TensorFlow最佳实践样例程序
Posted NodYoung
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了TensorFlow最佳实践样例程序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
此例程出自《TensorFlow实战Google深度学习框架》第5章 MNIST数字识别问题,很好的一个例子。
工程目录:
-mnist_best
-dataset //存放数据集的文件夹,可以http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/下载
-model //存放模型的文件夹
-mnist_eval.py //定义了测试过程
-mnist_inference.py //定义了前向传播的过程以及神经网络中的参数
-mnist_train.py //定义了神经网络的训练过程网络结构:
INPUT: [28x28x1] weights: 0
FC: [1x1x500] weights: (28*28*1+1)*500
FC: [1x1x10] weights: (1*1*500+1)*10代码实现
mnist_eval.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import time
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# 加载mnist_inference.py 和 mnist_train.py中定义的常量和函数
import mnist_inference
import mnist_train
# 每10秒加载一次最新的模型, 并在测试数据上测试最新模型的正确率
EVAL_INTERVAL_SECS = 10
def evaluate(mnist):
with tf.Graph().as_default() as g:
# 定义输入输出的格式
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, mnist_inference.INPUT_NODE], name='x-input')
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, mnist_inference.OUTPUT_NODE], name='y-input')
validate_feed = x: mnist.validation.images, y_: mnist.validation.labels
# 直接通过调用封装好的函数来计算前向传播的结果。
# 因为测试时不关注正则损失的值,所以这里用于计算正则化损失的函数被设置为None。
y = mnist_inference.inference(x, None)
# 使用前向传播的结果计算正确率。
# 如果需要对未知的样例进行分类,那么使用tf.argmax(y, 1)就可以得到输入样例的预测类别了。
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
# 通过变量重命名的方式来加载模型,这样在前向传播的过程中就不需要调用求滑动平均的函数来获取平局值了。
# 这样就可以完全共用mnist_inference.py中定义的前向传播过程
variable_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(mnist_train.MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY)
variable_to_restore = variable_averages.variables_to_restore()
saver = tf.train.Saver(variable_to_restore)
#每隔EVAL_INTERVAL_SECS秒调用一次计算正确率的过程以检测训练过程中正确率的变化
while True:
with tf.Session() as sess:
# tf.train.get_checkpoint_state函数会通过checkpoint文件自动找到目录中最新模型的文件名
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(mnist_train.MODEL_SAVE_PATH)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
# 加载模型
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
# 通过文件名得到模型保存时迭代的轮数
global_step = ckpt.model_checkpoint_path.split('/')[-1].split('-')[-1]
accuracy_score = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict = validate_feed)
print("After %s training step(s), validation accuracy = %f" % (global_step, accuracy_score))
else:
print("No checkpoint file found")
return
time.sleep(EVAL_INTERVAL_SECS)
def main(argv=None):
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("dataset/", one_hot=True)
evaluate(mnist)
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()mnist_inference.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
# 定义神经网络相关的参数
INPUT_NODE = 784
OUTPUT_NODE = 10
LAYER1_NODE = 500
# 通过tf.get_variable函数来获取变量。
# 在训练神经网络时会创建这些变量;在测试时会通过保存的模型加载这些变量的值。
# 而且更加方便的是,因为可以在变量加载时将滑动平均变量重命名,所以可以直接通过同样的名字在训练时使用变量自身,
# 而在测试时使用变量的滑动平均值。在这个函数中也会将变量的正则化损失加入损失集合。
def get_weight_variable(shape, regularizer):
weights = tf.get_variable("weights", shape, initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1))
# 当给出了正则化生成函数时,将当前变量的正则化损失加入名字为losses的集合。
# 在这里使用了add_to_collection函数将一个张量加入一个集合,而这个集合的名称为losses。
# 这是自定义的集合,不在Tensorflow自动管理的集合列表中。
if regularizer != None:
tf.add_to_collection('losses', regularizer(weights))
return weights
# 定义神经网络的前向传播过程。
def inference(input_tensor, regularizer):
# 声明第一层神经网络的变量并完成前向传播过程
with tf.variable_scope('layer1'):
# 这里使用tf.get_variable或tf.Variable没有本质区别,因为在训练或是测试中没有在同一个程序中多次调用这个函数。
# 如果在同一个程序中多次调用,在第一次调用之后需要将reuse参数置为True。
weights = get_weight_variable([INPUT_NODE, LAYER1_NODE], regularizer)
biases = tf.get_variable("biases", [LAYER1_NODE], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
layer1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(input_tensor, weights) + biases)
# 类似地声明第二层神经网络的变量并完成前向传播过程。
with tf.variable_scope('layer2'):
weights = get_weight_variable([LAYER1_NODE, OUTPUT_NODE], regularizer)
biases = tf.get_variable("biases", [OUTPUT_NODE], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
layer2 = tf.matmul(layer1, weights) + biases
# 返回最后前向传播的结果
return layer2mnist_train.py
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# 加载mnist_inference.py中定义的常量和前向传播的函数
import mnist_inference
# 配置神经网络的参数
BATCH_SIZE = 100
LEARNING_RATE_BASE = 0.8
LEARNING_RATE_DECAY = 0.99
REGULARAZTION_RATE = 0.0001
TRAINING_STEPS = 30000
MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY = 0.99
# 模型保存的路径和文件名
MODEL_SAVE_PATH = "model/"
MODEL_NAME = "model.ckpt"
def train(mnist):
# 定义输入输出placeholder。
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, mnist_inference.INPUT_NODE], name='x-input')
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, mnist_inference.OUTPUT_NODE], name='y-input')
regularizer = tf.contrib.layers.l2_regularizer(REGULARAZTION_RATE)
# 直接使用mnist_inference.py中定义的前向传播过程
y = mnist_inference.inference(x, regularizer)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
#定义损失函数、学习率、滑动平均操作以及训练过程
variable_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY, global_step)
variable_averages_op = variable_averages.apply(tf.trainable_variables())
cross_entropy = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=y, labels=tf.argmax(y_, 1))
cross_entropy_mean = tf.reduce_mean(cross_entropy)
loss = cross_entropy_mean + tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('losses'))
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(LEARNING_RATE_BASE, global_step, mnist.train.num_examples/BATCH_SIZE, LEARNING_RATE_DECAY)
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss, global_step=global_step)
with tf.control_dependencies([train_step, variable_averages_op]):
train_op = tf.no_op(name='train')
# 初始化Tensorflow持久化类
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
# 验证和测试的过程将会有一个独立的程序来完成
for i in range(TRAINING_STEPS):
xs, ys = mnist.train.next_batch(BATCH_SIZE)
_, loss_value, step = sess.run([train_op, loss, global_step], feed_dict=x: xs, y_: ys)
#每1000轮保存一次模型。
if i%1000 == 0:
# 输出当前的训练情况。这里只输出了模型在当前训练batch上的损失函数大小。通过损失函数的大小可以大概了解训练的情况。
# 在验证数据集上的正确率信息会有一个单独的程序来生成。
print("After %d training step(s), loss on training batch is %f." % (step, loss_value))
# 保存当前的模型。注意这里隔出了global_step参数,这样可以让每个被保存模型的文件名末尾加上训练的轮数,比如“model.ckpt-1000”表示训练1000轮后得到的模型
saver.save(sess, os.path.join(MODEL_SAVE_PATH, MODEL_NAME), global_step=global_step)
def main(argv=None):
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("dataset/", one_hot=True)
train(mnist)
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()实验及分析
训练过程:
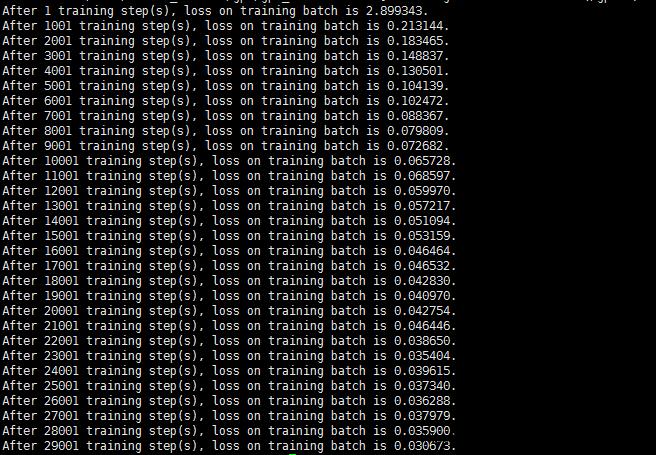
测试结果:

正常。
以上是关于TensorFlow最佳实践样例程序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章