LayerNorm的理解
Posted Jimyang1ssa
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LayerNorm的理解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
LayerNorm计算公式:
y
=
x
−
E
(
x
)
Var
(
x
)
+
ϵ
∗
γ
+
β
y=\\fracx-E(x)\\sqrt\\operatornameVar(x)+\\epsilon * \\gamma+\\beta
y=Var(x)+ϵx−E(x)∗γ+β
一般有两种计算LayerNorm的方式,这两种方式的区别在与进行归一化操作的维度不同,假设输入的tensor维度为NxCxHxW,则两种计算方式分别如下:
(1)计算一个batch中所有channel中所有参数的均值和方差,然后进行归一化,操作维度为CxHxW,一般常用于CV领域(不过CV领域更长用的是BN)
(2)计算一个batch中所有channel中的每一个参数的均值和方差进行归一化,操作维度为C,一般常用于NLP领域
计算LayerNorm,pytorch中有现成的计算API:
torch.nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape, eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
normalized_shape: 输入尺寸
[∗×normalized_shape[0]×normalized_shape[1]×…×normalized_shape[−1]],归一化的维度,int(最后一维)list(list里面的维度)
eps: 为保证数值稳定性(分母不能趋近或取0),给分母加上的值。默认为1e-5。
elementwise_affine: 布尔值,当设为true,给该层添加可学习的仿射变换参数。
第一种归一化方法(CV中使用的LayerNorm)
对所有channel所有像素计算;
计算一个batch中所有channel中所有参数的均值和方差,然后进行归一化,即对CxHxW维度上的元素进行归一化(如下图蓝色区域部分所示,蓝色区域部分元素使用相同的mean合var进行归一化操作)
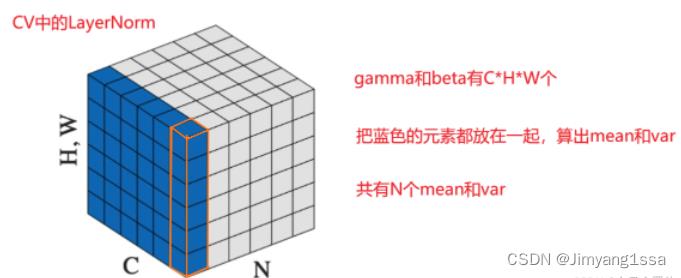
调用API计算示例如下:
N, C, H, W = 2, 3, 4, 5
input = torch.randn(N, C, H, W)
# Normalize over the last three dimensions (i.e. the channel and spatial dimensions) as shown in the image below
layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm([C, H, W])
out=layer_norm(input)
print('out shape: '.format(out.shape))
print('out data: '.format(out))
"""
out shape: torch.Size([2, 3, 4, 5])
out data: tensor([[[[-0.1054, 0.5613, 0.9684, -0.7211, -3.3157],
[ 0.1993, -0.3108, 0.1403, 0.4901, -0.4136],
[-0.8457, -1.1607, -0.7967, 0.2736, -1.2216],
[-0.3253, 1.3176, 0.1544, -0.5213, 0.7506]],
[[ 1.6987, -2.3863, 0.7939, 0.2268, 0.3961],
[-0.3590, 0.1052, -0.3119, 0.2033, -2.2351],
[ 0.5327, 1.5541, 0.8168, 1.3824, -1.7577],
[-0.1080, 0.1581, 0.3912, 0.3980, -0.5219]],
[[-0.7660, -0.3298, 0.3871, 0.0186, 1.0544],
[-0.1583, 0.0251, -1.4124, -0.0570, 1.1680],
[ 1.3687, -0.1523, 1.2398, -0.1628, 0.8833],
[ 1.5717, -1.2190, 0.5367, 0.9975, -1.0882]]],
[[[ 1.0945, 0.1024, -1.8453, 0.1361, 1.6499],
[ 0.2284, 0.1938, -0.3570, 1.7049, -0.7654],
[-0.9878, -0.6431, -0.3868, 1.5572, 0.4809],
[ 0.7264, -0.1426, -1.6283, -0.1583, -1.1346]],
[[ 0.0462, -1.4155, 0.6029, -0.1333, 0.2013],
[-0.2044, -1.0898, 1.5928, 0.0257, 0.2310],
[ 1.0854, -0.2363, -0.3721, -1.2205, -0.6438],
...
[ 0.9354, 0.6988, -0.2594, 0.0404, -1.9282],
[ 1.0362, -0.4182, -2.1887, 0.4830, 0.5986],
[ 0.0198, -0.7105, -1.1114, 0.7437, 0.7484]]]],
grad_fn=<AddcmulBackward>)
"""
对应的,手动计算LayerNorm,在CHW维度上进行归一化操作如下:
ln_mean=input.reshape([batch_size,-1]).mean(dim=1,keepdim=True).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(3) #计算后维度N*1*1*1
ln_std=input.reshape([batch_size,-1]).std(dim=1,keepdim=True,unbiased=False).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(3) #计算后维度N*1*1*1
ln_y=(input-ln_mean)/(ln_std+1e-5)
print('out shape: '.format(ln_y.shape))
print('out data: '.format(ln_y))
"""
out shape: torch.Size([2, 3, 4, 5])
out data: tensor([[[[-0.1054, 0.5613, 0.9684, -0.7211, -3.3157],
[ 0.1993, -0.3108, 0.1403, 0.4901, -0.4136],
[-0.8457, -1.1607, -0.7967, 0.2736, -1.2216],
[-0.3253, 1.3176, 0.1544, -0.5213, 0.7506]],
[[ 1.6987, -2.3863, 0.7939, 0.2268, 0.3961],
[-0.3590, 0.1052, -0.3119, 0.2033, -2.2351],
[ 0.5327, 1.5541, 0.8167, 1.3824, -1.7577],
[-0.1080, 0.1581, 0.3912, 0.3980, -0.5219]],
[[-0.7660, -0.3298, 0.3871, 0.0186, 1.0544],
[-0.1583, 0.0251, -1.4124, -0.0570, 1.1680],
[ 1.3686, -0.1523, 1.2397, -0.1628, 0.8833],
[ 1.5717, -1.2190, 0.5367, 0.9975, -1.0882]]],
[[[ 1.0945, 0.1024, -1.8453, 0.1361, 1.6499],
[ 0.2284, 0.1938, -0.3570, 1.7049, -0.7654],
[-0.9878, -0.6431, -0.3868, 1.5572, 0.4809],
[ 0.7264, -0.1426, -1.6283, -0.1583, -1.1346]],
[[ 0.0462, -1.4155, 0.6029, -0.1333, 0.2013],
[-0.2044, -1.0898, 1.5928, 0.0257, 0.2310],
[ 1.0854, -0.2363, -0.3721, -1.2205, -0.6438],
...
[[-0.8811, -0.9786, -0.8169, -0.8120, 0.8833],
[ 0.9354, 0.6988, -0.2594, 0.0404, -1.9282],
[ 1.0362, -0.4182, -2.1887, 0.4830, 0.5986],
[ 0.0198, -0.7105, -1.1114, 0.7437, 0.7484]]]])
"""
第二种归一化方法(NLP中常用的LayerNorm)
计算一个batch中所有channel中的每一个参数的均值和方差进行归一化,即只在C维度上进行归一化计算(与CV中在CxHxW维度上计算不同)
下面是调用API计算的示例:
batch_size=2
time_steps=3
embedding_dim=4
inputx=torch.randn(batch_size,time_steps,embedding_dim)#N*L*C
layer_norm=nn.LayerNorm(embedding_dim,elementwise_affine=False)
ln_y=layer_norm(inputx)
print('out shape: '.format(ln_y.shape))
print('out data: '.format(ln_y))
"""
out shape: torch.Size([2, 3, 4])
out data: tensor([[[ 0.8237, -0.3322, -1.4888, 0.9972],
[ 1.5845, -0.0058, -1.1379, -0.4408],
[-1.5878, 0.7535, 0.9477, -0.1134]],
[[-0.0703, 0.3985, -1.5393, 1.2111],
[ 1.0949, 0.0075, 0.4960, -1.5985],
[ 0.0843, -0.0753, -1.4164, 1.4074]]])
"""
下面是对应的手动计算方式:
inputx_mean=inputx.mean(dim=-1,keepdim=True) #只在维度C上计算均值,计算后维度为N*L*1
inputx_std=inputx.std(dim=-1,keepdim=True,unbiased=False) #只在维度C上计算标准差,计算后维度为N*L*1
verify_ln_y=(inputx-inputx_mean)/(inputx_std+1e-5)
print('out shape: '.format(verify_ln_y.shape))
print('out data: '.format(verify_ln_y))
"""
out shape: torch.Size([2, 3, 4])
out data: tensor([[[ 0.8237, -0.3322, -1.4888, 0.9972],
[ 1.5845, -0.0058, -1.1379, -0.4408],
[-1.5878, 0.7535, 0.9477, -0.1134]],
[[-0.0703, 0.3985, -1.5393, 1.2111],
[ 1.0949, 0.0075, 0.4960, -1.5984],
[ 0.0843, -0.0753, -1.4164, 1.4074]]])
"""
以上是关于LayerNorm的理解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章