mybatis 之 插件
Posted better_hui
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了mybatis 之 插件相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
一、自定义插件
mybatis的插件是代理模式 与 责任链模式的结合。 每一个插件以责任链并进行封装,都是一层对Executor的代理
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = MappedStatement.class, Object.class , RowBounds.class , ResultHandler.class))
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable
System.out.println("my Interceptor ...........");
return invocation.proceed();
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target)
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties)
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(properties));
配置文件
<plugins> <plugin interceptor="hee.frame.test.MyInterceptor"> <property name="dialect" value="mysql"/> </plugin> </plugins>
二、扫描
注意这是最原始的xml配置方式。以下是简述的扫描流程:
//1、 根据字节流或者字符流加载配置文件
new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().builder(reader);
//2、 根据配置文件 , 创建sqlSessionFactory
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties)
try
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse()); //这一行是关键
catch (Exception e)
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
finally
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try
reader.close();
catch (IOException e)
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
//3、解析各种标签
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root)
try
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); //issue #117 read properties first
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); //这一行是关键
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings"));
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
catch (Exception e)
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
//4、添加到责任链
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception
if (parent != null)
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren())
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
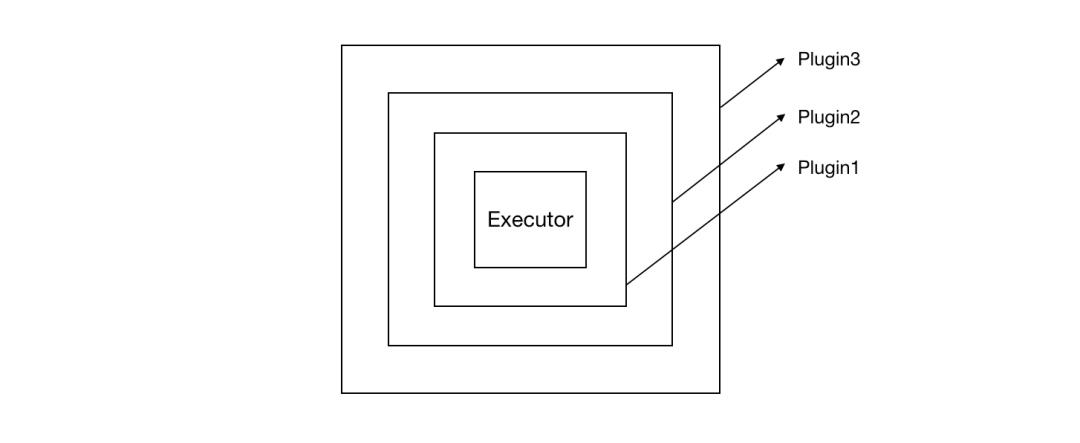
三、封装
封装的过程就是将解析后的interceptor配置,生成executor的一层层代理。
//1、sqlSession工厂 ,获取一个session
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//2、打开一个session
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit)
Transaction tx = null;
try
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType); //这一步是关键
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
catch (Exception e)
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
finally
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
//3、生成sqlSession内部执行器Executor
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType)
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType)
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType)
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
else
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
if (cacheEnabled)
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
//这一步是关键 , 在executor的外面包上一层层的代理
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
public Object pluginAll(Object target)
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors)
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
return target;
//4、封装代理
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor)
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0)
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
return target;
综上 , 我们得到的sqlSession的内部执行器Executor , 实际上是一层层的代理。
四、执行
我们在使用自定义的mapper调用接口时 , 实际上调用的是MapperProxy代理类,核心的代码如下:
// 1、代理的执行
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass()))
try
return method.invoke(this, args);
catch (Throwable t)
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
//获取映射的method , MapperMethod 包含了两个属性
//SqlCommand command;
//MethodSignature method;
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//执行映射的方法 ,
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
//2、下面以查询为例 , 且忽略其他方法 MapperMethod.execute
// sqlSession的查询
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args)
//填充参数到sql
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//执行查询,sqlSession的执行 , 实际干活的是内部的Executor
Object result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
return result;
//3、下面是内部执行器的逻辑,executor.query()
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds)
try
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//内部执行器的查询
List<E> result = executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
return result;
catch (Exception e)
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
finally
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
//4、我们之前说过Executor的外面包了一层层的代理 , 这个代理的逻辑就是这个Plugin对象 ,implements InvocationHandler
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable
try
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method))
//如果这个方法是被拦截的方法 , 那么就执行代理的逻辑
//注意这里是一层层的代理 , 所以会链式的执行
// interceptor1.intercept -> interceptor2.intercept -> ....... -> executor.query()
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
return method.invoke(target, args);
catch (Exception e)
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
五、应用
1、水平分表
2、权限控制
3、数据库加解密
以上是关于mybatis 之 插件的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章