springsecurity如何保存重定向地址
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了springsecurity如何保存重定向地址相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
基于SpringSecurity OAuth2实现单点登录——未认证的请求是如何重定向到登录地址的?(SpringSecurity的认证流程)1、前言
在上一篇《入门示例和流程分析》的流程分析过程中,当第一次(未认证的情况下)访问应用A(http://localhost:8082/index)时,会重定向到应用A的登录http://localhost:8082/login地址(Get请求),从浏览器这个视角我们看到的是这样的情况,那么在应用A的服务端又经历了什么呢?我们通过代码进行分析。
2、SpringSecurity过滤器链
这节分析的问题,其实就是SpringSecurity关于认证过程的逻辑。SpringSecurity实现认证逻辑,就是通过SpringSecurity 过滤器链实现的,我们先了解一下SpringSecurity过滤器链中的核心类FilterChainProxy。
2.1、FilterChainProxy
在这里插入图片描述
在SpringSecurity中,SpringSecurity 的过滤器并不是直接内嵌到Servlet Filter中的,而是通过FilterChainProxy来统一管理的,即所有的Spring Security Filter的执行,都在FilterChainProxy中进行管理的,所以我们选择从FilterChainProxy类入手进行分析。
为了实现上述描述的功能,SpringSecurity 过滤器由FilterChainProxy统一管理,然后在在内部定义了一个VirtualFilterChain内部类,用于表示SpringScurity内部的过滤器链,其中doFilter()方法用于执行过滤器链中的过滤器。如下所示:
//FilterChainProxy#VirtualFilterChain,省略了Debug相关信息
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException
if (currentPosition == size)
// Deactivate path stripping as we exit the security filter chain
this.firewalledRequest.reset();
//执行Web中的过滤器
originalChain.doFilter(request, response);
else //执行SpringSecurity过滤器链中的过滤器
currentPosition++;
//additionalFilters中定义了SpringSecurity过滤器链中的所有过滤器
Filter nextFilter = additionalFilters.get(currentPosition - 1);
nextFilter.doFilter(request, response, this);
我们通过断点,可以查看additionalFilters变量中的过滤器集合,即SpringSecurity过滤器链中所有过滤器,下面是应用A中的SpringSecurity 过滤器,如下所示:
nextFilter.doFilter
3、FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器
通过Debug执行代码,我们发现,在执行完FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器时,前端页面重定向到了应用A的登录http://localhost:8082/login地址(Get请求)。在执行过滤器FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器时,发生了什么呢?我们通过Debug方式,进行逐步的分析。
首先,我们进入FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器的doFilter()方法,在doFilter()方法中又调用了invoke()方法,而在invoke()方法中,又调用了父类AbstractSecurityInterceptor的beforeInvocation()方法,如下所示:
//FilterSecurityInterceptor.java
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException
FilterInvocation fi = new FilterInvocation(request, response, chain);
invoke(fi);
public void invoke(FilterInvocation fi) throws IOException, ServletException
if ((fi.getRequest() != null)
&& (fi.getRequest().getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
&& observeOncePerRequest)
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
else
// first time this request being called, so perform security checking
if (fi.getRequest() != null && observeOncePerRequest)
fi.getRequest().setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
//访问应用A的地址,首先会经过beforeInvocation()方法获取请求中的Token
InterceptorStatusToken token = super.beforeInvocation(fi);
try
fi.getChain().doFilter(fi.getRequest(), fi.getResponse());
finally
super.finallyInvocation(token);
super.afterInvocation(token, null);
在上述代码中,调用父类AbstractSecurityInterceptor的beforeInvocation()方法,来获取请求需要的Token值,因为第一次访问,还没有进行认证,所以会抛出认证异常(AccessDeniedException ),如下所示:
//AbstractSecurityInterceptor.java
protected InterceptorStatusToken beforeInvocation(Object object)
// …… 省略
Authentication authenticated = authenticateIfRequired();
// Attempt authorization
try
//用于判断当前请求是否有权限进行访问,如果没有权限就会抛出AccessDeniedException 异常。
this.accessDecisionManager.decide(authenticated, object, attributes);
catch (AccessDeniedException accessDeniedException)
publishEvent(new AuthorizationFailureEvent(object, attributes, authenticated,
accessDeniedException));
throw accessDeniedException;
// …… 省略
在执行上面代码时,抛出了AccessDeniedException 异常,这个异常就会被ExceptionTranslationFilter过滤器捕获,如下所示:
//ExceptionTranslationFilter.java
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
try
chain.doFilter(request, response);
logger.debug("Chain processed normally");
catch (IOException ex)
throw ex;
catch (Exception ex)
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
if (ase == null)
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
if (ase != null)
if (response.isCommitted())
throw new ServletException("Unable to handle the Spring Security Exception because the response is already committed.", ex);
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
else
if (ex instanceof ServletException)
throw (ServletException) ex;
else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException)
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
当出现AccessDeniedException 异常时,会被ExceptionTranslationFilter过滤器的doFilter()方法中第二个catch 代码块进行拦截,然后交由handleSpringSecurityException()方法进行异常的处理,具体如下:
//ExceptionTranslationFilter.java
private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException
if (exception instanceof AuthenticationException)
//省略 debug……
sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain,
(AuthenticationException) exception);
else if (exception instanceof AccessDeniedException)
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) || authenticationTrustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication))
//省略 debug……
sendStartAuthentication(
request,
response,
chain,
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
messages.getMessage(
"ExceptionTranslationFilter.insufficientAuthentication",
"Full authentication is required to access this resource")));
else
//省略 debug……
accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response,
(AccessDeniedException) exception);
在handleSpringSecurityException()方法中,根据AuthenticationException或AccessDeniedException异常类型,进行下一步执行,因为我们上一步抛出的是AccessDeniedException异常,所以会执行其中sendStartAuthentication()的方法(其实两类异常都是执行这个方法,只不过参数不一样而已)。sendStartAuthentication()方法的实现如下:
//ExceptionTranslationFilter
protected void sendStartAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
AuthenticationException reason) throws ServletException, IOException
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(null);
requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);
logger.debug("Calling Authentication entry point.");
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);
在sendStartAuthentication()方法中, 又调用了authenticationEntryPoint的commence()方法,这里的authenticationEntryPoint默认的是LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint实例,最终的页面跳转也是在commence()方法中,其中又调用redirectStrategy的sendRedirect()方法来完成最终的重定向。其中LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint的commence()方法定义如下:
//LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint.java
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException
String redirectUrl = null;
if (useForward)
if (forceHttps && "http".equals(request.getScheme()))
redirectUrl = buildHttpsRedirectUrlForRequest(request);
if (redirectUrl == null)
String loginForm = determineUrlToUseForThisRequest(request, response,
authException);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Server side forward to: " + loginForm);
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(loginForm);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
return;
else
//构建重定向地址
redirectUrl = buildRedirectUrlToLoginPage(request, response, authException);
//这里redirectUrl对应的就是http://localhost:8082/login地址
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, redirectUrl);
至此,通过执行redirectStrategy.sendRedirect()方法,就实现了重定向到应用A的登录地址了。
4、写在最后
这一节我们主要分析了未认证的请求是如何重定向到登录地址(当前应用)的,下一节我们开始分析授权服务器是如何进行授权的,敬请期待!!! 参考技术A Spring Security可以在登录表单中使用一个名为“targetUrlParameter”的参数来保存重定向地址。 可以在登录表单中添加一个隐藏字段,该字段的值为重定向地址,然后在Spring Security配置文件中设置targetUrlParameter参数的值为该隐藏字段的名称。
Spring Security会自动检测该参数,并将用户重定向到该地址。 参考技术B 分析。
为了实现上述描述的功能,SpringSecurity 过滤器由FilterChainProxy统一管理,然后在在内部定义了一个VirtualFilterChain内部类,用于表示SpringScurity内部的过滤器链,其中doFilter()方法用于执行过滤器链中的过滤器。如下所示:
//FilterChainProxy#VirtualFilterChain,省略了Debug相关信息
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException
if (currentPosition == size)
// Deactivate path stripping as we exit the security filter chain
this.firewalledRequest.reset();
//执行Web中的过滤器
originalChain.doFilter(request, response);
else //执行SpringSecurity过滤器链中的过滤器
currentPosition++;
//additionalFilters中定义了SpringSecurity过滤器链中的所有过滤器
Filter nextFilter = additionalFilters.get(currentPosition - 1);
nextFilter.doFilter(request, response, this);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
我们通过断点,可以查看additionalFilters变量中的过滤器集合,即SpringSecurity过滤器链中所有过滤器,下面是应用A中的SpringSecurity 过滤器,如下所示:
nextFilter.doFilter
3、FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器
通过Debug执行代码,我们发现,在执行完FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器时,前端页面重定向到了应用A的登录http://localhost:8082/login地址(Get请求)。在执行过滤器FilterSecurityInterceptor过滤器时,发生了什么呢?我们通过Debug方式,进行逐步的分析。
自定义SpringSecurity授权跳转地址
自定义SpringSecurity授权跳转地址
在我们用SpringSecurity+Oauth2做权限验证和访问控制的时候,如果要访问的请求处于未登录状态,会被框架进行拦截,并重定向到一个/login的请求(1),再重定向我们授权服务器的/oauth/authorize请求(这里是使用的授权码模式),接着再重定向到我们授权服务器的/login请求上,即我们授权服务器的登录页面。在工作中遇到了一个要修改(1)这个地方请求的问题。既然要修改(1)的/login请求,我们首先要弄清楚这里的/login是从哪里来的,因为我们从来没有在业务系统中定义过这个请求。


在弄清楚/login请求是从哪里来的之前,我们需要先弄明白,我们的请求为什么会被拦截。在SpringSecurity中定义了一堆的Filter来进行权限验证和访问控制,显然请求被拦截也是Filter来处理的。我们先看看一个未授权的请求会被哪些过滤器处理。
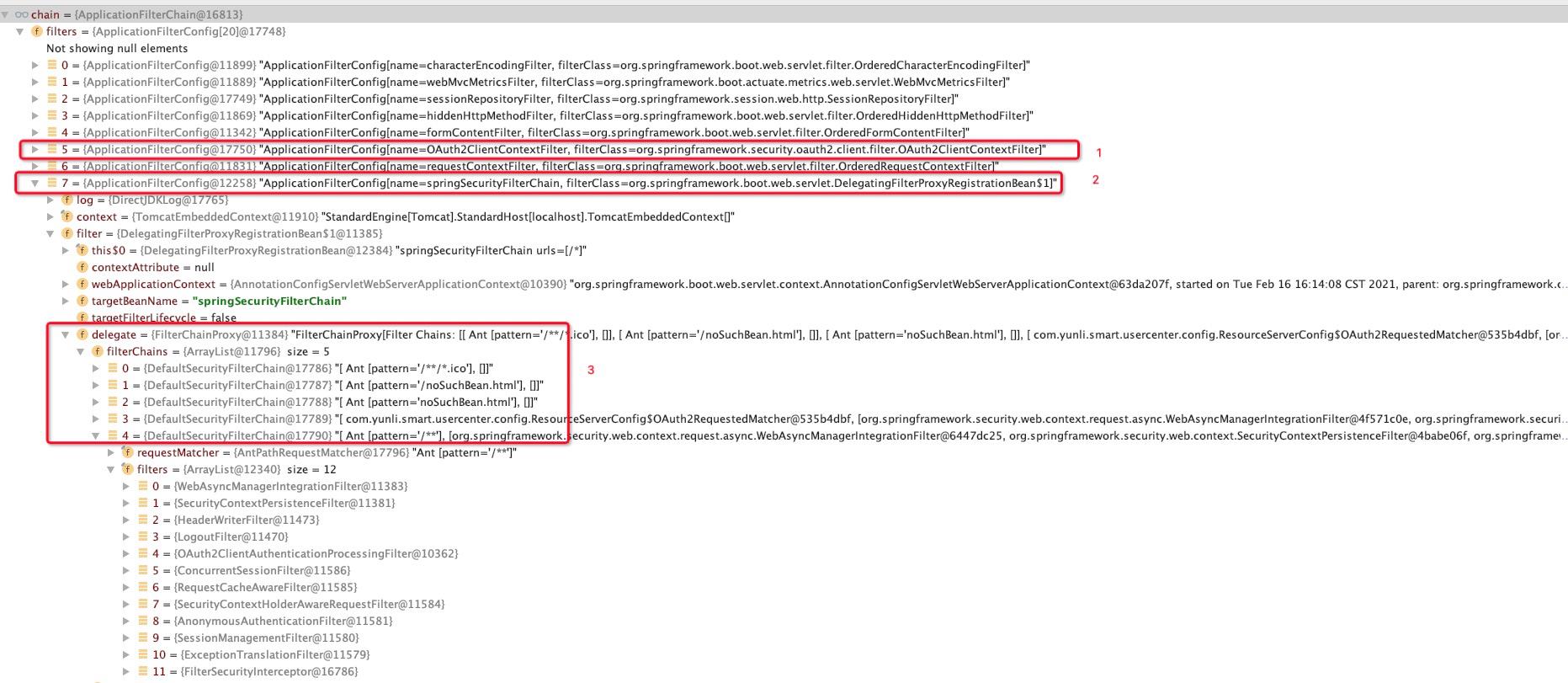
在上图中我们目前需要关注的是2和3这个地方,那我们先看看2这里是怎么处理的,在这里牵扯到的逻辑太多,我们只说重点的部分。在我们的框架中通过DelegatingFilterProxyRegistrationBean生成了DelegatingFilterProxy,再通过DelegatingFilterProxy引用了FilterChainProxy,非常的绕,不过我们不用管那么多,只需要记得,我们所有的请求都会被org.springframework.security.web.FilterChainProxy#doFilter来处理就行来。FilterChainProxy#doFilter的代码如下:
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException
boolean clearContext = request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) == null;
if (clearContext)
try
request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
//这里是重点
doFilterInternal(request, response, chain);
finally
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
request.removeAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED);
else
doFilterInternal(request, response, chain);
private void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException
// 对request、response进行再包装
FirewalledRequest fwRequest = firewall
.getFirewalledRequest((HttpServletRequest) request);
HttpServletResponse fwResponse = firewall
.getFirewalledResponse((HttpServletResponse) response);
//这里就是获取SpringSecurity的Filter了
List<Filter> filters = getFilters(fwRequest);
if (filters == null || filters.size() == 0)
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug(UrlUtils.buildRequestUrl(fwRequest)
+ (filters == null ? " has no matching filters"
: " has an empty filter list"));
fwRequest.reset();
chain.doFilter(fwRequest, fwResponse);
return;
//组装SpringSecurity的过滤器链,作用和ApplicationFilterChain类似。chain是原链,filters
//是SpringSecurity处理自己逻辑的过滤器的集合
VirtualFilterChain vfc = new VirtualFilterChain(fwRequest, chain, filters);
vfc.doFilter(fwRequest, fwResponse);
在上面的代码中,我们最终获取到的SpringSecurity的Filter如下图所示:
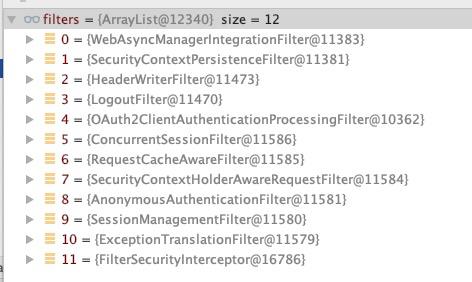
这些过滤器的作用这里先不讨论,只说后面的几个过滤器:SessionManagementFilter、ExceptionTranslationFilter、FilterSecurityInterceptor我们先来看看SessionManagementFilter的doFilter方法的代码:
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
//如果这里有FILTER_APPLIED这个属性的话,说明这个请求经过Session验证了,直接进行下一个过滤器处理
if (request.getAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED) != null)
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
//这里是给FILTER_APPLIED赋一个值,说明请求Session验证过了。
request.setAttribute(FILTER_APPLIED, Boolean.TRUE);
//从Request中获取Session信息,如果没有获取到则进行下面的逻辑处理
if (!securityContextRepository.containsContext(request))
//从Security上下文中获取授权信息
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext()
.getAuthentication();
//如果获取到授权,且不是匿名授权,则进行下面的权限验证
if (authentication != null && !trustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication))
// The user has been authenticated during the current request, so call the
// session strategy
try
//session验证 后面可以单独分析
sessionAuthenticationStrategy.onAuthentication(authentication,
request, response);
catch (SessionAuthenticationException e)
// The session strategy can reject the authentication
logger.debug(
"SessionAuthenticationStrategy rejected the authentication object",
e);
SecurityContextHolder.clearContext();
failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, e);
return;
// Eagerly save the security context to make it available for any possible
// re-entrant
// requests which may occur before the current request completes.
// SEC-1396.
securityContextRepository.saveContext(SecurityContextHolder.getContext(),
request, response);
else
// No security context or authentication present. Check for a session
// timeout
if (request.getRequestedSessionId() != null
&& !request.isRequestedSessionIdValid())
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Requested session ID "
+ request.getRequestedSessionId() + " is invalid.");
//这里如果有自定义的session过期策略的话,会走session过期处理的逻辑,
//就不会走后续的过滤器处理了
if (invalidSessionStrategy != null)
invalidSessionStrategy
.onInvalidSessionDetected(request, response);
return;
chain.doFilter(request, response);
ExceptionTranslationFilter#doFilter 这个方法的主要作用就是对授权异常进行处理
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;d
try
chain.doFilter(request, response);
catch (IOException ex)
throw ex;
catch (Exception ex)
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
//从异常栈中获取相应的异常信息
Throwable[] causeChain = throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
//AuthenticationException 权限验证异常 这是一个抽象类,有很多的具体实现子类
RuntimeException ase = (AuthenticationException) throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
if (ase == null)
//访问权限异常
ase = (AccessDeniedException) throwableAnalyzer.getFirstThrowableOfType(
AccessDeniedException.class, causeChain);
if (ase != null)
//如果请求已经结束了
if (response.isCommitted())
throw new ServletException("Unable to handle the Spring Security Exception because the response is already committed.", ex);
//这里是处理的重点方法,我们要重点分析
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, ase);
else
//如果是其他的异常 则不处理,抛出去
// Rethrow ServletExceptions and RuntimeExceptions as-is
if (ex instanceof ServletException)
throw (ServletException) ex;
else if (ex instanceof RuntimeException)
throw (RuntimeException) ex;
// Wrap other Exceptions. This shouldn't actually happen
// as we've already covered all the possibilities for doFilter
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
//看方法名就知道是做什么的,这里不得不说一下 FilterChain chain这个参数估计是之前冗余用的参数,在后面没有一点用处
private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception)
throws IOException, ServletException
if (exception instanceof AuthenticationException)
//具体的异常处理
sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain,
(AuthenticationException) exception);
else if (exception instanceof AccessDeniedException)
//从SpringSecurity上下文中获取授权信息
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
//如果是匿名权限验证或者是配置了RememberMe
if (authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication) || authenticationTrustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication))
//具体的异常处理 重点
sendStartAuthentication(
request,
response,
chain,
//包装出来一个AuthenticationException的具体实现类,为了后面的通用处理
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
messages.getMessage(
"ExceptionTranslationFilter.insufficientAuthentication",
"Full authentication is required to access this resource")));
else
//访问拒绝的处理类 这个是可以配置的
accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response,
(AccessDeniedException) exception);
protected void sendStartAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
AuthenticationException reason) throws ServletException, IOException
// SEC-112: Clear the SecurityContextHolder's Authentication, as the
// existing Authentication is no longer considered valid
//先清空之前的授权信息
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(null);
requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);
logger.debug("Calling Authentication entry point.");
//重点来了 这里默认的authenticationEntryPoint DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint如下图所示
authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);
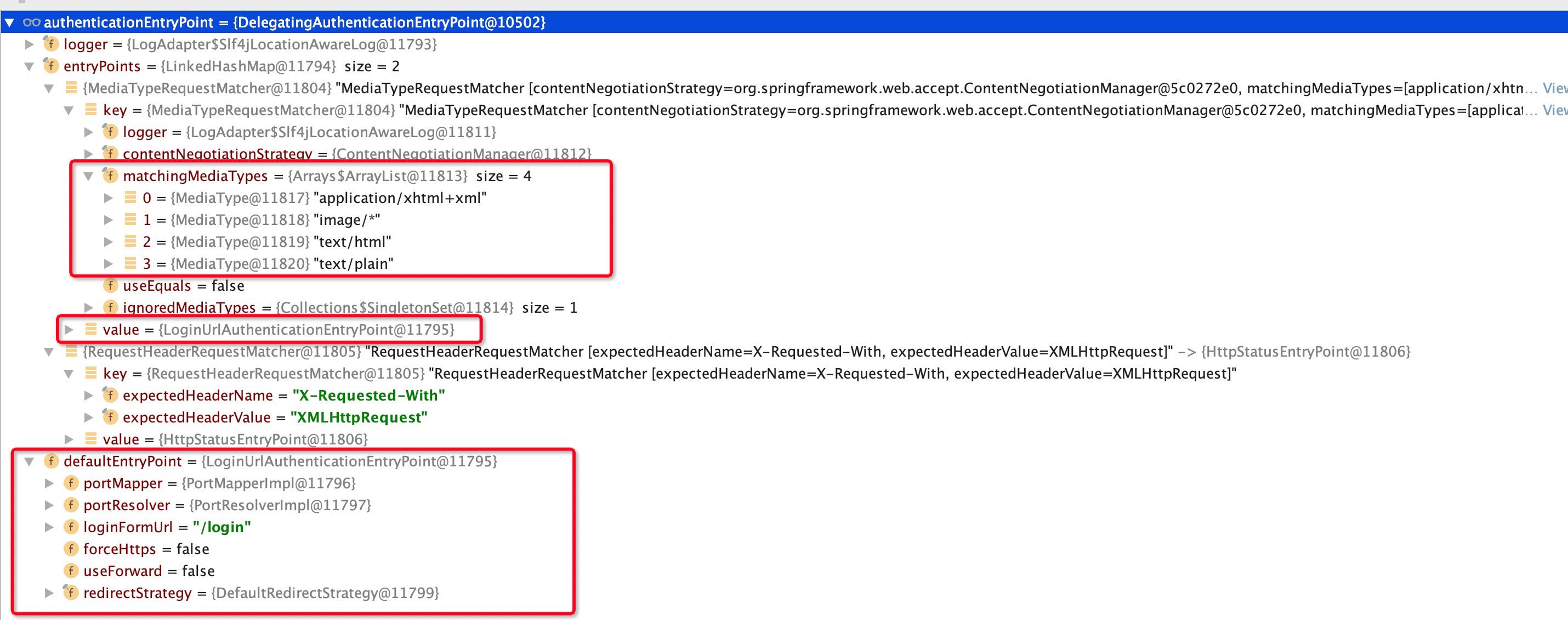
我们接着去看DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint#commence方法
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException
//这里的entryPoints就是上图中的MediaTypeRequestMatcher和RequestHeaderRequestMatcher
for (RequestMatcher requestMatcher : entryPoints.keySet())
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Trying to match using " + requestMatcher);
//这里主要的实现是根据请求header中的accept来判断的,如果我们是从网页来发送请求的话,
//基本上就是匹配的LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint
if (requestMatcher.matches(request))
AuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = entryPoints.get(requestMatcher);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Match found! Executing " + entryPoint);
//按照上面的分析,我们这里就是调用的LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint的commence方法
entryPoint.commence(request, response, authException);
return;
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("No match found. Using default entry point " + defaultEntryPoint);
// No EntryPoint matched, use defaultEntryPoint
//如果没有找到匹配的EntryPoint就用默认的EntryPoint,默认的是LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint
defaultEntryPoint.commence(request, response, authException);
LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint#commence方法
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException authException) throws IOException, ServletException
String redirectUrl = null;
//如果使用的是转发,默认的是false
if (useForward)
if (forceHttps && "http".equals(request.getScheme()))
// First redirect the current request to HTTPS.
// When that request is received, the forward to the login page will be
// used.
//构建https的请求 暂时不用管
redirectUrl = buildHttpsRedirectUrlForRequest(request);
if (redirectUrl == null)
String loginForm = determineUrlToUseForThisRequest(request, response,
authException);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled())
logger.debug("Server side forward to: " + loginForm);
RequestDispatcher dispatcher = request.getRequestDispatcher(loginForm);
dispatcher.forward(request, response);
return;
else
// redirect to login page. Use https if forceHttps true
//获取重定向的URL 这里默认获取到的URI即是 /login
redirectUrl = buildRedirectUrlToLoginPage(request, response, authException);
//请求重定向
redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, redirectUrl);
//这里获取到的loginFormUrl是可以配置的,也终于到我们要分析的地方了,所以一路分析下来,我们问题的
//重点是怎么配置loginFormUrl的值
protected String determineUrlToUseForThisRequest(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception)
return getLoginFormUrl();
//可以配置
public String getLoginFormUrl()
return loginFormUrl;
按照上面的分析,咱们需要关注的是在哪里给loginFormUrl来进行赋值。通过我们打断点分析来看,赋值是在org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.SsoSecurityConfigurer#configure这里进行赋值的。

public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception
//在这里可以看到OAuth2SsoProperties是从Spring IOC中获取的,我们再看看OAuth2SsoProperties是什么
OAuth2SsoProperties sso = this.applicationContext
.getBean(OAuth2SsoProperties.class);
// Delay the processing of the filter until we know the
// SessionAuthenticationStrategy is available:
http.apply(new OAuth2ClientAuthenticationConfigurer(oauth2SsoFilter(sso)));
addAuthenticationEntryPoint(http, sso);
//从这里来看loginPath是一个配置项的值了,也就是说我们通过配置就可以达到我们的要求了,配置一个security.oauth2.sso.loginPath
//的值
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "security.oauth2.sso")
public class OAuth2SsoProperties
public static final String DEFAULT_LOGIN_PATH = "/login";
/**
* Path to the login page, i.e. the one that triggers the redirect to the OAuth2
* Authorization Server.
*/
private String loginPath = DEFAULT_LOGIN_PATH;
以上是关于springsecurity如何保存重定向地址的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章