Android 实现FlowLayout流式布局(类似热门标签)
Posted 峰子_it
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android 实现FlowLayout流式布局(类似热门标签)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
今天跟大家分享一下FlowLayout,最近项目中有遇到热门标签这个样的布局(文章末尾可下载源码),如下图:
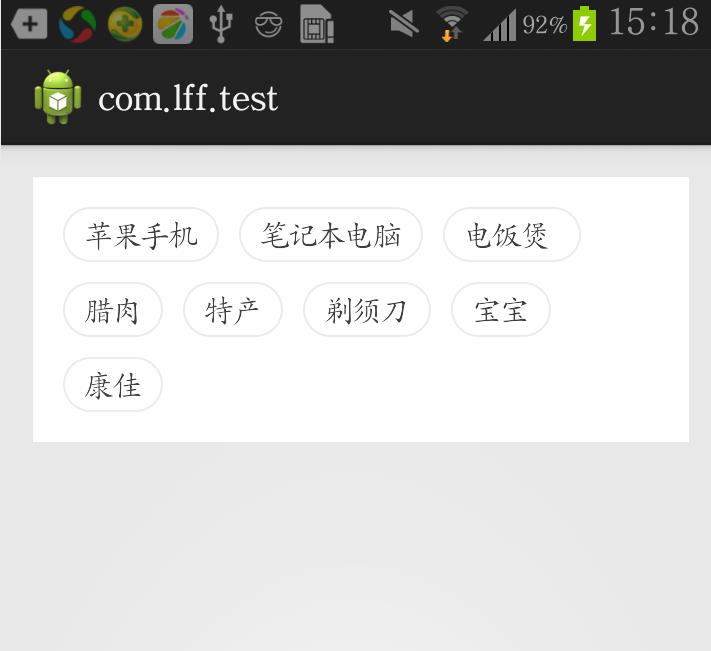
一,创建FlowLayout并继承ViewGroup
FlowLayout 类主要实现onMeasure,onLayout和generateLayoutParams方法,具体如下看代码注释;
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle)
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs)
this(context, attrs, 0);
public FlowLayout(Context context)
this(context, null);
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// 如果是warp_content情况下,记录宽和高
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
// 记录每一行的宽度与高度
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
// 得到内部元素的个数
int cCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++)
// 通过索引拿到每一个子view
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 测量子View的宽和高,系统提供的measureChild
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 得到LayoutParams
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
// 子View占据的宽度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin
+ lp.rightMargin;
// 子View占据的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin
+ lp.bottomMargin;
// 换行 判断 当前的宽度大于 开辟新行
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight())
// 对比得到最大的宽度
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
// 重置lineWidth
lineWidth = childWidth;
// 记录行高
height += lineHeight;
lineHeight = childHeight;
else
// 未换行
// 叠加行宽
lineWidth += childWidth;
// 得到当前行最大的高度
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
// 特殊情况,最后一个控件
if (i == cCount - 1)
width = Math.max(lineWidth, width);
height += lineHeight;
setMeasuredDimension(
modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeWidth : width + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight(),
modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeHeight : height + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom()//
);
/**
* 存储所有的View
*/
private List<List<View>> mAllViews = new ArrayList<List<View>>();
/**
* 每一行的高度
*/
private List<Integer> mLineHeight = new ArrayList<Integer>();
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b)
mAllViews.clear();
mLineHeight.clear();
// 当前ViewGroup的宽度
int width = getWidth();
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
// 存放每一行的子view
List<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<View>();
int cCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++)
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 如果需要换行
if (childWidth + lineWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > width - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight())
// 记录LineHeight
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
// 记录当前行的Views
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
// 重置我们的行宽和行高
lineWidth = 0;
lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
// 重置我们的View集合
lineViews = new ArrayList<View>();
lineWidth += childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin
+ lp.bottomMargin);
lineViews.add(child);
// for end
// 处理最后一行
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
// 设置子View的位置
int left = getPaddingLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
// 行数
int lineNum = mAllViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lineNum; i++)
// 当前行的所有的View
lineViews = mAllViews.get(i);
lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++)
View child = lineViews.get(j);
// 判断child的状态
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE)
continue;
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
int lc = left + lp.leftMargin;
int tc = top + lp.topMargin;
int rc = lc + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int bc = tc + child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 为子View进行布局
child.layout(lc, tc, rc, bc);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin
+ lp.rightMargin;
left = getPaddingLeft();
top += lineHeight;
/**
* 与当前ViewGroup对应的LayoutParams
*/
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs)
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
二,在MainActivity调用实现
public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity
private String[] mVals = new String[] "苹果手机", "笔记本电脑", "电饭煲 ", "腊肉",
"特产", "剃须刀", "宝宝", "康佳" ;
private LayoutInflater mInflater;
private FlowLayout mFlowLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
mFlowLayout = (FlowLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_flowlayout);
initData();
public void initData()
/**
* 找到搜索标签的控件
*/
for (int i = 0; i < mVals.length; i++)
TextView tv = (TextView) mInflater.inflate(
R.layout.search_label_tv, mFlowLayout, false);
tv.setText(mVals[i]);
final String str = tv.getText().toString();
//点击事件
tv.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
);
mFlowLayout.addView(tv);//添加到父View
1,MainActivity的xml布局
注意 布局当中的com.example.com.lff.test.FlowLayout
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="com.example.com.lff.test.MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
<com.example.com.lff.test.FlowLayout
android:id="@+id/id_flowlayout"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FFFFFF"
android:padding="10dp" >
</com.example.com.lff.test.FlowLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
2,单个标签空间的布局,也就是上述Activity中的search_label_tv.xml
search_label_tv
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:textColor="#3f3e3e"
android:background="@drawable/search_label_bg"
android:textSize="14sp"
android:text="Helloworld" >
</TextView>
结束语:简单,清晰,明了。欢迎大家指正吐槽。
源码奉上!!!
点击下载源码
以上是关于Android 实现FlowLayout流式布局(类似热门标签)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Android view的测绘练习-流式布局-FlowLayout
text Android的流式布局的FlowLayout,一款针对标签的布局