基于OpenCV实现二值图细化,骨骼化并求出端点和交叉点
Posted 晴堂
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于OpenCV实现二值图细化,骨骼化并求出端点和交叉点相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
所谓细化就是经过一层层的剥离,从原来的图中去掉一些点,但仍要保持原来的形状,直到得到图像的骨架。骨架,可以理解为物体的中轴,例如一个长方形的骨架是它的长方向上的中轴线;正方形的骨架是它的中心点;圆的骨架是它的圆心,直线的骨架是它自身,孤立点的骨架也是自身。得到了骨架,就相当于突出物体的主要结构和形状信息,去除了多余信息,根据这些信息可以实现图像上特征点的检测,如端点,交叉点和拐点。
下面先介绍经典的Zhang并行快速细化算法:
设p1点的八邻域为:
p9 p2 p3
p8 p1 p4
p7 p6 p5
(其中p1为白点也就是物体,如果以下四个条件同时满足,则删除p1,即令p1=0)
其中迭代分为两个子过程:
过程1 细化删除条件为:
(1)、2 <=N(p1) <= 6, N(x)为x的8邻域中黑点的数目
(2)、A(p1)=1,A(x)指的是将p2-p8之间按序前后分别成对值为0、1的个数(背景色:0)
(3)、p2*p4*p6=0
(4)、p4*p6*p8=0
如果同时满足以上四个条件则该点可以删除(赋值为0)。
过程2 细化删除条件为:
(1)、2 <=N(p1) <= 6, N(x)为x的8邻域中黑点的数目
(2)、A(p1)=1,A(x)指的是将p2-p8之间按序前后分别为0、1的对数(背景色:0)
(3)、p2*p4*p8=0
(4)、p2*p6*p8=0
如果同时满足以上四个条件则该点可以删除。这样反复迭代,直到获取细化图像为止。
过滤部分较为简单:
如果p2+p3+p8+p9>=1,则该点可以删除(赋值为0)。实现每两个白点之间不能紧靠在一起
检测部分比较复杂需要反复实验:
过程1 确定卷积邻域范围:
p25 p10 p11 p12 p13
p24 p9 p2 p3 p14
p23 p8 p1 p4 p15
p22 p7 p6 p5 p16
p21 p20 p19 p18 p17
(这里是使用5x5,实际上为了更好的检测需要至少6x6的卷积且为圆形)
过程2 统计卷积范围内白点个数:
如果白点个数较多,则说明p1为交叉点。
如果白点个数较少,则说明p1为端点。
过程3 对检测出的点进行合并:
如果两个点之间距离太近,取平均值。(下面代码没有实现该功能)
所有程序源代码:
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
/**
* @brief 对输入图像进行细化,骨骼化
* @param src为输入图像,用cvThreshold函数处理过的8位灰度图像格式,元素中只有0与1,1代表有元素,0代表为空白
* @param maxIterations限制迭代次数,如果不进行限制,默认为-1,代表不限制迭代次数,直到获得最终结果
* @return 为对src细化后的输出图像,格式与src格式相同,元素中只有0与1,1代表有元素,0代表为空白
*/
cv::Mat thinImage(const cv::Mat & src, const int maxIterations = -1)
assert(src.type() == CV_8UC1);
cv::Mat dst;
int width = src.cols;
int height = src.rows;
src.copyTo(dst);
int count = 0; //记录迭代次数
while (true)
count++;
if (maxIterations != -1 && count > maxIterations) //限制次数并且迭代次数到达
break;
std::vector<uchar *> mFlag; //用于标记需要删除的点
//对点标记
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i)
uchar * p = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < width; ++j)
//如果满足四个条件,进行标记
// p9 p2 p3
// p8 p1 p4
// p7 p6 p5
uchar p1 = p[j];
if (p1 != 1) continue;
uchar p4 = (j == width - 1) ? 0 : *(p + j + 1);
uchar p8 = (j == 0) ? 0 : *(p + j - 1);
uchar p2 = (i == 0) ? 0 : *(p - dst.step + j);
uchar p3 = (i == 0 || j == width - 1) ? 0 : *(p - dst.step + j + 1);
uchar p9 = (i == 0 || j == 0) ? 0 : *(p - dst.step + j - 1);
uchar p6 = (i == height - 1) ? 0 : *(p + dst.step + j);
uchar p5 = (i == height - 1 || j == width - 1) ? 0 : *(p + dst.step + j + 1);
uchar p7 = (i == height - 1 || j == 0) ? 0 : *(p + dst.step + j - 1);
if ((p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9) >= 2 && (p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9) <= 6)
int ap = 0;
if (p2 == 0 && p3 == 1) ++ap;
if (p3 == 0 && p4 == 1) ++ap;
if (p4 == 0 && p5 == 1) ++ap;
if (p5 == 0 && p6 == 1) ++ap;
if (p6 == 0 && p7 == 1) ++ap;
if (p7 == 0 && p8 == 1) ++ap;
if (p8 == 0 && p9 == 1) ++ap;
if (p9 == 0 && p2 == 1) ++ap;
if (ap == 1 && p2 * p4 * p6 == 0 && p4 * p6 * p8 == 0)
//标记
mFlag.push_back(p + j);
//将标记的点删除
for (std::vector<uchar *>::iterator i = mFlag.begin(); i != mFlag.end(); ++i)
**i = 0;
//直到没有点满足,算法结束
if (mFlag.empty())
break;
else
mFlag.clear();//将mFlag清空
//对点标记
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i)
uchar * p = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < width; ++j)
//如果满足四个条件,进行标记
// p9 p2 p3
// p8 p1 p4
// p7 p6 p5
uchar p1 = p[j];
if (p1 != 1) continue;
uchar p4 = (j == width - 1) ? 0 : *(p + j + 1);
uchar p8 = (j == 0) ? 0 : *(p + j - 1);
uchar p2 = (i == 0) ? 0 : *(p - dst.step + j);
uchar p3 = (i == 0 || j == width - 1) ? 0 : *(p - dst.step + j + 1);
uchar p9 = (i == 0 || j == 0) ? 0 : *(p - dst.step + j - 1);
uchar p6 = (i == height - 1) ? 0 : *(p + dst.step + j);
uchar p5 = (i == height - 1 || j == width - 1) ? 0 : *(p + dst.step + j + 1);
uchar p7 = (i == height - 1 || j == 0) ? 0 : *(p + dst.step + j - 1);
if ((p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9) >= 2 && (p2 + p3 + p4 + p5 + p6 + p7 + p8 + p9) <= 6)
int ap = 0;
if (p2 == 0 && p3 == 1) ++ap;
if (p3 == 0 && p4 == 1) ++ap;
if (p4 == 0 && p5 == 1) ++ap;
if (p5 == 0 && p6 == 1) ++ap;
if (p6 == 0 && p7 == 1) ++ap;
if (p7 == 0 && p8 == 1) ++ap;
if (p8 == 0 && p9 == 1) ++ap;
if (p9 == 0 && p2 == 1) ++ap;
if (ap == 1 && p2 * p4 * p8 == 0 && p2 * p6 * p8 == 0)
//标记
mFlag.push_back(p + j);
//将标记的点删除
for (std::vector<uchar *>::iterator i = mFlag.begin(); i != mFlag.end(); ++i)
**i = 0;
//直到没有点满足,算法结束
if (mFlag.empty())
break;
else
mFlag.clear();//将mFlag清空
return dst;
/**
* @brief 对骨骼化图数据进行过滤,实现两个点之间至少隔一个空白像素
* @param thinSrc为输入的骨骼化图像,8位灰度图像格式,元素中只有0与1,1代表有元素,0代表为空白
*/
void filterOver(cv::Mat thinSrc)
assert(thinSrc.type() == CV_8UC1);
int width = thinSrc.cols;
int height = thinSrc.rows;
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i)
uchar * p = thinSrc.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = 0; j < width; ++j)
// 实现两个点之间至少隔一个像素
// p9 p2 p3
// p8 p1 p4
// p7 p6 p5
uchar p1 = p[j];
if (p1 != 1) continue;
uchar p4 = (j == width - 1) ? 0 : *(p + j + 1);
uchar p8 = (j == 0) ? 0 : *(p + j - 1);
uchar p2 = (i == 0) ? 0 : *(p - thinSrc.step + j);
uchar p3 = (i == 0 || j == width - 1) ? 0 : *(p - thinSrc.step + j + 1);
uchar p9 = (i == 0 || j == 0) ? 0 : *(p - thinSrc.step + j - 1);
uchar p6 = (i == height - 1) ? 0 : *(p + thinSrc.step + j);
uchar p5 = (i == height - 1 || j == width - 1) ? 0 : *(p + thinSrc.step + j + 1);
uchar p7 = (i == height - 1 || j == 0) ? 0 : *(p + thinSrc.step + j - 1);
if (p2 + p3 + p8 + p9 >= 1)
p[j] = 0;
/**
* @brief 从过滤后的骨骼化图像中寻找端点和交叉点
* @param thinSrc为输入的过滤后骨骼化图像,8位灰度图像格式,元素中只有0与1,1代表有元素,0代表为空白
* @param raudis卷积半径,以当前像素点位圆心,在圆范围内判断点是否为端点或交叉点
* @param thresholdMax交叉点阈值,大于这个值为交叉点
* @param thresholdMin端点阈值,小于这个值为端点
* @return 为对src细化后的输出图像,格式与src格式相同,元素中只有0与1,1代表有元素,0代表为空白
*/
std::vector<cv::Point> getPoints(const cv::Mat &thinSrc, unsigned int raudis = 4, unsigned int thresholdMax = 6, unsigned int thresholdMin = 4)
assert(thinSrc.type() == CV_8UC1);
int width = thinSrc.cols;
int height = thinSrc.rows;
cv::Mat tmp;
thinSrc.copyTo(tmp);
std::vector<cv::Point> points;
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < width; ++j)
if (*(tmp.data + tmp.step * i + j) == 0)
continue;
int count=0;
for (int k = i - raudis; k < i + raudis+1; k++)
for (int l = j - raudis; l < j + raudis+1; l++)
if (k < 0 || l < 0||k>height-1||l>width-1)
continue;
else if (*(tmp.data + tmp.step * k + l) == 1)
count++;
if (count > thresholdMax||count<thresholdMin)
Point point(j, i);
points.push_back(point);
return points;
int main(int argc, char*argv[])
cv::Mat src;
//获取图像
if (argc != 2)
src = cv::imread("src.jpg", cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
else
src = cv::imread(argv[1], cv::IMREAD_GRAYSCALE);
if (src.empty())
std::cout << "读取文件失败!" << std::endl;
return -1;
//将原图像转换为二值图像
cv::threshold(src, src, 128, 1, cv::THRESH_BINARY);
//图像细化,骨骼化
cv::Mat dst = thinImage(src);
//过滤细化后的图像
filterOver(dst);
//查找端点和交叉点
std::vector<cv::Point> points = getPoints(dst,6,9,6);
//二值图转化成灰度图,并绘制找到的点
dst = dst * 255;
src = src * 255;
vector<cv::Point>::iterator it = points.begin();
for (;it != points.end(); it++)
circle(dst, *it,4,255, 1);
imwrite("dst.jpg", dst);
//显示图像
cv::namedWindow("src1", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::namedWindow("dst1", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow("src1", src);
cv::imshow("dst1", dst);
cv::waitKey(0);
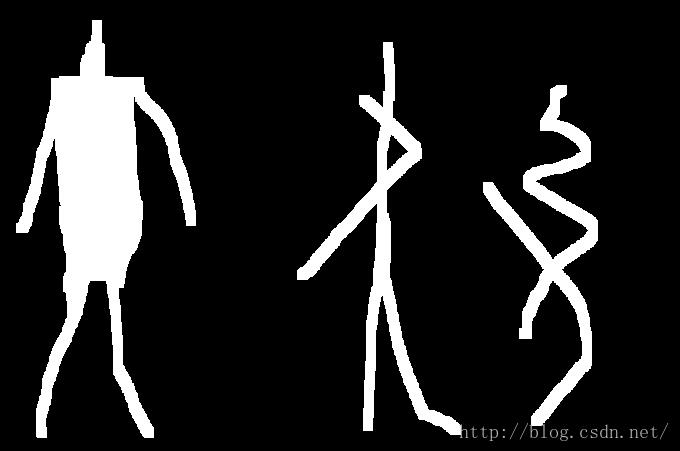
原图
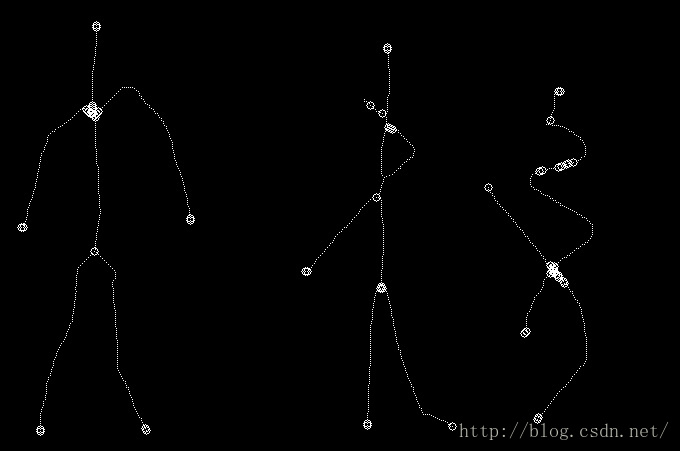
细化及检测结果
测试结果2图片:

原图

细化及检测结果
整个程序运行时间大约需要0.02秒,不会占用什么资源,代码还可以进一步优化,检测出的点也没有过滤合并。对于拐点的检测可以使用局部求导,多点拟合
或者傅里叶变换。有实现的朋友大家可以共享代码。
以上是关于基于OpenCV实现二值图细化,骨骼化并求出端点和交叉点的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章