Java-I/O流实验
Posted 康小庄
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java-I/O流实验相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
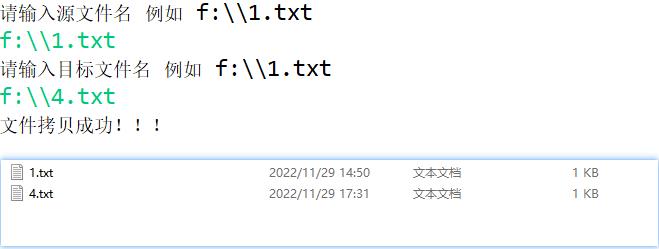
1.编写文本文件复制程序,即把源文件复制到目标文件,运行时用参数方式输入源文件名和目标文件名,设入口主类为FileCopy,则运行方式为:java FileCopy 源文件名 目标文件名
FileCopy
public class FileCopy
public static void main(String[] args)
copyFile();
public static void copyFile()
System.out.println("请输入源文件名 例如 f:\\\\\\\\1.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String srcFilePath = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入目标文件名 例如 f:\\\\\\\\1.txt");
String desFilePath = scanner.nextLine();
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath);
fos = new FileOutputStream(desFilePath);
// 定义字节数组
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = fis.read(buf)) != -1)
// 一遍读一边写
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
System.out.println("文件拷贝成功!!!");
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
try
fis.close();
fos.close();
catch (IOException e)
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
scanner.close();
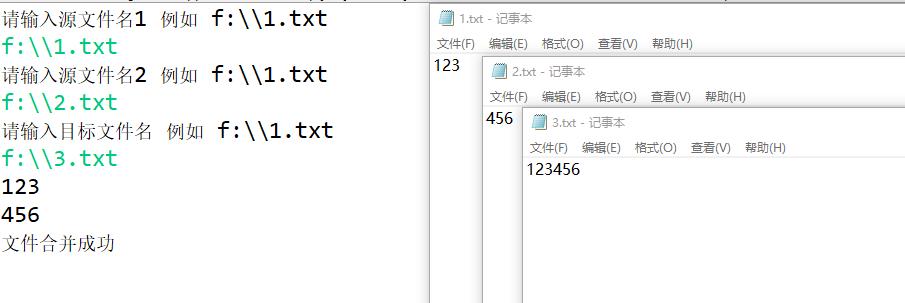
2.将任意两个文件合并到一个文件,要求采用java命令行方式在控制台按照“源文件1 源文件2 目标文件” 方式录入,注意多种异常处理。
FileMerge
public class FileMerge
public static void main(String[] args)
mergeFile();
public static void mergeFile()
System.out.println("请输入源文件名1 例如 f:\\\\\\\\1.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String srcFilePath1 = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入源文件名2 例如 f:\\\\\\\\1.txt");
String srcFilePath2 = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入目标文件名 例如 f:\\\\\\\\1.txt");
String desFilePath = scanner.nextLine();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int readData = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream1 = null;
FileInputStream fileInputStream2 = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try
fileInputStream1 = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath1);
fileInputStream2 = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath2);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(desFilePath, true);
/*
* 从输入流最多读取b.length字节的数据到字节数组 返回-1 读取完毕 读取正常 返回实际读取的字节数
*/
while ((readData = fileInputStream1.read(buf)) != -1)
String str = new String(buf, 0, readData);
System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, readData));// 显示
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes("UTF-8"));
while ((readData = fileInputStream2.read(buf)) != -1)
String str = new String(buf, 0, readData);
System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, readData));// 显示
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes("UTF-8"));
System.out.println("文件合并成功");
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
try
scanner.close();
fileInputStream1.close();
fileInputStream2.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();
3.编写程序实现将一个文件内容追加到另一个文件内容后,如将D盘file文件夹下的f1.txt追加到E盘根目录下的f2.txt中。(必须异常处理)
FileSupple
public class FileSupple
public static void main(String[] args)
suppleFile();
public static void suppleFile()
System.out.println("请输入源文件名 例如 f:\\\\\\\\1.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String srcFilePath = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入目标文件名 例如 f:\\\\\\\\1.txt");
String desFilePath = scanner.nextLine();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int readData = 0;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcFilePath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(desFilePath, true);
/*
* 从输入流最多读取b.length字节的数据到字节数组 返回-1 读取完毕 读取正常 返回实际读取的字节数
*/
while ((readData = fileInputStream.read(buf)) != -1)
String str = new String(buf, 0, readData);
// 显示
System.out.println(new String(buf, 0, readData));
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes("UTF-8"));
System.out.println("文件追加成功");
catch (Exception e)
e.printStackTrace();
finally
try
scanner.close();
fileInputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
catch (IOException e)
e.printStackTrace();

以上是关于Java-I/O流实验的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章