Android事件总线EventBus的用法详解
Posted 小威少威
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android事件总线EventBus的用法详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
android中模块更新的机制有很多种,EventBus又是其中使用起来较为方便简单的一种,本文就针对EventBus在平常工作中的用法,做一个个人总结。主要分为以下几点来展示:
- 介绍
- 源码分析
- 用法示例
下图也就是本文要讲的主要内容:
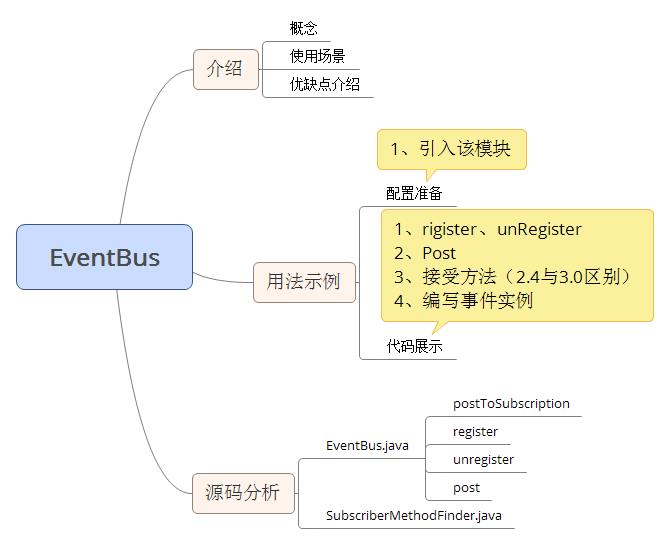
1、介绍:
EventBus是针一款对Android的发布/订阅事件总线。它可以让我们很轻松的实现在Android各个组件之间传递消息,并且代码的可读性更好,耦合度更低。我们可以在要进行实时界面更新的交互上使用该模块以替代一些消息机制的处理。EventBus的·优点是用法简单,不必写繁琐的代码,而且耦合度也低。缺点其实个人发现无明显的缺点,可能就是得针对每个事件定义也一个事件类,感觉会造成重复造轮子的感觉。此外,关于事件总线还有的一个框架是Otto,这边就不分析这个框架了。
2、源码分析:
按照惯例,我们在代码里面查看EventBus.java的源码,这里就不贴出整个类的源码了。我们首先看下,该类的构造方法:
/**
* Creates a new EventBus instance; each instance is a separate scope in which events are delivered. To use a
* central bus, consider @link #getDefault().
*/
public EventBus()
this(DEFAULT_BUILDER);
EventBus(EventBusBuilder builder)
subscriptionsByEventType = new HashMap<Class<?>, CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription>>();
typesBySubscriber = new HashMap<Object, List<Class<?>>>();
stickyEvents = new ConcurrentHashMap<Class<?>, Object>();
mainThreadPoster = new HandlerPoster(this, Looper.getMainLooper(), 10);
backgroundPoster = new BackgroundPoster(this);
asyncPoster = new AsyncPoster(this);
subscriberMethodFinder = new SubscriberMethodFinder(builder.skipMethodVerificationForClasses);
logSubscriberExceptions = builder.logSubscriberExceptions;
logNoSubscriberMessages = builder.logNoSubscriberMessages;
sendSubscriberExceptionEvent = builder.sendSubscriberExceptionEvent;
sendNoSubscriberEvent = builder.sendNoSubscriberEvent;
throwSubscriberException = builder.throwSubscriberException;
eventInheritance = builder.eventInheritance;
executorService = builder.executorService;
主要是一些要用到类的对象的初始化,用的是Builder模式。
注册的方法:
/**
* Registers the given subscriber to receive events. Subscribers must call @link #unregister(Object) once they
* are no longer interested in receiving events.
* <p/>
* Subscribers have event handling methods that must be annotated by @link Subscribe.
* The @link Subscribe annotation also allows configuration like @link
* ThreadMode and priority.
*/
public void register(Object subscriber)
Class<?> subscriberClass = subscriber.getClass();
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass);
synchronized (this)
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods)
subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
通过SubscriberMethodFinder该类的findSubscriberMethods方法,查询到SubscriberMethod列表,SubscriberMethod类的构造方法:
public SubscriberMethod(Method method, Class<?> eventType, ThreadMode threadMode, int priority, boolean sticky)
this.method = method;
this.threadMode = threadMode;
this.eventType = eventType;
this.priority = priority;
this.sticky = sticky;
可知,五个参数为方法、事件类型、线程模式、优先级、sticky,SubscriberMethod的其他方法:
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other)
if (other == this)
return true;
else if (other instanceof SubscriberMethod)
checkMethodString();
SubscriberMethod otherSubscriberMethod = (SubscriberMethod)other;
otherSubscriberMethod.checkMethodString();
// Don't use method.equals because of http://code.google.com/p/android/issues/detail?id=7811#c6
return methodString.equals(otherSubscriberMethod.methodString);
else
return false;
private synchronized void checkMethodString()
if (methodString == null)
// Method.toString has more overhead, just take relevant parts of the method
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(64);
builder.append(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
builder.append('#').append(method.getName());
builder.append('(').append(eventType.getName());
methodString = builder.toString();
现在清楚了,其实就是查询SubscriberMethodFinder类的作用是在Subscriber中找到所有以methodName(即默认的onEvent)开头的方法,具体我们可以看下findSubscriberMethods方法的代码。
EventBus中 findSubscriberMethods方法 2.4源码:
List<SubscriberMethod> findSubscriberMethods(Class<?> subscriberClass)
String key = subscriberClass.getName();
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods;
synchronized (methodCache)
subscriberMethods = methodCache.get(key);
if (subscriberMethods != null)
return subscriberMethods;
subscriberMethods = new ArrayList<SubscriberMethod>();
Class<?> clazz = subscriberClass;
HashSet<String> eventTypesFound = new HashSet<String>();
StringBuilder methodKeyBuilder = new StringBuilder();
while (clazz != null)
String name = clazz.getName();
if (name.startsWith("java.") || name.startsWith("javax.") || name.startsWith("android."))
// Skip system classes, this just degrades performance
break;
// Starting with EventBus 2.2 we enforced methods to be public (might change with annotations again)
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods)
String methodName = method.getName();
if (methodName.startsWith(ON_EVENT_METHOD_NAME))
int modifiers = method.getModifiers();
if ((modifiers & Modifier.PUBLIC) != 0 && (modifiers & MODIFIERS_IGNORE) == 0)
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length == 1)
String modifierString = methodName.substring(ON_EVENT_METHOD_NAME.length());
ThreadMode threadMode;
if (modifierString.length() == 0)
threadMode = ThreadMode.PostThread;
else if (modifierString.equals("MainThread"))
threadMode = ThreadMode.MainThread;
else if (modifierString.equals("BackgroundThread"))
threadMode = ThreadMode.BackgroundThread;
else if (modifierString.equals("Async"))
threadMode = ThreadMode.Async;
else
if (skipMethodVerificationForClasses.containsKey(clazz))
continue;
else
throw new EventBusException("Illegal onEvent method, check for typos: " + method);
Class<?> eventType = parameterTypes[0];
methodKeyBuilder.setLength(0);
methodKeyBuilder.append(methodName);
methodKeyBuilder.append('>').append(eventType.getName());
String methodKey = methodKeyBuilder.toString();
if (eventTypesFound.add(methodKey))
// Only add if not already found in a sub class
subscriberMethods.add(new SubscriberMethod(method, threadMode, eventType));
else if (!skipMethodVerificationForClasses.containsKey(clazz))
Log.d(EventBus.TAG, "Skipping method (not public, static or abstract): " + clazz + "."
+ methodName);
clazz = clazz.getSuperclass();
if (subscriberMethods.isEmpty())
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriberClass + " has no public methods called "
+ ON_EVENT_METHOD_NAME);
else
synchronized (methodCache)
methodCache.put(key, subscriberMethods);
return subscriberMethods;
现在应该豁然开朗,就是2.4版本,必须使用三种方法接收post过来的消息:MainThread、BackgroundThread、Async。而在3.0中的源码则是这样的:
List<SubscriberMethod> findSubscriberMethods(Class<?> subscriberClass)
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = METHOD_CACHE.get(subscriberClass);
if (subscriberMethods != null)
return subscriberMethods;
if (ignoreGeneratedIndex)
subscriberMethods = findUsingReflection(subscriberClass);
else
subscriberMethods = findUsingInfo(subscriberClass);
if (subscriberMethods.isEmpty())
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriberClass
+ " and its super classes have no public methods with the @Subscribe annotation");
else
METHOD_CACHE.put(subscriberClass, subscriberMethods);
return subscriberMethods;
subscriberMethods = findUsingReflection(subscriberClass);说的是利用反射来查询方法。
所以我们3.0通过注解,可以使用自定义的方法,不在受限,看完了注册的代码,
接下来就看下post的源码。
/** Posts the given event to the event bus. */
public void post(Object event)
PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get();
List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue;
eventQueue.add(event);
if (!postingState.isPosting)
postingState.isMainThread = Looper.getMainLooper() == Looper.myLooper();
postingState.isPosting = true;
if (postingState.canceled)
throw new EventBusException("Internal error. Abort state was not reset");
try
while (!eventQueue.isEmpty())
postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState);
finally
postingState.isPosting = false;
postingState.isMainThread = false;
发现操作的对象是PostingThreadState,然后就是这段代码:
postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState);继续查看相关的代码:
private void postSingleEvent(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState) throws Error
Class<?> eventClass = event.getClass();
boolean subscriptionFound = false;
if (eventInheritance)
List<Class<?>> eventTypes = lookupAllEventTypes(eventClass);
int countTypes = eventTypes.size();
for (int h = 0; h < countTypes; h++)
Class<?> clazz = eventTypes.get(h);
subscriptionFound |= postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, clazz);
else
subscriptionFound = postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, eventClass);
if (!subscriptionFound)
if (logNoSubscriberMessages)
Log.d(TAG, "No subscribers registered for event " + eventClass);
if (sendNoSubscriberEvent && eventClass != NoSubscriberEvent.class &&
eventClass != SubscriberExceptionEvent.class)
post(new NoSubscriberEvent(this, event));
private boolean postSingleEventForEventType(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState, Class<?> eventClass)
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions;
synchronized (this)
subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventClass);
if (subscriptions != null && !subscriptions.isEmpty())
for (Subscription subscription : subscriptions)
postingState.event = event;
postingState.subscription = subscription;
boolean aborted = false;
try
postToSubscription(subscription, event, postingState.isMainThread);
aborted = postingState.canceled;
finally
postingState.event = null;
postingState.subscription = null;
postingState.canceled = false;
if (aborted)
break;
return true;
return false;
private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread)
switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode)
case POSTING:
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
break;
case MAIN:
if (isMainThread)
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
else
mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
break;
case BACKGROUND:
if (isMainThread)
backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
else
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
break;
case ASYNC:
asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);
这里就用到ThreadMode了:
如果是PostThread,直接执行
如果是MainThread,判断当前线程,如果本来就是UI线程就直接执行,否则加入mainThreadPoster队列
如果是后台线程,如果当前是UI线程,加入backgroundPoster队列,否则直接执行
如果是Async,加入asyncPoster队列。关于post,就暂时写到这里啊,主要是理清内部的处理机制。
另外还有优先级和Stick的使用。这里就不阐述了。EventBus关键的部分源码我就写到这里,以下写下我们如何在代码中简单使用该模块。
3、使用示例:
一、首先是引入该模块:
我用的是gradle构建(demo源码和资源在最后会提供):
// compile files('libs/eventbus-2.4.0.jar')
compile 'org.greenrobot:eventbus:3.0.0'//3.0二、create方法中注册:
EventBusManager.getInstance().getGlobaEventBus().register(this);EventBusManager.java自己封装的类:
//import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;//2.4
import org.greenrobot.eventbus.EventBus;//3.0
/**
* @创建者 :viviant
* @时间 :2016/06/28 13:47
* @描述 : 事件总线管理
*/
public class EventBusManager
private static EventBusManager busManager;
private EventBus globalEventBus;
private EventBusManager()
public EventBus getGlobaEventBus()
if (globalEventBus == null)
globalEventBus = new EventBus();
return globalEventBus;
public static EventBusManager getInstance()
if (busManager == null)
synchronized (EventBusManager.class)
if (busManager == null)
busManager = new EventBusManager();
return busManager;
Event实体类编写:
/**
* 作者:viviant on 2016/7/4 10:35
* 描述:
*/
public class TestEvent
private String eventName;
public void setEventName(String eventName)
this.eventName = eventName;
public String getEventName()
return eventName;
接收页面方法编写(demo源码中有说明版本区别):
/**
* 不同模块之间数据的同步
*2.4的用法必须使用以下的几个方法,不需要注解
* @param event
*/
@Subscribe
public void onEventReceive(TestEvent event)
Log.d("weiwei", "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" );
if (event.getEventName().equals("tv1"))
tv1.setText("change by bt1");
else if (event.getEventName().equals("tv2"))
tv2.setText("tv2");
else if (event.getEventName().equals("tv3"))
else if (event.getEventName().equals("tv4"))
操作activity中的相关代码:
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import constraintlayout.test.test.viviant.eventbustest.event.TestEvent;
import constraintlayout.test.test.viviant.eventbustest.manager.EventBusManager;
/**
* 作者:viviant on 2016/7/4 10:37
* 描述:
*/
public class SecActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_sec);
Button bt1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt1);
Button bt2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt2);
Button bt3 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt3);
Button bt4 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt4);
bt1.setOnClickListener(this);
bt2.setOnClickListener(this);
bt3.setOnClickListener(this);
bt4.setOnClickListener(this);
@Override
public void onClick(View view)
TestEvent te = new TestEvent();
switch (view.getId())
case R.id.bt1:
te.setEventName("tv1");
EventBusManager.getInstance().getGlobaEventBus().post(te);
break;
case R.id.bt2:
te.setEventName("tv2");
EventBusManager.getInstance().getGlobaEventBus().post(te);
break;
case R.id.bt3:
break;
case R.id.bt4:
break;
default:
break;
云行之后我们先点击跳转activity,再点击相应but,然后返回去,便可以看到发生相应的变化。
MainActivity界面:
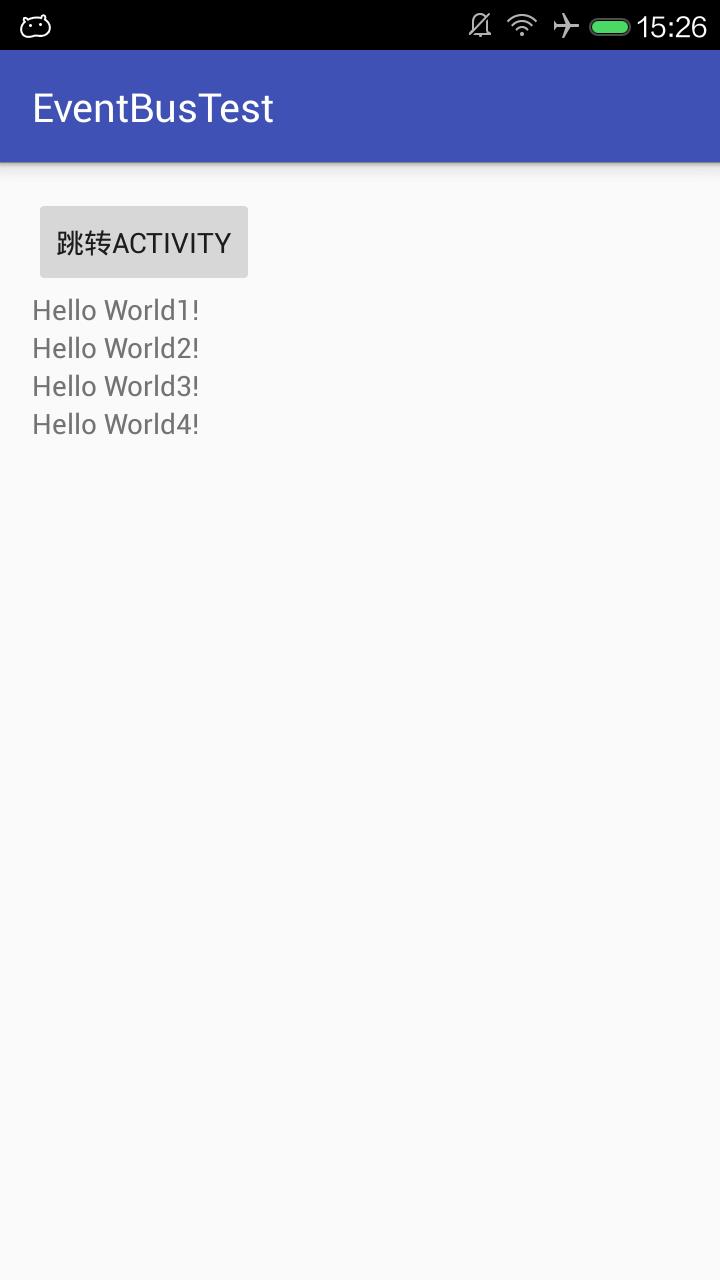
SecActivity界面:
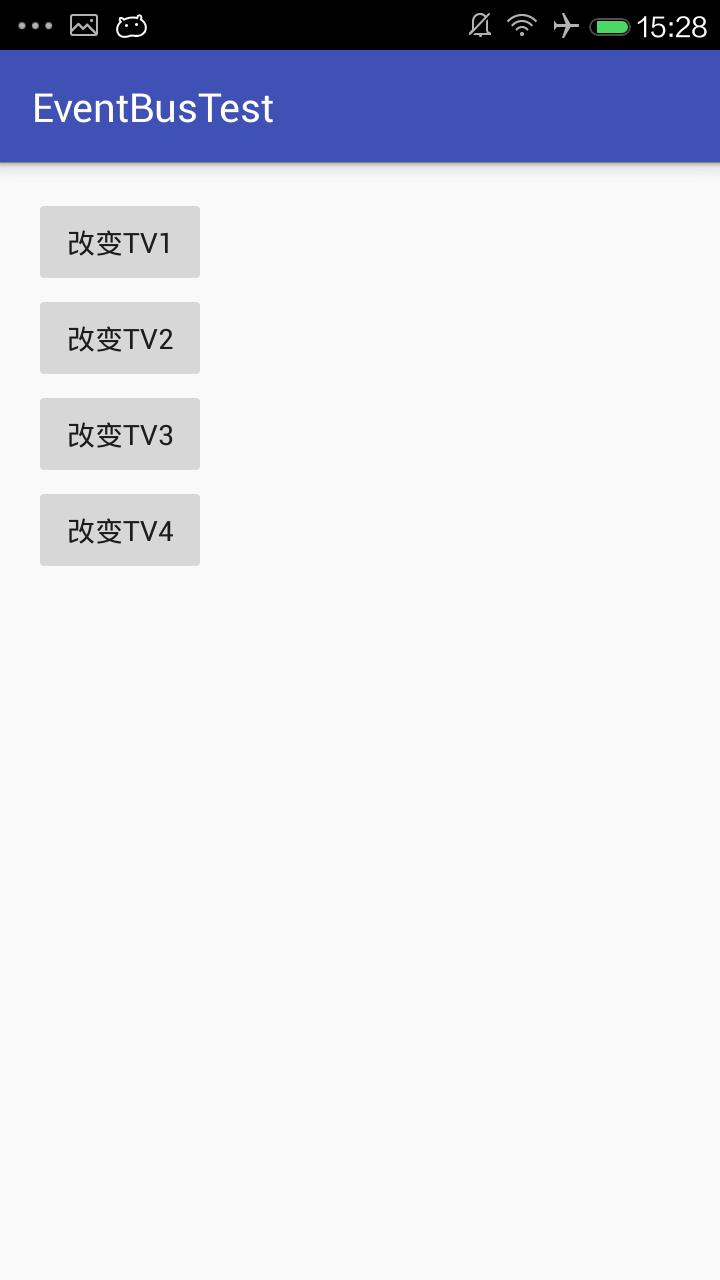
点击第一个按钮后回到MainActivity的界面:
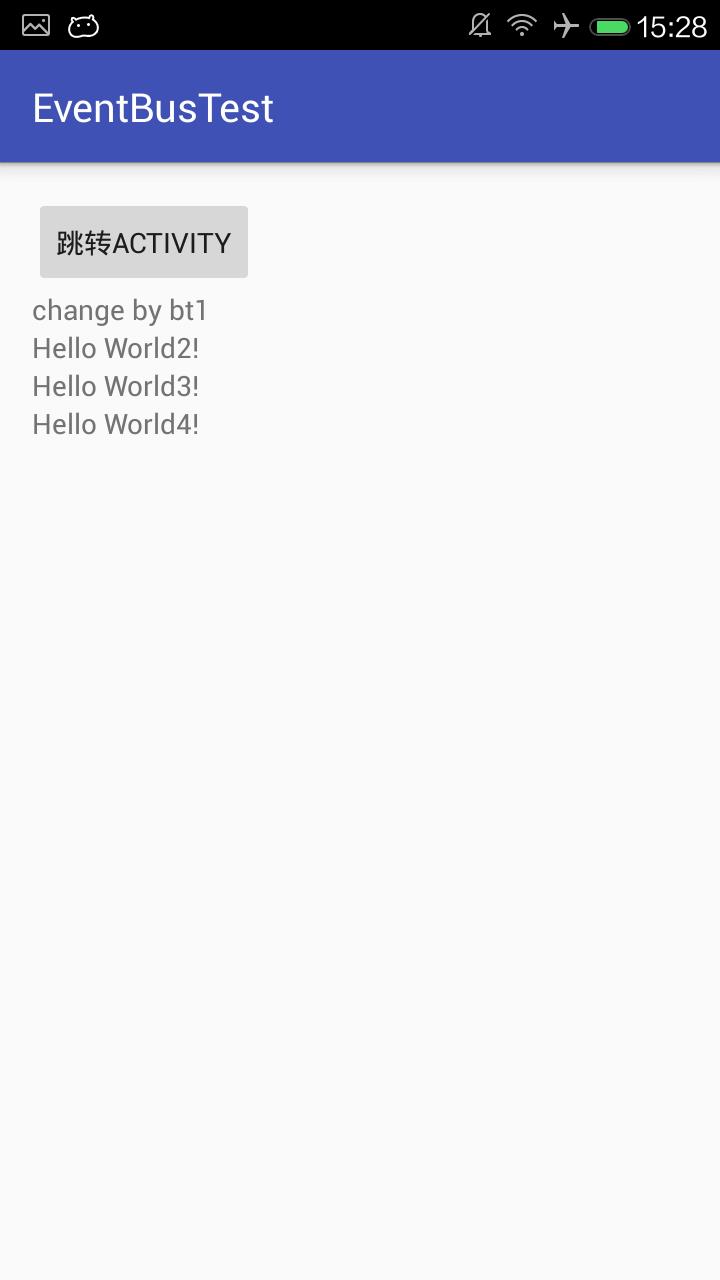
源码地址:
https://github.com/viviant1224/EventBusTest
2.4jar包下载地址:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/u013606974/9566754
、
demo中查看gradle中可切换EventBus版本。改完之后也要改相应的引包类。
以上是关于Android事件总线EventBus的用法详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章