Android 水波纹显示进度效果
Posted 刘永祥
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android 水波纹显示进度效果相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
关于水波纹的效果想必大家见的已经很多了,我就在这里再啰嗦一次,为了加深自己的印象。先来看看效果图

关于这个效果的实现不必想的太过复杂了,要想实现这个效果,我们还需要了解一下PorterDuff及Xfermode
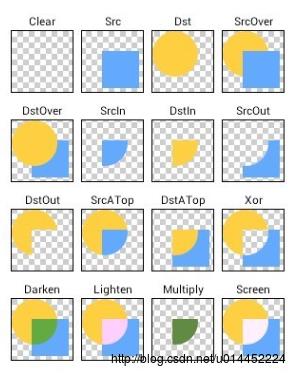
关于上面的这张图想必大家也见过很多次了。这其实就是PorterDuff的16种模式。效果想比大家已经见到了,下面我们就来一一了解如何使用。
PorterDuff.Mode.CLEAR (所绘制不会提交到画布上)
PorterDuff.Mode.SRC(显示上层绘制图片)
PorterDuff.Mode.DST(显示下层绘制图片)
PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_OVER(正常绘制显示,上下层绘制叠盖)
PorterDuff.Mode.DST_OVER(上下层都显示。下层居上显示)
PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_IN(取两层绘制交集。显示上层)
PorterDuff.Mode.DST_IN(取两层绘制交集。显示下层)
PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_OUT( 取上层绘制非交集部分)
PorterDuff.Mode.DST_OUT(取下层绘制非交集部分)
PorterDuff.Mode.SRC_ATOP(取下层非交集部分与上层交集部分)
PorterDuff.Mode.DST_ATOP(取上层非交集部分与下层交集部分)
PorterDuff.Mode.XOR( 异或:去除两图层交集部分)
PorterDuff.Mode.DARKEN( 取两图层全部区域,交集部分颜色加深)
PorterDuff.Mode.LIGHTEN(取两图层全部,点亮交集部分颜色)
PorterDuff.Mode.MULTIPLY(取两图层交集部分叠加后颜色)
PorterDuff.Mode.SCREEN( 取两图层全部区域,交集部分变为透明色)
Xfermode有三个子类 :
AvoidXfermode 指定了一个颜色和容差,强制Paint避免在它上面绘图(或者只在它上面绘图)。
PixelXorXfermode 当覆盖已有的颜色时,应用一个简单的像素异或操作。
PorterDuffXfermode 这是一个非常强大的转换模式,使用它可以使用图像合成的上图中的任意一种来控制Paint如何与已有的Canvas图像进行交互。要应用转换模式,可以使用setXferMode方法
paint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.DST_ATOP));
这些只能够显示一些合成的效果也就是上面的16种的任意一种效果而已,要想实现水波纹的效果还是不够的,我们还需要借助于贝塞尔曲线来实现水波效果。我们使用到的是Path类的quadTo(x1, y1, x2, y2)方法,属于二阶贝塞尔曲线,使用一张图来展示二阶贝塞尔曲线,这里的(x1,y1)是控制点,(x2,y2)是终止点,起始点默认是Path的起始点(0,0)。关于使用贝塞尔曲线来实现水波效果的原理就是:通过for循环画出两个波纹,我们以WL代表水波纹的长度。需要波纹的-WL点、-3/4*WL点、-1/2*WL、-1/4*WL四个点,通过path的quadTo画出,并无限重复。实现的效果其实也就是我们平时的正弦效果。那么我们也需要了解一下path的使用。先来看一下效果图

实现代码为
public class WaveView extends View
private Paint mPaint;
private Path mPath;
private Point assistPoint;
public WaveView(Context context)
super(context);
public WaveView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr)
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
public WaveView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
super(context, attrs);
mPath = new Path();
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
assistPoint = new Point(250, 350);
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL_AND_STROKE);
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh)
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
super.onDraw(canvas);
mPath.reset();
mPath.moveTo(50, 300);
mPath.quadTo(assistPoint.x, assistPoint.y, 450, 300);
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPaint);
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
switch (event.getAction())
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
assistPoint.x = (int) event.getX();
assistPoint.y = (int) event.getY();
invalidate();
break;
return true;
先来说一下mPath.moveTo(50, 300);这个方法的作用是将起点移动到屏幕坐标为(50, 300)的位置。mPath.quadTo(assistPoint.x, assistPoint.y, 450, 300);这个方法就是重点了,对应的源码为
public void quadTo(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2)
isSimplePath = false;
native_quadTo(mNativePath, x1, y1, x2, y2);
第一个坐标是对应的控制点的坐标(assistPoint.x, assistPoint.y),第二个坐标是终点坐标也就是我们看到的水平线的终点位置坐标。上图之所以会出现移动的效果就是因为控制点的位置随着鼠标的位置在移动而产生的。
下面我们再来看一个效果图

这个图形的实现代码为
public class WaveViewTest extends View
private int width;
private int height;
private Path mPath;
private Paint mPathPaint;
private int mWaveHight = 150;//水波纹的高度
private int mWaveWidth = 100;//水波纹的宽度
private String mWaveColor = "#FFFFFF";
private int maxProgress = 100;
private int currentProgress = 0;
private float currentY;
public WaveViewTest(Context context)
this(context,null,0);
public WaveViewTest(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
this(context, attrs, 0);
public WaveViewTest(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
public void setCurrent(int currentProgress,String currentText)
this.currentProgress = currentProgress;
public void setWaveColor(String mWaveColor)
this.mWaveColor = mWaveColor;
private void init()
mPath = new Path();
mPathPaint = new Paint();
mPathPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPathPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
currentY = height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
mPathPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor(mWaveColor));
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
float currentMidY = height*(maxProgress-currentProgress)/maxProgress;
if(currentY>currentMidY)
currentY = currentY - (currentY-currentMidY)/10;
mPath.reset();
mPath.moveTo(0,300);
//显示的区域内的水波纹的数量
int waveNum = width/mWaveWidth;
int num = 0;
for(int i =0;i<waveNum;i++)
mPath.quadTo(mWaveWidth*(num+1),300-mWaveHight,mWaveWidth*(num+2),300);
mPath.quadTo(mWaveWidth*(num+3),300+mWaveHight,mWaveWidth*(num+4),300);
num+=4;
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPathPaint);
再来一个效果图以及实现代码
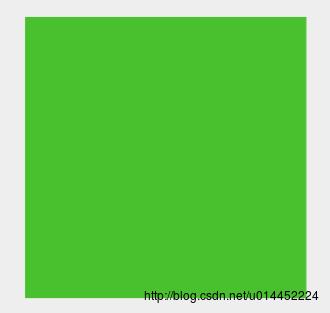
public class WaveViewTest extends View
private int width;
private int height;
private Path mPath;
private Paint mPathPaint;
private String mWaveColor = "#FF49C12E";
public WaveViewTest(Context context)
this(context,null,0);
public WaveViewTest(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
this(context, attrs, 0);
public WaveViewTest(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
private void init()
mPath = new Path();
mPathPaint = new Paint();
mPathPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPathPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
mPathPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor(mWaveColor));
mPath.reset();
mPath.moveTo(0,0);
mPath.lineTo(0,height);
mPath.lineTo(width,height);
mPath.lineTo(width,0);
mPath.close();
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPathPaint);
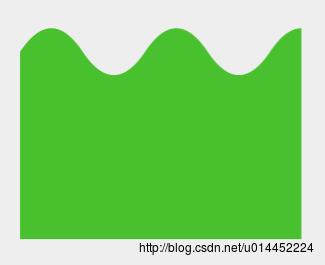
上图是我们看到的一个静态的图,但是距离我们实现的效果已经很接近了,实现代码为
public class WaveViewTest extends View
private int width;
private int height;
private Path mPath;
private Paint mPathPaint;
private float mWaveWidth = 100f;//水波纹的宽度
private String mWaveColor = "#FF49C12E";
public WaveViewTest(Context context)
this(context,null,0);
public WaveViewTest(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
this(context, attrs, 0);
public WaveViewTest(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
private void init()
mPath = new Path();
mPathPaint = new Paint();
mPathPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPathPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
canvas.drawBitmap(createImage(), 0, 0, null);
private Bitmap createImage()
mPathPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor(mWaveColor));
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
Bitmap bmp = Bitmap.createBitmap(width,height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bmp);
mPath.reset();
mPath.moveTo(0,300);
//显示的区域内的水波纹的数量
int waveNum = width/((int)mWaveWidth);
int num = 0;
for(int i =0;i<waveNum;i++)
mPath.quadTo(mWaveWidth*(num+1),300-150,mWaveWidth*(num+2),300);
mPath.quadTo(mWaveWidth*(num+3),300+150,mWaveWidth*(num+4),300);
num+=4;
mPath.lineTo(width,height);
mPath.lineTo(0,height);
mPath.close();
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPathPaint);
return bmp;

这个效果的产生其实就是上面的图形通过for循环产生移动距离产生的,代码如下
public class WaveView extends View
private int width;
private int height;
private Path mPath;
private Paint mPathPaint;
private float mWaveHight = 30f;
private float mWaveWidth = 100f;//水波纹的宽度
private String mWaveColor = "#FFFFFF";
private int mWaveSpeed = 30;
private int maxProgress = 100;
private int currentProgress = 0;
private float currentY;
private float distance = 0;
private int RefreshGap = 10;
private static final int INVALIDATE = 0X777;
private Handler handler = new Handler()
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg)
super.handleMessage(msg);
switch (msg.what)
case INVALIDATE:
invalidate();
sendEmptyMessageDelayed(INVALIDATE,RefreshGap);
break;
;
public WaveView(Context context)
this(context,null,0);
public WaveView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
this(context, attrs, 0);
public WaveView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
public void setCurrent(int currentProgress,String currentText)
this.currentProgress = currentProgress;
public void setWaveColor(String mWaveColor)
this.mWaveColor = mWaveColor;
private void init()
mPath = new Path();
mPathPaint = new Paint();
mPathPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPathPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
handler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(INVALIDATE,100);
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
currentY = height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
canvas.drawBitmap(createImage(), 0, 0, null);
private Bitmap createImage()
mPathPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor(mWaveColor));
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
Bitmap bmp = Bitmap.createBitmap(width,height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bmp);
float currentMidY = height*(maxProgress-currentProgress)/maxProgress;
if(currentY>currentMidY)
currentY = currentY - (currentY-currentMidY)/10;
mPath.reset();
//之所以0-distance是因为有原点向上增加的
mPath.moveTo(0-distance,currentY);
//显示的区域内的水波纹的数量
int waveNum = width/((int)mWaveWidth);
int num = 0;
for(int i =0;i<waveNum;i++)
mPath.quadTo(mWaveWidth*(num+1)-distance,currentY-mWaveHight,mWaveWidth*(num+2)-distance,currentY);
mPath.quadTo(mWaveWidth*(num+3)-distance,currentY+mWaveHight,mWaveWidth*(num+4)-distance,currentY);
num+=4;
distance +=mWaveWidth/mWaveSpeed;
distance = distance%(mWaveWidth*4);
mPath.lineTo(width,height);
mPath.lineTo(0,height);
mPath.close();
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPathPaint);
return bmp;
通过对比代码你会发现,其实就是通过移动定时刷新不停的调用onDraw方法,通过distance 的不断变化而产生的动画效果。如果想要实现我们最上面的动画效果还需要借助于PorterDuff及Xfermode,关于PorterDuff及Xfermode上面已经说过了。剩下的就是它们之间的配合使用了
完整的实现的代码如下:
自定义view
public class WaveProgressView extends View
private int width;
private int height;
private Bitmap backgroundBitmap;
private Path mPath;
private Paint mPathPaint;
private float mWaveHight = 30f;
private float mWaveWidth = 100f;
private String mWaveColor = "#FFFFFF";
private int mWaveSpeed = 30;
private Paint mTextPaint;
private String currentText = "";
private String mTextColor = "#FFFFFF";
private int mTextSize = 35;
private int maxProgress = 100;
private int currentProgress = 0;
private float currentY;
private float distance = 0;
private int RefreshGap = 10;
private static final int INVALIDATE = 0X777;
private Handler handler = new Handler()
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg)
super.handleMessage(msg);
switch (msg.what)
case INVALIDATE:
invalidate();
sendEmptyMessageDelayed(INVALIDATE,RefreshGap);
break;
;
public WaveProgressView(Context context)
this(context,null,0);
public WaveProgressView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
this(context, attrs, 0);
public WaveProgressView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init();
public void setCurrent(int currentProgress,String currentText)
this.currentProgress = currentProgress;
this.currentText = currentText;
public void setWaveColor(String mWaveColor)
this.mWaveColor = mWaveColor;
private void init()
if(null==getBackground())
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("background is null."));
else
backgroundBitmap = getBitmapFromDrawable(getBackground());
mPath = new Path();
mPathPaint = new Paint();
mPathPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPathPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
mTextPaint = new Paint();
mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mTextPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);
handler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(INVALIDATE,100);
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
currentY = height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas)
if(backgroundBitmap!=null)
canvas.drawBitmap(createImage(), 0, 0, null);
private Bitmap createImage()
mPathPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor(mWaveColor));
mTextPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor(mTextColor));
mTextPaint.setTextSize(mTextSize);
mPathPaint.setColor(Color.parseColor(mWaveColor));
Paint paint = new Paint();
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
Bitmap bmp = Bitmap.createBitmap(width,height, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bmp);
float currentMidY = height*(maxProgress-currentProgress)/maxProgress;
if(currentY>currentMidY)
currentY = currentY - (currentY-currentMidY)/10;
mPath.reset();
//之所以0-distance是因为有原点向上增加的
mPath.moveTo(0-distance,currentY);
//显示的区域内的水波纹的数量
int waveNum = width/((int)mWaveWidth);
int num = 0;
for(int i =0;i<waveNum;i++)
mPath.quadTo(mWaveWidth*(num+1)-distance,currentY-mWaveHight,mWaveWidth*(num+2)-distance,currentY);
mPath.quadTo(mWaveWidth*(num+3)-distance,currentY+mWaveHight,mWaveWidth*(num+4)-distance,currentY);
num+=4;
distance +=mWaveWidth/mWaveSpeed;
distance = distance%(mWaveWidth*4);
mPath.lineTo(width,height);
mPath.lineTo(0,height);
mPath.close();
canvas.drawPath(mPath, mPathPaint);
int min = Math.min(width,height);
backgroundBitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(backgroundBitmap,min,min,false);
paint.setXfermode(new PorterDuffXfermode(PorterDuff.Mode.DST_ATOP));
canvas.drawBitmap(backgroundBitmap,0,0,paint);
canvas.drawText(currentText, width/2, height/2, mTextPaint);
return bmp;
private Bitmap getBitmapFromDrawable(Drawable drawable)
if (drawable == null)
return null;
if (drawable instanceof BitmapDrawable)
return ((BitmapDrawable) drawable).getBitmap();
try
Bitmap bitmap;
bitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(drawable.getIntrinsicWidth(), drawable.getIntrinsicHeight(),Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
Canvas canvas = new Canvas(bitmap);
drawable.setBounds(0, 0, canvas.getWidth(), canvas.getHeight());
drawable.draw(canvas);
return bitmap;
catch (OutOfMemoryError e)
return null;
MainActivity.class
public class MainActivity extends Activity
private WaveProgressView wpv;
private static final int FLAG_ONE = 0X0001;
private int max_progress = 100;
private int progress;
private Handler handler = new Handler()
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg)
super.handleMessage(msg);
progress++;
switch (msg.what)
case FLAG_ONE:
if (progress <= max_progress)
wpv.setCurrent(progress, progress + "%");
sendEmptyMessageDelayed(FLAG_ONE, 100);
else
return;
break;
;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
private void initView()
wpv = (WaveProgressView) findViewById(R.id.wpv);
wpv.setWaveColor("#FF49C12E");
handler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(FLAG_ONE, 1000);
布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="20dp">
<com.lyxrobert.waveprogressview.WaveProgressView
android:id="@+id/wpv"
android:background="@drawable/bg"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="230dp"
android:layout_height="230dp" />
</RelativeLayout>点击下载源码
以上是关于Android 水波纹显示进度效果的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章