当InheritableThreadLocal遇到线程池:主线程本地变量修改后,子线程无法读取到新值
Posted OkidoGreen
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了当InheritableThreadLocal遇到线程池:主线程本地变量修改后,子线程无法读取到新值相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
InheritableThreadLocal可以在子线程创建的时候,将父线程的本地变量拷贝到子线程中。
那么问题就来了,是只有在创建的时候才拷贝,只拷贝一次,然后就放到线程中的inheritableThreadLocals属性缓存起来。由于使用了线程池,该线程可能会存活很久甚至一直存活,那么inheritableThreadLocals属性将不会看到父线程的本地变量的变化
public class InheritableThreadLocalTest1
public static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
public static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
System.out.println("主线程开启");
threadLocal.set(1);
executorService.submit(() ->
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
threadLocal.set(2);
executorService.submit(() ->
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
);
运行结果:
主线程开启
子线程读取本地变量:1
子线程读取本地变量:1public class InheritableThreadLocalTest1
public static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
public static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
System.out.println("主线程开启");
threadLocal.set(1);
executorService.submit(() ->
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.remove();
);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
threadLocal.set(2);
executorService.submit(() ->
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.set(3);
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.remove();
);
运行结果:
主线程开启
子线程读取本地变量:1
子线程读取本地变量:null
子线程读取本地变量:3
可以看到,由于两次执行复用了同一个线程,所以即使父线程的本地变量发生了改变,子线程的本地变量依旧是首次创建线程时赋的值。
很多时候我们可能需要在提交任务到线程池时,线程池中的线程可以实时的读取父线程的本地变量值到子线程中,当然可以当作参数传递如子线程,但是代码不够优雅,不够美观。此时可以使用alibaba的开源项目transmittable-thread-local
InheritableThreadLocal是再new Thread对象的时候复制父线程的对象到子线程的。
new Thread中会调用init方法:
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,
boolean inheritThreadLocals)
if (name == null)
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
this.name = name;
Thread parent = currentThread();
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (g == null)
/* Determine if it's an applet or not */
/* If there is a security manager, ask the security manager
what to do. */
if (security != null)
g = security.getThreadGroup();
/* If the security doesn't have a strong opinion of the matter
use the parent thread group. */
if (g == null)
g = parent.getThreadGroup();
/* checkAccess regardless of whether or not threadgroup is
explicitly passed in. */
g.checkAccess();
/*
* Do we have the required permissions?
*/
if (security != null)
if (isCCLOverridden(getClass()))
security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);
g.addUnstarted();
this.group = g;
this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();
this.priority = parent.getPriority();
if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass()))
this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader();
else
this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader;
this.inheritedAccessControlContext =
acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext();
this.target = target;
setPriority(priority);
if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
//关键代码:复制父线程的inheritableThreadLocals值到当前线程
this.inheritableThreadLocals =
ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
/* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */
this.stackSize = stackSize;
/* Set thread ID */
tid = nextThreadID();
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap)
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap)
Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;
int len = parentTable.length;
setThreshold(len);
table = new Entry[len];
//循环取父线程的值到当前线程
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++)
Entry e = parentTable[j];
if (e != null)
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ThreadLocal<Object> key = (ThreadLocal<Object>) e.get();
if (key != null)
Object value = key.childValue(e.value);
Entry c = new Entry(key, value);
int h = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
while (table[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
table[h] = c;
size++;
注意: 值传递
就像方法传参都是值传递(如果是对象,则传递的是引用的拷贝)一样,InheritableThreadLocal父子线程传递也是值传递!!
public class InheritableThreadLocalTest1
public static ThreadLocal<Stu> threadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
public static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
System.out.println("主线程开启");
threadLocal.set(new Stu("aaa",1));
executorService.submit(() ->
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.get().setAge(55);
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("主线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.get().setAge(99);
executorService.submit(() ->
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
);
输出结果:
主线程开启
子线程读取本地变量:Stu(name=aaa, age=1)
子线程读取本地变量:Stu(name=aaa, age=55)
主线程读取本地变量:Stu(name=aaa, age=55)
子线程读取本地变量:Stu(name=aaa, age=99)为什么是值传递,还要从源码分析,源码中未进行拷贝,直接返回父线程对象的引用。
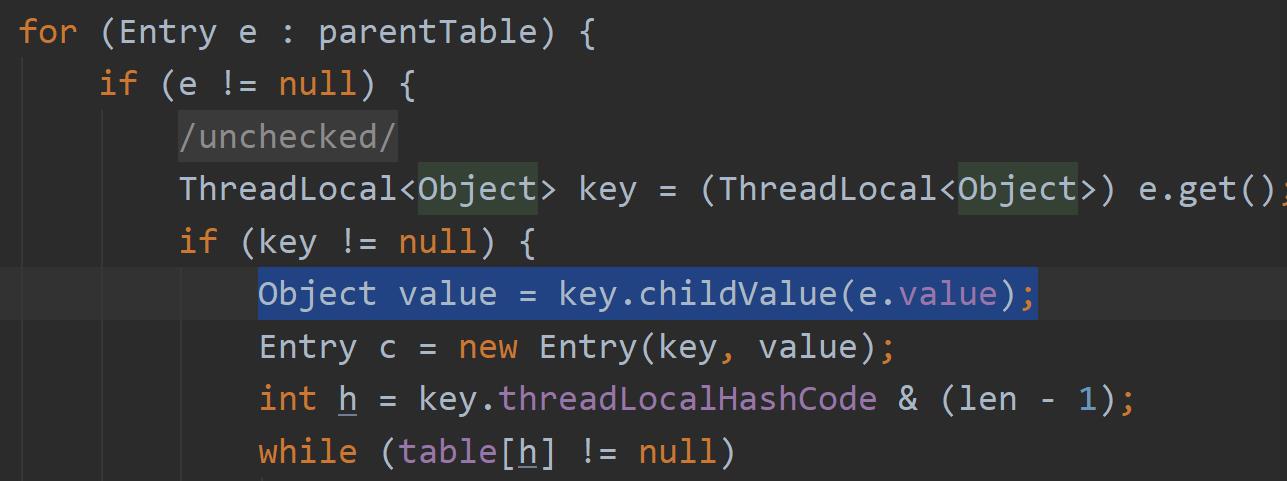
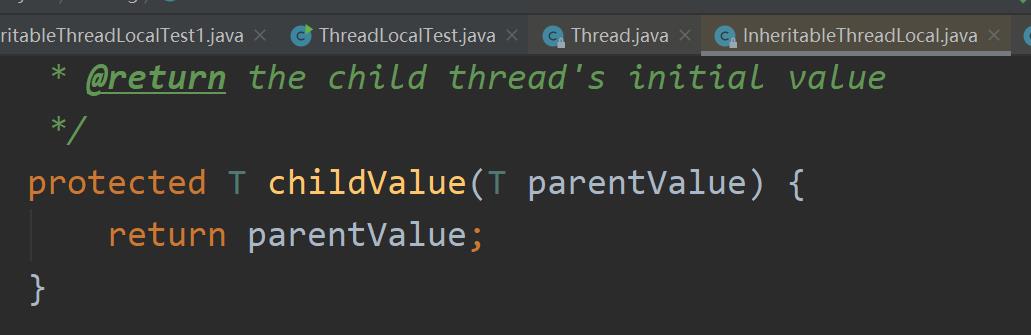
所以,务必关心传递对象的线程安全问题!!
实现线程本地变量的拷贝
上面一节讲到,InheritableThreadLocal是复制的对象引用,所以主子线程其实都引用的同一个对象,存在线程安全的问题。那么如何实现对象值的复制呢?
很简单,只需要重写java.lang.InheritableThreadLocal#childValue方法即可.
这里自定义一个MyInheritableThreadLocal类,实现对象的拷贝。
我这里使用的序列化反序列化的方式,当然也可以用其他方式。
public class MyInheritableThreadLocal<T> extends InheritableThreadLocal<T>
protected T childValue(T parentValue)
String s = JSONObject.toJSONString(parentValue);
return (T)JSONObject.parseObject(s,parentValue.getClass());
将上面测试类的InheritableThreadLocal改为我自己定义的MyInheritableThreadLocal类
public class InheritableThreadLocalTest1
public static ThreadLocal<Stu> threadLocal = new MyInheritableThreadLocal<>();
public static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException
System.out.println("主线程开启");
threadLocal.set(new Stu("aaa",1));
executorService.submit(() ->
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.get().setAge(55);
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
);
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("主线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
threadLocal.get().setAge(99);
System.out.println("主线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
executorService.submit(() ->
System.out.println("子线程读取本地变量:" + threadLocal.get());
);
运行结果:
主线程开启
子线程读取本地变量:Stu(name=aaa, age=1)
子线程读取本地变量:Stu(name=aaa, age=55)
主线程读取本地变量:Stu(name=aaa, age=1)
主线程读取本地变量:Stu(name=aaa, age=99)
子线程读取本地变量:Stu(name=aaa, age=55)这样,主子线程的对象才算真正的复制过去,而不是仅仅复制了一个引用。如此就不存在线程安全的问题了
以上是关于当InheritableThreadLocal遇到线程池:主线程本地变量修改后,子线程无法读取到新值的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章