TopK问题与堆排序
Posted .阿Q.
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了TopK问题与堆排序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
(11)✳删除堆顶数据(拿最大堆举例,即:删除后仍保持是大堆)
1、堆的实现
因为堆是一棵完全二叉树,所以使用数组结构,不会浪费空间。
所以,使用数组结构实现堆。
代码以大堆,作为插入堆、删除根节点为例子,后续不再说明:
(1)定义堆
可以看到,堆的结构定义和顺序表类似
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap
HPDataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
HP;(2)初始化堆
//初始化堆
void HeapInit(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
(3)交换父子结点
//交换父子结点数据
void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py)
HPDataType tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
(4)打印堆内数据
//打印堆内数据
void HeapPrint(HP* hp)
for (int i = 0; i < hp->size; ++i)
printf("%d ", hp->a[i]);
printf("\\n");
(5)堆是否为空
//堆为空
bool HeapEmpty(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
return hp->size == 0;
(6)取堆顶数据
//获取堆顶数据
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(hp));
return hp->a[0];
(7)销毁堆
//销毁堆
void HeapDestroy(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
free(hp->a);
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
(8)✳向上调整
插入堆如何实现呢?
注意:插入数据后,还要保证堆依旧是大堆(此处以大堆为列)
分析:

所以,需要向上调整。
- 先将元素插入到堆的末尾,即最后一个孩子之后
- 插入之后如果堆的性质遭到破坏,则将新插入节点顺着其双亲往上调整到合适位置即可

向上调整的执行逻辑:
//向上调整(大堆)
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child)
assert(a);
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
//while (parent >= 0) //这样写有Bug!
while (child > 0)
if (a[child] > a[parent])
/*HPDataType tmp = a[child];
a[child] = a[parent];
a[parent] = tmp;*/
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
else
break;
(9)✳数据插入堆(拿最大堆举例,即:插入后仍是保持大堆)
//往堆插入数据
void HeapPush(HP* hp, HPDataType x)
assert(hp);
//不够就扩容
if (hp->size == hp->capacity)
int newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;
HPDataType* tmp = realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
printf("realloc fail!\\n");
exit(-1);
hp->a = tmp;
hp->capacity = newcapacity;
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1);
对于插入堆来说,最大堆、最小堆都是向上调整
区别:
最大堆向上调整,插入后的结点数据,要不改变最大堆(ps:定义 最大堆是每个节点的数据值都大于等于其子树数据值),影响了插入节点到根节点那段路径上的结点( 产生变化!):
- 将插入结点作为child,与其父亲parent比较,如果a[child] > a[parent],就交换节点数据值,直到child是根节点,才截至!
最小堆向上调整,插入后的结点数据,要不改变最小堆(ps:定义 最小堆是每个节点的数据值都小于等于其子树数据值),影响了插入节点到根节点那段路径上的结点( 产生变化!):
- 将插入结点作为child,与其父亲parent比较,如果a[child] < a[parent],就交换节点数据值,直到child是根节点,才截至!
(10)✳向下调整
分析:
删除堆顶数据,还要依旧保持是大堆,则需要向下调整:
- 将堆顶元素与堆中最后一个元素进行交换
- 删除堆中最后一个元素
- 将堆顶元素向下调整到满足堆特性为止

向下调整过程:
注意:向下调整的循环结束条件:(大堆为例!)
- 父亲 >= 大的孩子,则停止 即:父亲比两个孩子都大
- 调整到叶子结点 (叶子特征:没有左孩子,即:左孩子下标超出数组范围,就不存在了)
//向下调整(大堆)
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
assert(a);
int child = parent * 2 + 1;//左孩子
while (child < n)
//选出大孩子
if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] > a[child])
child++;
//交换 并 迭代 parent 和 child
if (a[parent] < a[child])
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
else
break;
(11)✳删除堆顶数据(拿最大堆举例,即:删除后仍保持是大堆)
//删除堆顶数据
void HeapPop(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(&hp));
Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);//堆顶数据与末尾数据交换
hp->size--;
AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);
对于删除堆顶数据来说,最大堆、最小堆都是需要向下调整
需要注意的是,根节点,也就是堆顶结点,我们直接删除是不行的!!
需要将最后一个结点与根节点位置互换,因为我们删除尾结点(堆本质上是数组嘛~~~~~)是方便的!!!
然后再进行“ 根结点 ” 向下调整...................
区别:
最大堆删除堆顶数据,看是否此时还仍然符合最大堆的要求,若不符合,那么就需要向下调整,调成符合最大堆的形式。
考虑到完全二叉树中,任意一个父亲节点左孩子存在,而右孩子不一定存在(细品!!!),所以我们需要判断,避免造成非法访问数组元素。如果右孩子存在,即:child + 1 < n ,右孩子大于左孩子,即:a[child + 1] > a[ child ](选出大孩子)。那么就child指向右孩子。
(即:该代码段是用child指向左右孩子中较大孩子)
如果说,a[child] > a[parent],那么就交换父子结点,然后继续向下调整。
最小堆删除堆顶数据,看是否此时还仍然符合最小堆的要求,若不符合,那么就需要向下调整,调成符合最小堆的形式。
考虑到完全二叉树中,任意一个父亲节点左孩子存在,而右孩子不一定存在(细品!!!),所以我们需要判断,避免造成非法访问数组元素。如果右孩子存在,即:child + 1 < n ,右孩子小于左孩子,即:a[child + 1] < a[ child ](选出小孩子)。那么就child指向右孩子。
(即:该代码段是用child指向左右孩子中较小孩子)
如果说,a[child] < a[parent],那么就交换父子结点,然后继续向下调整。
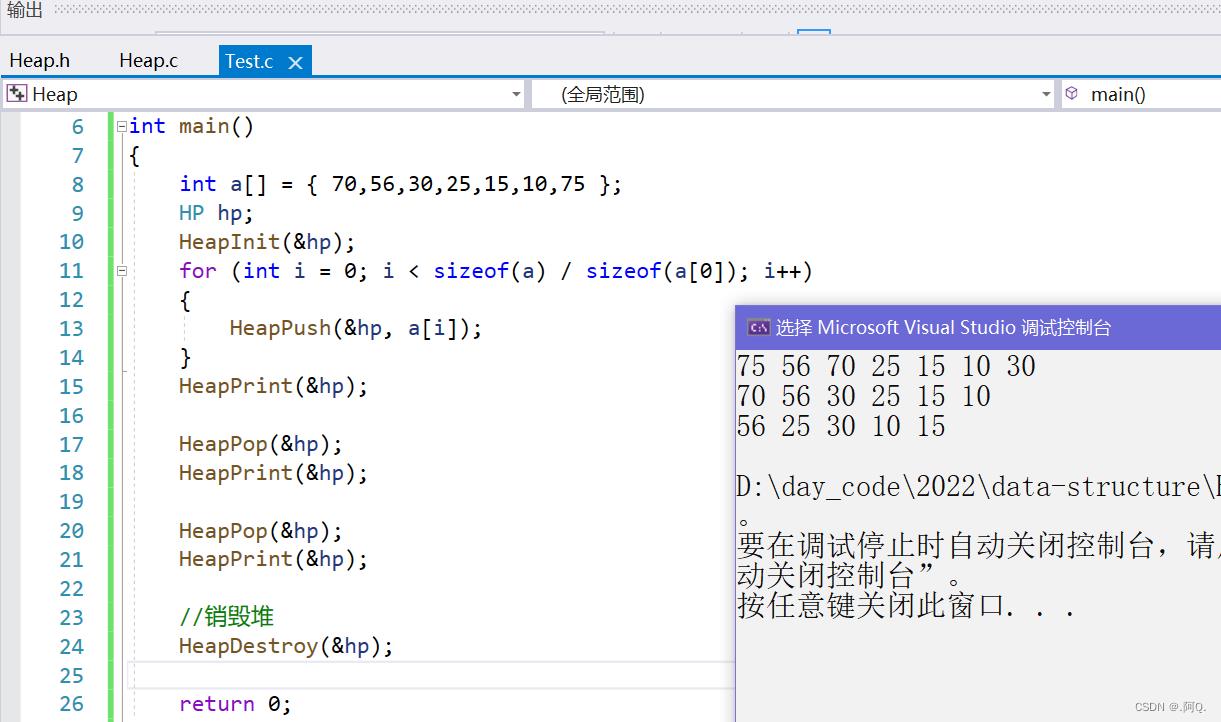
测试 【插入、删除大根堆】 的效果:
※向下、向上调整的时间复杂度log2_N
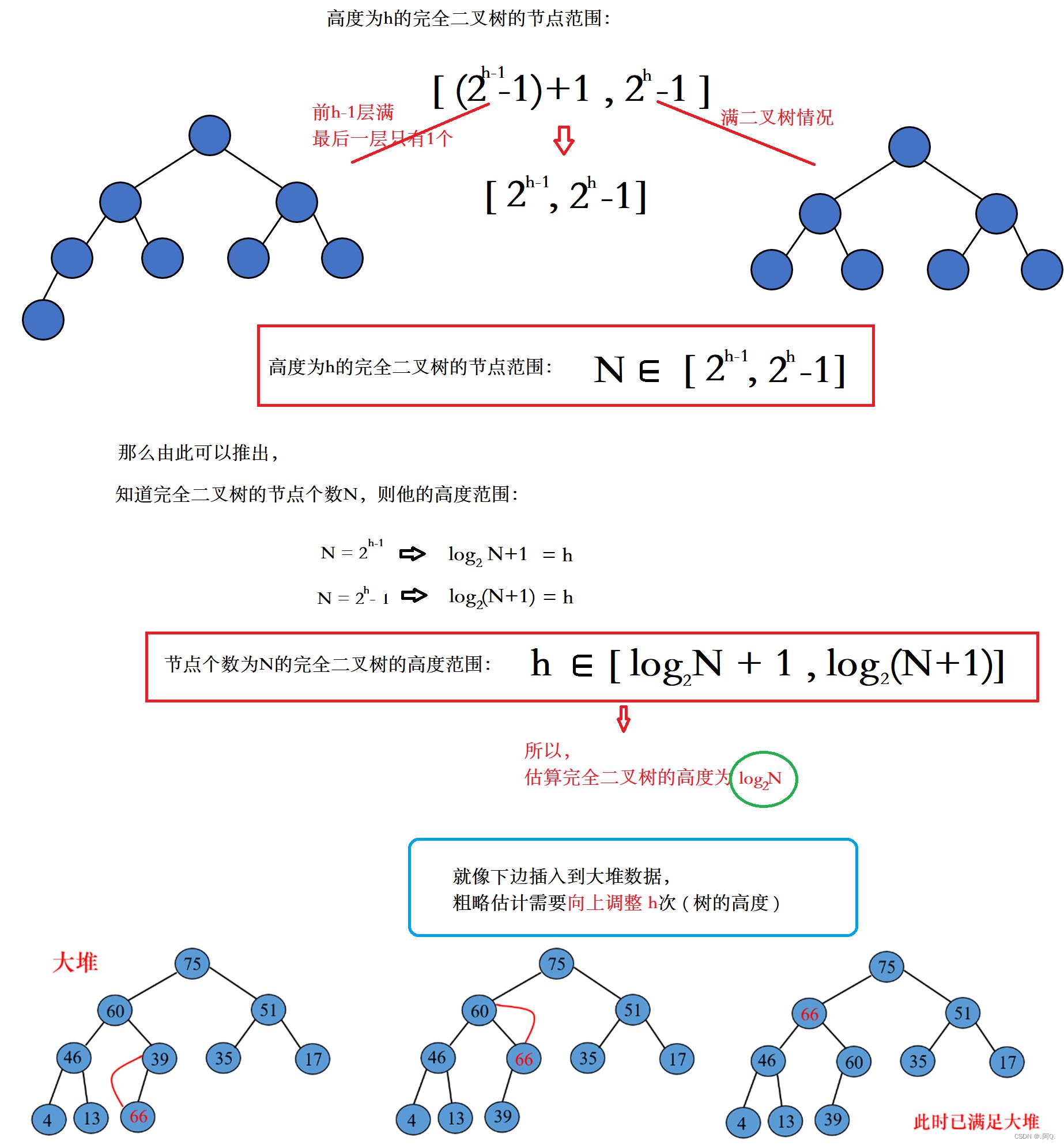
所以,向上向下调整都需要调整树的高度h次,即:时间复杂度为:O(log2_N)
堆的实现总代码:
//Heap.h文件
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//实现大堆
typedef int HPDataType;
//定义堆
typedef struct Heap
HPDataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
HP;
//初始化堆
void HeapInit(HP* hp);
//交换父子结点数据
void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py);
//打印堆内数据
void HeapPrint(HP* hp);
//堆为空
bool HeapEmpty(HP* hp);
//销毁堆
void HeapDestroy(HP* hp);
//数据插入堆
void HeapPush(HP* hp, HPDataType x);
//向上调整
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child);
//删除堆顶数据
void HeapPop(HP* hp);
//向下调整
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent);
//获取堆顶数据
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* hp);//Heap.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"Heap.h"
//初始化堆
void HeapInit(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
hp->a = NULL;
hp->size = hp->capacity = 0;
//销毁堆
void HeapDestroy(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
free(hp->a);
hp->capacity = hp->size = 0;
//交换父子结点数据
void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py)
HPDataType tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
//获取堆顶数据
HPDataType HeapTop(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(hp));
return hp->a[0];
向上调整(大堆)
//void AdjustUp(int* a, int child)
//
// assert(a);
//
// int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
// //while (parent >= 0)
// while (child > 0)
//
// if (a[child] > a[parent])
//
// /*HPDataType tmp = a[child];
// a[child] = a[parent];
// a[parent] = tmp;*/
// Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
//
// child = parent;
// parent = (child - 1) / 2;
//
// else
//
// break;
//
//
//
//向上调整(小堆)
void AdjustUp(int* a, int child)
assert(a);
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
//while (parent >= 0)
while (child > 0)
if (a[child] < a[parent])
/*HPDataType tmp = a[child];
a[child] = a[parent];
a[parent] = tmp;*/
Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
else
break;
//往堆插入数据
void HeapPush(HP* hp, HPDataType x)
assert(hp);
//不够就扩容
if (hp->size == hp->capacity)
int newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2;
HPDataType* tmp = realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
printf("realloc fail!\\n");
exit(-1);
hp->a = tmp;
hp->capacity = newcapacity;
hp->a[hp->size] = x;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1);
//判断堆是否为空
bool HeapEmpty(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
return hp->size == 0;
//堆的数据个数
int HeapSize(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
return hp->size;
//打印堆内数据
void HeapPrint(HP* hp)
for (int i = 0; i < hp->size; ++i)
printf("%d ", hp->a[i]);
printf("\\n");
向下调整(大堆)
//void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
//
// assert(a);
//
// int child = parent * 2 + 1;//左孩子
// while (child < n)
//
// //选出大孩子
// if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] > a[child])
// child++;
//
// //交换 并 迭代 parent 和 child
// if (a[parent] < a[child])
//
// Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
// parent = child;
// child = parent * 2 + 1;
//
// else
//
// break;
//
//
//
//向下调整(小堆)
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
assert(a);
int child = parent * 2 + 1;//左孩子
while (child < n)
//选出小孩子
if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] < a[child])
child++;
//交换 并 迭代 parent 和 child
if (a[parent] > a[child])
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
else
break;
//删除堆顶数据
void HeapPop(HP* hp)
assert(hp);
assert(!HeapEmpty(&hp));
Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);//堆顶数据与末尾数据交换
hp->size--;
AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);
//Test.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"Heap.h"
//在N个数中找出最大的前K个最大值 (或者最小的前K个最小值)
int main()
int a[] = 70,56,30,25,15,10,75 ;
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); i++)
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapPop(&hp);
HeapPrint(&hp);
HeapPop(&hp);
HeapPrint(&hp);
//销毁堆
HeapDestroy(&hp);
return 0;
2、建堆的应用
- topk问题
- 堆排序算法
(1)TopK问题
首先想想为什么要用堆实现Topk问题?在N非常大的时候,其他算法为什么不行?

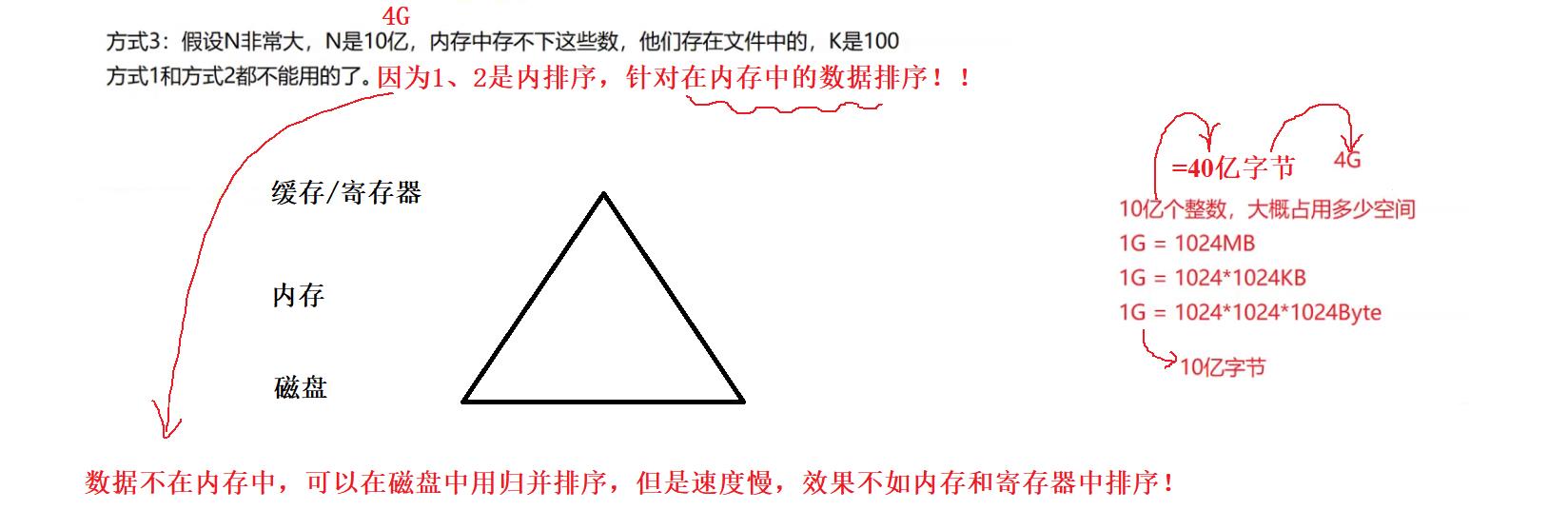
以选最大的K个数为例,建立小堆。
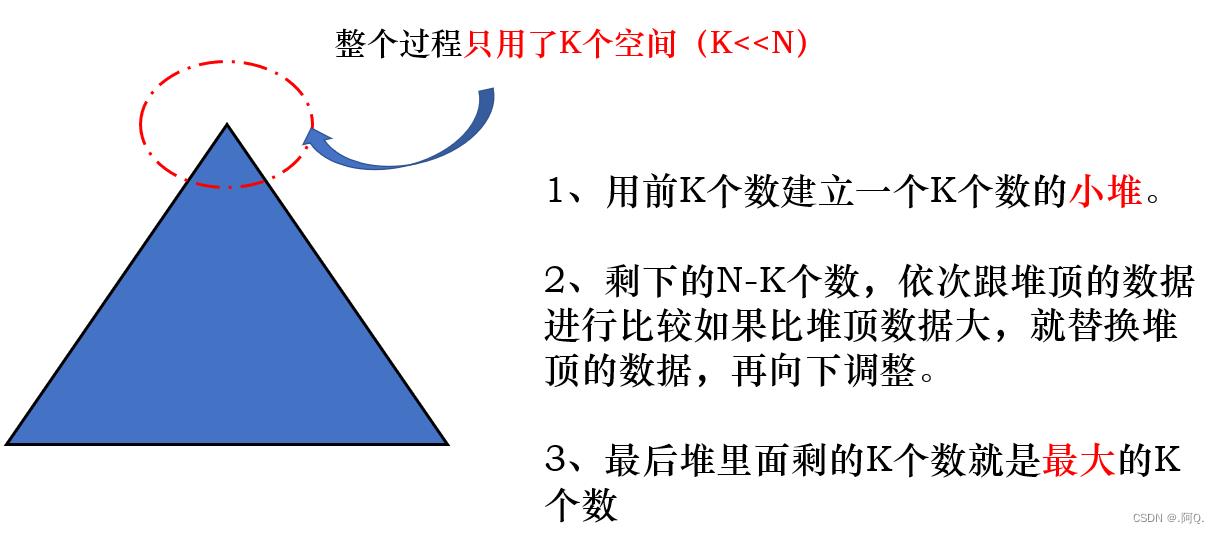
建立K个数的小堆,最终达到选出N个数中最大的K个数,在这个过程中需要注意的是:
- 选最大的K个数,是建立小堆。因为小堆的堆顶数据最小的,而用剩下的N-K个数去和最小的比较...然后大于它...就取代,就会保证每次选出的K个数都是到目前为止最大的K个数。
- 因为K<<N,所以通过该方法实现了仅仅用K个空间就可以实现N个数据中的Topk问题。空间节约了,而且没有多余去管其他的N-K个数具体的大小,针对性的解决了要求的K个数。
实现TopK算法(最小的K个数)-- 建立小堆
TopK算法(Test.c文件)
//Test.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"Heap.h"
//从N个数中,选出K个最大的数
//(只有建立 【小堆】 一种办法,大堆不行)
void PrintTopK(int* a, int n, int k)
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
// 1. 建堆--用a中的K个数创建一个小堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);//小堆的HeapPush
// 2. 将剩余N-K个元素依次与堆顶数据比较,比他大,就替换他,进堆
for (int i = k; i < n; ++i)
if (a[i] > HeapTop(&hp))
//方法1
//HeapPop(&hp);//小堆的HeapPop
//HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);
//方法2
hp.a[0] = a[i];
AdjustDown(hp.a, hp.size, 0);//==>为了保持是小堆
HeapPrint(&hp);
//HeapDestroy(&hp);
void TestTopk()
int n = 10000;
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
srand(time(0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
//随机生成数字,%100w就保证了数字小于100w
a[i] = rand() % 1000000;
//手动设置10个大于100w的数字( 即:要选出的K个最大数 )
a[5] = 1000000 + 1;
a[1231] = 1000000 + 2;
a[531] = 1000000 + 3;
a[5121] = 1000000 + 4;
a[115] = 1000000 + 5;
a[2335] = 1000000 + 6;
a[9999] = 1000000 + 7;
a[76] = 1000000 + 8;
a[423] = 1000000 + 9;
a[3144] = 1000000 + 10;
PrintTopK(a, n, 10);
int main()
TestTopk();
return 0;
//Heap.h文件 #pragma once #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<assert.h> #include<stdbool.h> //实现大堆 typedef int HPDataType; //定义堆 typedef struct Heap HPDataType* a; int size; int capacity; HP; //初始化堆 void HeapInit(HP* hp); //交换父子结点数据 void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py); //打印堆内数据 void HeapPrint(HP* hp); //堆为空 bool HeapEmpty(HP* hp); //销毁堆 void HeapDestroy(HP* hp); //数据插入堆 void HeapPush(HP* hp, HPDataType x); //向上调整 void AdjustUp(int* a, int child); //删除堆顶数据 void HeapPop(HP* hp); //向下调整 void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent); //获取堆顶数据 HPDataType HeapTop(HP* hp);
//Heap.c文件 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include"Heap.h" //初始化堆 void HeapInit(HP* hp) assert(hp); hp->a = NULL; hp->size = hp->capacity = 0; //销毁堆 void HeapDestroy(HP* hp) assert(hp); free(hp->a); hp->capacity = hp->size = 0; //交换父子结点数据 void Swap(HPDataType* px, HPDataType* py) HPDataType tmp = *px; *px = *py; *py = tmp; //获取堆顶数据 HPDataType HeapTop(HP* hp) assert(hp); assert(!HeapEmpty(hp)); return hp->a[0]; //向上调整(小堆) void AdjustUp(int* a, int child) assert(a); int parent = (child - 1) / 2; //while (parent >= 0) while (child > 0) if (a[child] < a[parent]) /*HPDataType tmp = a[child]; a[child] = a[parent]; a[parent] = tmp;*/ Swap(&a[child], &a[parent]); child = parent; parent = (child - 1) / 2; else break; //往堆插入数据 void HeapPush(HP* hp, HPDataType x) assert(hp); //不够就扩容 if (hp->size == hp->capacity) int newcapacity = hp->capacity == 0 ? 4 : hp->capacity * 2; HPDataType* tmp = realloc(hp->a, sizeof(HPDataType) * newcapacity); if (tmp == NULL) printf("realloc fail!\\n"); exit(-1); hp->a = tmp; hp->capacity = newcapacity; hp->a[hp->size] = x; hp->size++; AdjustUp(hp->a, hp->size - 1); //判断堆是否为空 bool HeapEmpty(HP* hp) assert(hp); return hp->size == 0; //堆的数据个数 int HeapSize(HP* hp) assert(hp); return hp->size; //打印堆内数据 void HeapPrint(HP* hp) for (int i = 0; i < hp->size; ++i) printf("%d ", hp->a[i]); printf("\\n"); //向下调整(小堆) void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent) assert(a); int child = parent * 2 + 1;//左孩子 while (child < n) //选出小孩子 if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] < a[child]) child++; //交换 并 迭代 parent 和 child if (a[parent] > a[child]) Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]); parent = child; child = parent * 2 + 1; else break; //删除堆顶数据 void HeapPop(HP* hp) assert(hp); assert(!HeapEmpty(&hp)); Swap(&hp->a[0], &hp->a[hp->size - 1]);//堆顶数据与末尾数据交换 hp->size--; AdjustDown(hp->a, hp->size, 0);
测试效果

(2)堆排序
堆排序 - 升序 - 空间复杂度为O(N)的写法 (不推荐)
堆排序算法(Test.c文件)
该算法是建立小堆,并且用了HeapPush等建堆操作;所以是额外开辟使用了空间,并且还得事先实现堆以及堆的操作才能做。
而堆本身就是数组,那么能否直接对数组a进行构建堆?(不用堆的任何相关操作~)
//Test.c文件
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"Heap.h"
//堆排序 - 升序 - 空间复杂度( O(N) )
//降序同理,Push、Pop小堆变大堆即可
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
HP hp;
HeapInit(&hp);
//建立一个小堆
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
HeapPush(&hp, a[i]);//小堆的HeapPush
//Pop N 次
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
a[i] = HeapTop(&hp);
HeapPop(&hp);//小堆的HeapPop
//HeapDestroy(&hp);
int main()
int a[] = 70,56,30,25,15,10,75 ;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\\n");
HeapSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\\n");
return 0;
该程序空间复杂度是O(N),那么能否优化到O(1)呢?
(即:不能用Heap避免了HeapPush开辟新空间,直接对数组a进行操作)
堆排序 - 升序 - 空间复杂度为 O(1) 的写法 (推荐!)
考虑到原来使用了HeapPush建堆,新开辟了N个空间。所以空间复杂度是O(N),而优化到O(1)即优化建堆的操作。
所以,优化建堆的操作就是对数组a直接操作,不开辟新空间。其有两种方式:
- 向上调整 (依次加入)
- 向下调整 (倒着走)

那么建堆完成后,如何实现升序呢?

所以,排升序,用大堆+向下调整建堆方式

堆排序 - (向下调整建x堆+x堆)
堆排序:
- 排升序,建大堆
- 排降序,建小堆
*注释:大小堆,在堆排序中的区别就体现在AdjustDown函数实现的是大堆还是小堆
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
//把a构建成堆(向下调整)
//注意:需要找到 [最后一个节点] 的 [父亲节点] ,从那开始,向下调整
int end = n - 1;//最后一个节点
for (int i = (end - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
//实现升序
end = n - 1;//最后一个数
for (int i = end; i > 0; i--)
Swap(&a[i], &a[0]);
AdjustDown(a, i, 0);
排升序 - (向下调整建大堆+大堆)
//向下调整(大堆)
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent);
//堆排序 - 升序 -(向下调整建大堆+大堆)
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
//把a构建成堆(向下调整)
//注意:需要找到 [最后一个节点] 的 [父亲节点] ,从那开始,向下调整
int end = n - 1;//最后一个节点
for (int i = (end - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
//实现升序
end = n - 1;//最后一个数
for (int i = end; i > 0; i--)
Swap(&a[i], &a[0]);
AdjustDown(a, i, 0);
//向下调整(大堆)
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
assert(a);
int child = parent * 2 + 1;//左孩子
while (child < n)
//选出大孩子
if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] > a[child])
child++;
//交换 并 迭代 parent 和 child
if (a[parent] < a[child])
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
else
break;
整体代码
//堆排序 - 升序 -(向下调整建大堆+大堆)
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
//建堆操作:
//方法1:
//把a构建成堆(向上调整)
/*for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
AdjustUp(a, i);
*/
//方法2:
//把a构建成堆(向下调整)
//注意:需要找到 [最后一个节点] 的 [父亲节点] ,从那开始,向下调整
int end = n - 1;//最后一个节点
for (int i = (end - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
//实现升序
end = n - 1;//最后一个数
for (int i = end; i > 0; i--)
Swap(&a[i], &a[0]);
AdjustDown(a, i, 0);
int main()
int a[] = 70,56,30,25,15,10,75,33,50,69 ;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\\n");
HeapSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\\n");
return 0;

同理,堆排序 - 排降序是建立小堆
排降序 - (向下调整建小堆+小堆)
//向下调整(小堆)
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent);
//堆排序 - 降序
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
//把a构建成堆(向下调整)
//注意:需要找到 [最后一个节点] 的 [父亲节点] ,从那开始,向下调整
int end = n - 1;//最后一个节点
for (int i = (end - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
//实现降序
end = n - 1;//最后一个数
for (int i = end; i > 0; i--)
Swap(&a[i], &a[0]);
AdjustDown(a, i, 0);
//向下调整(小堆)
void AdjustDown(int* a, int n, int parent)
assert(a);
int child = parent * 2 + 1;//左孩子
while (child < n)
//选出小孩子
if (child + 1 < n && a[child + 1] < a[child])
child++;
//交换 并 迭代 parent 和 child
if (a[parent] > a[child])
Swap(&a[parent], &a[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
else
break;
整体代码:
//堆排序 - 降序
void HeapSort(int* a, int n)
//建堆操作:
//方法1:
//把a构建成堆(向上调整)
/*for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
AdjustUp(a, i);
*/
//方法2:
//把a构建成堆(向下调整)
//注意:需要找到 [最后一个节点] 的 [父亲节点] ,从那开始,向下调整
int end = n - 1;//最后一个节点
for (int i = (end - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
AdjustDown(a, n, i);
//实现降序
end = n - 1;//最后一个数
for (int i = end; i > 0; i--)
Swap(&a[i], &a[0]);
AdjustDown(a, i, 0);
int main()
int a[] = 70,56,30,25,15,10,75,33,50,69 ;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\\n");
HeapSort(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); ++i)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("\\n");
return 0;

建堆的时间复杂度O(N)证明

以上是关于TopK问题与堆排序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章