Day699.Tomcat的Session管理机制 -深入拆解 Tomcat & Jetty
Posted 阿昌喜欢吃黄桃
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Day699.Tomcat的Session管理机制 -深入拆解 Tomcat & Jetty相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Tomcat的Session管理机制
Hi,我是阿昌,今天学习的是关于Tomcat的Session管理机制。
我们可以通过 Request 对象的 getSession 方法来获取 Session,并通过 Session 对象来读取和写入属性值。
而 Session 的管理是由 Web 容器来完成的,主要是对 Session 的创建和销毁,除此之外 Web 容器还需要将 Session 状态的变化通知给监听者。当然 Session 管理还可以交给 Spring 来做,好处是与特定的 Web 容器解耦,Spring Session 的核心原理是通过 Filter 拦截 Servlet 请求,将标准的 ServletRequest 包装一下,换成 Spring 的 Request 对象,这样当我们调用 Request 对象的 getSession 方法时,Spring 在背后为我们创建和管理 Session。
那么 Tomcat 的 Session 管理机制我们还需要了解吗?我觉得还是有必要,因为只有了解这些原理,我们才能更好的理解 Spring Session,以及 Spring Session 为什么设计成这样。
一、Session 的创建
Tomcat 中主要由每个 Context 容器内的一个 Manager 对象来管理 Session。默认实现类为 StandardManager。
下面我们通过它的接口来了解一下 StandardManager 的功能:
public interface Manager
public Context getContext();
public void setContext(Context context);
public SessionIdGenerator getSessionIdGenerator();
public void setSessionIdGenerator(SessionIdGenerator sessionIdGenerator);
public long getSessionCounter();
public void setSessionCounter(long sessionCounter);
public int getMaxActive();
public void setMaxActive(int maxActive);
public int getActiveSessions();
public long getExpiredSessions();
public void setExpiredSessions(long expiredSessions);
public int getRejectedSessions();
public int getSessionMaxAliveTime();
public void setSessionMaxAliveTime(int sessionMaxAliveTime);
public int getSessionAverageAliveTime();
public int getSessionCreateRate();
public int getSessionExpireRate();
public void add(Session session);
public void changeSessionId(Session session);
public void changeSessionId(Session session, String newId);
public Session createEmptySession();
public Session createSession(String sessionId);
public Session findSession(String id) throws IOException;
public Session[] findSessions();
public void load() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException;
public void remove(Session session);
public void remove(Session session, boolean update);
public void addPropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener)
public void removePropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener);
public void unload() throws IOException;
public void backgroundProcess();
public boolean willAttributeDistribute(String name, Object value);
不出意外我们在接口中看到了添加和删除 Session 的方法;
另外还有 load 和 unload 方法,它们的作用是分别是将 Session 持久化到存储介质和从存储介质加载 Session。
当我们调用HttpServletRequest.getSession(true)时,这个参数 true 的意思是“如果当前请求还没有 Session,就创建一个新的”。
那 Tomcat 在背后为我们做了些什么呢?
HttpServletRequest 是一个接口,Tomcat 实现了这个接口,具体实现类是:org.apache.catalina.connector.Request。
但这并不是我们拿到的 Request,Tomcat 为了避免把一些实现细节暴露出来,还有基于安全上的考虑,定义了 Request 的包装类,叫作 RequestFacade,我们可以通过代码来理解一下:
public class Request implements HttpServletRequest
public class RequestFacade implements HttpServletRequest
protected Request request = null;
public HttpSession getSession(boolean create)
return request.getSession(create);
因此我们拿到的 Request 类其实是 RequestFacade,RequestFacade 的 getSession 方法调用的是 Request 类的 getSession 方法,我们继续来看 Session 具体是如何创建的:
Context context = getContext();
if (context == null)
return null;
Manager manager = context.getManager();
if (manager == null)
return null;
session = manager.createSession(sessionId);
session.access();
从上面的代码可以看出,Request 对象中持有 Context 容器对象,而 Context 容器持有 Session 管理器 Manager,这样通过 Context 组件就能拿到 Manager 组件,最后由 Manager 组件来创建 Session。
因此最后还是到了 StandardManager,StandardManager 的父类叫 ManagerBase,这个 createSession 方法定义在 ManagerBase 中,StandardManager 直接重用这个方法。
接着我们来看 ManagerBase 的 createSession 是如何实现的:
@Override
public Session createSession(String sessionId)
//首先判断Session数量是不是到了最大值,最大Session数可以通过参数设置
if ((maxActiveSessions >= 0) &&
(getActiveSessions() >= maxActiveSessions))
rejectedSessions++;
throw new TooManyActiveSessionsException(
sm.getString("managerBase.createSession.ise"),
maxActiveSessions);
// 重用或者创建一个新的Session对象,请注意在Tomcat中就是StandardSession
// 它是HttpSession的具体实现类,而HttpSession是Servlet规范中定义的接口
Session session = createEmptySession();
// 初始化新Session的值
session.setNew(true);
session.setValid(true);
session.setCreationTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(getContext().getSessionTimeout() * 60);
String id = sessionId;
if (id == null)
id = generateSessionId();
session.setId(id);// 这里会将Session添加到ConcurrentHashMap中
sessionCounter++;
//将创建时间添加到LinkedList中,并且把最先添加的时间移除
//主要还是方便清理过期Session
SessionTiming timing = new SessionTiming(session.getCreationTime(), 0);
synchronized (sessionCreationTiming)
sessionCreationTiming.add(timing);
sessionCreationTiming.poll();
return session
到此我们明白了 Session 是如何创建出来的,创建出来后 Session 会被保存到一个 ConcurrentHashMap 中:
protected Map<String, Session> sessions = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
请注意 Session 的具体实现类是 StandardSession,StandardSession 同时实现了javax.servlet.http.HttpSession和org.apache.catalina.Session接口,并且对程序员暴露的是 StandardSessionFacade 外观类,保证了 StandardSession 的安全,避免了程序员调用其内部方法进行不当操作。
StandardSession 的核心成员变量如下:
public class StandardSession implements HttpSession, Session, Serializable
protected ConcurrentMap<String, Object> attributes = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
protected long creationTime = 0L;
protected transient volatile boolean expiring = false;
protected transient StandardSessionFacade facade = null;
protected String id = null;
protected volatile long lastAccessedTime = creationTime;
protected transient ArrayList<SessionListener> listeners = new ArrayList<>();
protected transient Manager manager = null;
protected volatile int maxInactiveInterval = -1;
protected volatile boolean isNew = false;
protected volatile boolean isValid = false;
protected transient Map<String, Object> notes = new Hashtable<>();
protected transient Principal principal = null;
二、Session 的清理
看看 Tomcat 是如何清理过期的 Session。在 Tomcat热加载和热部署的文章里,容器组件会开启一个 ContainerBackgroundProcessor 后台线程,调用自己以及子容器的 backgroundProcess 进行一些后台逻辑的处理,和 Lifecycle 一样,这个动作也是具有传递性的,也就是说子容器还会把这个动作传递给自己的子容器。
你可以参考下图来理解这个过程。
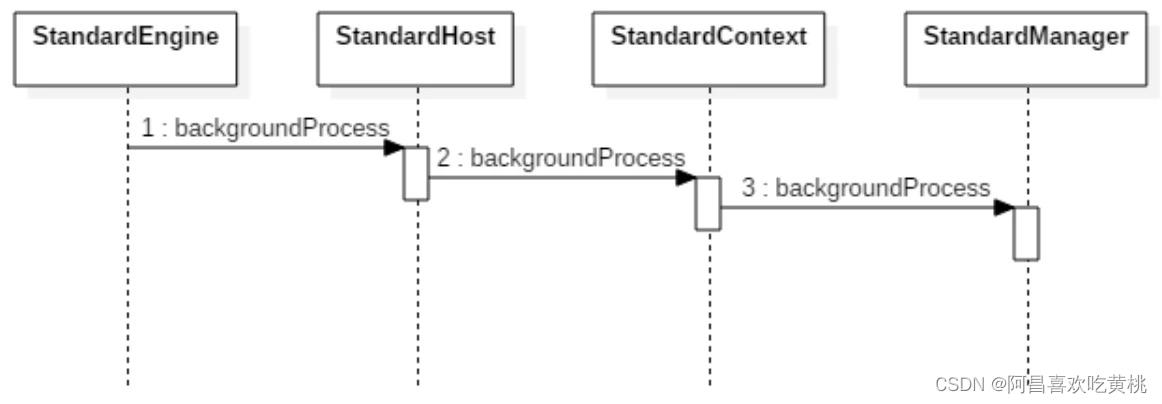
其中父容器会遍历所有的子容器并调用其 backgroundProcess 方法,而 StandardContext 重写了该方法,它会调用 StandardManager 的 backgroundProcess 进而完成 Session 的清理工作,下面是 StandardManager 的 backgroundProcess 方法的代码:
public void backgroundProcess()
// processExpiresFrequency 默认值为6,而backgroundProcess默认每隔10s调用一次,也就是说除了任务执行的耗时,每隔 60s 执行一次
count = (count + 1) % processExpiresFrequency;
if (count == 0) // 默认每隔 60s 执行一次 Session 清理
processExpires();
/**
* 单线程处理,不存在线程安全问题
*/
public void processExpires()
// 获取所有的 Session
Session sessions[] = findSessions();
int expireHere = 0 ;
for (int i = 0; i < sessions.length; i++)
// Session 的过期是在isValid()方法里处理的
if (sessions[i]!=null && !sessions[i].isValid())
expireHere++;
backgroundProcess 由 Tomcat 后台线程调用,默认是每隔 10 秒调用一次,但是 Session 的清理动作不能太频繁,因为需要遍历 Session 列表,会耗费 CPU 资源,所以在 backgroundProcess 方法中做了取模处理,backgroundProcess 调用 6 次,才执行一次 Session 清理,也就是说 Session 清理每 60 秒执行一次。
三、Session 事件通知
按照 Servlet 规范,在 Session 的生命周期过程中,要将事件通知监听者,Servlet 规范定义了 Session 的监听器接口:
public interface HttpSessionListener extends EventListener
//Session创建时调用
public default void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se)
//Session销毁时调用
public default void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se)
注意到这两个方法的参数都是 HttpSessionEvent,所以 Tomcat 需要先创建 HttpSessionEvent 对象,然后遍历 Context 内部的 LifecycleListener,并且判断是否为 HttpSessionListener 实例,如果是的话则调用 HttpSessionListener 的 sessionCreated 方法进行事件通知。这些事情都是在 Session 的 setId 方法中完成的:
session.setId(id);
@Override
public void setId(String id, boolean notify)
//如果这个id已经存在,先从Manager中删除
if ((this.id != null) && (manager != null))
manager.remove(this);
this.id = id;
//添加新的Session
if (manager != null)
manager.add(this);
//这里面完成了HttpSessionListener事件通知
if (notify)
tellNew();
从代码我们看到 setId 方法调用了 tellNew 方法,那 tellNew 又是如何实现的呢?
public void tellNew()
// 通知org.apache.catalina.SessionListener
fireSessionEvent(Session.SESSION_CREATED_EVENT, null);
// 获取Context内部的LifecycleListener并判断是否为HttpSessionListener
Context context = manager.getContext();
Object listeners[] = context.getApplicationLifecycleListeners();
if (listeners != null && listeners.length > 0)
//创建HttpSessionEvent
HttpSessionEvent event = new HttpSessionEvent(getSession());
for (int i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++)
//判断是否是HttpSessionListener
if (!(listeners[i] instanceof HttpSessionListener))
continue;
HttpSessionListener listener = (HttpSessionListener) listeners[i];
//注意这是容器内部事件
context.fireContainerEvent("beforeSessionCreated", listener);
//触发Session Created 事件
listener.sessionCreated(event);
//注意这也是容器内部事件
context.fireContainerEvent("afterSessionCreated", listener);
上面代码的逻辑是,先通过 StandardContext 将 HttpSessionListener 类型的 Listener 取出,然后依次调用它们的 sessionCreated 方法。
五、总结
今天从 Request 谈到了 Session 的创建、销毁和事件通知,里面涉及不少相关的类
下面我画了一张图帮你理解和消化一下这些类的关系:
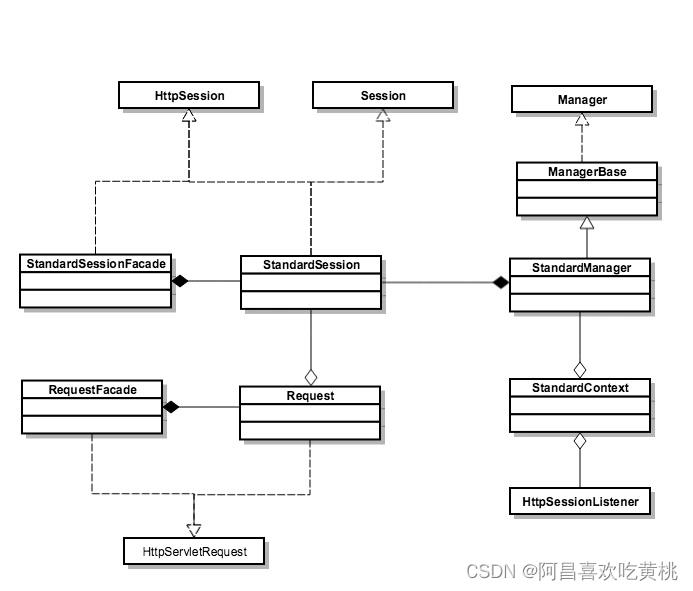
Servlet 规范中定义了 HttpServletRequest 和 HttpSession 接口,Tomcat 实现了这些接口,但具体实现细节并没有暴露给开发者,因此定义了两个包装类,RequestFacade 和 StandardSessionFacade。
Tomcat 是通过 Manager 来管理 Session 的,默认实现是 StandardManager。
StandardContext 持有 StandardManager 的实例,并存放了 HttpSessionListener 集合,Session 在创建和销毁时,会通知监听器。
TCP 连接的过期时间和 Session 的过期时间有什么区别?
tcp 是传输层协议,连接过期,需要重新三次握手。
Session,是服务端的凭证,过期,表示会话过期,需要重新连接。此时tcp可能未过期。
一个是传输层连接的断开时间,另一个是应用层用户会话的过期时间,两者没啥关系,但是超时目的其实都是为了减少服务器资源占用
以上是关于Day699.Tomcat的Session管理机制 -深入拆解 Tomcat & Jetty的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章