c++_STL_string类简介
Posted Zheng"Rui
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了c++_STL_string类简介相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
STL:STL是c++中的标准模板库,在其中有很多大佬封装的模板类,帮助我们的代码,使c++的编程更加方便。
下面介绍string类的一些常见用法:
1、string的构造函数
string(); // string 的默认构造函数
string(const char*s);// 使用c风格的字符串来构造一个string对象
string(size_t n,char c);//使用n个字符c来构造一个string对象
string(const string&s);// 使用另一个string对象构造string对象
使用举例:
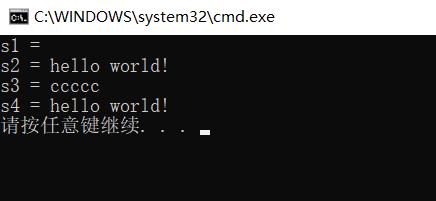
string s1;//默认构造
cout << "s1 = "<< s1 << endl;//打印空串
char *s = "hello world!";
string s2(s);//使用字符串s来构造s2
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
string s3(5, 'c');//使用5个字符c来构造s3
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
string s4 = s2;//使用s2来拷贝构造s4
cout << "s4 = " << s4 << endl;
结果展示:
2.string常用的容量操作
size_t size();//返回string中的有效字符数
size_t lenth();//返回string中的有效字符数
size_t capacity();//返回string中的空间大小
bool empty();//检测string中是否为空串,是则返回true,否则返回false
void clear();//清空有效字符
void reserve(size_t n=0);//为字符串预留空间
void resize(size_t n,char c);//将字符串的有效字符数改为n,多出的空间用字符c填充
void resize(size_t n,char c);//将字符串的有效字符数改为n,多出的空间用字符'\\0'填充
使用举例:
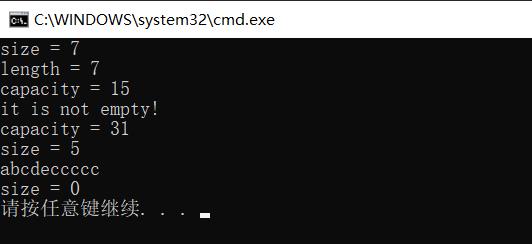
//初始化string对象
string s1 = "abcdefg";
//输出s1的size,length,capacity的信息
cout << "size = " << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "length = " << s1.length() << endl;
cout << "capacity = " << s1.capacity() << endl;
//判断s1是否为空
if (s1.empty())
cout << "it is empty!" << endl;
else
cout << "it is not empty!" << endl;
//为s1预留20个字节的有效字符空间
s1.reserve(20);
cout << "capacity = " << s1.capacity() << endl;
//将s1的有效字符大小改为5,和10,并用'c'填充
s1.resize(5);
cout << "size = " << s1.size() << endl;
s1.resize(10, 'c');
cout << s1 << endl;
//清空字符串
s1.clear();
cout << "size = " << s1.size() << endl;
结果展示:
3.string对象的访问及常用的遍历操作
char& operator[](int i);//对于方括号的重载
begin() + end();//begin获取第一个元素的迭代器,end获取最后一个字符的下一个位置的迭代器
rbegin() + rend();//rbegin获取最后一个字符的下一个位置的迭代器,rend获取第一个元素的迭代器
使用举例:
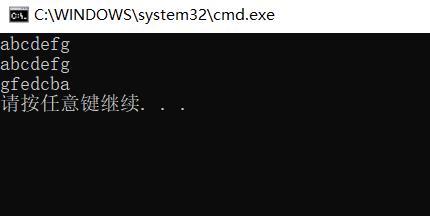
//初始化s1
string s1 = "abcdefg";
//使用传统的c风格的代码也可以遍历string对象
for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
cout << s1[i];//这里使用的是重载过的[]运算符
cout << endl;
//定义一个string对象的迭代器 it,指向s1的第一个字符
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
//当it不指向s1的最后一个字符的下一个位置,就输出it的内容,然后it++
while (it != s1.end())
cout << *it;
it++;
cout << endl;
//定义一个string对象的反向迭代器 rit,指向s1的最后一个字符的下一个位置
string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();
//当it不指向s1的第一个字符,就输出it的内容,然后it++(此时加加,意味着反向迭代器往前移动)
while (rit != s1.rend())
cout << *rit;
rit++;
cout << endl;
结果展示:
4.string类的对象修改操作
void push_back(char c);//在字符串尾插入一个字符c
void append(const char* s);//在字符串尾插入一个字符串s
string& operator+=(char *s);//在字符串尾追加一个字符串s
const char* c_str()const;//返回c风格的字符串
size_t find(char c,size_t pos = 0)const;//从位置pos开始,寻找字符'c',找到则返回位置,否则返回npos
size_t rfind(char c,size_t pos = npos)const;//从位置pos开始,反向寻找字符'c',找到则返回位置,否则返回npos
使用举例:
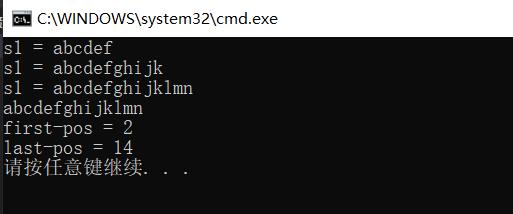
//初始化s1
string s1 = "abc";
//向s1的尾部插入'd','e','f'
s1.push_back('d');
s1.push_back('e');
s1.push_back('f');
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
//向s1的尾部插入"ghijk"
s1.append("ghijk");
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
//向s1的尾部插入"lmn"
s1 += "lmn";
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
//使用c风格的字符串接收s1中的字符串
const char* cstr = s1.c_str();
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(cstr); i++)
cout << cstr[i];
cout << endl;
//向s1的最后插入'c',分别从前往后寻找'c',从后往前寻找'c'
s1.push_back('c');
cout << "first-pos = " << s1.find('c') << endl;
cout << "last-pos = " << s1.rfind('c') << endl;
结果展示:
5.string类的非成员函数
string operator+(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//将lhs和rhs中的字符串进行拼接
istream& operator>>(istream& is,string& str);//从标准输入给str赋值
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,string& str);//将str中的字符串给标准输出
istream& getline(istream& is,string& str);//获取一行数据给str赋值
bool operator==(const string& lhs,const string& rhs);//判断lhs是否与rhs相等(string中有很多关系比较符的重载,这里只介绍==,其他的用法大致相同)
……
使用举例:
//初始化s1,s2
string s1 = "abc";
string s2 = "def";
//s3用s1+s2的结果初始化
string s3 = s1 + s2;
cout << "s3 = " << s3 << endl;
//从标准输入给s1赋值
cin >> s1;
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
//接收回车键
getchar();
//获取一行的输入,给s2赋值
getline(cin, s2);
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
//判断s1与s2是否相等
if (s1 == s2)
cout << "s1 = s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1 != s2" << endl;
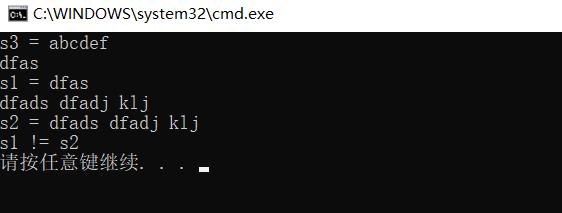
结果展示:
结语:
注意,string中有很多的内部方法,这里只介绍了其中常用的部分,而且,其中很多方法都有它的重载函数,这里只介绍了其中一种,剩下的方法可以自行查阅,用法大致相同。
以上是关于c++_STL_string类简介的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章