iOS - Runtime 详解
Posted 极客学伟
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了iOS - Runtime 详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Runtime
0. 概述
Objective-C Runtime 使得C具有了面向对象的能力,在程序运行时创建,检查,修改类,对象和它们的方法。Runtime 是 C和汇编写的,这里http://www.opensource.apple.com/source/objc4/可以下载Apple维护的开源代码,GUN也有一个开源的Runtime版本,它们都努力保持一致。Apple官方的runtime编程指南
1、Runtime 函数
Runtime 系统是由一系列的函数和数据结构组成的公共接口动态共享库,在/user/includeobjc 目录下可以看到头文件,可以用到其中一些函数通过C语言实现Objective-C中一样的功能。苹果官方文档 https://developer.apple.com/library/mac/documentation/Cocoa/Reference/ObjCRuntimeRef/index.html 里有详细的Runtime 函数文档。
2. Class 和 NSObject 基础数据结构
2.1 Class
objc/runtime.h 中objc_class 结构体的定义如下:
struct objc_class
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY; //isa指针指向Meta Class,因为Objc的类的本身也是一个Object,为了处理这个关系,runtime就创造了Meta Class,当给类发送[NSObject alloc]这样消息时,实际上是把这个消息发给了Class Object
#if !__OBJC2__
Class super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 父类
const char *name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 类名
long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 类的版本信息,默认为0
long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 类信息,供运行期使用的一些位标识
long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 该类的实例变量大小
struct objc_ivar_list *ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 该类的成员变量链表
struct objc_method_list **methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 方法定义的链表
struct objc_cache *cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 方法缓存,对象接到一个消息会根据isa指针查找消息对象,这时会在methodLists中遍历,如果cache了,常用的方法调用时就能够提高调用的效率。
struct objc_protocol_list *protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 协议链表
#endif
OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
objc_ivar_list 和 objc_method_list 的定义
//objc_ivar_list结构体存储objc_ivar数组列表
struct objc_ivar_list
int ivar_count OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#ifdef __LP64__
int space OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
/* variable length structure */
struct objc_ivar ivar_list[1] OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
//objc_method_list结构体存储着objc_method的数组列表
struct objc_method_list
struct objc_method_list *obsolete OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
int method_count OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#ifdef __LP64__
int space OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
/* variable length structure */
struct objc_method method_list[1] OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
2.2 objc_object 和 id
objc_object 是一个类的实例结构体,objc/objc.h 中 objc_object是一个类的实例结构体定义如下:
struct objc_object
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
;
typedef struct objc_object *id;向object发送消息时,Runtime 库会根据object的isa指针找到这个实例object所属于的类,然后在类的方法列表以及父类的方法列表中寻找对应的方法运行。id 是一个objc_object结构类型的指针,这个类型的对象能转换成任何一种对象。
2.3 objc_cache
objc_class 结构体中cache字段用于缓存调用过的method。cache指针指向objc_cache结构体,这个结构体定义如下:
struct objc_cache
unsigned int mask /* total = mask + 1 */ OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //指定分配缓存bucket的总数。runtime使用这个字段确定线性查找数组的索引位置
unsigned int occupied OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //实际占用缓存bucket总数
Method buckets[1] OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //指向Method数据结构指针的数组,这个数组的总数不能超过mask+1,但是指针是可能为空的,这就表示缓存bucket没有被占用,数组会随着时间增长。
;2.4 Meta Class
meta class 是一个类对象的类,当向对象发送消息时,runtime 会在这个对象所属类方法列表中查找发送消息对应的方法,但当向类发送消息时,runtime就会在这个类的meta class方法列表中查找。所有的meta class,包括Root class,SuperClass, SubClass的isa都指向Root clas的meta class,这样能够形成一个闭环。
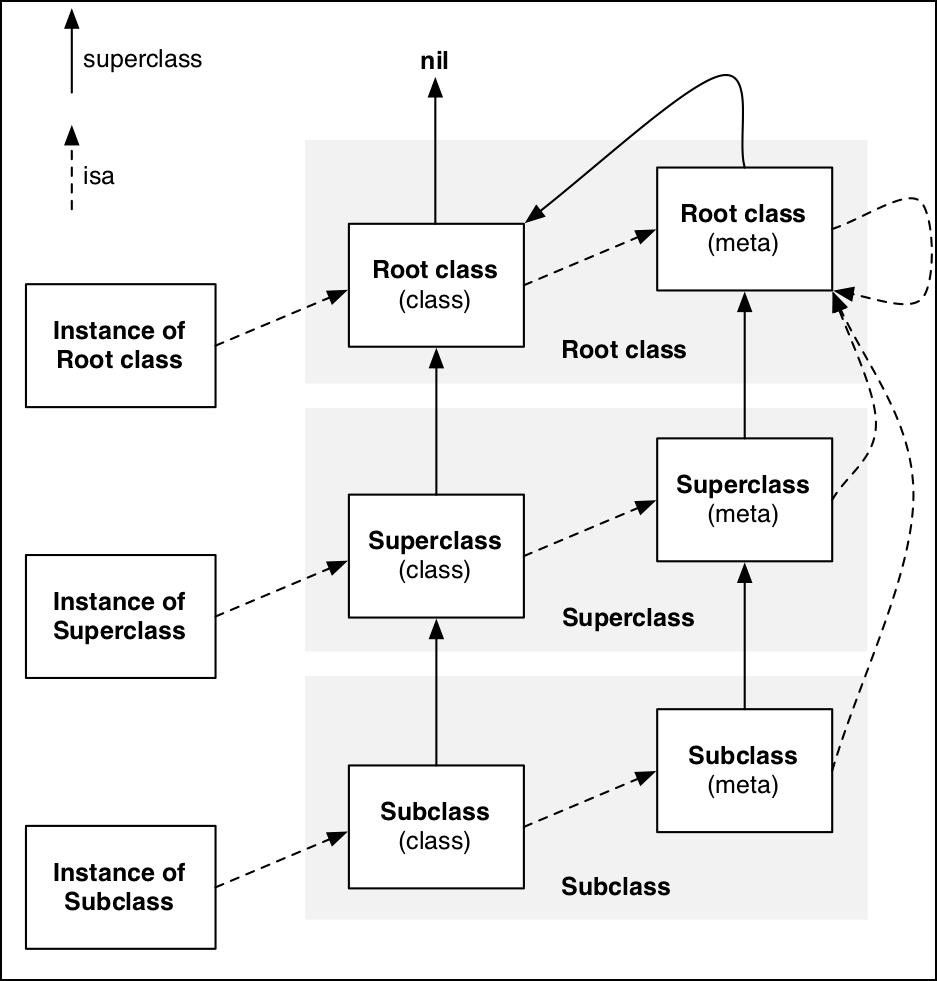
3.Runtime 类与对象操作函数
Runtime 有很多函数可以操作类和对象。类相关的是class为前缀,对象相关相关的函数是 objc 或者 object 为前缀。
3.1类相关操作函数
name
// 获取类的类名
const cahr * class_getName (Class cls);super_class 和 meta_class
// 获取类的父类
Class class_getSuperclass (Class cls);
// 判断给定的Class是否是一个meta class
BOOL class_isMetaClass (Class cls);instance_size
// 获取实例大小
size_t class_getInstanceSize (Class cls);3.2 成员变量(ivars)及属性
3.2.1 成员变量操作函数
// 获取类中指定名称实例成员变量的信息
Ivar class_getInstanceVariable (Class cls, const char *name);
// 获取类成员变量的信息
Ivar class_getClassVariable (Class cls, const char *name);
// 添加成员变量
BOOL class_addIvar (Class cls, const char *name, size_t size, uint8_t alignment, const char *types); //只能向在runtime时创建的类添加成员变量,这个方法只能在objc_allocateClassPair函数与objc_registerClassPair之间调用。另外,这个类也不能是元类。
// 获取整个成员变量列表
Ivar * class_copyIvarList (Class cls, unsigned int *outCount); // 必须使用free()来释放这个数组
测试成员变量
//成员变量
- (void)testIvar
BOOL isSuccessAddIvar = class_addIvar([NSString class], "_phone", sizeof(id), log2(sizeof(id)), "@");
if (isSuccessAddIvar)
NSLog(@"Add Ivar success");
else
NSLog(@"Add Ivar error");
unsigned int outCount;
Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList([People class], &outCount);
for (int i = 0; i < outCount; i++)
Ivar ivar = ivarList[i];
const char *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivar);
const char *type = ivar_getTypeEncoding(ivar);
ptrdiff_t offset = ivar_getOffset(ivar);
NSLog(@"ivar:%s, offset:%zd, type:%s", ivarName, offset, type);
3.2.2 属性操作函数
// 获取指定的属性
objc_property_t class_getProperty(Class cls, const char *name);
// 获取属性列表
objc_property_t * class_copyPropertyList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount);
// 为类添加属性
BOOL class_addProperty (Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount);
// 替换类的属性
void class_replaceProperty (Class cls, const char *name, const objc_property_attribute_t *attributes, unsigned int attributeCount);针对ivar来操作的,不过它只操作那些property的值,包括扩展中的property。
测试属性
- (void)testProperty
objc_property_attribute_t attribute1 = "T", "@\\"NSString\\"";
objc_property_attribute_t attribute2 = "C", "";
objc_property_attribute_t attribute3 = "N", "";
objc_property_attribute_t attribute4 = "V", "_addProperty";
objc_property_attribute_t attributesList[] = attribute1, attribute2, attribute3, attribute4;
BOOL isSuccessAddProperty = class_addProperty([People class], "addProperty", attributesList, 4);
if (isSuccessAddProperty)
NSLog(@"Add Property Success");
else
NSLog(@"Add Property Error");
unsigned int outCount;
objc_property_t * propertyList = class_copyPropertyList([People class], &outCount);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < outCount; i++)
objc_property_t property = propertyList[i];
const char *propertyName = property_getName(property);
const char *attribute = property_getAttributes(property);
NSLog(@"propertyName: %s, attribute: %s", propertyName, attribute);
unsigned int attributeCount;
objc_property_attribute_t *attributeList = property_copyAttributeList(property, &attributeCount);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < attributeCount; i++)
objc_property_attribute_t attribute = attributeList[i];
const char *name = attribute.name;
const char *value = attribute.value;
NSLog(@"attribute name: %s, value: %s",name,value);
运行结果
2018-05-01 17:14:52.957653+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] Add Property Success
2018-05-01 17:14:52.957871+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] propertyName: addProperty, attribute: T@"NSString",C,N,V_addProperty
2018-05-01 17:14:52.958034+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: T, value: @"NSString"
2018-05-01 17:14:52.958175+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: C, value:
2018-05-01 17:14:52.958309+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: N, value:
2018-05-01 17:14:52.958452+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: V, value: _addProperty
2018-05-01 17:14:52.958575+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] propertyName: name, attribute: T@"NSString",C,N,V_name
2018-05-01 17:14:52.958732+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: T, value: @"NSString"
2018-05-01 17:14:52.958850+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: C, value:
2018-05-01 17:14:52.958983+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: N, value:
2018-05-01 17:14:52.959096+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: V, value: _name
2018-05-01 17:14:52.959225+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] propertyName: age, attribute: T@"NSNumber",&,N,V_age
2018-05-01 17:14:52.959319+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: T, value: @"NSNumber"
2018-05-01 17:14:52.959420+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: &, value:
2018-05-01 17:14:52.959646+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: N, value:
2018-05-01 17:14:52.959847+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: V, value: _age
2018-05-01 17:14:52.960024+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] propertyName: sex, attribute: TQ,N,V_sex
2018-05-01 17:14:52.960186+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: T, value: Q
2018-05-01 17:14:52.960365+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: N, value:
2018-05-01 17:14:52.960584+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: V, value: _sex
2018-05-01 17:14:52.960737+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] propertyName: address, attribute: T@"NSString",C,N,V_address
2018-05-01 17:14:52.960928+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: T, value: @"NSString"
2018-05-01 17:14:52.961101+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: C, value:
2018-05-01 17:14:52.961274+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: N, value:
2018-05-01 17:14:52.961463+0800 RuntimeDemo[24515:910260] attribute name: V, value: _addressT 是固定的,放在第一个
@”NSString” 代表这个property是一个字符串对象
& 代表强引用,其中与之并列的是:’C’代表Copy,’&’代表强引用,’W’表示weak,assign为空,默认为assign。R 代表readOnly属性,readwrite时为空
N 区分的nonatomic和atomic,默认为atomic,atomic为空,’N’代表是nonatomic
V_exprice V代表变量,后面紧跟着的是成员变量名,代表这个property的成员变量名为_exprice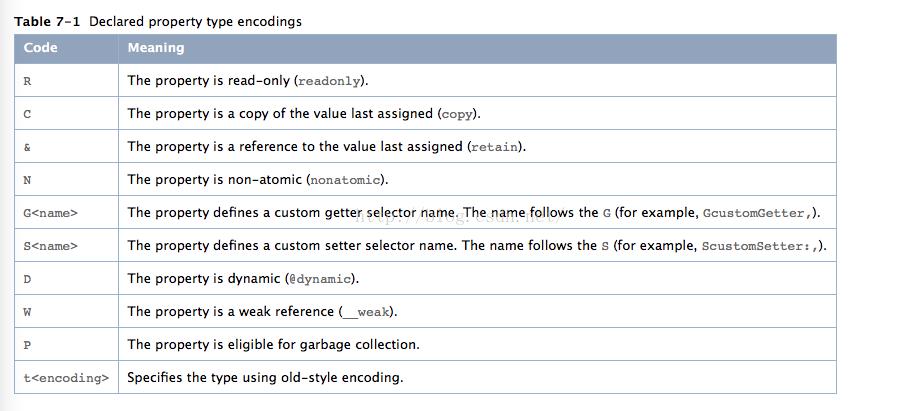
3.2.3 协议相关函数
// 添加协议
BOOL class_addProtocol ( Class cls, Protocol *protocol );
// 返回类是否实现指定的协议
BOOL class_conformsToProtocol ( Class cls, Protocol *protocol );
// 返回类实现的协议列表
Protocol * class_copyProtocolList ( Class cls, unsigned int *outCount );测试协议
@protocol PeopleProcol <NSObject>
@end
- (void)testProtocol
// 添加协议
Protocol *p = @protocol(PeopleProcol);
if (class_addProtocol([People class], p))
NSLog(@"Add Protoclol Success");
else
NSLog(@"Add protocol Fail");
if (class_conformsToProtocol([People class], p))
NSLog(@"实现了 PeopleProcol 协议");
else
NSLog(@"没有实现 PeopleProcol 协议");
unsigned int outCount;
Protocol *__unsafe_unretained *protocolList = class_copyProtocolList([People class], &outCount);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < outCount; i++)
Protocol *p = protocolList[i];
const char *protocolName = protocol_getName(p);
NSLog(@"协议名称: %s",protocolName);
运行结果
2018-05-01 17:29:12.580433+0800 RuntimeDemo[25007:940310] Add Protoclol Success
2018-05-01 17:29:12.580591+0800 RuntimeDemo[25007:940310] 实现了 PeopleProcol 协议
2018-05-01 17:29:12.580707+0800 RuntimeDemo[25007:940310] 协议名称: PeopleProcol3.2.4 版本号
- (void)testVersion
int version = class_getVersion([People class]);
NSLog(@"version %d",version);
class_setVersion([People class], 10086);
int nerVersion = class_getVersion([People class]);
NSLog(@"nerVersion %d",nerVersion);
运行结果
2018-05-01 17:38:29.593821+0800 RuntimeDemo[25266:956588] version 0
2018-05-01 17:38:29.593972+0800 RuntimeDemo[25266:956588] nerVersion 100863.3 动态创建类和对象
3.3.1. 动态创建类
// 创建一个新类和元类
Class objc_allocateClassPair (Class superclass, const char *name, size_t extraBytes);
// 销魂一个类及其相关联的类
void objc_disposeClassPair (Class cls);
// 在应用中注册由objc_allocateClassPair创建类
void objc_registerClassPair (Class cls);其中:
(1)objc_allocateClassPair函数:如果我们要创建一个根类,则superclass指定为Nil。extraBytes通常指定为0,该参数是分配给类和元类对象尾部的索引ivars的字节数。
(2)为了创建一个新类,我们需要调用objc_allocateClassPair。然后使用诸如class_addMethod,class_addIvar等函数来为新创建的类添加方法、实例变量和属性等。完成这些后,我们需要调用objc_registerClassPair函数来注册类,之后这个新类就可以在程序中使用了。
(3)实例方法和实例变量应该添加到类自身上,而类方法应该添加到类的元类上。
(4)objc_disposeClassPair只能销毁由objc_allocateClassPair创建的类,当有实例存在或者它的子类存在时,调用这个函数会抛出异常。
测试代码:
- (void)testAddClass
Class TestClass = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class], "myClass", 0);
if (class_addIvar(TestClass, "myIvar", sizeof(NSString *), sizeof(NSString *), "@"))
NSLog(@"Add Ivar Success");
class_addMethod(TestClass, @selector(method1:), (IMP)method0, "v@:");
// 注册这个类到runtime才可使用
objc_registerClassPair(TestClass);
// 生成一个实例化对象
id myObjc = [[TestClass alloc] init];
NSString *str = @"qiuxuewei";
//给刚刚添加的变量赋值
//object_setInstanceVariable(myobj, "myIvar", (void *)&str);在ARC下不允许使用
[myObjc setValue:str forKey:@"myIvar"];
[myObjc method1:10086];
- (void)method1:(int)a
void method0(id self, SEL _cmd, int a)
Ivar v = class_getInstanceVariable([self class], "myIvar");
id o = object_getIvar(self, v);
NSLog(@"%@ \\n int a is %d", o,a);
运行结果:
2018-05-01 22:30:30.159096+0800 RuntimeDemo[31292:1162987] Add Ivar Success
2018-05-01 22:30:30.159344+0800 RuntimeDemo[31292:1162987] qiuxuewei
int a is 100863.3.2. 动态创建对象
// 创建类的实例
id class_createInstance (Class cls, size_t extraBytes);
// 在指定位置创建类实例
id objc_constructInstance (Class cls, void *bytes);
// 销毁类实例
void * objc_destructInstance (id obj);
class_createInstance函数:创建实例时,会在默认的内存区域为类分配内存。extraBytes参数表示分配的额外字节数。这些额外的字节可用于存储在类定义中所定义的实例变量之外的实例变量。该函数在ARC环境下无法使用。
调用class_createInstance的效果与+alloc方法类似。不过在使用class_createInstance时,我们需要确切的知道我们要用它来做什么。
测试代码
- (void)testCreteInstance
id testInstance = class_createInstance([NSString class], sizeof(unsigned));
id str1 = [testInstance init];
NSLog(@"%@",[str1 class]);
id str2 = [[NSString alloc] initWithString: @"Test"];
NSLog(@"%@",[str2 class]);
运行结果:
2018-05-01 23:43:25.941205+0800 RuntimeDemo[32783:1223167] NSString
2018-05-01 23:43:25.941364+0800 RuntimeDemo[32783:1223167] __NSCFConstantString3.3.3. 其他类和对象相关的操作函数
类
// 获取已注册的类定义的列表
int objc_getClassList(Class *buffer, int bufferCount);
// 创建并返回一个指向所有已注册类的指针列表
Class * objc_copyClassList (unsigned int * outCount);
// 返回指定类的类定义
Class objc_lookUpClass ( const char *name );
Class objc_getClass ( const char *name );
Class objc_getRequiredClass ( const char *name );
// 返回指定类的元类
Class objc_getMetaClass ( const char *name );
对象
// 返回指定对象的一份拷贝
id object_copy ( id obj, size_t size );
// 释放指定对象占用的内存
id object_dispose ( id obj );
// 修改类实例的实例变量的值
Ivar object_setInstanceVariable ( id obj, const char *name, void *value );
// 获取对象实例变量的值
Ivar object_getInstanceVariable ( id obj, const char *name, void **outValue );
// 返回指向给定对象分配的任何额外字节的指针
void * object_getIndexedIvars ( id obj );
// 返回对象中实例变量的值
id object_getIvar ( id obj, Ivar ivar );
// 设置对象中实例变量的值
void object_setIvar ( id obj, Ivar ivar, id value );
// 返回给定对象的类名
const char * object_getClassName ( id obj );
// 返回对象的类
Class object_getClass ( id obj );
// 设置对象的类
Class object_setClass ( id obj, Class cls );
获取类的定义
// 获取已注册的类定义的列表
int objc_getClassList (Class *)
3.3.4. 应用实例
1. Json 转 Model
操作函数
- (instancetype)initWithDict:(NSDictionary *)dict
if (self = [self init])
NSMutableArray <NSString *>*keys = [NSMutableArray array];
NSMutableArray <NSString *>*attributes = [NSMutableArray array];
unsigned int outCount;
objc_property_t * propertyList = class_copyPropertyList([self class], &outCount);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < outCount; i++)
objc_property_t property = propertyList[i];
const char *name = property_getName(property);
NSString *propertyName = [NSString stringWithCString:name encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
[keys addObject:propertyName];
const char *attribute = property_getAttributes(property);
NSString *attributeName = [NSString stringWithCString:attribute encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
[attributes addObject:attributeName];
free(propertyList);
for (NSString *key in keys)
if ([dict valueForKey:key])
[self setValue:[dict valueForKey:key] forKey:key];
return self;
2. 快速归解档
遵循 NSCoding 协议
// 归档
- (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder
if (self = [super init])
unsigned int outCount;
Ivar * ivarList = class_copyIvarList([self class], &outCount);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < outCount; i++)
Ivar ivar = ivarList[i];
NSString *key = [NSString stringWithCString:ivar_getName(ivar) encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
[self setValue:[aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:key] forKey:key];
return self;
// 解档
- (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder
unsigned int outCount;
Ivar * ivarList = class_copyIvarList([self class], &outCount);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < outCount; i++)
Ivar ivar = ivarList[i];
NSString *key = [NSString stringWithCString:ivar_getName(ivar) encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
[aCoder encodeObject:[self valueForKey:key] forKey:key];
测试
- (void)testCoder
NSString *key = @"peopleKey";
People * people = [[People alloc] init];
people.name = @"邱学伟";
people.age = @18;
NSData *peopleData = [NSKeyedArchiver archivedDataWithRootObject:people];
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:peopleData forKey:key];
NSData *testData = [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] objectForKey:key];
People *testPeople = [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithData:testData];
NSLog(@"%@",testPeople.name);
3. 关联对象
// 关联对象
void objc_setAssociatedObject (id object, const void * key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy);
// 获取关联的对象
id objc_getAssociatedObject (id object, const void * key);
// 移除关联的对象
void objc_removeAssociatedObjects (id object);参数说明
id object : 被关联的对象
const void *key : 关联的key, set和get 需统一
id value : 关联的对象
objc_AssociationPolicy policy : 内存管理的策略objc_AssociationPolicy policy的enum值有:、
typedef OBJC_ENUM(uintptr_t, objc_AssociationPolicy)
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN = 0, /**< Specifies a weak reference to the associated object. */
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC = 1, /**< Specifies a strong reference to the associated object.
* The association is not made atomically. */
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC = 3, /**< Specifies that the associated object is copied.
* The association is not made atomically. */
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN = 01401, /**< Specifies a strong reference to the associated object.
* The association is made atomically. */
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY = 01403 /**< Specifies that the associated object is copied.
* The association is made atomically. */
;
应用实例
//
// People+Category.h
// RuntimeDemo
//
// Created by 邱学伟 on 2018/5/3.
// Copyright © 2018年 邱学伟. All rights reserved.
//
#import "People.h"
@interface People (Category)
/**
新增属性
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *blog;
@end
//
// People+Category.m
// RuntimeDemo
//
// Created by 邱学伟 on 2018/5/3.
// Copyright © 2018年 邱学伟. All rights reserved.
//
#import "People+Category.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation People (Category)
static const char * cPeopleBlogKey = "cPeopleBlogKey";
- (NSString *)blog
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, cPeopleBlogKey);
- (void)setBlog:(NSString *)blog
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, cPeopleBlogKey, blog, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY);
@end4. 方法与消息
4.1 SEL
SEL 又叫方法选择器, 是表示一个方法的selector的指针,其定义如下
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;方法的selector用于表示运行时方法的名字,Objective-C在编译时,会根据每一个方法的名字,参数序列,生成一个唯一的整型标示(Int类型的地址),这个标识就是SEL. 如下
+ (void)load
SEL sel = @selector(testMethod);
NSLog(@"Programmer sel = %p",sel);
- (void)testMethod
NSLog(@"testMethod");
两个类之间,不管它们是父类与子类的关系,还是之间没有这种关系,只要方法名相同,那么方法的SEL就是一样的。每一个方法都对应着一个SEL。所以在Objective-C同一个类(及类的继承体系)中,不能存在2个同名的方法,即使参数类型不同也不行。相同的方法只能对应一个SEL。这也就导致Objective-C在处理相同方法名且参数个数相同但类型不同的方法方面的能力很差.
当然,不同的类可以拥有相同的selector,这个没有问题。不同类的实例对象执行相同的selector时,会在各自的方法列表中去根据selector去寻找自己对应的IMP。
本质上,SEL只是一个指向方法的指针(准确的说,只是一个根据方法名hash化了的KEY值,能唯一代表一个方法),它的存在只是为了加快方法的查询速度。这个查找过程我们将在下面讨论。
我们可以在运行时添加新的selector,也可以在运行时获取已存在的selector,我们可以通过下面三种方法来获取SEL:
(1)sel_registerName函数
(2)Objective-C编译器提供的@selector()
(3)NSSelectorFromString()方法
4.2 IMP
IMP 是一个函数指针,指向方法实现的首地址。
id (*IMP)(id,SEL,...)这个函数使用当前CPU架构实现的标准的C调用约定。第一个参数是指向self的指针(如果是实例方法,则是类实例的内存地址;如果是类方法,则是指向元类的指针),第二个参数是方法选择器(selector),接下来是方法的实际参数列表。
前面介绍过的SEL就是为了查找方法的最终实现IMP的。由于每个方法对应唯一的SEL,因此我们可以通过SEL方便快速准确地获得它所对应的IMP,查找过程将在下面讨论。取得IMP后,我们就获得了执行这个方法代码的入口点,此时,我们就可以像调用普通的C语言函数一样来使用这个函数指针了。
通过取得IMP,我们可以跳过Runtime的消息传递机制,直接执行IMP指向的函数实现,这样省去了Runtime消息传递过程中所做的一系列查找操作,会比直接向对象发送消息高效一些。
4.3 Method
Method 用于表示类定义中的方法,定义如下:
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
struct objc_method
SEL method_name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 方法名
char *method_types OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //是个char指针,存储着方法的参数类型和返回值类型
IMP method_imp OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; // 方法实现,函数指针
该结构体中包含一个SEL和IMP,实际上相当于在SEL和IMP之间作了一个映射。有了SEL,我们便可以找到对应的IMP,从而调用方法的实现代码。
4.4 objc_method_description
objc_method_description定义了一个Objective-C方法,其定义如下:
struct objc_method_description SEL name; char *types; ;4.5 Method 相关操作函数
// 调用指定方法的实现
id method_invoke (id receiver, Method m, ...);
// 调用返回一个数据结构的方法的实现
void method_invoke_stret (id receiver, Method m, ...);
// 获取方法名
SEL method_getName (Method m);
// 获取方法的实现
IMP method_getImplementation (Method m);
// 获取描述方法参数和返回值类型的字符串
const char * method_getTypeEncoding (Method m);
// 获取方法的返回值类型的字符串
char * method_copyReturnType ( Method m );
// 获取方法的指定位置参数的类型字符串
char * method_copyArgumentType ( Method m, unsigned int index );
// 通过引用返回方法的返回值类型字符串
void method_getReturnType ( Method m, char *dst, size_t dst_len );
// 返回方法的参数的个数
unsigned int method_getNumberOfArguments ( Method m );
// 通过引用返回方法指定位置参数的类型字符串
void method_getArgumentType ( Method m, unsigned int index, char *dst, size_t dst_len );
// 返回指定方法的方法描述结构体
struct objc_method_description * method_getDescription ( Method m );
// 设置方法的实现
IMP method_setImplementation ( Method m, IMP imp );
// 交换两个方法的实现
void method_exchangeImplementations ( Method m1, Method m2 );(1)method_invoke函数,返回的是实际实现的返回值。参数receiver不能为空。这个方法的效率会比method_ge
以上是关于iOS - Runtime 详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章