杂谈记录——论Long类型的大数据量求交集
Posted 唐 昊
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了杂谈记录——论Long类型的大数据量求交集相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、优化内外层比较的结构
『外层遍历 + 内层遍历』查找:
复杂度 O (NM) ,一般使用 contains () 检查是否包含
『外层遍历 + 内层 Hash』查找:
复杂度 O (N),一般将内层 List 转化为 HashSet 实现
『外层遍历 + 内层 bitMap』查找:
复杂度 O (N),一般将内层 List 转化为字节映射实现
package com.jw.demo.com.colllection.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.*;
public class SetOperation
@Test
public void setOperation()
int size = 5000000;
HashSet<Long> la = new HashSet<>(size);
HashSet<Long> lb = new HashSet<>(size);
for (int i = 0; i < 300000; i++)
la.add(Long.valueOf(i));
for (int i = 0; i < 300000; i++)
lb.add(Long.valueOf(i));
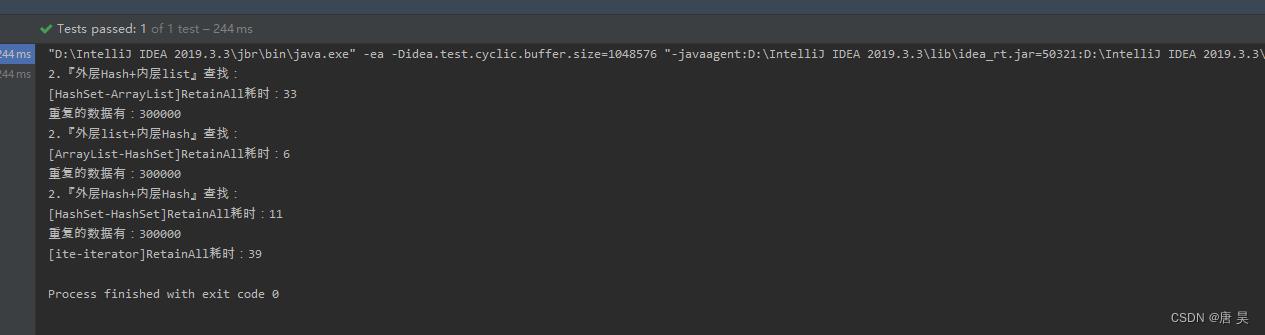
System.out.println("2.『外层Hash+内层list』查找:");
outHastSetInnerHashSet(la, new ArrayList<>(lb));
System.out.println("重复的数据有:"+la.size());
//『外层list+内层Hash』查找:
System.out.println("2.『外层list+内层Hash』查找:");
outArrayListInnerHashSet(new ArrayList<>(la), lb);
System.out.println("重复的数据有:"+la.size());
System.out.println("2.『外层Hash+内层Hash』查找:");
outHashSetInnerHashSet(la,lb);
System.out.println("重复的数据有:"+la.size());
receiveDefectList(new ArrayList<>(la),new ArrayList<>(lb));
// 外层:HashSet,内层:HashSet
private void outHastSetInnerHashSet (HashSet<Long> listA, List<Long> listB)
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
HashSet<Long> setB = new HashSet<>(listB);
listA.retainAll(setB);
// System.out.println("重复的数据有:"+listA.size());
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[HashSet-ArrayList]RetainAll耗时:" + (end - begin));
// 外层:ArrayList,内层:HashSet
private void outArrayListInnerHashSet(List<Long> listA, HashSet<Long> listB)
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
ArrayList<Long> setA = new ArrayList<>(listA);
Set<Long> set = new HashSet<>();
Long[] arr = set.toArray(new Long[set.size()]);
Arrays.sort(arr);
setA.retainAll(listB);
// System.out.println("重复的数据有:"+setA.size());
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[ArrayList-HashSet]RetainAll耗时:" + (end - begin));
private void outHashSetInnerHashSet(HashSet<Long> la, HashSet<Long> lb)
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
la.retainAll(lb);
// System.out.println("重复的数据有:"+la.size());
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[HashSet-HashSet]RetainAll耗时:" + (end - begin));
private void receiveDefectList(List<Long> firstArrayList, List<Long> secondArrayList)
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<Long> resultList = new ArrayList<Long>();
LinkedList<Long> result = new LinkedList<Long>(firstArrayList);// 大集合用linkedlist
HashSet<Long> othHash = new HashSet<Long>(secondArrayList);// 小集合用hashset
Iterator<Long> iter = result.iterator();// 采用Iterator迭代器进行数据的操作
while(iter.hasNext())
if(othHash.contains(iter.next()))
iter.remove();
resultList = new ArrayList<Long>(result);
firstArrayList.clear();
resultList.forEach(o-> firstArrayList.add(o));
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[ite-iterator]RetainAll耗时:" + (end - begin));
private void test3(List<Long> array1,List<Long> array2)
Set<Long> set = new HashSet<>();
Long[] arr = set.toArray(new Long[set.size()]);
Arrays.sort(arr);
// 通过HashMap:求两个集合中交集
Map<Long,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<Math.min(array1.size(),array2.size());i++)
contains(map,array1.get(i));
contains(map,array2.get(i));
// 遍历
for(Map.Entry<Long, Integer>m:map.entrySet())
if(m.getValue()>1)
array1.remove(m.getKey());
// System.out.println(m.getKey());
private void contains(Map<Long,Integer>map,Long k)
if(map.containsKey(k))
Integer tmp=map.get(k);
tmp++;
map.put(k, tmp);
else
map.put(k,1);
二、java交集retainAll 和 Sets.intersection 性能比较(链接)
三、用JDK方法求交集retainAll(链接)
四、利用guava集合求交集(链接)
五、利用bitmap求两个list的交集(链接)
jar包获取地址(点击)
参考链接
1、十万以上数据的两个集合进行交集,差集运算,ArrayList为什么特别慢?HashSet为什么效率如此高?(地址)
2、Java 中大集合 求交集的方法比较(地址)
3、bitmap技术解析:redis与roaringBitnap(地址)
4、一文读懂比BitMap有更好性能的Roaring Bitmap(地址)
以上是关于杂谈记录——论Long类型的大数据量求交集的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章