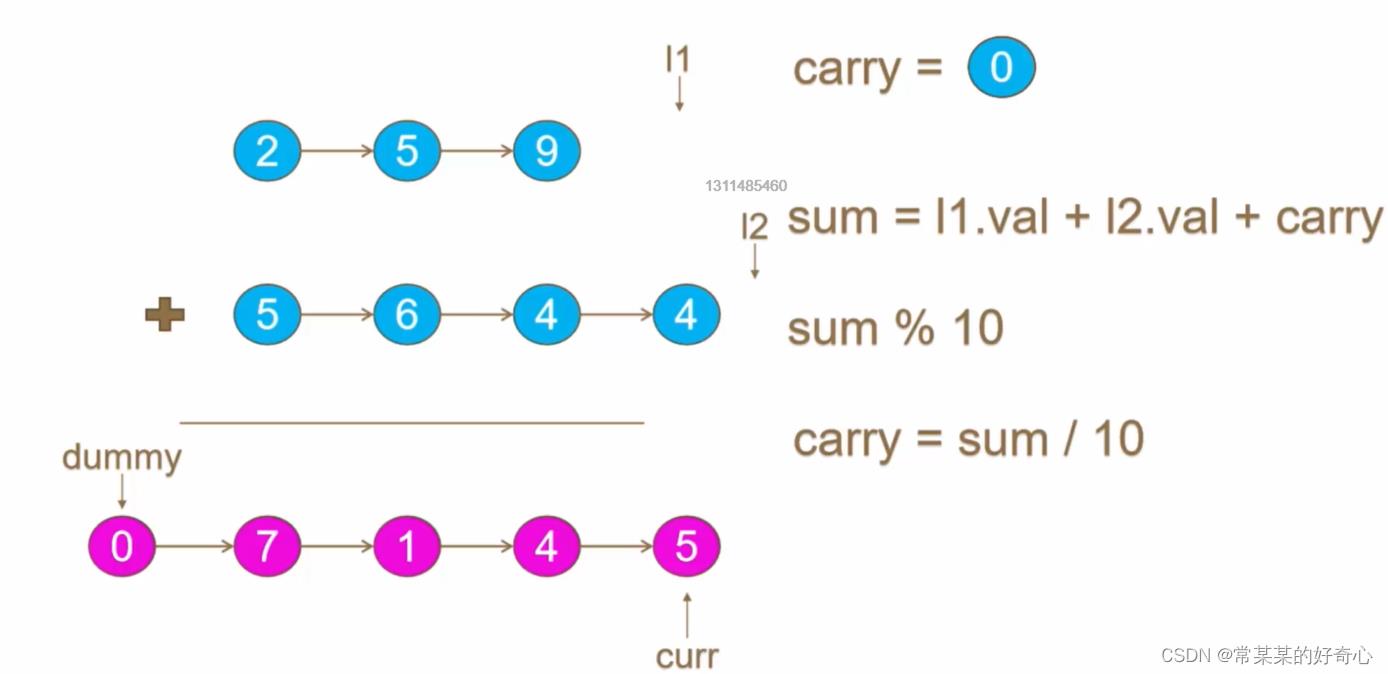
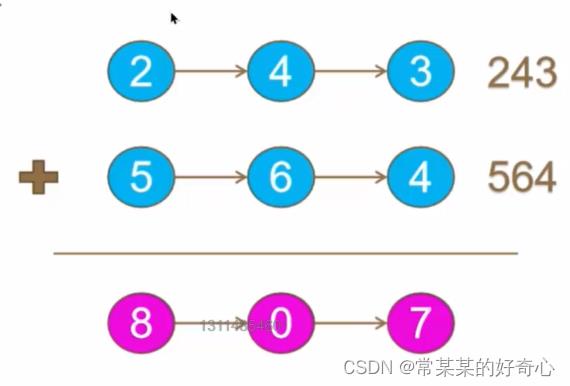
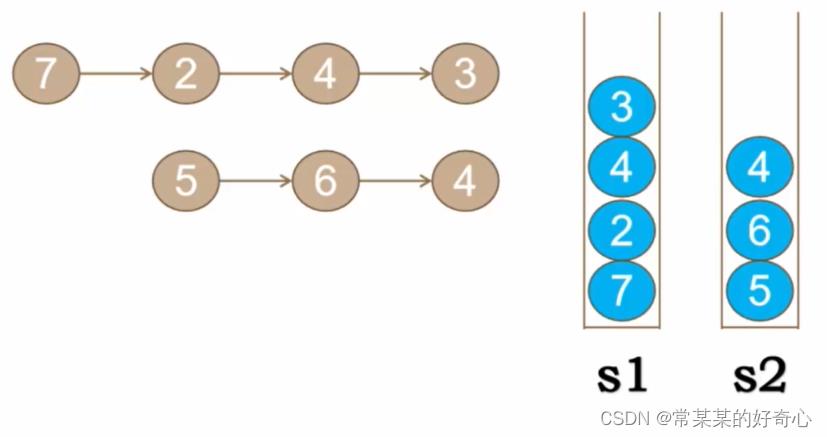
lc 2 【top100】:两数相加
https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-two-numbers/
提示:
每个链表中的节点数在范围 [1, 100] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 9
题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
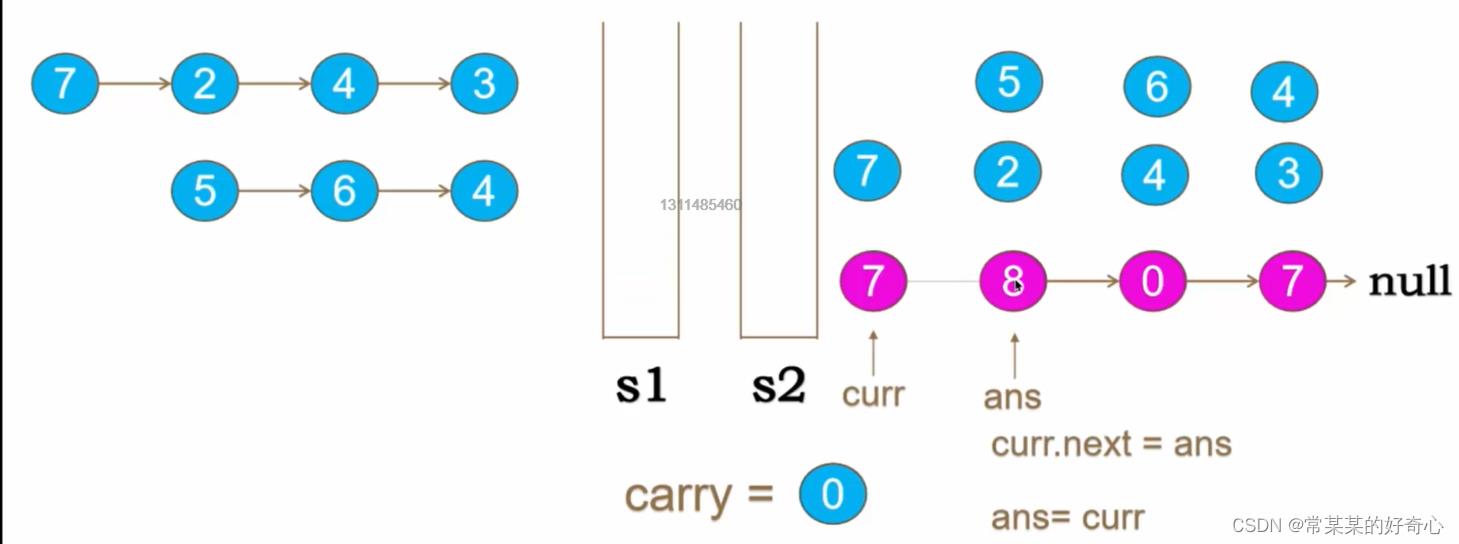
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
#
dummynode=ListNode(-1)
curr=dummynode
carry=0
while l1 or l2:
n1=l1.val if l1 else 0
n2=l2.val if l2 else 0
sumA=n1+n2+carry
carry=sumA//10
#
curr.next=ListNode(sumA%10)
#
curr=curr.next
l1=l1.next if l1 else None
l2=l2.next if l2 else None
if carry==1:curr.next=ListNode(carry)
return dummynode.next
lc 445【剑指 025】 :两数相加 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/add-two-numbers-ii/
提示:
链表的长度范围为 [1, 100]
0 <= node.val <= 9
输入数据保证链表代表的数字无前导 0
进阶:
如果输入链表不能翻转该如何解决?
#方案一:反转链表
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
newl1=self.reverseList(l1)
newl2=self.reverseList(l2)
#
dummynode=ListNode(-1)
curr=dummynode
carry=0
while newl1 or newl2:
n1=newl1.val if newl1 else 0
n2=newl2.val if newl2 else 0
sum=n1+n2+carry
curr.next=ListNode(sum%10)
carry=sum//10
#
curr=curr.next
newl1=newl1.next if newl1 else None
newl2=newl2.next if newl2 else None
if carry==1:curr.next=ListNode(carry)
return self.reverseList(dummynode.next)
def reverseList(self,node):
prev=None
curr=node
while curr:
next=curr.next
curr.next=prev
prev=curr
curr=next
return prev
#方案二:使用栈
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not l1:return l2
if not l2:return l1
#
stack1=[]
stack2=[]
while l1:
stack1.append(l1)
l1=l1.next
while l2:
stack2.append(l2)
l2=l2.next
#
dummynode=ListNode(-1)
curr=dummynode
carry=0
while stack1 or stack2:
n1=stack1.pop().val if stack1 else 0
n2=stack2.pop().val if stack2 else 0
sum=n1+n2+carry
curr.next=ListNode(sum%10)
carry=sum//10
#
curr=curr.next
if carry==1:curr.next=ListNode(carry)
return self.reverseList(dummynode.next)
def reverseList(self,node):
prev=None
curr=node
while curr:
next=curr.next
curr.next=prev
prev=curr
curr=next
return prev
#方案三:使用栈(优化)
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not l1:return l2
if not l2:return l1
#
stack1=[]
stack2=[]
while l1:
stack1.append(l1)
l1=l1.next
while l2:
stack2.append(l2)
l2=l2.next
#
ans=None
carry=0
while stack1 or stack2:
n1=stack1.pop().val if stack1 else 0
n2=stack2.pop().val if stack2 else 0
sum=n1+n2+carry
curr=ListNode(sum%10)
curr.next=ans
carry=sum//10
#
ans=curr
if carry==1:
curr=ListNode(carry)
curr.next=ans
ans=curr
return ans
# def reverseList(self,node):
# prev=None
# curr=node
# while curr:
# next=curr.next
# curr.next=prev
# prev=curr
# curr=next
# return prev
lc 21【剑指 25】【top100】:合并两个有序链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
提示:
两个链表的节点数目范围是 [0, 50]
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
l1 和 l2 均按 非递减顺序 排列
#方案一:迭代
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
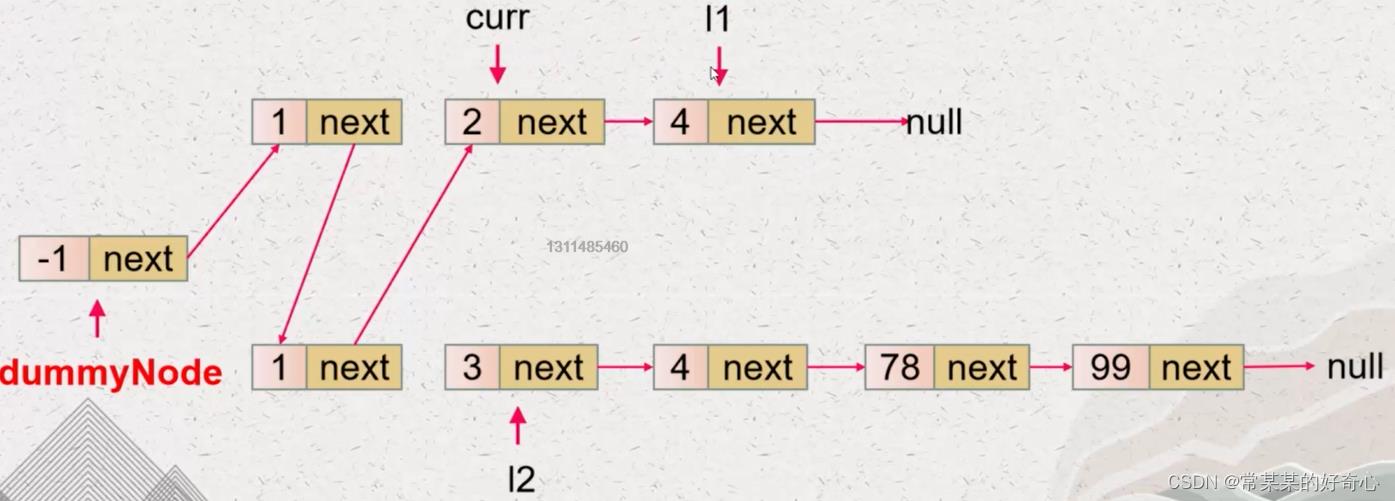
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
#
if not list1:return list2
if not list2:return list1
#
dummy=ListNode(-1)
curr=dummy
while list1 and list2:
if list1.val <= list2.val:
curr.next=list1
list1=list1.next
else:
curr.next=list2
list2=list2.next
curr=curr.next
if not list1:curr.next=list2
if not list2:curr.next=list1
return dummy.next
#方案二:递归
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
#
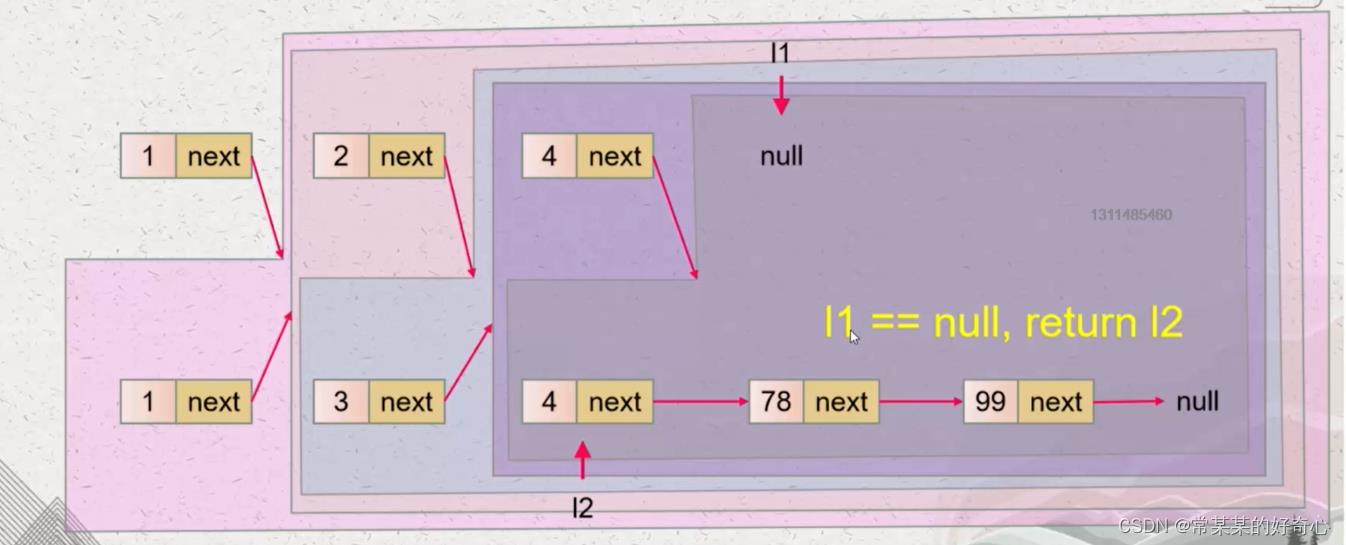
if not list1:return list2
if not list2:return list1
#
if list1.val<=list2.val:
list1.next=self.mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2)
return list1
else:
list2.next=self.mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next)
return list2
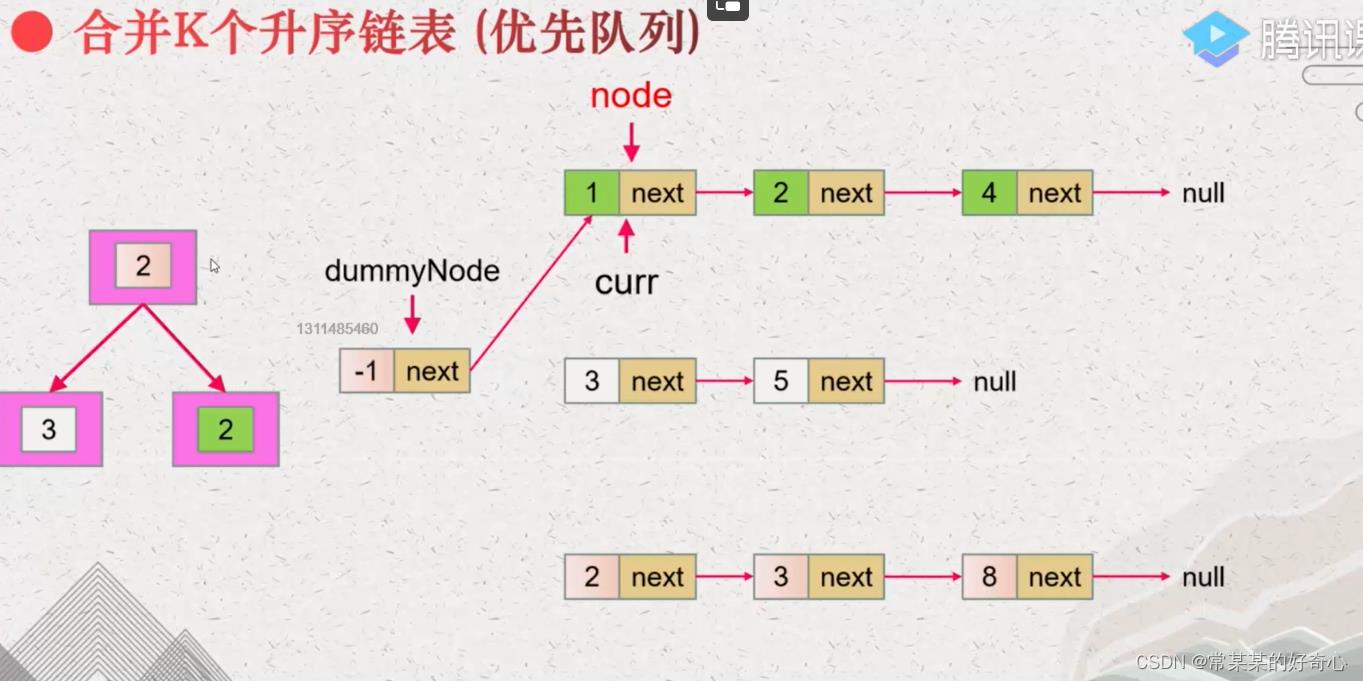
lc 23【剑指 078】【top100】:合并K个升序链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
提示:
k == lists.length
0 <= k <= 10^4
0 <= lists[i].length <= 500
-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4
lists[i] 按 升序 排列
lists[i].length 的总和不超过 10^4
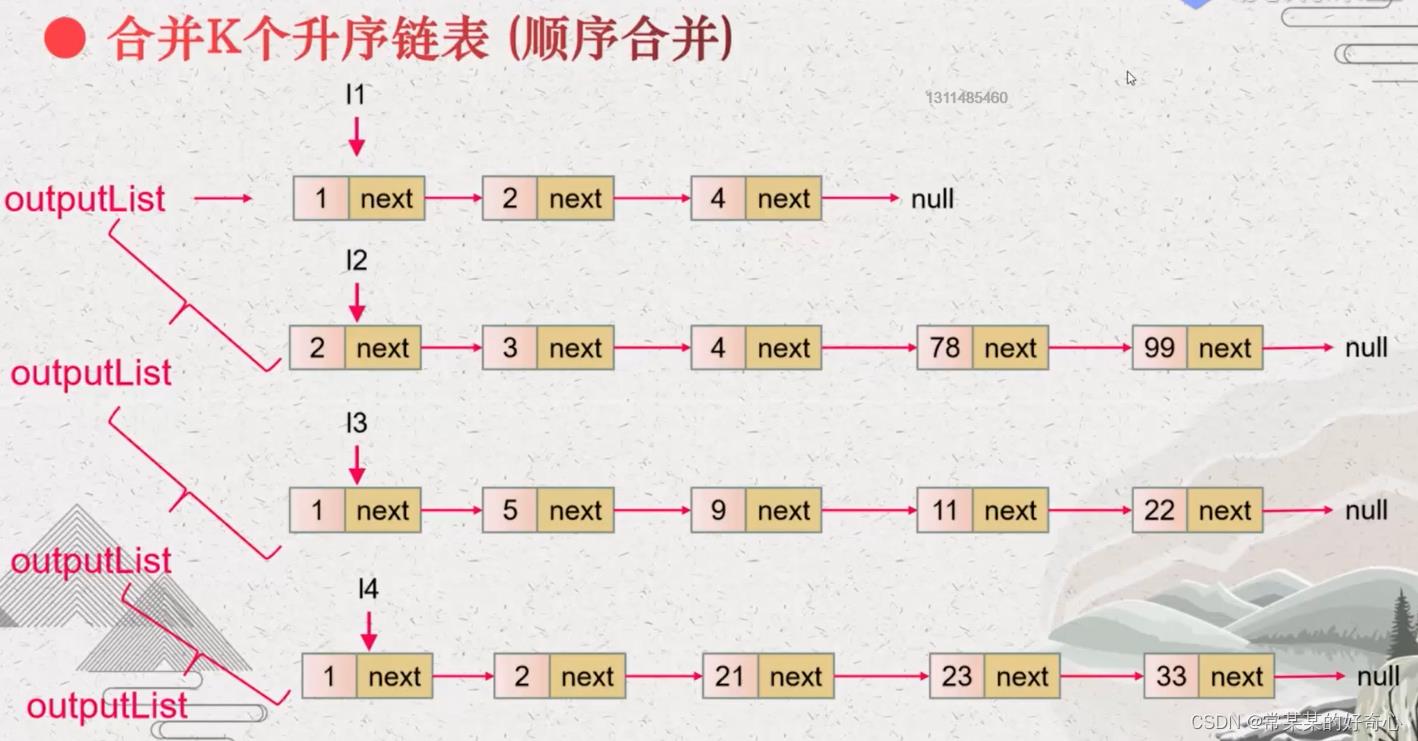
#方案一:顺序合并
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[Optional[ListNode]]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
#o((k^2)*n),o(1)
if len(lists)==0:return None
outlist=lists[0]
for i in range(1,len(lists)):
outlist=self.merge2Lists(outlist,lists[i])
return outlist
def merge2Lists(self,list1,list2):
#
if not list1:return list2
if not list2:return list1
#
if list1.val<=list2.val:
list1.next=self.merge2Lists(list1.next,list2)
return list1
else:
list2.next=self.merge2Lists(list1,list2.next)
return list2
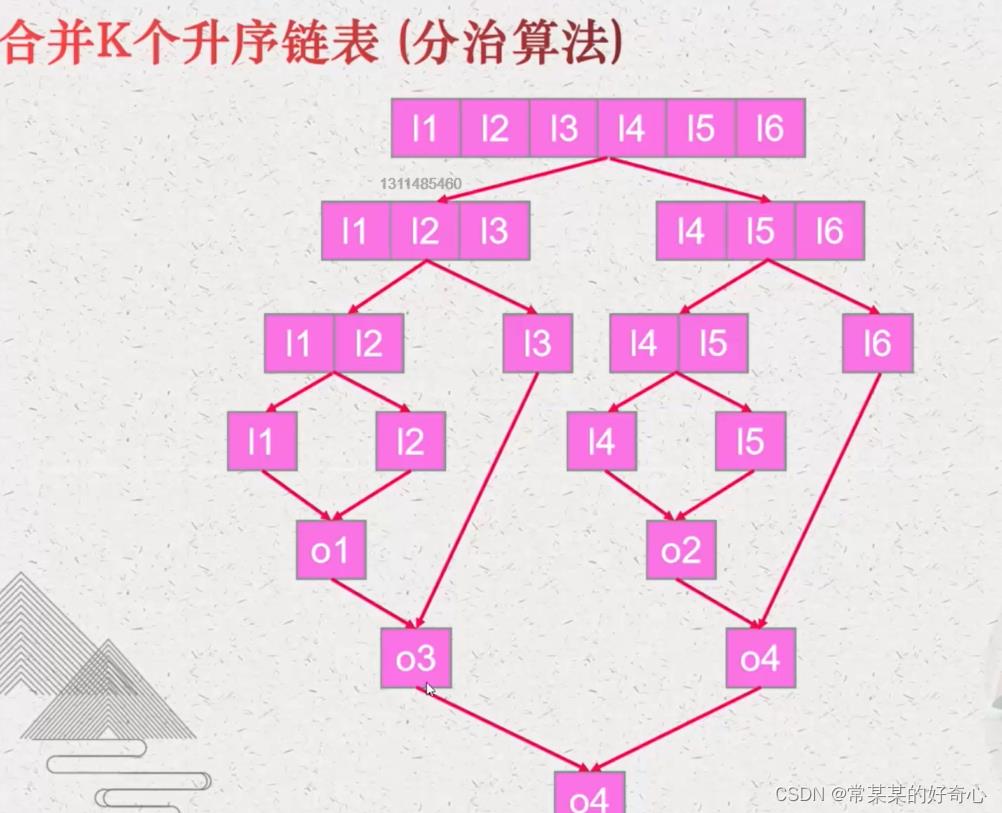
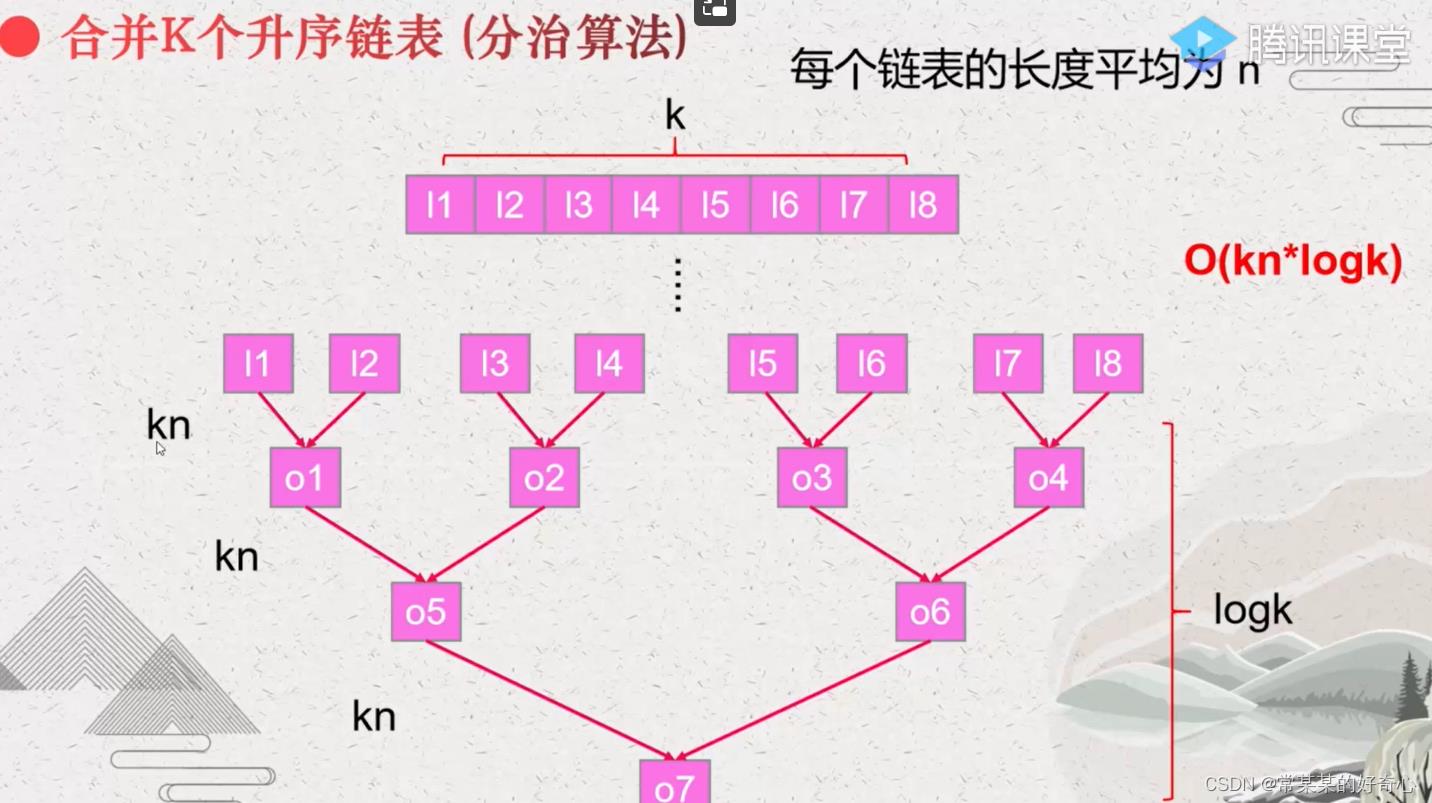
#方案二:分治
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val以上是关于日常系列LeetCode《15·链表2》的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章