11Spring源码-分析篇-事务源码分析
Posted 波波烤鸭
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了11Spring源码-分析篇-事务源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

Spring源码分析-事务源码分析
一、事务的本质
1. 何为事务管理
数据库事务(Database Transaction) ,是指作为单个逻辑工作单元执行的一系列操作,要么完全地执行,要么完全地不执行。
事务处理可以确保除非事务性单元内的所有操作都成功完成,否则不会永久更新面向数据的资源。通过将一组相关操作组合为一个要么全部成功要么全部失败的单元,可以简化错误恢复并使应用程序更加可靠。
一个逻辑工作单元要成为事务,必须满足所谓的 ACID(原子性、一致性、隔离性和持久性)属性。事务是数据库运行中的逻辑工作单位,由DBMS中的事务管理子系统负责事务的处理。
2. JDBC中的事务管理
事务的本质我们还是要先来看下JDBC中对事务的处理。首先准备如下两张表[案例讲解以mysql为主]
-- MYSQL
CREATE TABLE t_user (
id varchar(30) NOT NULL,
user_name varchar(60) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
CREATE TABLE t_log (
id varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
log varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL
);
然后创建对应的实体对象
/**
* 用户
*/
public class User implements Serializable
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5575893900970589345L;
private String id;
private String userName;
public String getId()
return id;
public void setId(String id)
this.id = id;
public String getUserName()
return userName;
public void setUserName(String userName)
this.userName = userName;
/**
* 日志
*/
public class Log implements Serializable
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5575893900970589345L;
private String id;
private String log;
public Log()
public Log(String id, String log)
super();
this.id = id;
this.log = log;
public String getId()
return id;
public void setId(String id)
this.id = id;
public String getLog()
return log;
public void setLog(String log)
this.log = log;
然后我们通过JDBC操作来同时完成添加用户和添加日志的操作。
public static void main(String[] args)
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try
// 注册 JDBC 驱动
// Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 打开连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC", "root", "123456");
// 执行查询
stmt = conn.createStatement();
conn.setAutoCommit(false); // 关闭自动提交
// 添加用户信息
String sql = "INSERT INTO T_USER(id,user_name)values(1,'管理员')";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
// 添加日志问题
sql = "INSET INTO t_log(id,log)values(1,'添加了用户:管理员')";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
conn.commit(); // 上面两个操作都没有问题就提交
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
// 出现问题就回滚
try
conn.rollback();
catch (SQLException throwables)
throwables.printStackTrace();
finally
try
if (stmt != null) stmt.close();
catch (SQLException se2)
try
if (conn != null) conn.close();
catch (SQLException se)
se.printStackTrace();
通过上面的代码我们发下关键的操作有这三个:

3. Spring中的事务管理
实际工作中我们更多的是结合Spring来做项目的这时我们要满足的情况是这种。
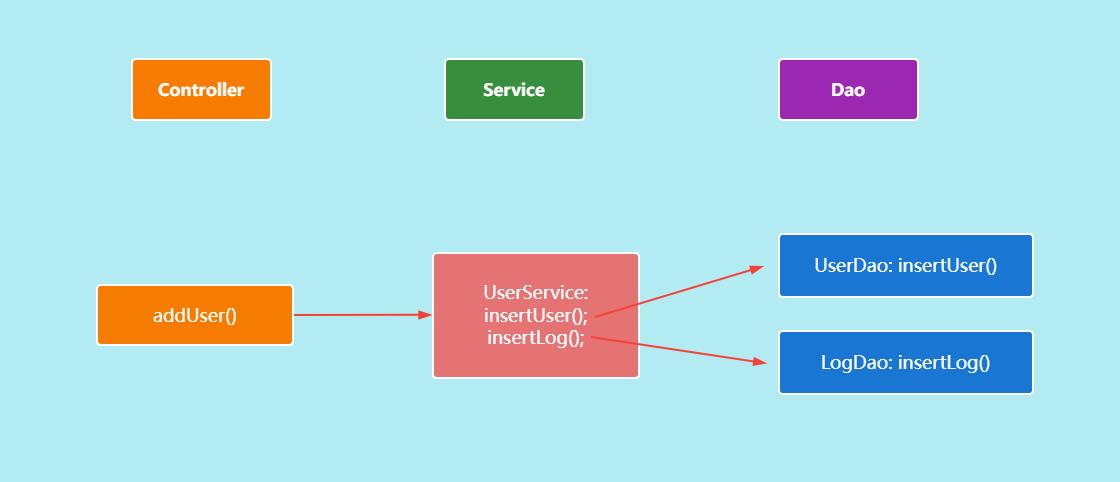
从上图可以看出我们在Service中是可能调用多个Dao的方法来操作数据库中的数据的,我们要做的就是要保证UserService中的 addUser()方法中的相关操作满足事务的要求。在Spring中支持两种事务的使用方式
第一种基于配置文件的方式:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.1.xsd">
<!-- 开启扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.dpb.*"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource" id="dataSource">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl"/>
<property name="driverClassName" value="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="username" value="pms"/>
<property name="password" value="pms"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置JdbcTemplate -->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" >
<constructor-arg name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--
Spring中,使用XML配置事务三大步骤:
1. 创建事务管理器
2. 配置事务方法
3. 配置AOP
-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="transactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<tx:advice id="advice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="fun*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- aop配置 -->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* *..service.*.*(..))" id="tx"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="advice" pointcut-ref="tx"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
第二种基于注解的使用方式:
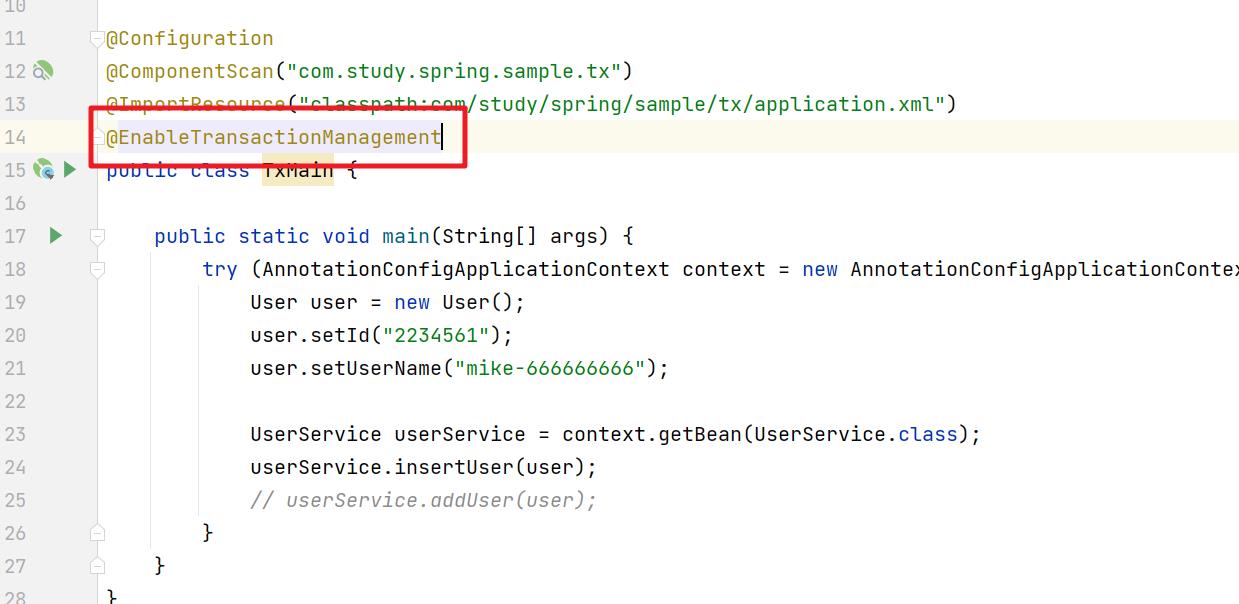
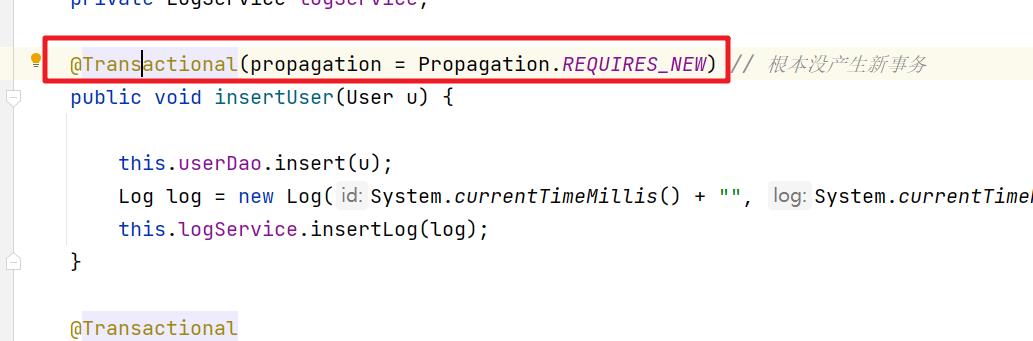
但是我们需要先开启事务注解的方式。然后在对应的方法头部可以添加 @Transactional
@Transactional
public void insertUser(User u)
this.userDao.insert(u);
Log log = new Log(System.currentTimeMillis() + "", System.currentTimeMillis() + "-" + u.getUserName());
this.logDao.insert(log);
当然上面的操作中涉及到了两个概念 事务的传播属性和 事务的隔离级别。参考这两篇文章
传播属性:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38526573/article/details/87898161
隔离级别:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38526573/article/details/87898730
二、Spring事务原理
然后我们来分析下Spring中事务这块的源码实现。
1.Spring事务的源码设计
1.1 事务管理器
我们来看看事务管理器(PlatformTransactionManager).
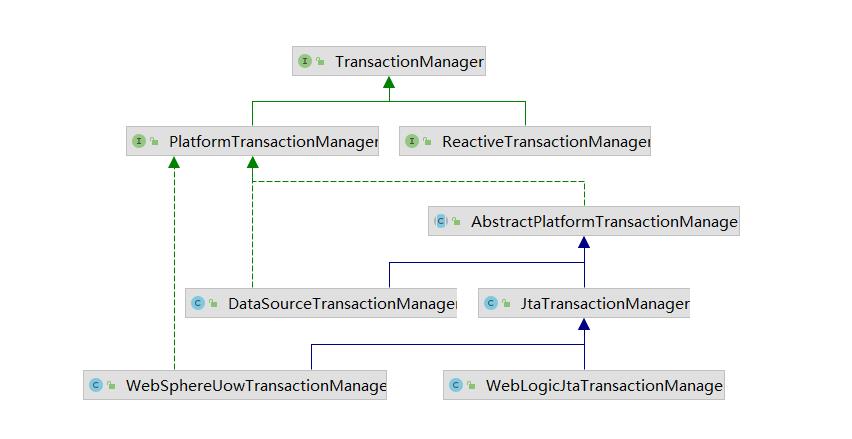
TransactionManager:是顶级接口,里面是空的。
public interface TransactionManager
PlatformTransactionManager:平台事务管理器
ReactiveTransactionManager:响应式编程的事务管理器
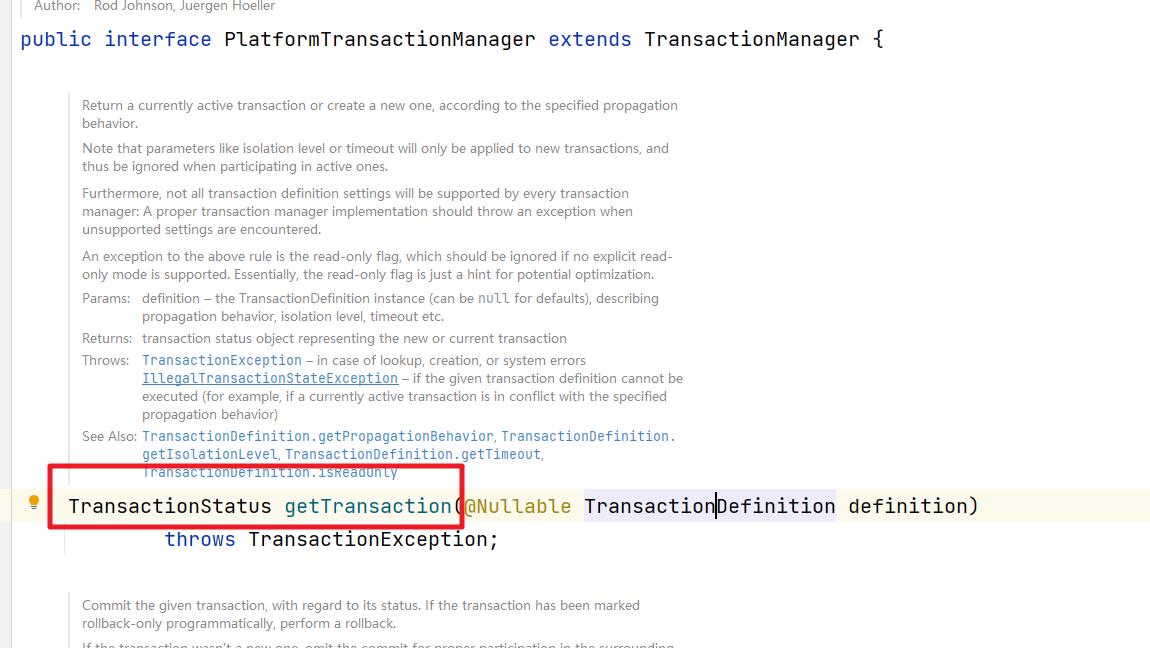
我们关注的重点是PlatformTransactionManager:
public interface PlatformTransactionManager extends TransactionManager
/**
获取事务
*/
TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException;
/**
提交数据
*/
void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
/**
回滚数据
*/
void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
PlatformTransactionManager也是个接口,在他下面的实现有两个比较重要实现

JtaTransactionManager:支持分布式事务【本身服务中的多数据源】
DataSourceTransactionManager:数据源事务管理器。在但数据源中的事务管理,这个是我们分析的重点。
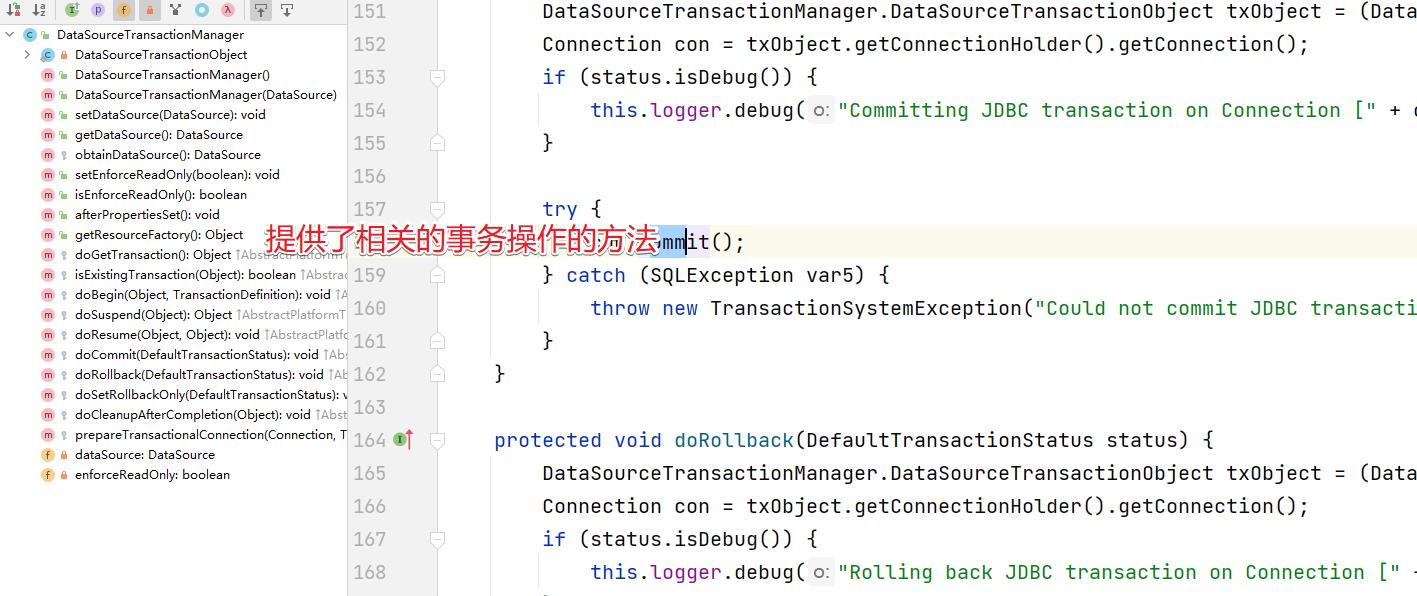
1.2 事务定义
然后我们在上面的 PlatformTransactoinManager中看到了 TransactionDefinition 这个对象,通过字面含义是 事务定义。我们来看看结构。
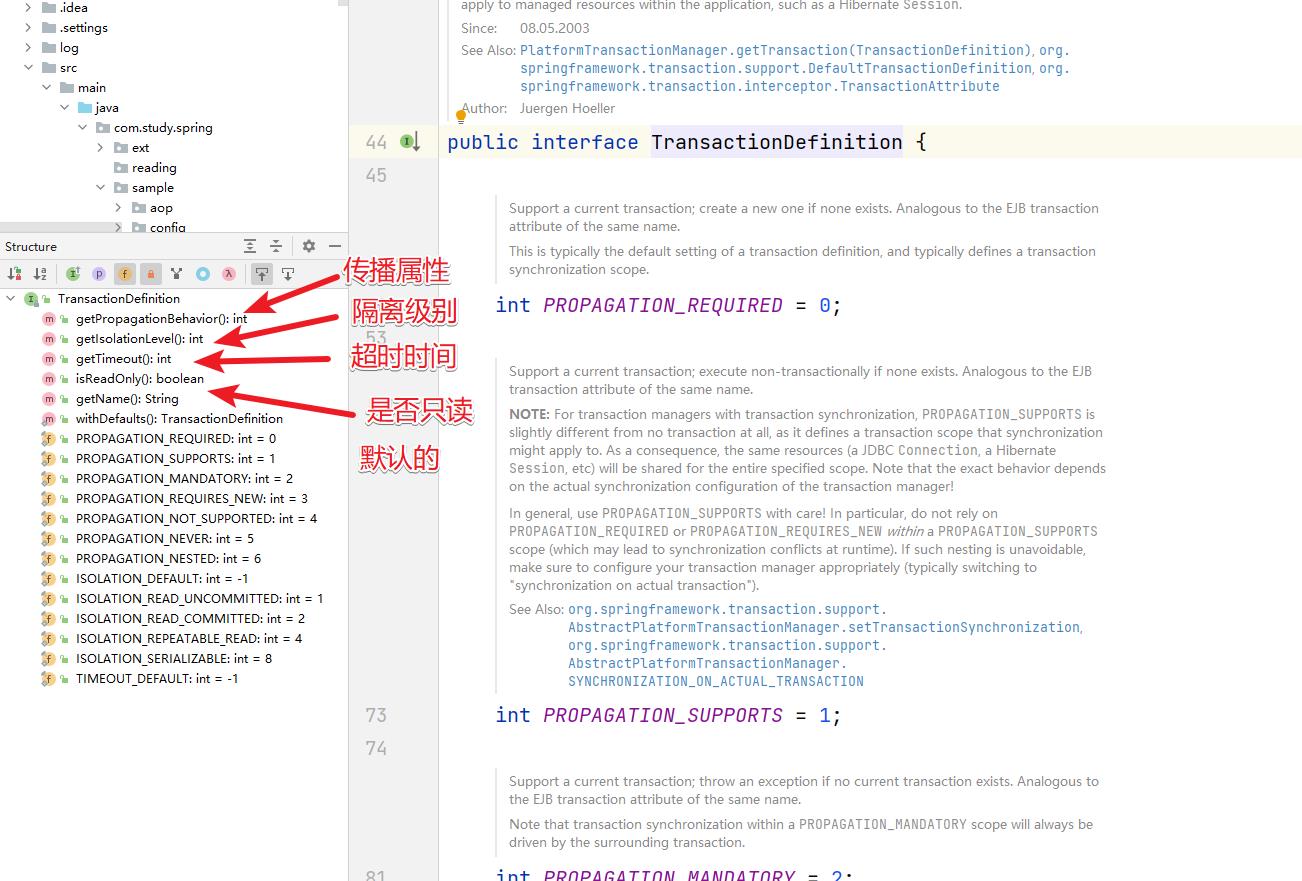
也就是 TransactionDefinition中定义了事务的 传播属性和 隔离级别,然后来看看具体的体系结构
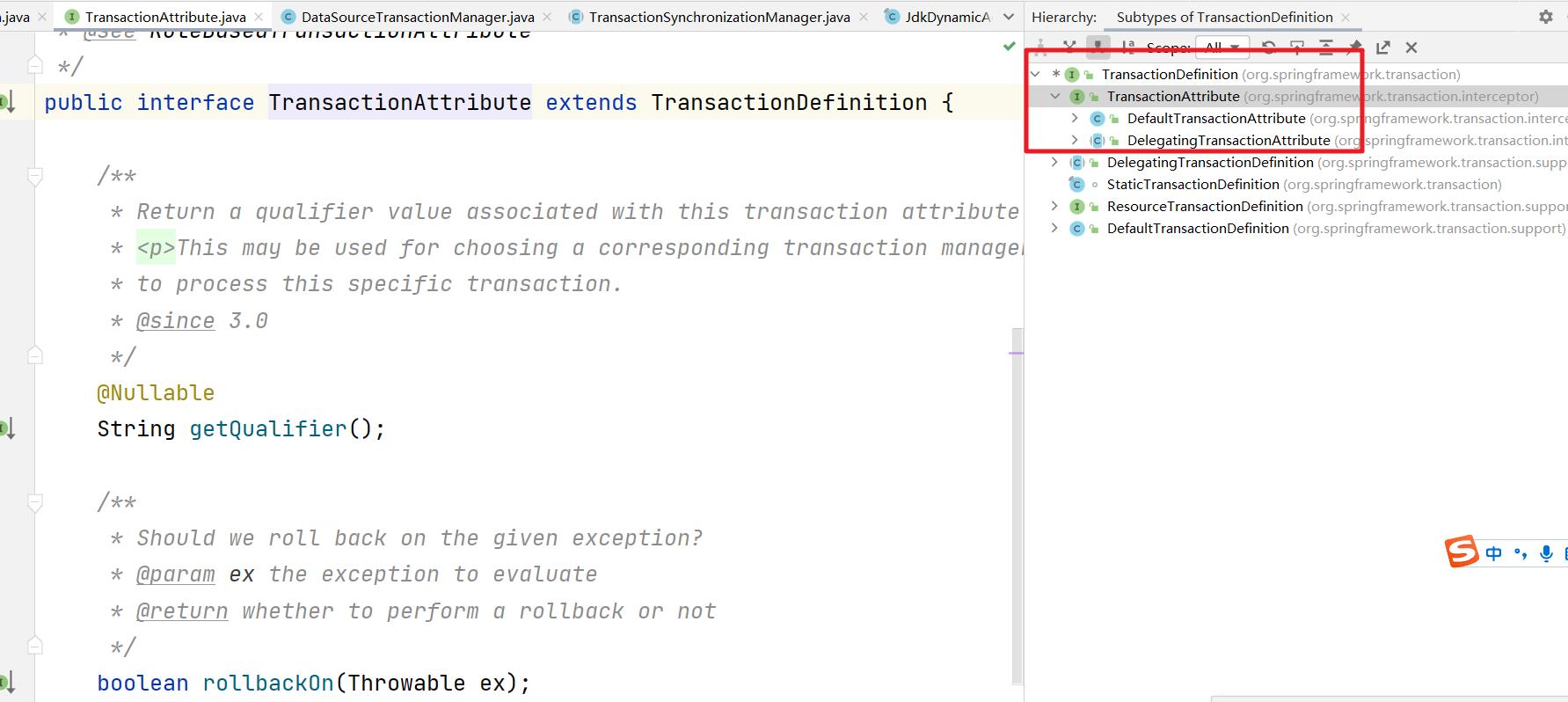
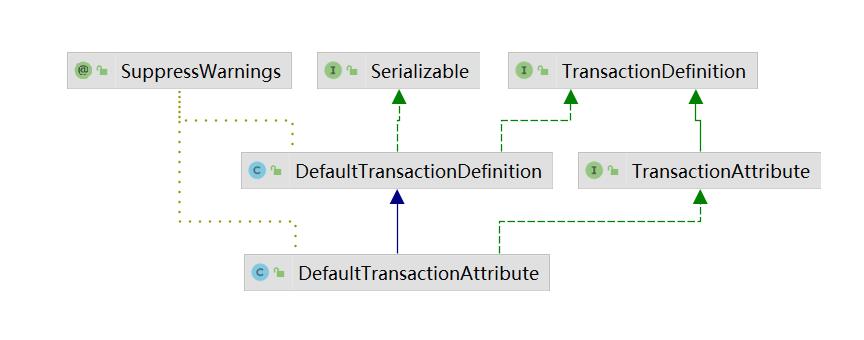
DefaultTransactionDefinition:是事务定义的默认实现
DefaultTransactionAttribute:扩展了TransactionAttribute中的属性的实现
@Transactional:该组件就会被解析加载为对应的 TransactionDefinition对象。
1.3 事务的开启
然后在 PlatformTransactionManager中获取事务的时候返回的是 TransactionStatus对象。我们来看看这个对象。
子类中扩展了
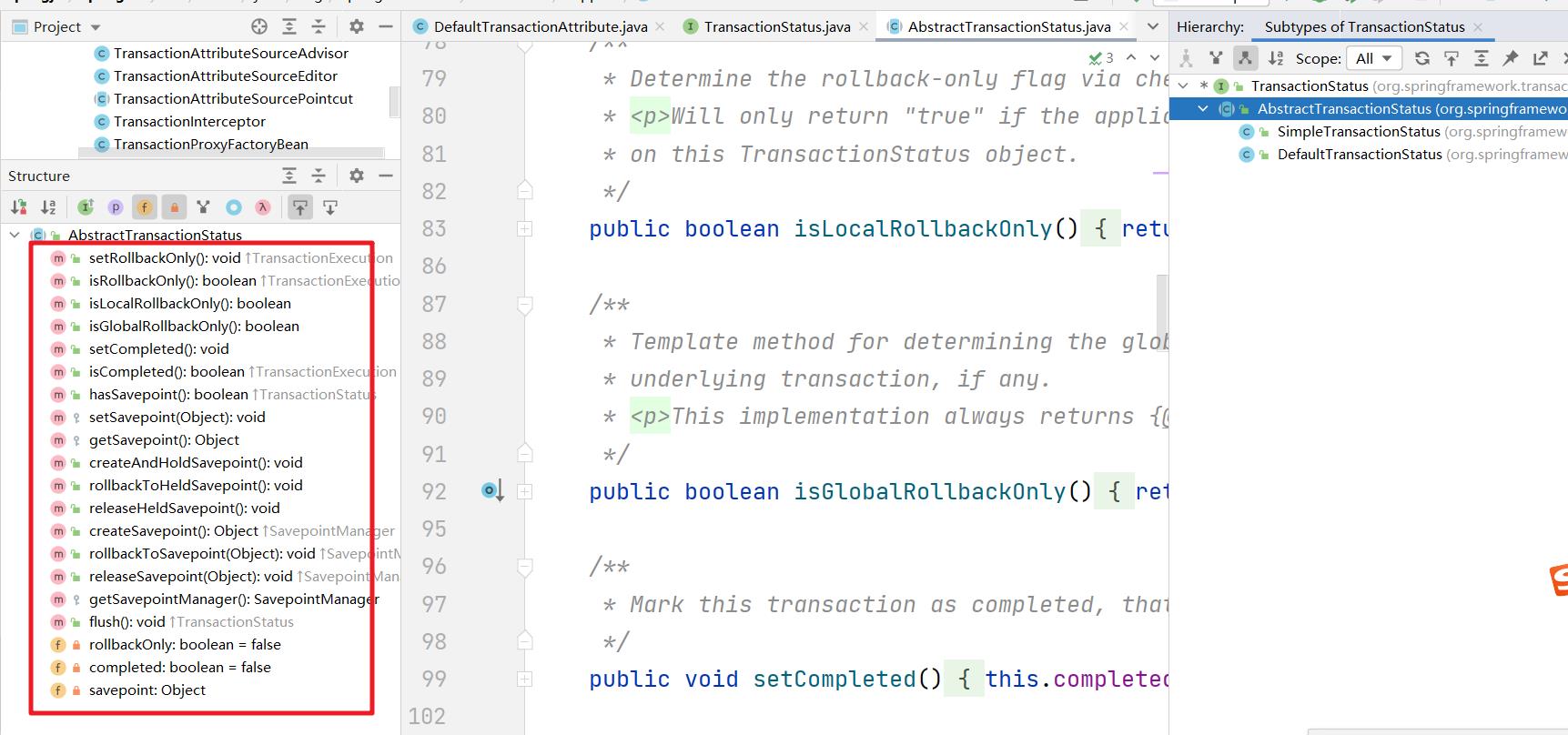
1.4 核心方法讲解
然后再看看核心的 getTransaction()方法
/**
* This implementation handles propagation behavior. Delegates to
* @code doGetTransaction, @code isExistingTransaction
* and @code doBegin.
* @see #doGetTransaction
* @see #isExistingTransaction
* @see #doBegin
*/
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition)
throws TransactionException
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
// 如果没有事务定义信息则使用默认的事务管理器定义信息
TransactionDefinition def = (definition != null ? definition : TransactionDefinition.withDefaults());
// 获取事务
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
// 判断当前线程是否存在事务,判断依据为当前线程记录的连接不为空且连接中的transactionActive属性不为空
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction))
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
// 当前线程已经存在事务
return handleExistingTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled);
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
// 事务超时设置验证
if (def.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT)
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", def.getTimeout());
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
// 如果当前线程不存在事务,但是PropagationBehavior却被声明为PROPAGATION_MANDATORY抛出异常
if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY)
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
// PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW,PROPAGATION_NESTED都需要新建事务
else if (def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
def.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED)
//没有当前事务的话,REQUIRED,REQUIRES_NEW,NESTED挂起的是空事务,然后创建一个新事务
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled)
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + def.getName() + "]: " + def);
try
return startTransaction(def, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex)
// 恢复挂起的事务
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
else
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
// 创建一个空的事务
if (def.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled())
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + def);
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus(def, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
关键的方法:doGetTransaction()方法
/**
* 创建一个DataSourceTransactionObject当作事务,设置是否允许保存点,然后获取连接持有器ConnectionHolder
* 里面会存放JDBC的连接,设置给DataSourceTransactionObject,当然第一次是空的
*
* @return
*/
@Override
protected Object doGetTransaction()
// 创建一个数据源事务对象
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = new DataSourceTransactionObject();
// 是否允许当前事务设置保持点
txObject.setSavepointAllowed(isNestedTransactionAllowed());
/**
* TransactionSynchronizationManager 事务同步管理器对象(该类中都是局部线程变量)
* 用来保存当前事务的信息,我们第一次从这里去线程变量中获取 事务连接持有器对象 通过数据源为key去获取
* 由于第一次进来开始事务 我们的事务同步管理器中没有被存放.所以此时获取出来的conHolder为null
*/
ConnectionHolder conHolder =
(ConnectionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(obtainDataSource());
// 非新创建连接则写false
txObject.setConnectionHolder(conHolder, false);
// 返回事务对象
return txObject;
然后事务管理的代码
/**
* Create a TransactionStatus for an existing transaction.
*/
private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction(
TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled)
throws TransactionException
/**
* 判断当前的事务行为是不是PROPAGATION_NEVER的
* 表示为不支持事务,但是当前又存在一个事务,所以抛出异常
*/
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER)
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'");
/**
* 判断当前的事务属性不支持事务,PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED,所以需要先挂起已经存在的事务
*/
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED)
if (debugEnabled)
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction");
// 挂起当前事务
Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
// 创建一个新的非事务状态(保存了上一个存在事务状态的属性)
return prepareTransactionStatus(
definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
/**
* 当前的事务属性状态是PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW表示需要新开启一个事务状态
*/
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW)
if (debugEnabled)
logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" +
definition.getName() + "]");
// 挂起当前事务并返回挂起的资源持有器
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
try
// 创建一个新的非事务状态(保存了上一个存在事务状态的属性)
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
catch (RuntimeException | Error beginEx)
resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx);
throw beginEx;
// 嵌套事务
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED)
// 不允许就报异常
if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed())
throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
"Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
"specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
if (debugEnabled)
logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
// 嵌套事务的处理
if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction())
// Create savepoint within existing Spring-managed transaction,
// through the SavepointManager API implemented by TransactionStatus.
// Usually uses JDBC 3.0 savepoints. Never activates Spring synchronization.
// 如果没有可以使用保存点的方式控制事务回滚,那么在嵌入式事务的建立初始简历保存点
DefaultTransactionStatus status =
prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
// 为事务设置一个回退点
status.createAndHoldSavepoint();
return status;
else
// Nested transaction through nested begin and commit/rollback calls.
// Usually only for JTA: Spring synchronization might get activated here
// in case of a pre-existing JTA transaction.
// 有些情况是不能使用保存点操作
return startTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled, null);
// Assumably PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS or PROPAGATION_REQUIRED.
if (debugEnabled)
logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction");
if (isValidateExistingTransaction())
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT)
Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel())
Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants;
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " +
(currentIsolationLevel != null ?
isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) :
"(unknown)"));
if (!definition.isReadOnly())
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly())
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is");
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
最后来看看 startTransaction() 方法
/**
* Start a new transaction.
*/
private TransactionStatus startTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction,
boolean debugEnabled, @Nullable SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources)
// 是否需要新同步
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
// 创建新的事务
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
// 开启事务和连接
doBegin(transaction, definition);
// 新同步事务的设置,针对于当前线程的设置
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
doBegin方法开启和连接事务
@Override
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition)
// 强制转化事务对象
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
Connection con = null;
try
// 判断事务对象没有数据库连接持有器
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction())
// 通过数据源获取一个数据库连接对象
Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection()以上是关于11Spring源码-分析篇-事务源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章