list介绍和基本使用
Posted DR5200
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了list介绍和基本使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一. list介绍
1). list是可以在常数范围内在任意位置进行插入和删除的序列式容器,并且该容器可以前后双向迭代。
2). list的底层是双向链表结构,双向链表中每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向其前一个元素和后一个元素。
3). list与forward_list非常相似:最主要的不同在于forward_list是单链表,只能朝后迭代,已让其更简单高效。
4).与其他的序列式容器相比(array,vector,deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率更好。
5). 与其他序列式容器相比,list和forward_list最大的缺陷是不支持任意位置的随机访问,比如:要访问list的第6个元素,必须从已知的位置(比如头部或者尾部)迭代到该位置,在这段位置上迭代需要线性的时间开销;list还需要一些额外的空间,以保存每个节点的相关联信息(对于存储类型较小元素的大list来说这可能是一个重要的因素)
二. list使用
constructor
1).构造一个空容器
list<int> lt;
2).构造一个含有n个值为val的容器
list<int> lt(10,5);
3).拷贝构造
list<int> lt2(lt);
4). 迭代器区间构造
int a[] = 16,2,77,29 ;
list<int> lt2(a,a + 4);
/* while(first != last)
*
* push_back(*first);
* ++first;
*
*/
print(lt2);
// swap,find,reverse,sort 常用的算法 <algorithm>
// 原生指针可以看作天然的迭代器
sort(a,a + 4);
sort(a, a + 4, greater<int>());
// sort排序底层是快速排序,迭代器类型只能是随机迭代器
// 比如三数取中优化,lt不支持随机访问
sort(lt.begin(),lt.end());
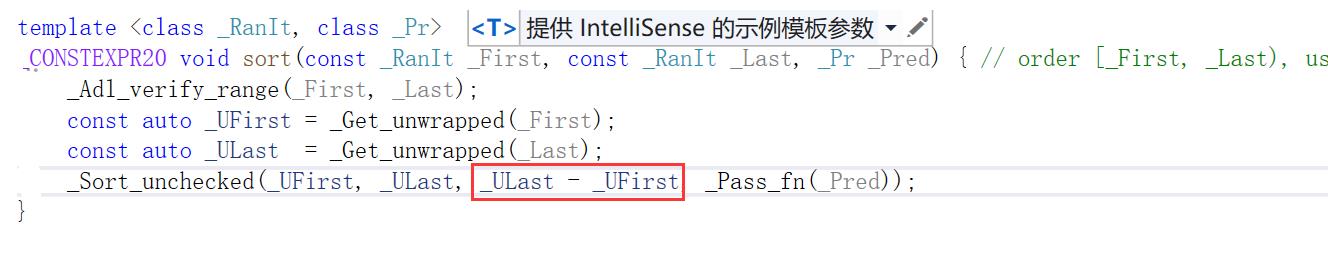
list迭代器是双向迭代器,不支持 - 操作,因此报错
这里顺便介绍一下迭代器的类型 :
单向迭代器 : 只能向后依次遍历(只支持++操作) (如 forward_list)
双向迭代器 : 可以向前向后依次遍历(支持++和–操作) (如 list)
随机迭代器 : 可以向前向后随机遍历(支持++ /- - / + / - / += / -= 操作) (如 vector/string)

iterator
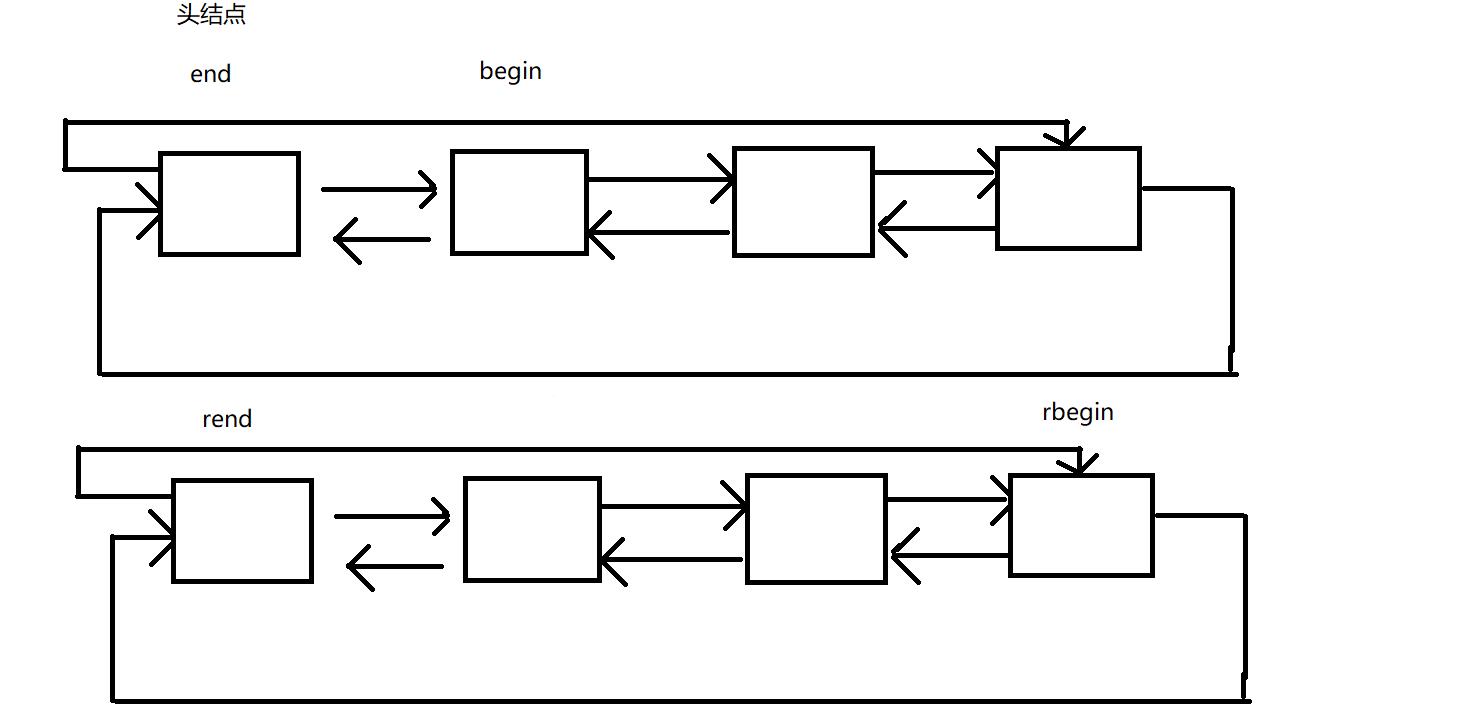
iterator begin();
const_iterator begin() const;
iterator end();
const_iterator end() const;
reverse_iterator rbegin();
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;
reverse_iterator rend();
const_reverse_iterator rend() const;
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
list<int> lt(10, 5);
//正向迭代器遍历容器
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
cout << endl;
// 反向迭代器遍历容器
list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = lt.rbegin();
while (rit != lt.rend())
cout << *rit << " ";
rit++;
cout << endl;
return 0;
capacity
empty
判断容器是否为空
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
list<int> lt;
cout << lt.empty() << endl; //1
return 0;
size
获取容器中的元素个数
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
cout << lt.size() << endl; //4
return 0;
Element access
front/back
front函数用于获取list容器当中的第一个元素的引用,back函数用于获取list容器当中的最后一个元素的引用
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
cout << lt.front() << endl; //1
cout << lt.back() << endl; //4
return 0;
Modifiers
assign
将新内容赋值给list容器,替换其当前内容,并相应地修改其大小
1). 将n个值为val的数据分配给容器。
2). 将所给迭代器区间当中的内容分配给容器。
// list::assign
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main ()
list<int> first;
list<int> second;
first.assign (7,100); // 7 ints with value 100
second.assign (first.begin(),first.end()); // a copy of first
int myints[]=1776,7,4;
first.assign (myints,myints+3); // assigning from array
cout << "Size of first: " << int (first.size()) << endl; // 3
cout << "Size of second: " << int (second.size()) << endl; // 7
return 0;
push_front/pop_front
头插,头删容器中的数据
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main ()
list<int> mylist (2,100); // two ints with a value of 100
mylist.push_front (200);
mylist.push_front (300);
cout << "mylist contains:";
for (list<int>::iterator it=mylist.begin(); it!=mylist.end(); ++it)
cout << ' ' << *it;
cout << endl;
return 0;
// output
// 300 200 100 100
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main ()
list<int> mylist;
mylist.push_back (100);
mylist.push_back (200);
mylist.push_back (300);
cout << "Popping out the elements in mylist:";
while (!mylist.empty())
cout << ' ' << mylist.front();
mylist.pop_front();
cout << "\\nFinal size of mylist is " << mylist.size() << endl;
return 0;
// output
// Popping out the elements in mylist: 100 200 300
// Final size of mylist is 0
push_back/pop_back
尾插,尾删容器中的数据
// list::push_back
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
int main ()
std::list<int> mylist;
int myint;
std::cout << "Please enter some integers (enter 0 to end):\\n";
do
std::cin >> myint;
mylist.push_back (myint);
while (myint);
std::cout << "mylist stores " << mylist.size() << " numbers.\\n";
return 0;
// list::pop_back
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
int main ()
std::list<int> mylist;
int sum (0);
mylist.push_back (100);
mylist.push_back (200);
mylist.push_back (300);
while (!mylist.empty())
sum+=mylist.back();
mylist.pop_back();
std::cout << "The elements of mylist summed " << sum << '\\n';
return 0;
// output
// The elements of mylist summed 600
insert
1).在指定迭代器位置插入一个数。
2). 在指定迭代器位置插入n个值为val的数。
3).在指定迭代器位置插入一段迭代器区间(左闭右开)。
// inserting into a list
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
int main ()
std::list<int> mylist;
std::list<int>::iterator it;
// set some initial values:
for (int i=1; i<=5; ++i) mylist.push_back(i); // 1 2 3 4 5
it = mylist.begin();
++it; // it points now to number 2 ^
mylist.insert (it,10); // 1 10 2 3 4 5
// "it" still points to number 2 ^
mylist.insert (it,2,20); // 1 10 20 20 2 3 4 5
--it; // it points now to the second 20 ^
std::vector<int> myvector (2,30);
mylist.insert (it,myvector.begin(),myvector.end());
// 1 10 20 30 30 20 2 3 4 5
// ^
std::cout << "mylist contains:";
for (it=mylist.begin(); it!=mylist.end(); ++it)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << '\\n';
return 0;
// output
// mylist contains: 1 10 20 30 30 20 2 3 4 5
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
int main()
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
list<int>::iterator pos = find(lt.begin(),lt.end(),3);
lt.insert(pos,30);
print(lt);
cout << *pos << endl; // 3
insert 不会导致迭代器失效,因为链表的插入并不会影响 it/pos 所指向的位置
erase
1).删除指定迭代器位置的元素。
2). 删除指定迭代器区间(左闭右开)的所有元素。
// erasing from list
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
int main ()
std::list<int> mylist;
std::list<int>::iterator it1,it2;
// set some values:
for (int i=1; i<10; ++i) mylist.push_back(i*10);
// 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
it1 = it2 = mylist.begin(); // ^^
advance (it2,6); // ^ ^
++it1; // ^ ^
it1 = mylist.erase (it1); // 10 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
// ^ ^
it2 = mylist.erase (it2); // 10 30 40 50 60 80 90
// ^ ^
++it1; // ^ ^
--it2; // ^ ^
mylist.erase (it1,it2); // 10 30 60 80 90
// ^
// it1 已经失效
std::cout << "mylist contains:";
for (it1=mylist.begin(); it1!=mylist.end(); ++it1)
std::cout << ' ' << *it1;
std::cout << '\\n';
return 0;
// Output:
// mylist contains: 10 30 60 80 90
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
list<int>::iterator pos = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 3);
// pos迭代器失效
lt.erase(pos);
print(lt);
cout << *pos << endl;
erase 会导致迭代器失效,因为链表的删除会使 pos 所指向的位置被释放,从而 pos 成为野指针
swap
swap用于交换两个容器的内容
// swap lists
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
int main ()
std::list<int> first (3,100); // three ints with a value of 100
std::list<int> second (5,200); // five ints with a value of 200
first.swap(second);
std::cout << "first contains:";
for (std::list<int>::iterator it=first.begin(); it!=first.end(); it++)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << '\\n';
std::cout << "second contains:";
for (std::list<int>::iterator it=second.begin(); it!=second.end(); it++)
std::cout << ' ' << *it;
std::cout << '\\n';
return 0;
// Output:
// first contains: 200 200 200 200 200
// second contains: 100 100 100
resize
1). 若 n 小于当前容器的 size ,size 减少到 n
2). 若 n 大于当前容器的 size,尾插入数据直到 n,值用 val 来填充
// resizing list
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
int main ()
std::list<int> mylist;
// set some initial content:
for (int i=1; i以上是关于list介绍和基本使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章