LeetCode之两数相加反转链表少箭射球二叉树
Posted 刘兆贤
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode之两数相加反转链表少箭射球二叉树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本文来自刘兆贤的博客_CSDN博客-Java高级,Android旅行,Android基础领域博主 ,引用必须注明出处!
以前也有刷一些题目,但是没有记录,不方便回头看解题思路,今天开始就记录一下。
力扣刷了300题,地址:iddo - 力扣(LeetCode)
两个链表,分别纪录从个数开始的数,相加后得到新的链表
思路:递归。保留当前结点,提高连结效率。
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2)
return getResult(l1,l2,null,null,0);
public ListNode getResult(ListNode l1,ListNode l2,ListNode target,ListNode next,int addHigh)
if(l1==null&&l2==null&&addHigh==0)
return target;
int lv=0;
int rv=0;
if(l1!=null)
lv=l1.val;
l1=l1.next;
if(l2!=null)
rv=l2.val;
l2=l2.next;
int total=lv+rv+addHigh;
int newVal=total;
int newHigh=0;
if(total>9)
if(total==10)
newVal=0;
else
newVal=total%10;
newHigh=1;
ListNode temp=new ListNode(newVal);
if(target==null)
target=temp;
else
if(next!=null)
next.next=temp;
next=next.next;
else
target.next=temp;
next=target.next;
return getResult(l1,l2,target,next,newHigh);

执行速度还是蛮快的,内存也还好。
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
解法一:分别获得各结点,然后重新组成新的链表。重组过程:每次移动指针,将结点绑定。以此为核心思路,演化出第二种解法。
private static ListNode reverseListNode(ListNode head)
List<ListNode> list = getListNodeSize(head, new ArrayList<>());
ListNode preNode = null;
for (int i = list.size() - 1; i > -1; i--)
ListNode node = list.get(i);
// 切断结点
node.next = null;
if (preNode == null)
// 赋值初结点
preNode = node;
else
// 临时结点
ListNode temp = preNode.next;
if (temp != null)
while (temp.next != null)
// 每次都将指针移到最后一个,查到最后一个结点
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = node;
else
preNode.next = node;
return preNode;
private static List<ListNode> getListNodeSize(ListNode head, List<ListNode> list)
while (head != null)
list.add(head);
return getListNodeSize(head.next, list);
return list;
解法二:关键在于,使用指针结点,对新的链表进行递归赋值;演化出第三种方法。
private static ListNode reverseListNode(ListNode head)
return reverseNode(head, null);
/**
*
* @param curNode
* 指针结点
* @param headNode
* 新的链表
* @return
*/
private static ListNode reverseNode(ListNode curNode, ListNode headNode)
// 指针结点为空
if (curNode == null)
return headNode;
// 新的链表
if (headNode == null)
headNode = new ListNode(curNode.val);
// 指针结点
ListNode nextNode = curNode.next;
if (nextNode == null)
return headNode;
// 新链表结点
curNode = new ListNode(nextNode.val);
curNode.next = headNode;
return reverseNode(nextNode, curNode);
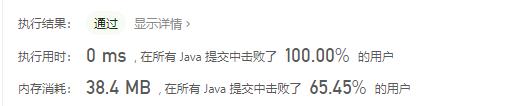
解法三:利用head结点作为基础,不断使用后续结点,充当head的父结点。
/**
* 内循环算法
*
* @param head
* @return
*/
public static ListNode reverseInnerLoop(ListNode head)
ListNode newNode = null;
while (head != null)
// 下个结点
ListNode nextNode = head.next;
// 将head的下一个,指向新结点
head.next = newNode;
// 得到新的结点,完成反指
newNode = head;
// 指针结点,实现循环
head = nextNode;
return newNode;
求完全二叉树(除底层,其他层次都满)的结点个数。
思路:笨办法,递归获得
public int countNodes(TreeNode root)
int count = 0;
if (root == null)
return count;
count++;
int index = 0;
if (root.left != null)
count += countNodes(root.left);
if (root.right != null)
count += countNodes(root.right);
return count;
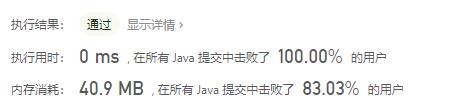
新算法:
public int countNodes(TreeNode root)
int count = 0;
if (root == null)
return count;
int ld=depth(root.left);
int rd=depth(root.right);
//根结点
if(ld==rd)
int lc=1<<ld;
System.out.println("lc:"+lc);
return lc+countNodes(root.right);
int rc=1<<rd;
System.out.println("rc:"+rc);
return rc+countNodes(root.left);
public int depth(TreeNode node)
int count=0;
while(node!=null)
count++;
node=node.left;
return count;
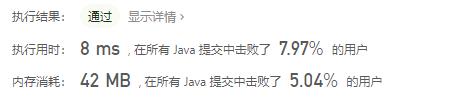
虽然使用了完全二叉树的原理,但是由于不断移位产生新的对象,耗时和内存都增加了。
贪心算法:求局部最优解。
二维空间中,x到y,给定气球坐标,全部射中需要的最少箭数。
思路:先排序,以数列首个数字从小到大排列,使用低位和高位循环匹配,不符合的需要再用一支箭头即结果+1,于是解出此题。
public static int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points)
if (points.length == 0)
return 0;
// 从大到小排序
Arrays.sort(points, new Comparator<int[]>()
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2)
return o1[0] - o2[0];
);
// 检查
int low = points[0][0];
int high = points[0][1];
int result = 1;
for (int aIndex = 1; aIndex < points.length; aIndex++)
int[] bttr = points[aIndex];
if (bttr[0] >= low && bttr[0] <= high)
// 默认第1个数据,就是低位和高位,后面逐步缩小范围,最后囊括所有数据
if (bttr[0] > low)
low = bttr[0];
if (bttr[1] < high)
high = bttr[1];
continue;
else
// 不符合,则使用新箭
low = points[aIndex][0];
high = points[aIndex][1];
result++;
return result;

又是贪心算法,求穿墙最少,需要几条垂线
public int leastBricks(List<List<Integer>> wall)
//注意,使用按key排序的map集合,将所有的值,和出现的次数保存起来
Map<Integer,Integer> map=new TreeMap();
//找出值最大的key
int maxKey=0;
for(List<Integer> sec:wall)
int key=0;
for(Integer value:sec)
key+=value;
Integer num=map.get(key);
if(key>maxKey)
maxKey=key;
if(num==null)
map.put(key,1);
else
map.put(key,num+1);
int nums=0;
int mostValue=0;
Iterator<Integer> iterator=map.keySet().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext())
Integer key=iterator.next();
Integer val=map.get(key);
if(val>=nums&&key<maxKey)
//找到数量最多的,同时小于最大key,以防穿墙
nums=val;
//它的索引
mostValue=key;
System.out.print(mostValue);
int count=0;
for(List<Integer> sec:wall)
int total=0;
boolean exist=false;
for(Integer se:sec)
total+=se;
if(total==mostValue)
//说明穿过缝隙
exist=true;
continue;
else if(total>mostValue)
//说明已经超过缝隙
continue;
if(!exist)
count++;
return count;

算法不够高明,但思路还算清晰。
二叉树,根据中序和后序,求原树。
中序:左根右
后序:左右根
前序:根左右
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode()
* TreeNode(int val) this.val = val;
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right)
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
*
*
*/
class Solution
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder)
//后序的最后一个肯定是根结点,根据此定律,做递归
if(inorder.length==0)
return null;
int iLen=inorder.length,pLen=postorder.length,val=postorder[pLen-1];
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(val);
for(int i=0;i<iLen;i++)
if(inorder[i]==val)
int[] in_left=Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,0,i);
int[] in_right=Arrays.copyOfRange(inorder,i+1,iLen);
int[] post_left=Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder,0,i);
int[] post_right=Arrays.copyOfRange(postorder,i,pLen-1);
root.left=buildTree(in_left,post_left);
root.right=buildTree(in_right,post_right);
break;
return root;

遍历:所有数据都访问到,且只访问一次。
求质数小技巧:最大质数小于等于值的平方根。
TreeMap,key自动排序的Map;TreeSet,值自动排序的List。
以上是关于LeetCode之两数相加反转链表少箭射球二叉树的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章