IPC初识进程和Binder
Posted 從前以後
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了IPC初识进程和Binder相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
*什么是IPC通信
IPC(Inter-Process Communication)通信,是跨越两个不同进程(Process)之通信,一般而言,一个android应用程序里的各组件(如Activity、Service等)都在同一个进程里执行。这种在同一进程内的通信,又称为短程通信,意味着,两个Activity在同一个进程(Process)里执行。相对地,远程(Remote)通信的意思是:两个组件(如Activity或Service)分别在不同的进程里执行;两者之间是IPC通信,又称远程通信。
*进程的概念
一个进程是一个独立的执行空间,不会被正在其它进程里的程序所侵犯。这种保护方法是Android的重要安全机制。于是,得先认识进程的内涵,才能进一步了解跨进程IPC机制。
在Android的进程里,有一个虚拟机(Virtual Machine,简称VM)的对象,可执行Java代码,也引导JNI本地程序的执行,实现Java与Native层的C/C++之间的沟通。
在Android框架里,一个应用程序通常含有多个Java类,这些类可以在同一个进程里执行;也可以在不同的进程里执行 。
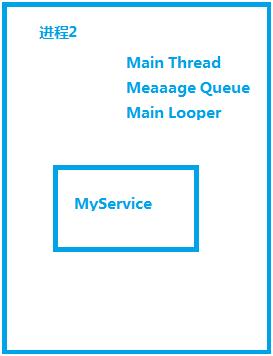
每一个进程在诞生时,都会诞生一个主线程(Main Thread),以及诞生一个Looper类的对象和一个MQ(Message Queue)数据结构。主线程最主要的工作就是处理UI画面的事件(Event),每当UI事件发生时,Android框架会丢信息(Message)到MQ里。主线程看到MQ有新的信息时,就取出信息,然后依据信息内容而去执行特定的函数。执行完毕,就再继续执行Looper类,不断地观察MQ的动态。

*设置不同的进程
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".MyService" android:process=":remote"/>
</application>
当给service 指定process=“:remote之后”MyService就运行在单独的进程中了。
此时Activity和Service运行在不同的进程当中

*IBinder接口
当两个类都在同一个进程里执行时,两者之间的沟通,只要采取一般的函数调用就行了,既快速又方便。一旦两个类分别在不同的进程里执行时,两者之IBinder接口定义了一些函数,可以让Client程序可以进行跨进程的調用(当然也能支持同进程的短程調用)。其中,最主要的一个函数就是:transact()函数。而进程
间的沟通,就不能采取一般的函数调用途径了。只好采取IPC沟通途径。 当跨进程调用,只要拿到了IBinder接口对象,就能调用到远程Binder的实现类中的onTransact()函数 了。
IBInder中的transact函数
public boolean transact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags)
throws RemoteException;*Binder
Binder是IBinder接口的实现类,Binder类很重要目的是支持跨进程調用Service,也就是让远程的Client可以跨进程調用某个Service。其中Binder类的主要的函数有
transact()函数
public final boolean transact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply,
int flags) throws RemoteException
if (false) Log.v("Binder", "Transact: " + code + " to " + this);
if (data != null)
data.setDataPosition(0);
boolean r = onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
if (reply != null)
reply.setDataPosition(0);
return r;
— 用来实现IBinder接口中的的transact()方法。
execTransact()函数
// Entry point from android_util_Binder.cpp's onTransact
private boolean execTransact(int code, long dataObj, long replyObj,
int flags)
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain(dataObj);
Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain(replyObj);
// theoretically, we should call transact, which will call onTransact,
// but all that does is rewind it, and we just got these from an IPC,
// so we'll just call it directly.
boolean res;
// Log any exceptions as warnings, don't silently suppress them.
// If the call was FLAG_ONEWAY then these exceptions disappear into the ether.
try
res = onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
catch (RemoteException e)
if ((flags & FLAG_ONEWAY) != 0)
Log.w(TAG, "Binder call failed.", e);
else
reply.setDataPosition(0);
reply.writeException(e);
res = true;
catch (RuntimeException e)
if ((flags & FLAG_ONEWAY) != 0)
Log.w(TAG, "Caught a RuntimeException from the binder stub implementation.", e);
else
reply.setDataPosition(0);
reply.writeException(e);
res = true;
catch (OutOfMemoryError e)
// Unconditionally log this, since this is generally unrecoverable.
Log.e(TAG, "Caught an OutOfMemoryError from the binder stub implementation.", e);
RuntimeException re = new RuntimeException("Out of memory", e);
reply.setDataPosition(0);
reply.writeException(re);
res = true;
checkParcel(this, code, reply, "Unreasonably large binder reply buffer");
reply.recycle();
data.recycle();
// Just in case -- we are done with the IPC, so there should be no more strict
// mode violations that have gathered for this thread. Either they have been
// parceled and are now in transport off to the caller, or we are returning back
// to the main transaction loop to wait for another incoming transaction. Either
// way, strict mode begone!
StrictMode.clearGatheredViolations();
return res;
— 该函数定位与transact()函数是相同的,只是这是用来让C/C++本地程序来向上调用的。
onTransact()函数
protected boolean onTransact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply,
int flags) throws RemoteException
if (code == INTERFACE_TRANSACTION)
reply.writeString(getInterfaceDescriptor());
return true;
else if (code == DUMP_TRANSACTION)
ParcelFileDescriptor fd = data.readFileDescriptor();
String[] args = data.readStringArray();
if (fd != null)
try
dump(fd.getFileDescriptor(), args);
finally
try
fd.close();
catch (IOException e)
// swallowed, not propagated back to the caller
// Write the StrictMode header.
if (reply != null)
reply.writeNoException();
else
StrictMode.clearGatheredViolations();
return true;
return false;
— 该函数是可以让子类来覆写的。上述的transact()和execTransact()两个函数最终都是调用到onTransact()函数。
init()函数
private native final void init();— 这是一个本地(Native)函数,让JNI模块来实现这个函数。Binder()构造函数会調用这个init()本地函数。
由于跨进程沟通时,并不是从Java层直接沟通的,而是透过底层的Binder Driver驱动来沟通的,所以Client端的Java类(如Activity)必须透过BinderProxy的IBinder接口,转而調用JNI本地模块来衔接到底层Binder Driver驱动服务,进而調用到正在另一个进程里执行的Service。
以上是关于IPC初识进程和Binder的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章