基于YOLOV7的openpose人体姿态检测识别,FPS可以达到“较高”的效果
Posted 醉公子~
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于YOLOV7的openpose人体姿态检测识别,FPS可以达到“较高”的效果相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

前不久yolov7(原yolov4团队)在yolov6(美团)开源不到两周的时间也更新了,
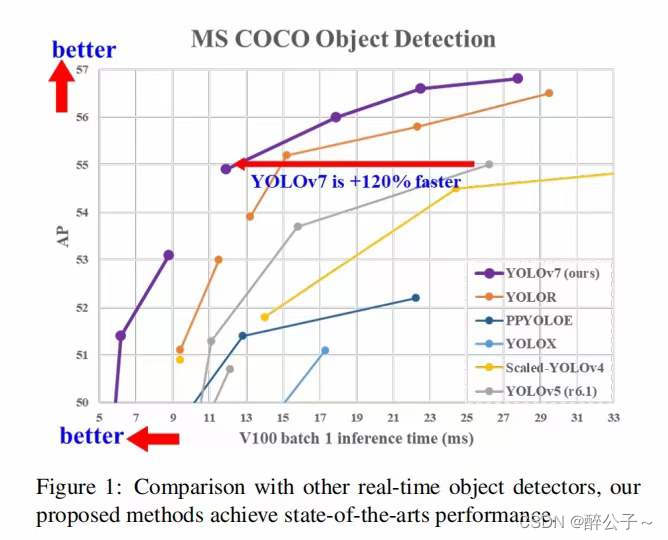
如下图所示,yolov7效果比前面的版本确实牛逼,在精度相同的情况下,速度上面提升了一大截,但是这是在比较好的设备上面;
YOLOv7 的发展方向与当前主流的实时目标检测器不同,研究团队希望它能够同时支持移动 GPU 和从边缘到云端的 GPU 设备。除了架构优化之外,该研究提出的方法还专注于训练过程的优化,将重点放在了一些优化模块和优化方法上。这可能会增加训练成本以提高目标检测的准确性,但不会增加推理成本。我想这才是运用到工业一个巨大的提升。
由于要训练自己的数据集,所以就需要人工标注数据,使用软件为labelme。该工具非常好用,基本可以满足深度学习众多任务的数据标注需求具体使用如下步骤所示:
http://labelme.csail.mit.edu/Release3.0/
安装labelme,数据标注
对于labelme标注工具,它是一个多功能的标注工具:
- 对图像进行多边形,矩形,圆形,多段线,线段,点形式的标注(可用于目标检测,图像分割,等任务)。
- 对图像进行进行 flag 形式的标注(可用于图像分类 和 清理 任务)。
- 视频标注
- 生成 VOC 格式的数据集(for semantic / instance segmentation)
- 生成 COCO 格式的数据集(for instance segmentation)
##################
## for Python 2 ##
##################
conda create --name=labelme python=2.7
source activate labelme
# conda install -c conda-forge pyside2
conda install pyqt
pip install labelme
# 如果想安装最新版本,请使用下列命令安装:
# pip install git+https://github.com/wkentaro/labelme.git
##################
## for Python 3 ##
##################
conda create --name=labelme python=3.6
source activate labelme
# conda install -c conda-forge pyside2
# conda install pyqt
pip install pyqt5 # pyqt5 can be installed via pip on python3
pip install labelme
OPENPOSE肢体检测
完整测试代码,只需要修改模型路径和测试视频路径
import torch
import cv2
import numpy as np
import time
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms
def xyxy2xywh(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x1, y1, x2, y2] to [x, y, w, h] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = (x[:, 0] + x[:, 2]) / 2 # x center
y[:, 1] = (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3]) / 2 # y center
y[:, 2] = x[:, 2] - x[:, 0] # width
y[:, 3] = x[:, 3] - x[:, 1] # height
return y
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def xywhn2xyxy(x, w=640, h=640, padw=0, padh=0):
# Convert nx4 boxes from [x, y, w, h] normalized to [x1, y1, x2, y2] where xy1=top-left, xy2=bottom-right
y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = w * (x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2) + padw # top left x
y[:, 1] = h * (x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2) + padh # top left y
y[:, 2] = w * (x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2) + padw # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = h * (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2) + padh # bottom right y
return y
def box_iou(box1, box2):
# https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/ops/boxes.py
"""
Return intersection-over-union (Jaccard index) of boxes.
Both sets of boxes are expected to be in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format.
Arguments:
box1 (Tensor[N, 4])
box2 (Tensor[M, 4])
Returns:
iou (Tensor[N, M]): the NxM matrix containing the pairwise
IoU values for every element in boxes1 and boxes2
"""
def box_area(box):
# box = 4xn
return (box[2] - box[0]) * (box[3] - box[1])
area1 = box_area(box1.T)
area2 = box_area(box2.T)
# inter(N,M) = (rb(N,M,2) - lt(N,M,2)).clamp(0).prod(2)
inter = (torch.min(box1[:, None, 2:], box2[:, 2:]) - torch.max(box1[:, None, :2], box2[:, :2])).clamp(0).prod(2)
return inter / (area1[:, None] + area2 - inter) # iou = inter / (area1 + area2 - inter)
def letterbox(img, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, stride=32):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = img.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better test mAP)
r = min(r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride) # wh padding
elif scaleFill: # stretch
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0] # width, height ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
def non_max_suppression_kpt(prediction, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.45, classes=None, agnostic=False, multi_label=False,labels=(), kpt_label=False, nc=None, nkpt=None):
"""Runs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results
Returns:
list of detections, on (n,6) tensor per image [xyxy, conf, cls]
"""
if nc is None:
nc = prediction.shape[2] - 5 if not kpt_label else prediction.shape[2] - 56 # number of classes
xc = prediction[..., 4] > conf_thres # candidates
# Settings
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) minimum and maximum box width and height
max_det = 300 # maximum number of detections per image
max_nms = 30000 # maximum number of boxes into torchvision.ops.nms()
time_limit = 10.0 # seconds to quit after
redundant = True # require redundant detections
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
t = time.time()
output = [torch.zeros((0,6), device=prediction.device)] * prediction.shape[0]
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[..., 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[..., 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
l = labels[xi]
v = torch.zeros((len(l), nc + 5), device=x.device)
v[:, :4] = l[:, 1:5] # box
v[:, 4] = 1.0 # conf
v[range(len(l)), l[:, 0].long() + 5] = 1.0 # cls
x = torch.cat((x, v), 0)
# If none remain process next image
if not x.shape[0]:
continue
# Compute conf
x[:, 5:5+nc] *= x[:, 4:5] # conf = obj_conf * cls_conf
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(x[:, :4])
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_label:
i, j = (x[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, j + 5, None], j[:, None].float()), 1)
else: # best class only
if not kpt_label:
conf, j = x[:, 5:].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float()), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
else:
kpts = x[:, 6:]
conf, j = x[:, 5:6].max(1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat((box, conf, j.float(), kpts), 1)[conf.view(-1) > conf_thres]
# Filter by class
if classes is not None:
x = x[(x[:, 5:6] == torch.tensor(classes, device=x.device)).any(1)]
# Apply finite constraint
# if not torch.isfinite(x).all():
# x = x[torch.isfinite(x).all(1)]
# Check shape
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
elif n > max_nms: # excess boxes
x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
boxes, scores = x[:, :4] + c, x[:, 4] # boxes (offset by class), scores
i = torchvision.ops.nms(boxes, scores, iou_thres) # NMS
if i.shape[0] > max_det: # limit detections
i = i[:max_det]
if merge and (1 < n < 3E3): # Merge NMS (boxes merged using weighted mean)
# update boxes as boxes(i,4) = weights(i,n) * boxes(n,4)
iou = box_iou(boxes[i], boxes) > iou_thres # iou matrix
weights = iou * scores[None] # box weights
x[i, :4] = torch.mm(weights, x[:, :4]).float() / weights.sum(1, keepdim=True) # merged boxes
if redundant:
i = i[iou.sum(1) > 1] # require redundancy
output[xi] = x[i]
if (time.time() - t) > time_limit:
print(f'WARNING: NMS time limit time_limits exceeded')
break # time limit exceeded
return output
def output_to_keypoint(output):
# Convert model output to target format [batch_id, class_id, x, y, w, h, conf]
targets = []
for i, o in enumerate(output):
kpts = o[:,6:]
o = o[:,:6]
for index, (*box, conf, cls) in enumerate(o.detach().cpu().numpy()):
targets.append([i, cls, *list(*xyxy2xywh(np.array(box)[None])), conf, *list(kpts.detach().cpu().numpy()[index])])
return np.array(targets)
def plot_skeleton_kpts(im, kpts, steps, orig_shape=None):
#Plot the skeleton and keypointsfor coco datatset
palette = np.array([[255, 128, 0], [255, 153, 51], [255, 178, 102<以上是关于基于YOLOV7的openpose人体姿态检测识别,FPS可以达到“较高”的效果的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章