数据结构-栈及其实现(使用数组和链表两种方式实现)
Posted 大扑棱蛾子
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构-栈及其实现(使用数组和链表两种方式实现)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
栈(Stack)是限定仅在表尾进行插入或删除操作的线程表。因此对栈来说表尾端有其特殊含义,称为栈顶(top),相应的表头端称为栈底(bottom)。
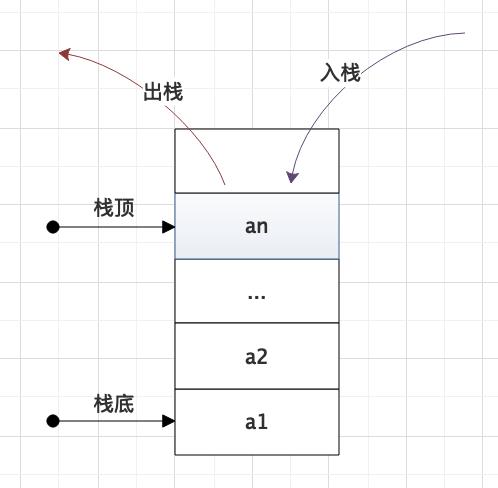
栈是一种后进先出(last in first out)的线性表,简称LIFO。
栈的抽象数据类型定义
package com.codestd.study.stack;
/**
* 栈ADT
*/
public interface Stack<E>
/**
* 查看栈顶元素,仅仅查看元素,不从栈中取出。
*/
E peek();
/**
* 向栈中添加元素。
*/
void push(E e);
/**
* 取出栈顶元素
*/
E pop();
/**
* 清空栈
*/
void clear();
/**
* 栈中元素的数量,如果栈为空,则返回0
*/
int size();
/**
* 判断栈是否为空
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
* 判断栈是否已满
*/
boolean isFull();
栈的表示和实现
前文讲过,计算机存储数据有两种方式,一种是顺序存储,一种是非顺序存储。栈对应两种存储方式有两种实现方式:一种是数组,一种是单向链表。
栈的数组实现
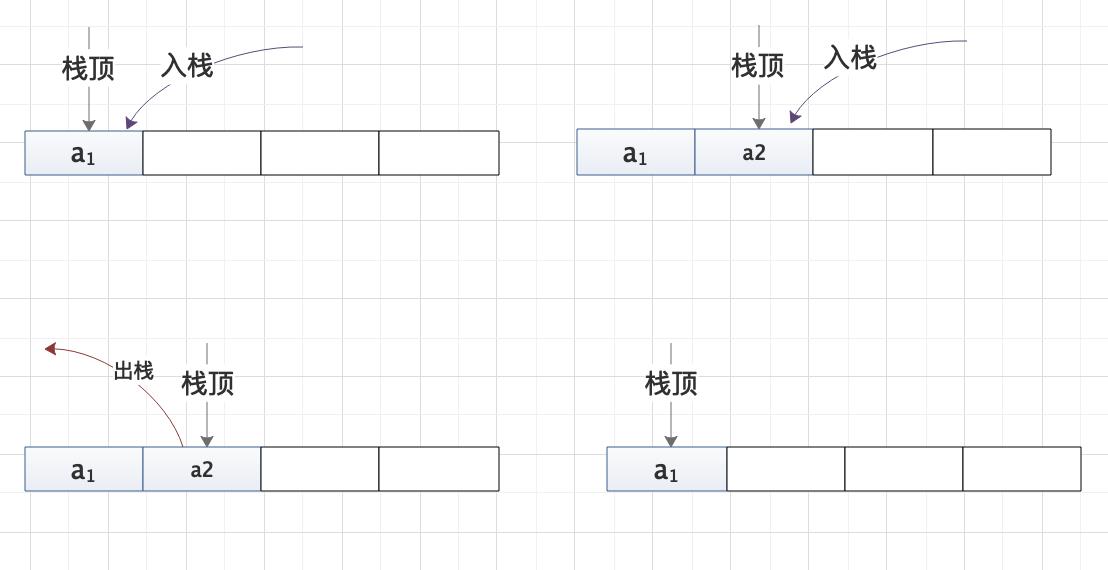
数组实现栈不需要记录栈底,只需要记录栈顶指针就可以了。入栈的时候栈顶指针后移,出栈的时候栈顶指针前移。使用数组实现是比较简单的,也是比较容易实现的。
package com.codestd.study.stack;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* 数组实现栈
*/
public class ArrayStack<E> implements Stack<E>
private final int maxSize;
private final E[] elementData;
private int top = -1;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ArrayStack(int maxSize)
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.elementData = (E[]) new Object[this.maxSize];
@Override
public E peek()
if (this.isEmpty())
throw new NoSuchElementException("栈空");
return this.elementData[this.top];
@Override
public void push(E e)
if (this.isFull())
throw new RuntimeException("栈满");
this.top++;
this.elementData[this.top] = e;
@Override
public E pop()
if (this.isEmpty())
throw new NoSuchElementException("栈空");
E el = this.elementData[this.top];
this.elementData[this.top] = null;
this.top--;
return el;
@Override
public void clear()
for (int i = 0; i < this.top + 1; i++)
this.elementData[i] = null;
this.top = -1;
@Override
public int size()
return this.top + 1;
@Override
public boolean isEmpty()
return this.size() == 0;
@Override
public boolean isFull()
return (this.top + 1) == this.maxSize;
栈的链表实现
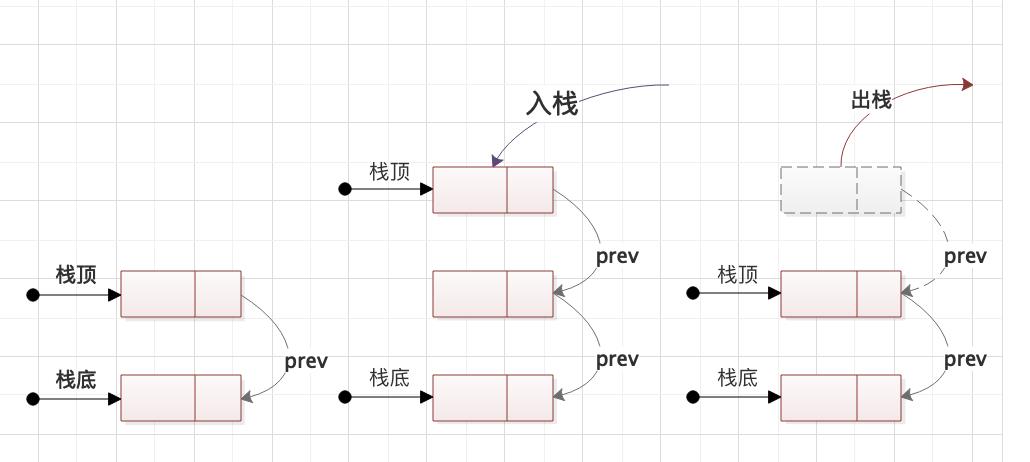
是用链表实现会相对复杂一点。这里我们使用的是单向链表。
与前面讲的单向链表不同,这里我们不再是使用next指向下一个节点,而是使用prev指向上一个节点。然后指针top始终指向最新的节点。如果取出栈顶数据,则指针指向栈顶元素的prev。
下面我们使用代码来实现。
package com.codestd.study.stack;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
/**
* 链表实现栈
*/
public class LinkedStack<E> implements Stack<E>
private Node<E> top;
private int size;
private int maxSize = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public LinkedStack()
public LinkedStack(int maxSize)
this.maxSize = maxSize;
@Override
public E peek()
if (this.isEmpty())
throw new NoSuchElementException("栈中没有元素");
return this.top.item;
@Override
public void push(E e)
if (this.isFull())
throw new RuntimeException("栈满");
if (this.top == null)
this.top = new Node<>(e);
else
Node<E> node = new Node<>(e);
node.prev = this.top;
this.top = node;
this.size++;
@Override
public E pop()
if (this.isEmpty())
throw new NoSuchElementException("栈中没有元素");
Node<E> node = this.top;
this.top = node.prev;
node.prev = null;
this.size--;
return node.item;
@Override
public void clear()
Node<E> node = this.top;
while (node != null)
Node<E> prev = node.prev;
node.prev = null;
node = prev;
this.top = null;
this.size = 0;
@Override
public int size()
return this.size;
@Override
public boolean isEmpty()
return this.size == 0;
@Override
public boolean isFull()
return this.size == this.maxSize;
private static class Node<E>
E item;
Node<E> prev;
public Node(E item)
this.item = item;
以上是关于数据结构-栈及其实现(使用数组和链表两种方式实现)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章